You can Download Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors Questions and Answers, Notes, 1st PUC Accountancy Question Bank with Answers Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Accountancy Question Bank Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors
1st PUC Accountancy Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is Trial balance?
Answer:
Trial balance is the list of all debit and credit balances of accounts taken out from the ledger at a given period.
Question 2.
Write the objective of preparing trial balance.
Answer:
- To know the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts.
- To identify any mistakes in the books of accounts entered.
- It contains all the accounts in a summarised from.
- To prepare final accounts of a concern.
Question 3.
Write the methods of preparing trial balance.
Answer:
- Balance method
- Total method
- Balance and total (mixed) method.
Question 4.
Write the principles of preparation of trial balance.
Answer:
The principle of preparation of trial balance is debit entry have automatic credit on some other account.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the features of trial balance.
Answer:
- It is a extraction of ledger balance
- It is prepared on a particular date.
- It is not the account it is a statement of balances.
Question 6.
Write the specimen of trial balance.
Answer:
Trial balance of m/s subhas publishing House as on 31-3-2011

Question 7.
Write any four items appeared on debit side of trial balance.
Answer:
The items appeared in debit side of trial balance are :
- Purchases
- Sales Return
- Building
- Cash balance.
Question 8.
Write any four items appeared on credit side of trial balance.
Answer:
The items appeared in trial balance credit side are :
- Sales
- Purchase return
- Capital
- Interest received
Question 9.
Write any four items not recorded in trial balance.
Answer:
Items not appeared in trial balance are :
- Closing stock
- Salary payable
- Commission receivable
- Depreciation provision during the year
Question 10.
What is suspense a/c?
Answer:
It is a temporary a/c in which the difference in Trial balance is placed and is wiped off when the errors are locked.
Question 11.
What is an accounting Errors?
Answer:
Errors mistakes committed by the book-keeper while writing of accounts.
![]()
Question 12.
Write the different types of errors.
Answer:
- Errors of commission
- Errors of ommission
- Errors of principle
- Compensating errors
Question 13.
What do you mean by errors of ommission?
Answer:
It is an error where a transaction is completely ommited or not recorded in the books of accounts.
Question 14.
What is error of commission?
Answer:
It is an error where a transactions has been wrongly entered in a subsidiary book or posting to wrong a/c.
Question 15.
What is errors of principles?
Answer:
It is an error where a transaction is not recorded strictly in accordance with principles of double entry system.
Question 16.
What is suspense account?
Ans.
It is Temporary account opened for recording the difference in trial balance and written off after errors are located.
Question 17.
Write the meaning of two sides errors.
Answer:
Any errors affects both side aspects of transaction, (debit and credit) it is called two sides errors.
1st PUC Accountancy Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors Two Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
State any two examples for errors of omission.
Answer:
Examples for omission are :
- Purchase goods from Murthy not recorded in purchase book. It is a omission of original entry.
- Sold goods to Mary recorded in sales book but not posted to ledger. It is a omission of postings.
Question 2.
Write the meaning of compensating errors.
Answer:
It is an error where one error committed on one account is compensated by some other error . on another account.
Question 3.
Write the meaning of one side error. Give example.
Answer:
Any errors affects only one side, either debit or credit aspects of transaction it is called one side error. Example : Pasting Rs. 500 as ₹ 50.
Question 4.
Write the objectives or importance of suspense account.
Answer:
(i) To Final accounts or importance of suspense account.
(ii) To rectify the mistakes and correct the trial balance.
![]()
Question 5.
Give any two examples for errors of commission.
Answer:
- Goods purchase for ₹ 9250 from Srinivas has been entered in the purchase book as ₹ 9520
- Goods sold to asha for ₹ 2000 has been wrongly posting to Ravi’s a/c
Question 6.
Give any two example for errors of principle.
Answer:
- Purchase of furniture from vishwantha ₹ 10000 but it is wrongly entered in purchase book.
- Sale of old machinery ₹ 1000 wrongly entered in to sales a/c.
Question 7.
Give two example for compensating errors.
Answer:
Examples for compensating errors are :
- Salary account overcast by ₹ 2000 and Electricity charges undercast by ₹ 2000.
- Purchase book is undercast by ₹ 4000 and purchases return under cast by ₹ 2000 and sales return overcast by ₹ 2000.
Question 8.
What is rectification of errors or rectification of entry?
Answer:
Correcting the mistakes made earlier by passing a new entry called rectification entries.
In other words an entry written to rectify the mistakes committed in the books of accounts called rectification entry.
Question 9.
Mention any two features of suspenses a/c.
Answer:
Features of suspense a/c are
- It is opened when trial balance not tallied.
- Suspense account may show debit balance or credit balance in trial balance.
- It is a temporary account.
Question 10.
Write the merit /use of suspense a/c.
Answer:
The use of suspense account is that it helps to prepare final accounts of a concern even when the trial balance shows a difference amount.
It also helpful for identifying the mistakes while maintaining books of accounts.
Question 11.
State the meaning of a Trial Balance?
Answer:
Trial Balance is a statement prepared with debit and credit balances of all accounts in ledger, to verify the arithmetical accuracy of the accounts. It is prepared after balancing all the ledger accounts.
![]()
Question 12.
Give the meaning of errors of principle with examples.
Answer:
Errors of principle refer to those errors that are committed when recording of transactions is done against the accounting principle. Below given are the examples of error of principle.
a. Wages paid for construction of building debited to Wages Account.
b. Amount spent on repair of machinery debited to Machinery Account.
Question 13.
What is errors of commission? Give examples.
Answer:
Errors of commission refer to those errors that are committed when transactions are recorded with wrong amounts; wrong balancing or wrong posting and / or wrong carrying forwarding is done. Examples of error of commission are.
a. Goods purchased worth ₹ 20,000 on credit are recorded in the purchases book as ₹ 1000.
b. Total of sales book is carried forward as ₹ 50,000 instead of ₹ 5,000.
1st PUC Accountancy Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors Six Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the methods of preparing trial balance?
Answer:
The two different methods to prepare trial balance.
a. Totals method : According to the totals method, the total of debit and credit sides of an accounts is shown in the debit and credit columns of the trial balance. If the total of the debit column and the total of credit column of trial balance are equal, then the trial balance is said to agree, otherwise not.
b. Balance method : According to the balance method, the balance of ledger accounts is shown in the debit and credit column of the Trial Balance. The balance of ledger may be either debit balance or credit balance. In the former case, the debit side of an account exceeds its credit side; whereas, in the latter case the credit side exceeds the debit side of the account. The sum total of the balances in the debit column of the trial balance must be equal to the sum total of the balances in the credit columns of the trial balance. It is a commonly used method.
c. Total cum balance method : It is a combination of both of the above methods, i.e., totals method and balance method.
Question 2.
What are the steps taken by an accountant to locate the errors in the trial balance?
Answer:
The following are various steps that an accountant takes to locate the errors in the trial balance.
a. Re-totalling of the debit and the credit columns of the trial balance to locate the difference in the total of both the columns.
b. Checking whether any account is omitted to be recorded with the exact difference amount.
c. Half the difference, then check whether any amount is posted in the wrong column of the trial balance.
d. Divide the difference by 9, if it is competely divisible, it is an error of transposition of figure, i.e. 546 is written as 645.
e. If there exist difference especially of ₹ 1, ₹ 10, ₹ 100, ₹ 1000, etc., it suggests that the casting of subsidiary books should be checked once again.
f. If difference still exists and it is not possible to detect the reason for the difference, then for the time being, the difference is transferred in the suspense account in order to proceed further. Otherwise a complete checking is suggested.
Question 3.
What is suspense account? Is it necessary that suspense account will balance off after rectification of the errors detected by the accountant? If not, then what happens to the balance still remaining in suspenses account?
Answer:
When trial balance does not agree, i.e., when the total of the debit column does not match that of the credit column, then the difference of the trial balance is transferred to a temporary account in order to avoid delay in preparation of the financial statements. This temporary account is termed as suspense account.
If the debit column falls short of the credit column, then the suspense account is debited and if the credit column falls short of the debit column then the suspense account is credited. If all the errors are detected and rectified, then the suspense account automatically gets closed (i.e. becomes zero).
