KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Circles Ex 4.2 are part of KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions. Here we have given Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Circles Exercise 4.2.
Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Circles Exercise 4.2
In Questions 1 to 3, choose the correct option and give justification.
Circles Exercise 4.2 Question 1.
From a point Q, the length of the tangent to a circle is 24 cm and the distance of Q from the centre is 25 cm. The radius of the circle is
A) 7 cm.
B) 12 cm.
C) 15 cm.
D) 24.5 cm.
Solution:
A) 7 cm.
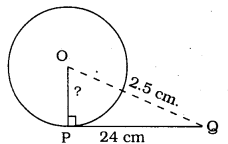
In ⊥∆OPQ, ∠P = 90°
∴ As per Pythagoras theorem,
OP2 + PQ2 = OQ2
OP2 + (24)2 = (25)2
OP2 + 576 = 625
OP2 = 625 – 576
OP2 = 49
∴ OP = 7 cm.
Circle Lesson Exercise 4.2 Question 2.
In the following figure, if TP and TQ are the two tangents to a circle with centre O so that ∠POQ = 110°, then ∠PTQ is equal to
A) 60°
B) 70°
C) 80°
D) 90°
Solution:
B) 70°
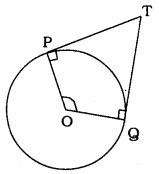
∠POQ =110° (given)
OP ⊥PT, OQ ⊥QT ( ∵ Angle between radius and tangent)
∴ ∠OPT = ∠OQT = 90°
Now, OPTQ is a quadrilateral.
∴ ∠O + ∠P + ∠Q + ∠T = 360°
110° + 90° + 90° + ∠T = 360°
290° + ∠T = 360°
∴∠T = 360° – 290°
∴ ∠T = 70°
∴ ∠PTQ = 70°
KSEEB Solutions For Class 10 Maths Circles Question 3.
If tangents PA and PB from a point P to a circle with centre O are inclined to each other at an angle of 80°, then ∠POA is equal to
A) 50°
B) 60°
C) 70°
D) 80°
Solution:
A) 50°
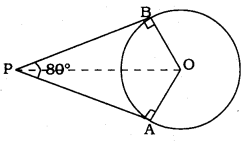
OA, OB are radii,
PA, PB are tangents
∴ ∠PAO = 90°, ∠PBO = 90°
In quadrilateral OAPB,
∠BOA = 180° – 80° = 100°
But
∴∠POA = 50°.
Exercise 4.2 Class 10 Circles Question 4.
Prove that the tangents drawn at the ends of a diameter of a circle are parallel.
Solution:
Data: The tangents drawn at the ends of a diameter of a circle are parallel.
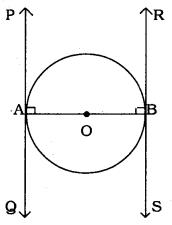
AOB is the p diameter in the circle with centre ‘O’.
Tangent PAQ is at the endpoint A, and
Tangent RBS is A at the endpoint B.
OA is the radius,
PAQ is tangent
∴ ∠PAO = 90°
OB is the radius,
RBS is tangent.
∴ RBO = 90°
Now, ∠PAO + ∠RBO = 90° + 90° = 180°
AB intersects straight lines PAQ and RBS.
Sum of a pair of interior angles is 180°. Hence these lines are parallel to each other.
∴ PQ || RS proved.
Circle Exercise 4.2 Question 5.
Prove that the perpendicular at the point of contact to the tangent to a circle passes through the centre.
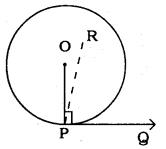
Solution:
Data: Perpendicular at the point of contact to the tangent to a circle passes through the centre.
PQ is the tangent to circle with centre ’O’.
Let the perpendicular drawn at the point P is ∠RPQ.
∠RPQ = 90° …………. (i)
Radius drawn to circle at the point of contact is perpendicular.
∴ ∠OPQ = 90° …………. (ii)
From eqn. (i) and eqn. (ii), we have
∠RPQ = ∠OPQ = 90° .
This is a contradiction, because
∠RPQ is the part of ∠OPQ.
∴ ∠RPQ < ∠OPQ
∴ ∠RPQ ≠∠OPQ.
∴ The perpendicular at the point of contact to the tangent to a circle passes through the centre.
