You can Download KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Questions and Answers Pdf, Notes help you to revise the complete syllabus.
Karnataka State Syllabus Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 1 Natural Resources
Crop Production and Management Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Select the correct word and fill in the blanks.
Float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation.
- The same kind of plants grown on a large scale at a place is called _________
- An important task in growing crops is _________ of soil.
- Damaged seeds would ___________ on top of the water.
- For growing crop sufficient sunlight and _________ and _________ from the soil are essential.
Answer:
- crop
- preparation
- float
- water, nutrients
![]()
Question 2.
Match items in column ‘A’ with those in column ‘B’:
| (A) | (B) |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Zayed crops | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilizers | (c) Animal excreta, cowdung, urine |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
Answer:
| (A) | (B) |
| (i) Kharif crops | (e) Paddy and maize |
| (ii) Zayed crops | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (iii) Chemical fertilizers | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iv) Organic manure | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine, and plant waste. |
Question 3.
Give two examples of each of the following:
(а) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Answer:
(a) Kharif crop – Maiz, paddy, soybean
(b) Rabi crop – Wheat, gram, pea
Question 4.
Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following:
(а) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
Answer:
(a) Preparation of soil. Preparation of soil involves two main steps-ploughing and levelling. Ploughing is the process of loosening and turning the soil so that the circulation of air is improved in the soil. It is done with the help of various types of ploughs like wooden iron for hard soil, bullock drawn, or tractor driven. Loosening of soil permits easy and deeper penetration of the roots and it provides good aeration to the roots. The ploughed land is levelled and pressed lightly with the help of a wooden plank or iron leveller.
(b) Sowing. Sowing is the process of putting seeds in the soil. Sowing can be done manually or by using a seed drill.
(c) Weeding. The removal of weeds is called weeding. It is necessary since weeds use nutrients from the soil. They compete for water and light and thus, affect the growth of crops by reducing the yield. Some weeds even interfere in the harvesting. Weeds can sometimes be poisonous for animals and human beings.
(d) Threshing. The process of separating grains from the harvested crop is called threshing. It may be done manually by striking the harvested crop against a hard surface or by using a machine called a thresher.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain how fertilizers are different from manure.
Answer:
Differences between Fertiliser and Manure
| Fertilizer | Manure |
| 1. A fertilizer is an inorganic salt. | 1. Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung, human waste, and plant residues. |
| 2. A fertilizer is prepared in factories. | 2. Manure can be prepared in the fields. |
| 3. A fertilizer does not provide any humus to the soil. | 3. Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| 4. Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. | 4. Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
Question 6.
What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer:
The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation.
Methods of irrigation which conserve water are:
1. Sprinkler system: This system is useful on uneven lands where water is available in smaller quantities. In this system, the perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on the top, are joined to the main pipe at regular intervals. When the water flows through the main pipe with the help of a pump, it escapes from the rotating nozzles. It is sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining.
2. Drip system. In this system, the waterfalls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. This system consists of the main pipe to which lateral pipes are joined. The specially prepared nozzles are attached to these lateral pipes. The nozzles are grounded just near the roots of the plants. It provides water to plants drop by drop. Water is not wasted at all.
![]()
Question 7.
If wheat is sown in Kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer:
If wheat is sown in the Kharif season then it would not grow because a lot of water due to rain will spoil the seeds. Wheat crops require low temperature which it does not get in the Kharif season. Therefore, the quantity of wheat produced will be very less and quality will also be very poor.
Question 8.
Explain how the soil is affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer:
Continuous plantation of crops in a field year after year makes the soil barren in a few years because all the nutrients present in the soil will be depleted.
Question 9.
What are weeds? How can we control them?
Answer:
The undesirable plants in the field are called weeds which have to be removed, otherwise, our own crop plants may not get sufficient water, space, and light. The various methods to control the weeds are:
- Mechanical method. Uprooting weeds with khurpi or hand, ploughing, burning, and flooding.
- Cultural method, lb prepare proper seedbed and sowing of seed timely and intercropping and crop rotation are the methods included under cultural method.
- Chemical method. By spraying chemicals known as herbicides or weedicides e.g. 2,4-D fluchloralin etc.
![]()
Question 10.
Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production:
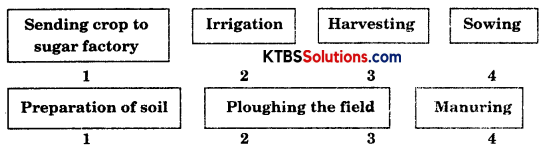
Answer:
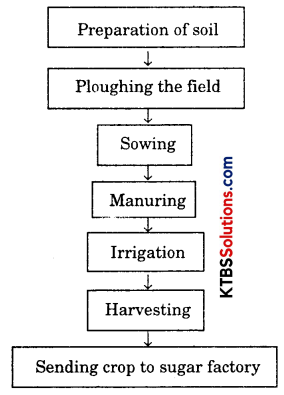
Question 11.
Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from the chaff.
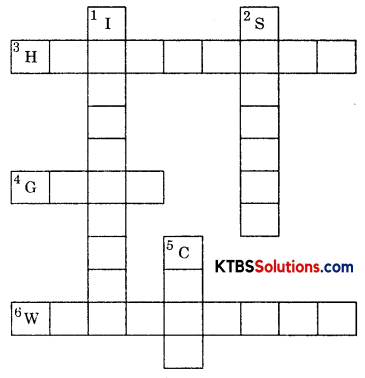
Answer:
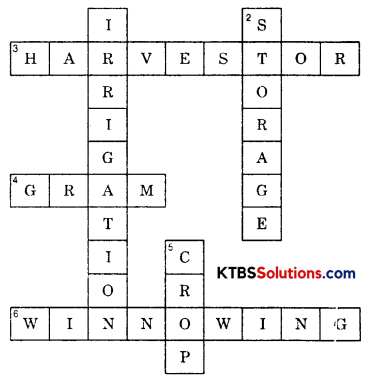
Crop Production and Management Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why do organisms need energy?
Answer:
Organisms need energy for carrying out their various body functions, such as digestion, respiration, and excretion.
Question 2.
What is agriculture?
Answer:
Agriculture is the study of science and the art of production of plants and animals useful to man.
![]()
Question 3.
What is a crop?
Answer:
The plants of the same kind grown at a place are called a crop. Examples are wheat, paddy, etc.
Question 4.
What are agricultural practices?
Answer:
The various tasks like preparation of soil, sowing seeds, irrigation, removal of weeds, use of manures and fertilizers, etc carried by farmers to cultivate crops are agricultural practices.
Question 5.
Why is soil loosened?
Answer:
- The loosened soil allows the roots to penetrate freely, deeper, and breathe easily.
- The loosened soil also helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes, who are friends of the farmer, since they aid in further turning and loosening the soil and add humus to it.
Question 6.
Why does the loosening of soil allow roots to breathe easily?
Answer:
Air easily enters the loosened soil and thus, allows roots to breathe easily.
![]()
Question 7.
Name the main tools used for ploughing. Explain their use and structure with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
The main tools used for ploughing are plough, hoe, and cultivator.
(i) Plough. It is used for tilling of the soil, adding fertilizers to the crop, removing the weeds, and scrapping of soil. Plough is made of wood and drawn by a pair of bulls. It contains a strong triangular iron strip called plough share. Its main part is a long log of wood called a plough shaft. There is a handle on one end. The other end is attached to a beam which is hung on the bull’s necks. One pair of bulls and a man operates the plough.
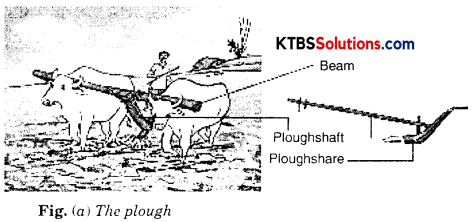
(ii) Hoe is a simple tool used for removing seeds and loosening the soil. Hoe has a long rod of wood or iron. A strong, broad, and bent plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and works as a blade. The other end of plough shaft is pulled by animals.
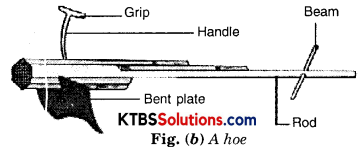
(iii) Cultivator. Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor driven cultivator. The use of a cultivator saves labour and time [Fig. (c)].

Question 8.
What is sowing?
Answer:
Sowing is the process of putting seeds in the soil.
Question 9.
What is meant by good quality seeds?