However, if still there exists any difference, then it should be transferred to the balance sheet. If the suspense account shows a debit balance, then it is shown in the assets side and if the suspense account shows a debit balance, then it is shown in the assets side and if the suspense account shows a credit balance, then it is shown in the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Question 4.
What kinds of errors would cause difference in the trial balance? Also list examples that would not be revealed by a trial balance?
Answer:
The errors that lead to the differences in the trial balance are termed as one-sided errors.
These are those errors that affect only one account. Below are given the errors that cause difference in the trial balance.
a. Wrong casting of any account, this is termed as the error of casting.
b. Wrong carrying forward of the balances from previous year’s books or from one end of page to another. These types of errors are termed as the errors in carrying forward.
c. If entries are posted in the wrong side of accounts.
d. Posting of a wrong amount in account, this is termed as the error of posting.
e. If entries are recorded partially, i.e., the entries are not recorded completely, then due to the error of partial omission, trial balance.
![]()
Question 5.
State the limitations of trial balance?
Answer:
The ineffectiveness of the trial balance is termed as the limitations of trial balance. The various limitations of the trial balance are given below.
- It does not assist to detect errors that arise if any entry is not recorded in the journal. Such errors are termed as the errors of Complete Omission.
- If the effect of one error is canceled by the effect of another error, then it cannot be ascertained by the trial balance. Such types of errors are termed as compensatory errors, which are rare to find.
- If correct amount is posted in the correct side; however, in the wrong account and if wrong amount is posted in the wrong side, but in the correct account, then the trial balance fails to reflect these errors.
- If there arises any error of principle, like capital expenditure mistakenly regarded as revenue expenditure or vice-versa, then such errors may not be revealed in form of mismatch between the two columns of the Trial balance.
- If any transaction is recorded wrongly in the looks of original entry, then such mistakes lead to the errors of recording which are not revealed by trial balance.
Question 6.
Describe the purpose for the preparation of trial balance.
Answer:
The important purposes for the preparation of trial balance are explained with the help of the following points:
- Ascertaining the arithmetical accuracy : When the total of all debit balance accounts are equal to all credit balance accounts, it is assumed that at least posting from journal to the respective accounts is arithmetically correct.
- Summarising the ledger accounts: Trial balance acts as a consolidated statement, providing a comprehensive list of all the accounts. Thus, a trial balance provides a summarised version of each account.
- Preparing final accounts : As the trial balance provides a summarised version of each account, so different accounts can be directly transferred to trading, profit and loss accounts, and balance sheet without referring to different ledgers.
- Locating and rectifying errors : If the trial balance does not agree, it indicates the occurrence of arithmetical error, which can be easily located. However, trial balance only helps in locate and rectify arithmetical error and no other types of errors.
Question 7.
Explain errors of principle and give two examples with measures to rectify them.
Answer:
Errors of principle refer to those errors that are committed when recording of transactions in the original book of entry is done against the accounting principle. These errors are not reflected in the trial balance. These errors are committed when proper distinction is not made between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure, or vice versa or between capital income and revenue income or vice versa.
Th following examples will illustrate the process of understanding and rectification of such errors.
Example 1 : Wages paid for construction of building are debited to Wages account.
Wrong entry made is:
Wages A/c Dr
To cash A/c
(Wages paid in cash)
In this case, wages paid for the construction of building should be treated as a capital expenditure and accordingly should be debited to the building account. However, the wages account is wrongly debited.
The correct entry that should have been made is:
Building A/c or To cash A/c
(wages paid for construction of building)
The rectifying entry should be :
Building A/c Dr
To Wages A/c
(Wages paid for construction of building was debited to wages account, now rectified)
Example 2:
The sale of old machinery recorded as sales.
wrong entry made:
Cash A/c Dr
To sales A/c
(Sales of old machinery, recorded as sales)
In this case, the sale of old machinery should not be recorded as sales; in fact the Machinery Account should be credited.
The correct entry that should have been made is:
Cash A/c Dr
To machinery A/c
(Old machinery sold for cash)
In order to rectify this error, sales account will be debited, as it is wrongly credited and machinery will be credited, as it willnot be recorded in the books.
The rectifying entry will be:
Sales A/c Dr
To Machinery A/c
(Sales of old machinery recorded as sales, now rectified)
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the errors of commission and give two examples with measures to rectify them.
Answer:
Errors of commission refer to those errors that are committed when transactions are recorded with wrong amounts, wrong balancing is done, wrong posting and/or wrong carrying forwarded is done. The following examples will illustrate the process of understanding and rectification of such errors.
Example 1 : Sales made to Mr A of ₹ 30,000 recorded as 3,000 from invoice.
In this case, Mr. X’s account has been debited with ₹ 3,000 instead of ₹ 30,000; hence the error of commission is committed. This requires a further debit of ₹ 27,000, in order to rectify this error of commission. This will be rectified by passing the following entry:
Mr A’s A/c Dr 9,000
To sales A/c 9,000.
(Good sold to Mr X of ₹ 30,000 was wrongly posted as ₹ 3,000, now rectified)
Purchase book Was under cast by ₹ 40,000. This error can be rectified in any of the following two stages:
a. If an error is located before preparing trial balance, then ₹ 10,000 should be recorded in the debit side of purchases account.
b. If an error is located after preparing trial balance, then the following entry need to be recorded.
Purchase A/c – 40,000
To Suspense A/c – 40,000
Question 9.
What are the different types of errors that are usually committed in recording business transactions?
Answer:
1. Errors of omission: When an entry gets omitted during recording in the book of original entry or during posting the transaction, then error of omission is committed. There are two types of errors of omission, viz.:
- Partial omission : When a transaction is correctly recorded in one side of account but is not recorded in the other side of the account.
- Complete omission : When a transaction gets completely omitted to be recorded in the books, then it is the case of complete omission. Such omission does not affect the trial balance.
2. Errors of principle : These refer to those errors that are committed when recording of transactions in the book of the original entry is done against the accounting, principle. These errors affect the trial balance. These errors are committed when proper distinction is not made between revenue income or expenditure and capital income or expenditure.
3. Errors of commission: These refer to those errors that are committed when transactions are recorded with wrong amounts, wrong balance, wrong posting and/or wrong carrying forwarded is done.
4. Compensating errors : When effects of one error are cancelled by the effects of another error of an equal amount, then compensating errors are committed.
Question 10.
As an accountant of a company, you are disappointed to learn that the totals in your new trial balance are not equal. After going through a careful analysis, you have discovered only one error. Specifically, the balance of the office equipment account has a debit balance of ₹ 15,600 on the trial balance. However, you have figured out that a correctly recorded credit purchase of pen-drive for ₹ 3,500 was posted from the journal to the ledger with a ₹ 3,500 debit to office equipment and another ₹ 3,500 debit to creditors accounts. Answer each of the following questions and present the amount of any misstatement:
a. Is the balance of the office equipment account overstated, understated, or correctly stated in the trial balance?
b. Is the balance of the creditors account overstated, understated, or correctly stated in the trial balance?
c. Is the debit column total of the trial balance overstated, understated, or correctly stated?
d. Is the credit column total of the trial balance overstated, understated, or correctly stated?
e. If the debit column total of the trial balance is ₹ 2,40,000 before correcting the error, what is the total of credit column.
Ans.
According to the given information trial balance does not agree. Pen-drive is wrongly debited to office equipment account, instead of stationery account and supplier account is debited instead of crediting. Due to these mistakes, the following errors are committed:
a. The balance of office equipment is overstated by ₹3,500.
b. The balance of creditors accounts is understated by ₹ 7,000
c. The total of the debit column of the trial balance is correctly stated.
d. The total of the credit column of the trial balance is understand by ₹ 7,000.
e. If the total of the debit column of the trial balance is ₹ 2,40,000 before rectifying error, the total of the credit column of the trial balance is ₹ 2,33,000 (i.e., ₹ 2,40,000 – ₹ 7,000).
![]()
1st PUC Accountancy Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors Numerical Questions and Answers
Question 1.