Circles Class 10 Exercise 4.2 Question 6.
The length of a tangent from a point A at distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle.
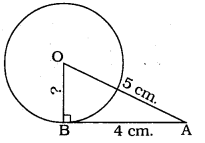
Solution:
Data: OB is the radius, BA is the tangent.
∴ ∠OBA = 90°, OA = 5 cm. (data)
Length of tangent, AB = 4 cm.
∴ Radius, OB =?
In ⊥∆OBA, ∠OBA = 90°
∴ OB2 + BA2 = OA2 .
OB2 + (4)2 = (5)2
OB2 + 16 = 25
OB2 = 25 – 16
OB2 = 9
∴ OB = 3 cm.
∴ Radius of circle, OB = 3 cm.
KSEEB Solutions For Class 10 Maths Question 7.
Two concentric circles are of radii 5 cm and 3 cm. Find the length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle.
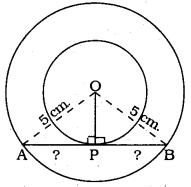
Solution:
Radius of big circle,
OA = OB = 5 cm.
Radius of small circle, OP = 3 cm.
Angle between radius and tangent is 90°.
∴ ∠OPA = ∠OPB = 90°
( ∵ Chord AB is tangent to small circle.)
Now, in ⊥∆ OPA, ∠OPA = 90°
OP2 + AP2 = OA2
(3)2 + AP2 = (5)2
9 + AP2 = 25
∴ AP2 = 25 – 9
AP2 = 16
∴ AP = 4 cm.
Similarly, in ⊥∆OPB, PB = 4 cm.
∴ Length of chord, AB = AP + PB = 4 + 4
∴ Chord, AB = 8 cm.
10th Maths Exercise 4.2 13th Sum Question 8.
A quadrilateral ABCD is drawn to circumscribe a circle (see the fig. given below). Prove that AB + CD = AD + BC.
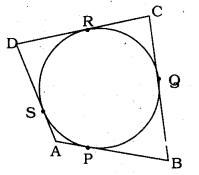
Solution:
Data: In the quadrilateral, ABCD is drawn to circumscribe a circle.
To Prove: AB + CD = AD + BC
The lengths of tangents drawn from an extremal point to a circle are equal.
∴ Tangents AP and AS are drawn from point A.
∴ AP = AS
Tangents BP and BQ are drawn from point B.
∴ BP = BQ
Tangents CQ, CR are drawn from point C.
∴ CQ = CR.
Tangents DR, DS are drawn from point A.
∴ DR = DS
L.H.S.: AB + CD = AP + PB + CR + RD
= AS + BQ + CQ + DS
= AS + SD + BQ + CQ
∴ AB + CD = AD + BC
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Exercise 4.2 Maths Class 10 Solutions Question 9.
In the following figure, XY and X’Y’ are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O and another tangent AB with the point of contact C intersecting XY at A and X’Y’ at B. Prove that ∠AOB = 90°.
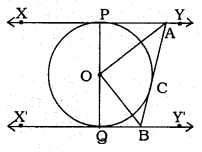
Solution:
Data: XY and X’Y’ are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O and another tangent AB with point of contact C intersecting XY at A and X’Y’ at B
To Prove: ∠AOB = 90°.
Tangent XY || Tangent X’Y’
∴ ∠PAB + ∠QBA = 180° (∵ interior angles)
∠OAB + ∠OBA = 90°
Now, in AOAB,
∠AOB + ∠OAB + ∠OBA = 180°
∠AOB + 90° = 180°
∴ ∠AOB = 180° – 90°
∴ ∠AOB = 90°.
10th Std Maths Notes Question 10.
Prove that the angle between the two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle is supplementary to the angle subtended by the line-segment joining the points of contact at the centre.
Solution:
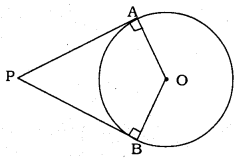
To Prove: ∠APB + ∠AOB = 180°
OA is radius, PA is tangent.
∴∠PAO = 90°
OB is radius, PB is tangent.
∴ ∠PBO = 90°
Now OAPB is a quadrilateral.