Answer:
Good quality seeds mean clean and healthy seeds of a good variety.
![]()
Question 10.
What are manures?
Answer:
Manures are organic materials which supply all the elements a plant needs in small amounts. Besides serving as a source of nutrients, organic manures improve the physical conditions of the soil.
Question 11.
What is organic manure?
Answer:
Any organic matter obtained from plant or animal wastes is called organic manure.
Question 12.
How do farmers make manure?
Answer:
Farmers dump plant and animal wastes at open places and allow them to be decomposed by organisms like bacteria and fungi. The decomposed matter is called manure.
Question 13.
What is irrigation?
Answer:
Once the seeds or the seedlings establish themselves in the field, water is again given in the field. This is known as irrigation.
Question 14.
What are the sources of irrigation?
Answer:
The sources of irrigation are wells, tubewells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dam,s and canals.
![]()
Question 15.
Draw a diagram to show’ sprinkler system and drip system.
Answer:
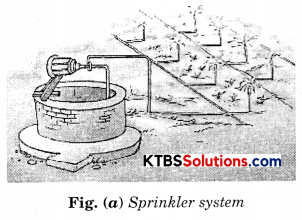
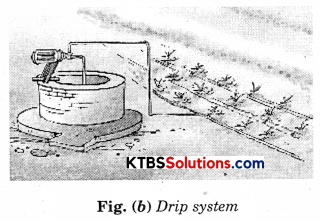
Question 16.
What are weeds?
Answer:
Weeds are undesirable plants which grow along with crops and compete for sunlight, water, and nutrients, thus decreases the yield of the main crop.
Question 17.
Give two examples of weeds?
Answer:
Wild oat, Chenopodium, Amaranthus.
Question 18.
What is weeding? Why is it necessary?
Answer:
The removal of weeds is called weeding. It is necessary since weeds use nutrients from the soil. They compete for water and light and thus, affect the growth of crops by reducing the yield. Some weeds even interfere in the harvesting. Weeds can sometimes be poisonous for animals and humans beings.
![]()
Question 19.
What is harvesting?
Answer:
Harvesting is the process of cutting and collecting the matured crop from the fields.
Question 20.
What is threshing?
Answer:
The process of separating grains from the harvested crop is called threshing. It may be done manually by striking the harvested crop against a hard surface or by using a machine called a thresher.
Question 21.
What does storage mean?
Answer:
Storage means keeping the harvested fruits till they are taken finally to the consumer. Seeds are stored to protect them from birds, insects, rodents, and micro-organisms and also for use during periods of food scarcity.
Question 22.
What precautions are taken before storing the grains?
Answer:
Before storing the grains they are sun-dried to reduce the moisture level of grains so that they are saved from pest attacks. Humidity in storage places must also be controlled to prevent the growth of fungus.
![]()
Question 23.
Why are dried neem leaves used for storing food grains at home?
Answer:
Dried neem leaves protect food grains from pests and microorganisms.
Question 24.
Name the foods obtained from animals?
Answer:
Milk, eggs, fish, and meat.
Activities
Activity 1.1
Take a beaker and fill half of it with water. Put a handful of wheat seeds and stir well, wait for some time.
Question (i).
Are there seeds that float on water?
Answer:
Yes
Question (ii).
Would those be lighter or heavier than those which sink?
Answer:
Those would be lighter than those which sink.
Question (iii).
Why would they be lighter?
Answer:
They would be lighter because damaged seeds become hollow and are thus, lighter. Therefore, they float on water.
![]()
Activity 1.2
Take moong or gram seeds and germinate them. Select three equal-sized seedlings out of these. Now take three empty glasses or similar vessels. Mark them A, E, and C. To glass A add a little amount of soil mixed with a little cow dung manure. In the glass, B put the same amount of soil mixed with a little urea. Take the same amount of soil in glass C without adding anything [Fig. 1.3(a)]. Now pour the same amount of water into each glass and plant the seedlings in them. Keep them in a safe place and water them daily. After 7 to 10 days observe their growth [Fig. 1.3(b)]

Question (i).
Did all the plants in all the glasses grow at the same pace?
Answer:
No.
Question (ii).
Which glass showed better growth of plants?
Answer:
Glass A.
![]()
Question (iii).
In which glass was the growth fastest?
Answer:
Glass B.