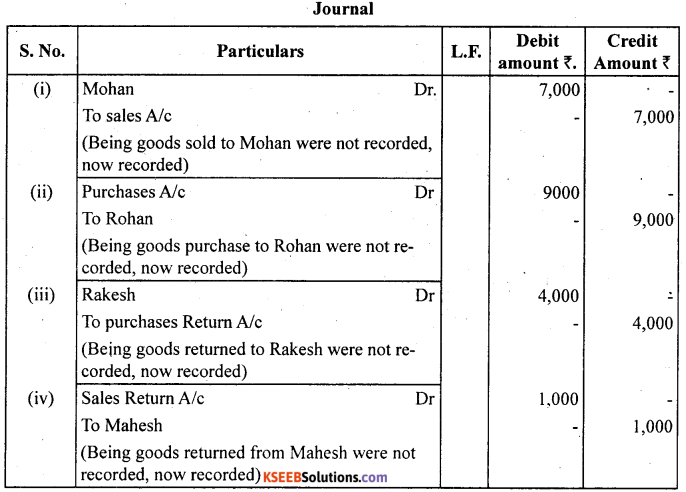
Rectify the following errors :
(i) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were not recorded.
(ii) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were not recorded.
(iii) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were not recorded.
(iv) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were not recorded.
Answer:
Question 2.
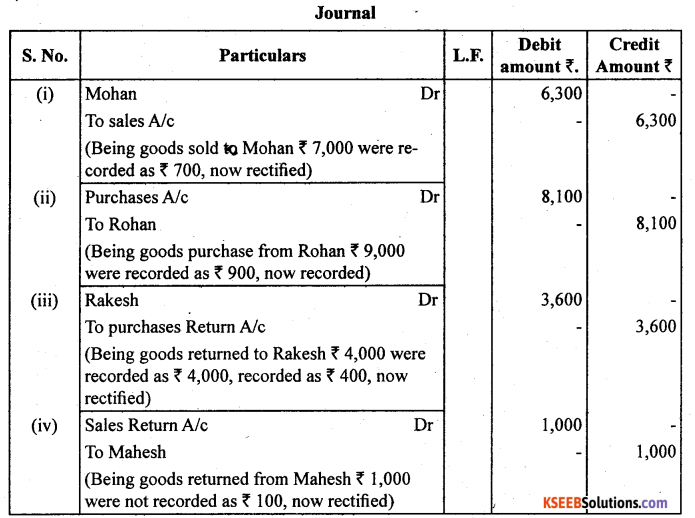
Rectify the following errors :
(i) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were not recorded as ₹ 700.
(ii) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were not recorded as ₹ 900.
(iii) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were recorded as ₹ 400.
(iv) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were not recorded ₹ 100
Answer:
Question 3.
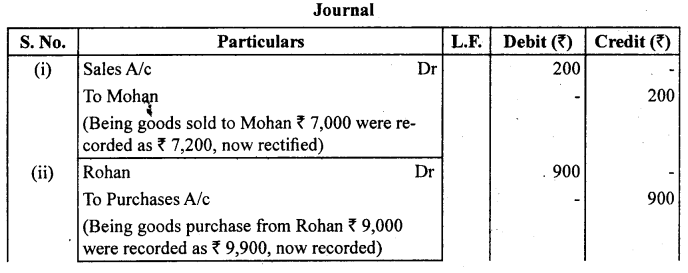
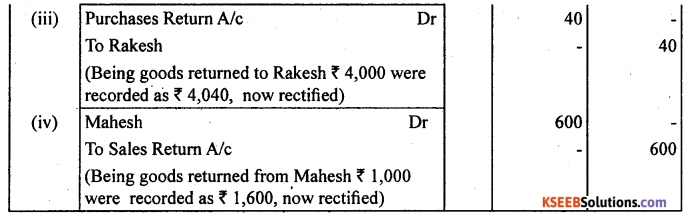
Rectify the following errors :
(i) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were not recorded as ₹ 7,200.
(ii) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were recorded as ₹ 9,900.
(iii) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were recorded as ₹ 4,040.
(iv) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were not recorded ₹ 1,600.
Answer:
Question 4.
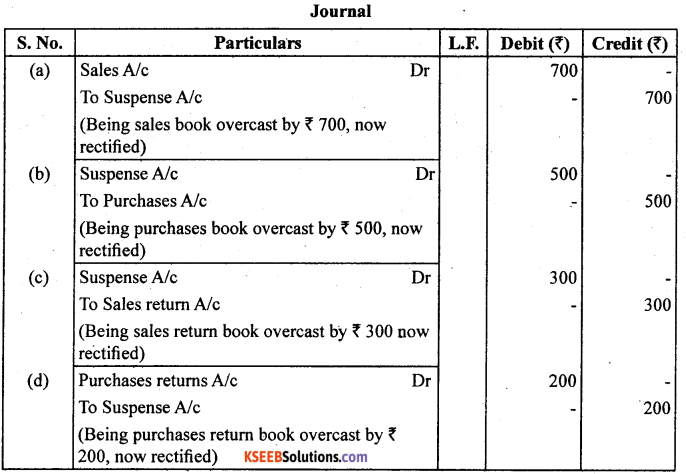
Rectify t le following errors :
(a) Sales book overcast by ₹ 700.
(b) Purchases book overcast by ₹ 500.
(c) Sales return book overcast by ₹ 300.
(d) Purchase return book overcast by ₹ 200.
Answer:
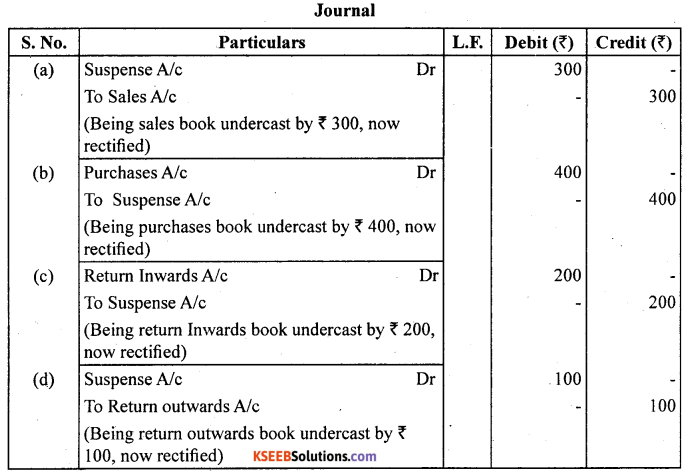
Question 5.
Rectify the following errors :
(a) Sales book undercast by ₹ 300.
(b) Purchases book undercast by ₹ 400.
(c) Return Inwards book undercast by ₹ 200.
(d) Purchase return book undercast by ₹ 100.
Answer:
![]()
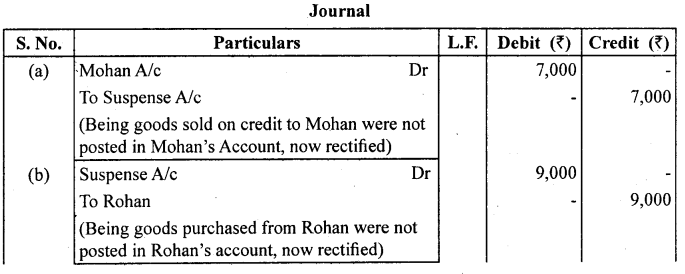
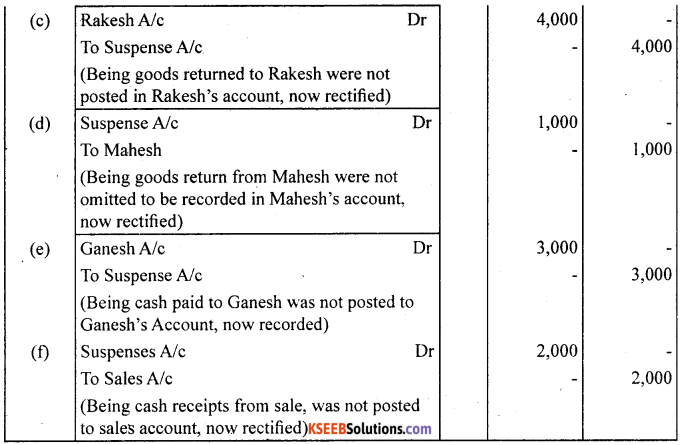
Question 6.
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were not posted.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were not posted.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were not posted.
(d) Good returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were not posted.
(e) Cash paid to Ganesh ₹ 3,000 was not posted.
(f) Cash sales ₹ 2,000 were not posted.