∴∠PAO + ∠PBO = 90° + 90° = 180°
Sum of four angles of a quadrilateral is 360°
∴ ∠PAO + ∠PBO + ∠APB + ∠AOB = 360°
180° + ∠APB + ∠AOB = 360°
∠APB + ∠AOB = 360° – 180°
∴ ∠APB + ∠AOB = 180°
If the sum of two angles is equal to 180°, then they are supplementary angles.
∴ ∠APB and ∠AOB are supplementary angles.
10th Standard Karnataka State Syllabus Maths Guide Question 11.
Prove that the parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus.
Solution:
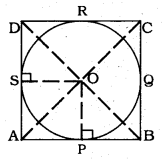
To prove: Parallelogram ABCD is a rhombus.
ABCD is a parallelogram in which ‘O’ is the centre of the interior circle drawn in the parallelogram.
Tangents AC and BD are drawn which intersect at ‘OP’.
Sides of the parallelogram AB. BC. CD and AD touch at the points P, Q, R, and S respectively.
OP, OS joined.
We have OP ⊥ AB, OS ⊥ AD.
In ⊥∆ OPB and ∆OSD,
∠OPB = ∠OSD =90°
OB = OD (tangent is bisected)
OP = OS (Radii)
∴ ∆OPB = ∆OSD
∴ PB = SD → (1)
AP = AS → (2) (∵ tangent of the external point)
By combining eqn. (1) and Eqn. (2),
AP + PB = AS + SC
AB = AD
Similarly, AB = BC = CD = DA
∴ Parallelogram ABCD is a rhombus
10th Maths Notes In Kannada Pdf Question 12.
A triangle ABC is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius 4 cm such that the segments BD and DC into which BC is divided by the point of contact D are of lengths 8 cm and 6 cm. respectively, (see the figure given). Find the sides AB and AC.
Solution:
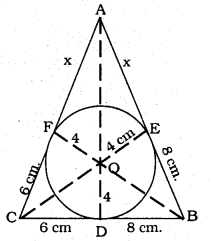
To Prove: Side AB = ? and Side AC = ?
BD = 8 cm. DC = 6 cm.
BE = 8 cm. CF = 6 cm.
AE = AF = x cm.
In ∆ABC,
a = BC = BD + DC =8 + 6 =14 cm.
b = CA = (x + 6) cm.
c = AB = (x + 8) cm.
\(S=\frac{a+b+c}{2} \quad=\frac{14+(x+6)+(x+8)}{2}\)
\(=\frac{2 x+28}{2}\)
= (x + 14) cm.
Area of ∆ABC = \(=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(=\sqrt{(x+14) \times x \times 8 \times 6}\)
\(=\sqrt{48 x \times(x+14)} c m^{2}\) …………….. (i)
Area of ∆ABC
= ∆OBC + ∆OCA + ∆OAB W.
\(=\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times a+\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times b+\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times c\)
– 2(a + b + c)
= 2 × 2S
= 4S
= 4(x +14) cm2………………. (ii)
From eqn. (i) and eqn. (ii),
\(\sqrt{48 x \times(x+14)}=4(x+14)\)
48x × (x + 14) = 16 x (x + 14)2
3x = x + 14
∴ x = 7 cm.
AB = c = x + 8 = 7 + 8 = 15 cm.
AC = b = x + 6 = 7 + 6 = 13 cm.
10th Maths Notes Question 13.
Prove that opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the centre of the circle.
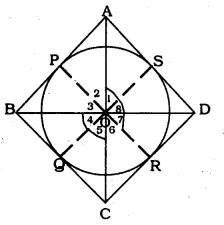
Solution:
Data: Circle with centre ‘O’ is circumscribed in a quadrilateral ABCD.
To Prove: ∠AOD + ∠BOC = 180°
Sides of the quadrilateral AB, BC, CD, and DA touches at the points P, Q, R, and S respectively.
OA. OB, OC, OD, and OP, OQ, OR, OS are joined.
OA bisects ∠POS.
∠1 =∠2
∠3 = ∠4
∠5 = ∠6
∠7 = ∠8
2(∠1 + ∠4 + ∠5 + ∠8) = 360°
(∠1 + ∠8) (∠4 + ∠5) = 180°
∴ ∠AOD = ∠BOD = 180°
∴ Opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the centre of the circle.
We hope the given KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Circles Ex 4.2 will help you. If you have any query regarding Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Circles Exercise 4.2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.