Answer:
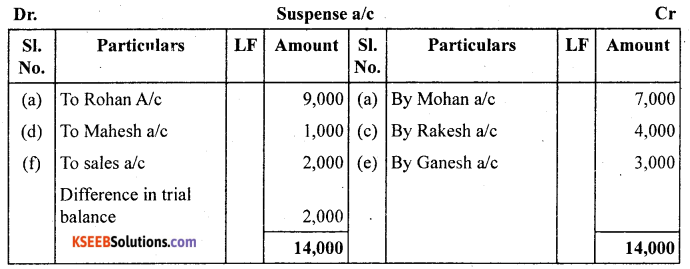
Question 7.
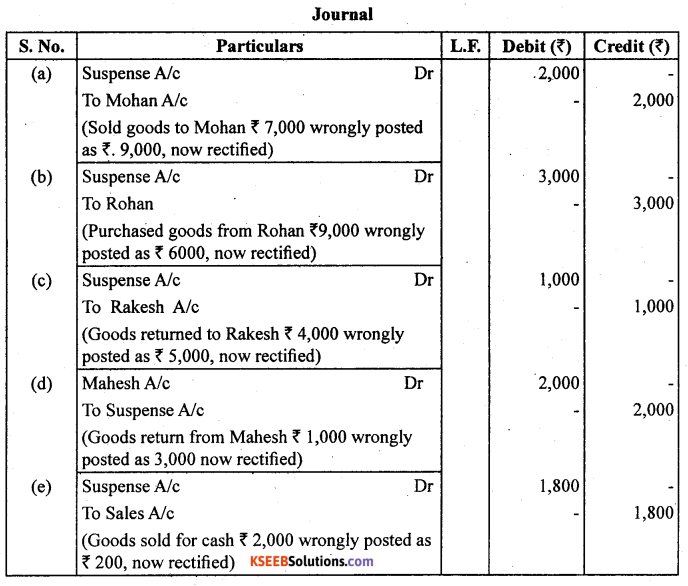
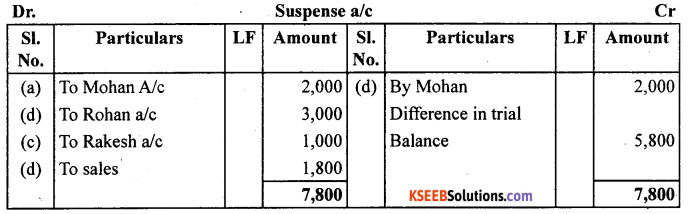
Rectify the following errors and ascertain the amount of different in trial balance by preparing suspense account:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were posted as ₹ 9,000.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were posted as ₹ 6,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were posted as ₹ 5,000.
(d) Good returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were posted as ₹ 3,000.
(e) Cash sales ₹ 2,000 were posted as ₹ 200.
Answer:
![]()
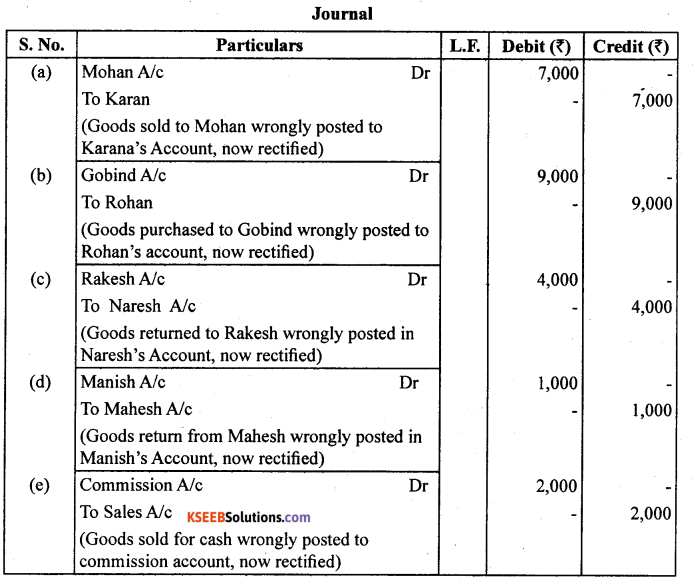
Question 8.
Rectify the following errors :
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were posted to Karan.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were posted to Gobind.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were posted to Naresh.
(d) Good returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were posted to Manish.
(e) Cash sales ₹ 2,000 were posted to commission account.
Answer:
Question 9.
Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened.
Ascertain the difference in trial balance.
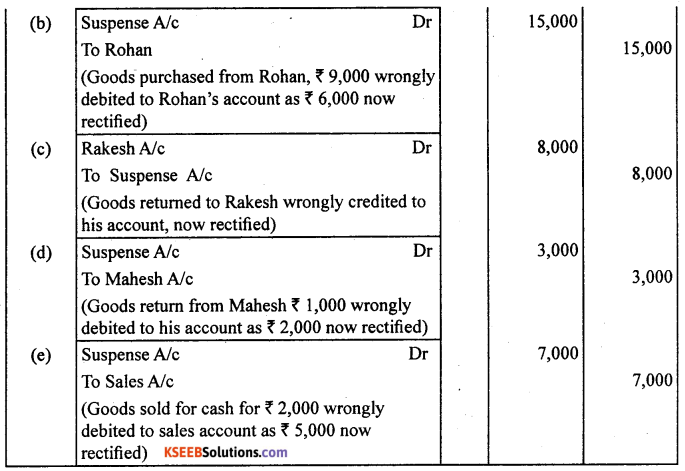
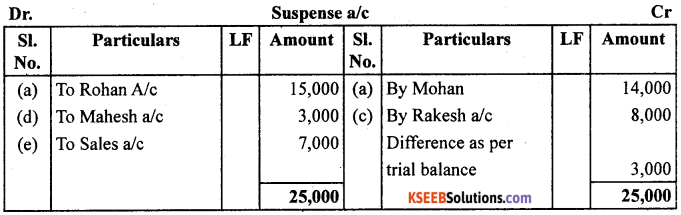
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were posted to the credit of his account.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were posted to the debit of his account as ₹ 6,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were posted to the credit of his account.
(d) Good returned from Mahesh 1,000 were posted to the debit of his account as ₹ 2,000.
(e) Cash sales ₹ 2,000 were posted to the debit of sales account as ₹ 5,000.
Answer:

Question 10.
Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened.
Ascertain the difference in trial balance.
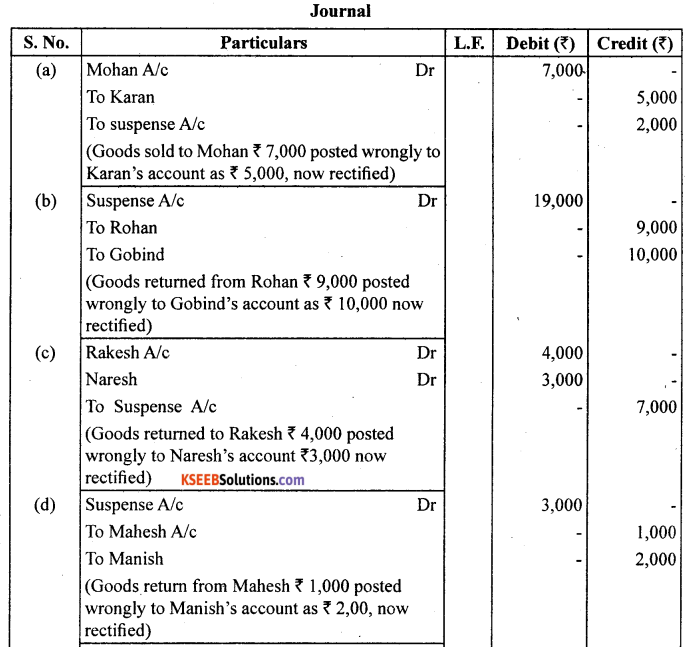
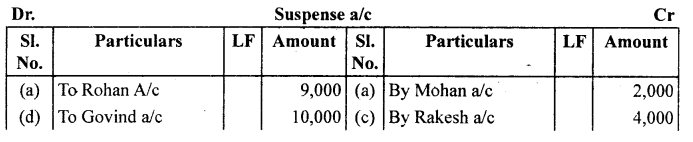
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were posted to Karan as ₹ 5,000.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were posted to the debit of Govind as ₹ 10,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were posted to the credit of Naresh as ₹ 3,000.
(d) Good returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were posted to the debit of Manish as ₹ 2,000.
(e) Cash sales ₹ 2,000 were posted to commission account as ₹ 200.
Answer:

![]()
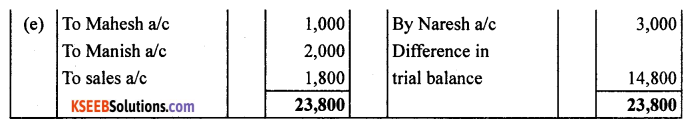
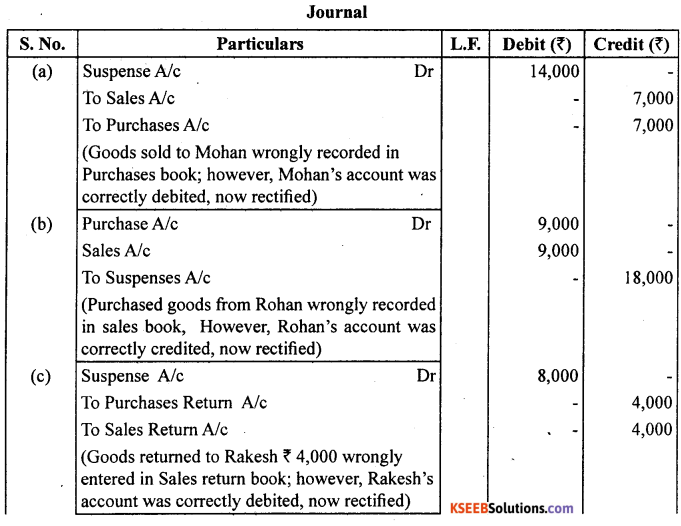
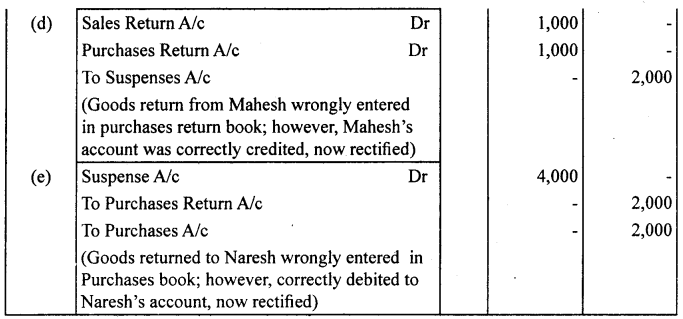
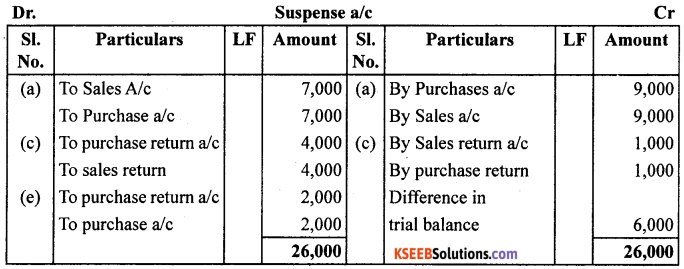
Question 11.
Rectify the following errors assuming that suspense account was opened.
Ascertain the difference in trial balance.
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were recorded in purchase book. However, Mohan’s account was correctly debited.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were recorded in sales book. However, Rohan’s account was correctly credited.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were recorded in sales return book. However, Rakesh’s account was correctly debited.
(d) Good returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were recorded through purchases return book. However, Mahesh’s account was correctly credited.
(e) Goods retuned to Naresh ₹ 2,000 were recorded through purchases book. However, Naresh’s account was correctly debited.
Answer:
Question 12.
Rectify the following errors :
(a) Furniture purchased for ₹ 10,000 wrongly debited to purchases account.
(b) Machinery purchased on credit from Raman for ₹ 20,000 was recorded through purchases book.
(c) Repairs on machinery ₹ 1,400 debited to machinery account.
(d) Repairs on overhauling of secondhand machinery purchased ₹ 2,000 was debited to repairs account.
(e) Sale of old machinery at book value of ₹ 3,000 was credited to sales account.
Answer:

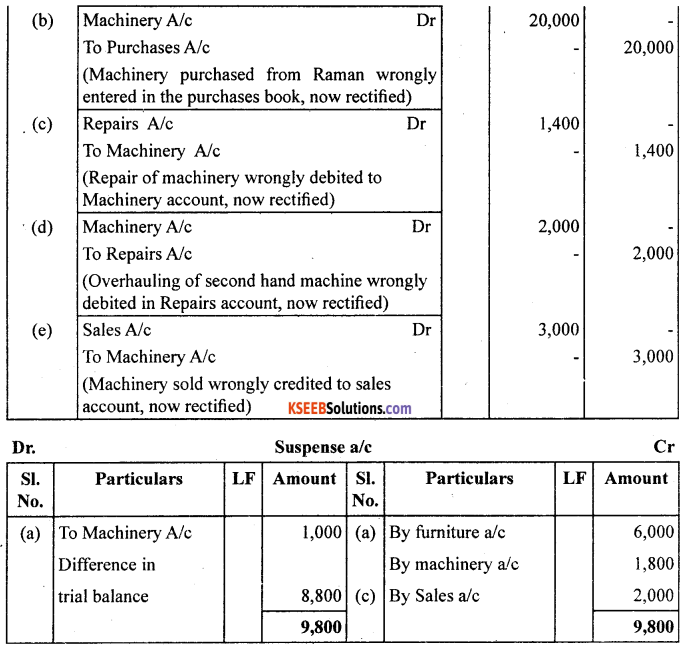
Question 13.
Rectify the following errors assuming that suspension account was opened ascertain the difference in trial balance :
(a) Furniture purchased for ₹ 10,000 wrongly debited to purchases account as ₹ 4,000.
(b) Machinery purchased on credit from Raman for ₹ 20,000 recorded through purchases book as ₹ 6,000.
(c) Repairs on machinery ₹ 1,400 debited to machinery account as ₹ 2,400.
(d) Repairs on overhauling of secondhand machinery purchased ₹ 2,000 was debited to repairs account as ₹ 200.
(e) Sale of old machinery at book value of ₹ 3,000 was credited to sales account as ₹ 5,000.
Answer:
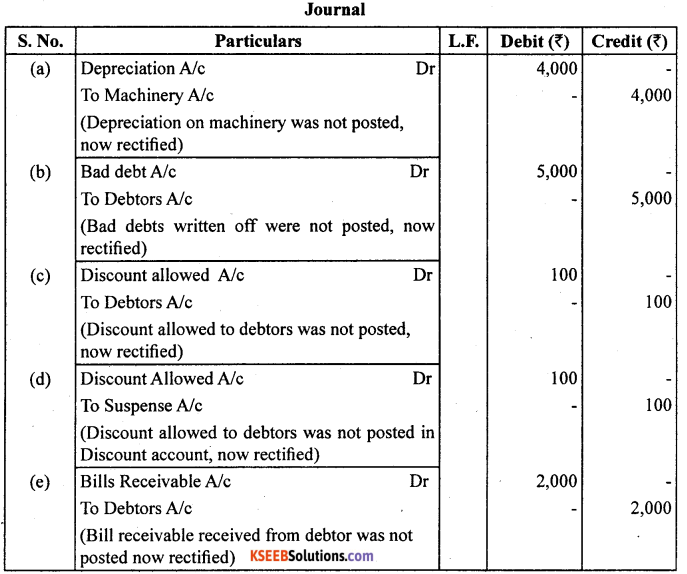
Question 14.
Rectify the following errors :
(a) Depreciation provided on machinery ₹ 4,000 was not posted.
(b) Bad debts written off ₹ 5,000 were not posted.
(c) Discount allowed to a debtor ₹ 100 on receiving cash from him was not posted.
(d) Discount allowed to a debtor ₹ 100 on receiving cash from him was not posted to discount account.
(e) Bill receivable for ₹ 2,000 received from a debtor was not posted. Ans. Journal
Answer:
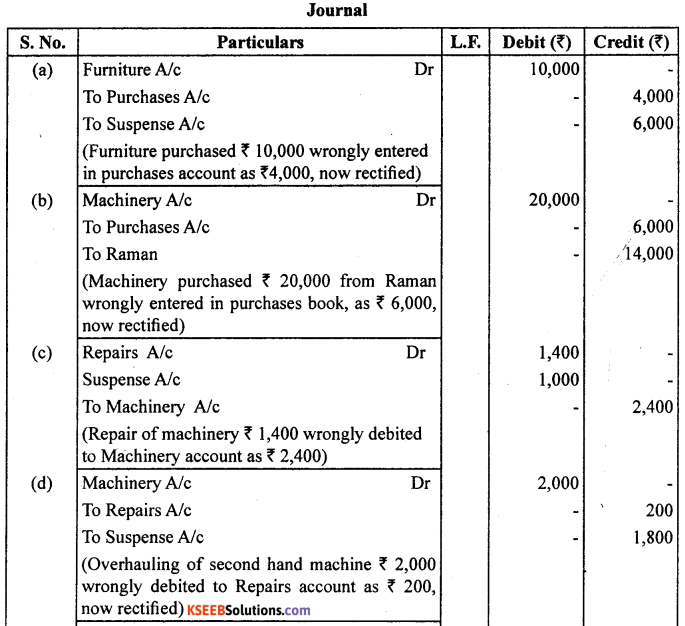

![]()
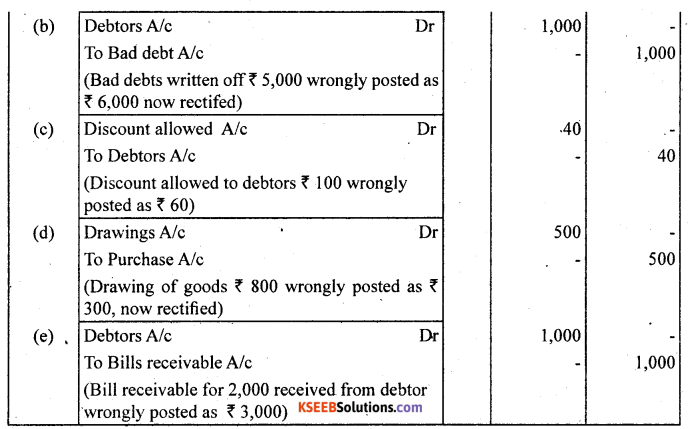
Question 15.
Rectify the following errors :
(a) Depreciation provided on machinery ₹ 4,000 was posted as ₹ 400.
(b) Bad debts written off ₹ 5,000 were as posted as ₹ 6,000.
(c) Discount allowed to a debtor ₹ 100 on receiving cash from him was posted as ₹ 60.
(d) Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use ₹ 800 were posted as ₹ 300.
(e) Bill receivable for ₹ 2,000 received from a debtor was posted as ₹ 3,000.
Answer:
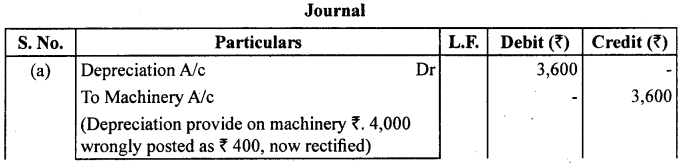
Question 16.
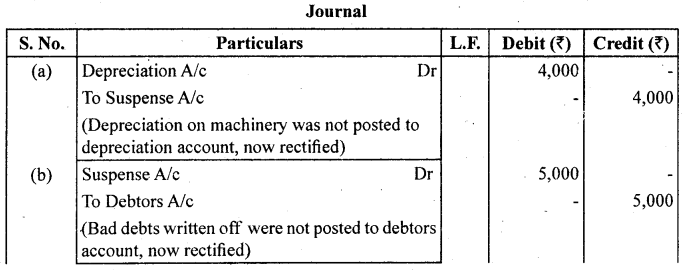
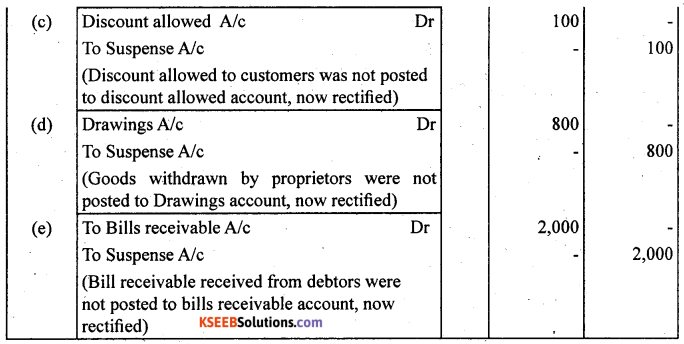
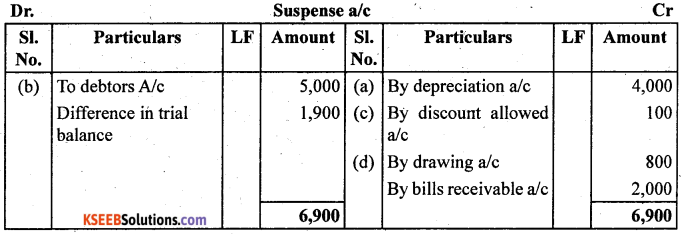
Rectify the following errors assuming that suspense account was opened :
Ascertain the difference in trial balance.
(a) Depreciation provided on machinery ₹ 4,000 was posted to depreciation account.
(b) Bad debts written off ₹ 5,000 were not posted to Debtors account.
(c) Discount allowed to a debtor ₹ 100 on receiving cash from him was not posted to discount allowed account.
(d) Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use ₹ 800 were not posted to drawing account.
(e) Bill receivable for ₹ 2,000 received from a debtor was not posted to bills receivable account.
Answer:
Question 17.
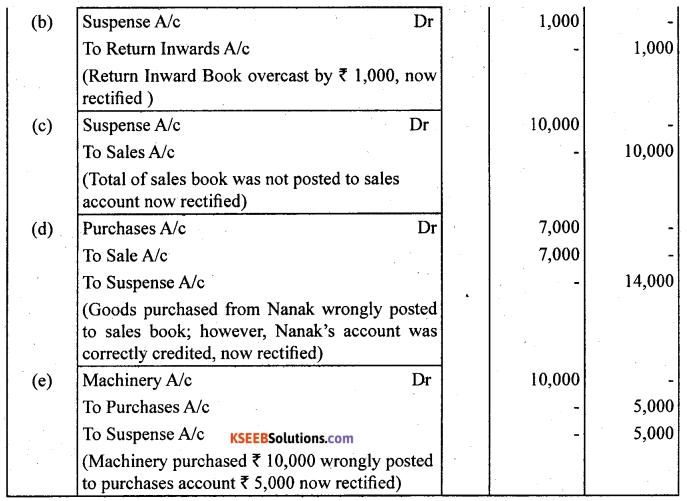
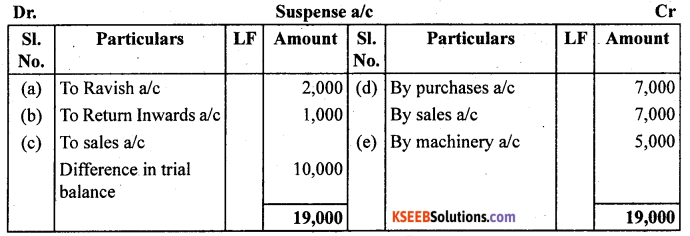
Trial balance of Anuj did not agree. It showed on excess credit of ₹ 6,000.
He put the difference to suspense account. He discovered the following errors
(a) Cash received from Ravish ₹ 8,000 posted to his account as ₹ 6,000.
(b) Returns inwards book overcast by ₹ 1,000.
(c) Total of sales book ₹ 10,000 was not posted to sales account.
(d) Credit purchases from Nanak ₹ 7,000 were recorded in sales book. However, Nanak’s account was correctly credited.
(e) Machinery purchased for ₹ 10,000 was posted to purchases account as ₹ 5,000. Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account.
Answer:

![]()
Question 18.
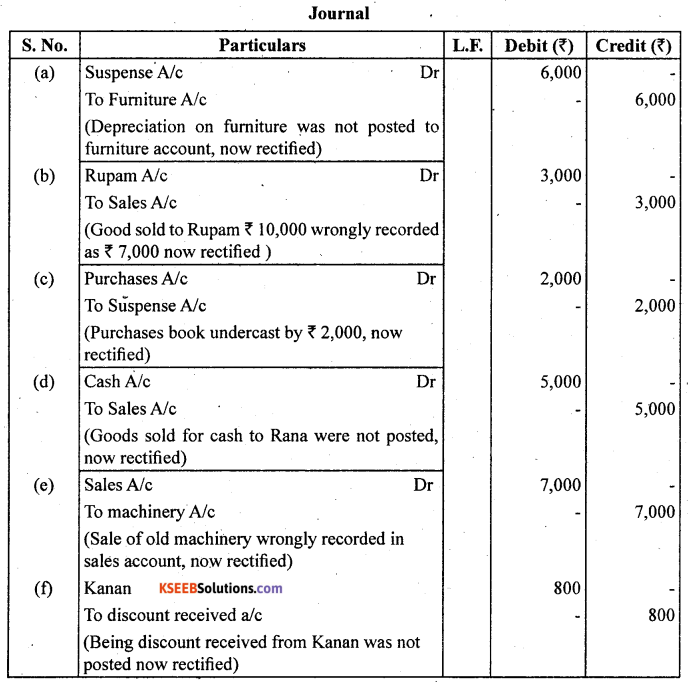
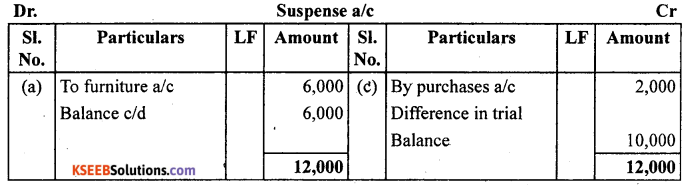
Trial balance of Raju showed an excess debit of ₹ 10,000. He put the difference to suspense account and discovered the following errors:
(a) Depreciation written – off the furniture ₹ 6,000 was not posted to furniture account.
(b) Credit sales to Rupam ₹ 10,000 were recorded as ₹ 7,000. ‘
(c) Purchases book undercast by ₹ 2,000.
(d) Cash sales to Rana ₹ 5,000 were not posted.
(e) Old machinery sold for ₹ 7,000 was credited to sales account.
(f) Discount received ₹ 800 from Kanan on playing cash to him was not posted. Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account.
Answer:
Question 19.
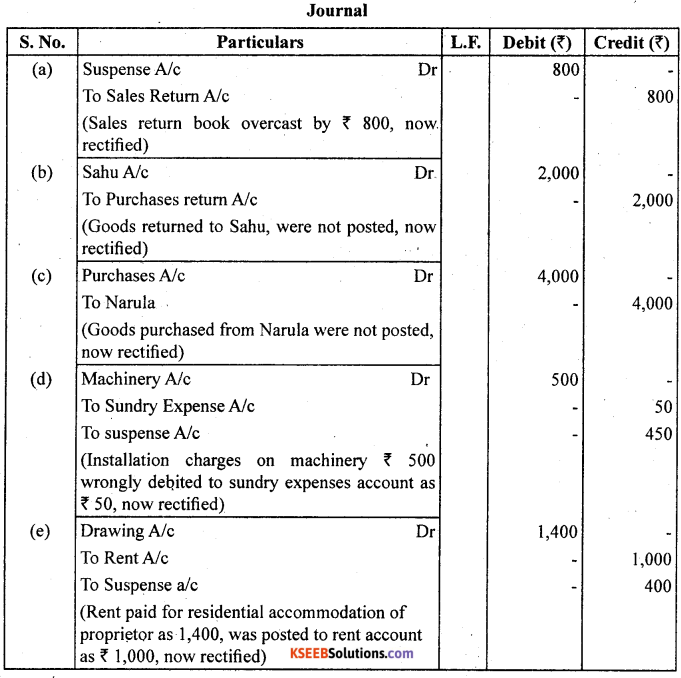
Trial balance of Madan did not agree and he put the difference to suspense account. He discovered the following errors:
(a) Sales return book overcast by ₹ 800.
(b) Purchases return to Sahu ₹ 2,000 were not posted.
(c) Goods purchased on credit from Narula ₹ 4,000 though taken into stock, but no entry was passed in the books.
(d) Installation charges on new machinery purchased ₹ 500 were debited to sundry expenses account as ₹ 50.
(e) Rent paid for residential accommodation of madam (the proprietor) ₹ 1,400 was debited to rent account as ₹ 1,000.
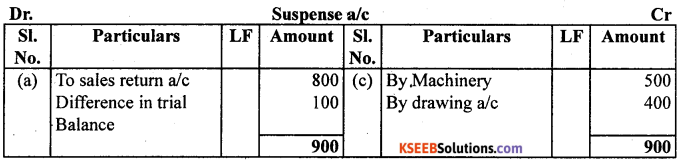
Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account to ascertain the difference in trial balance.
Answer:
![]()
Question 20.
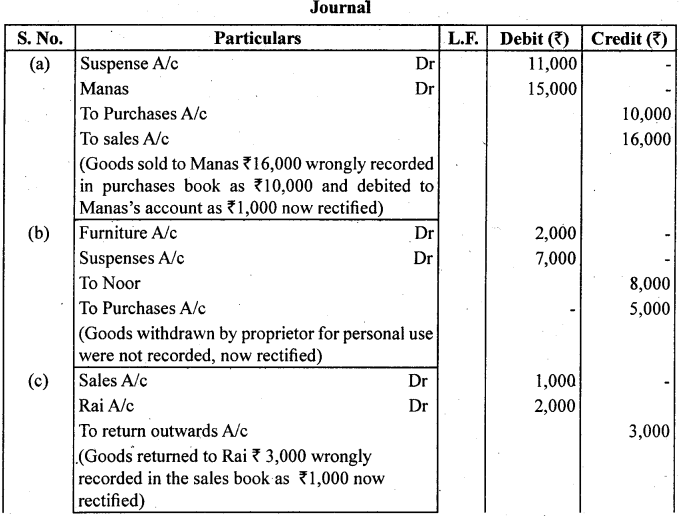
Trial balance of Khatau did not agree. He put the difference to suspense account and discovered the following errors:
(a) Credit sales to Manas ₹ 16,000 wre recorded in the purchases book as 10,000 and posted to the debit of Manas as ₹ 1,000.
(b) Furniture purchases from Noor 6,000 was recorded through purchases book as
5,0 and posted to the debit of Noor ₹ 2,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rai ₹ 3,000 recorded through the sales book as 1,000.
(d) Old machinery sold for ₹ 2,000 to Maneesh recorded through sales book as ₹ 1,800 and posted to the credit of Manish as ₹ 1,200.
(e) Total of returns inwards book ₹ 2,800 posted to Purchase account.
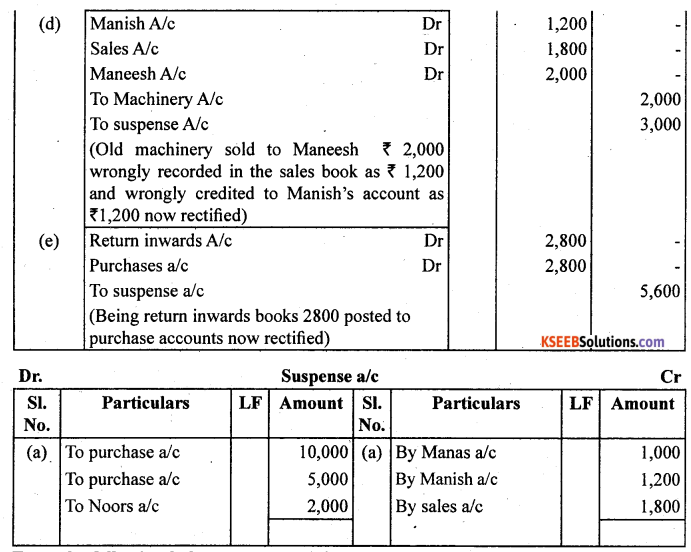
Rectify the following errors.
Answer:
Question 21.
From the following balances extracted from the books of Bopal as on 31st December 2007, prepare a trial balance.
Ranga’s capital 3,500
Purchases 4,000
Rent paid 120
Ranga’s Drawings 200
Bills receivable 600
Opening stock 500
Purchase returns 140
Sales returns 80
Plant and Machinery 2,000
Sales 4,800
Sundry detstors 2,800
Furniture 250
Salaries 360
Sundry creditors 2,800
Carriage 50
Insurance 20
Cash in hand 75
Cash at Bank 20
Bill payable 790
Discount received 15
Discount allowed 20
Answer:
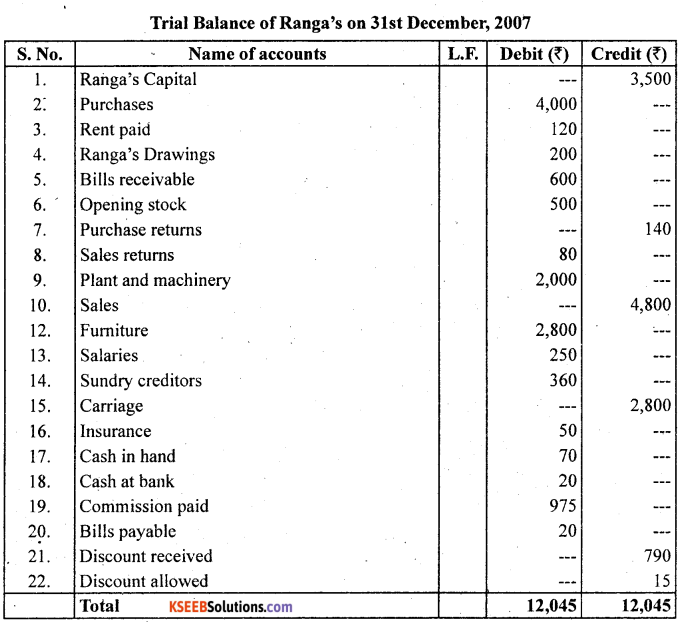
Question 22.
From the following trial balance (containg some errors) prepare correct trial balance.


Answer:
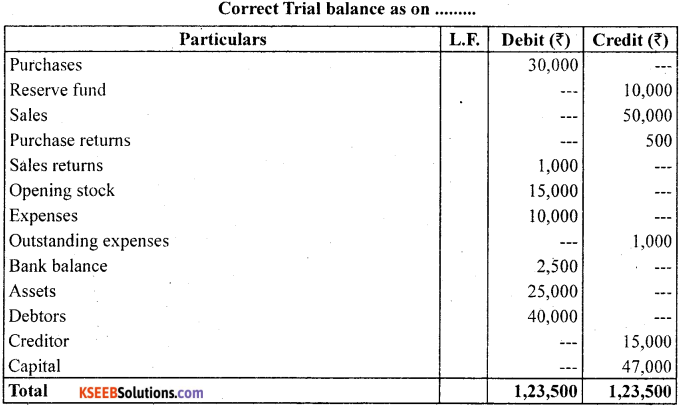
Question 23.
From the following ledger balances a Trial Balance of Mr. Santosh for the year ended 31-3-2001:
1. Salaries ₹ 5,000
2. Creditors ₹ 30,000
3. Debtors ₹ 42,000
4. Buildings ₹ 90,000
5. Capital ₹ 50,000
6. Motor Car ₹ 10,000
7. Purchases ₹ 45,000
8. Sales ₹ 74,500
9. Loan from bank ₹ 42,500
10. Drawings ₹ 5,000
Answer:
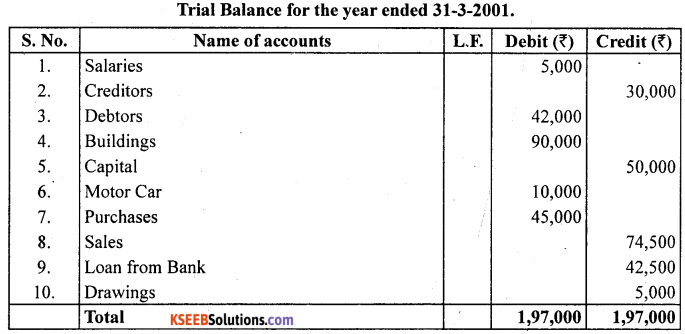
![]()
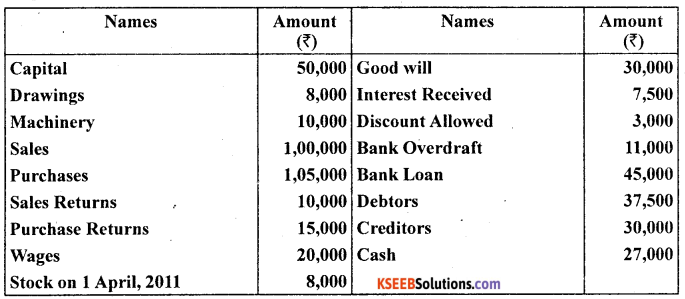
Question 24.
From the following incorrect Trial Balance prepare a correct Trial Balance as on 31st December 2010.
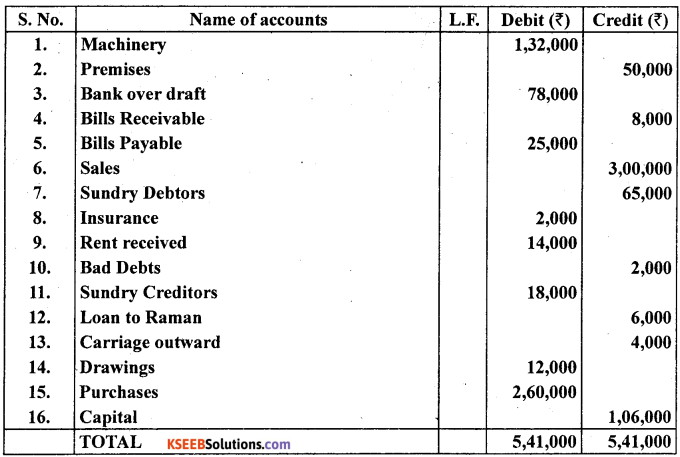
Answer:

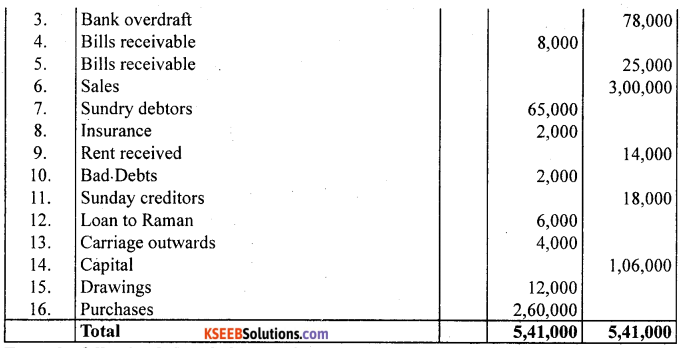
Question 25.
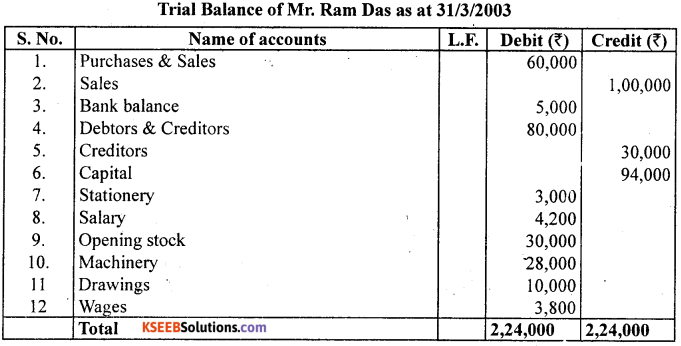
From the following ledger balances of Mr. Ram Das, Prepare a Trial Balance as on 31st March 2003.
Answer:
![]()
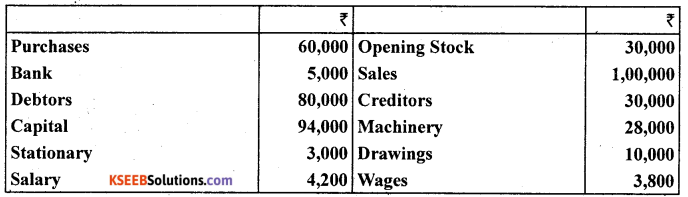
Question 26.
Prepare a triai balance as on Mar. 31, 2012 based on the following ledger balances.
Answer:
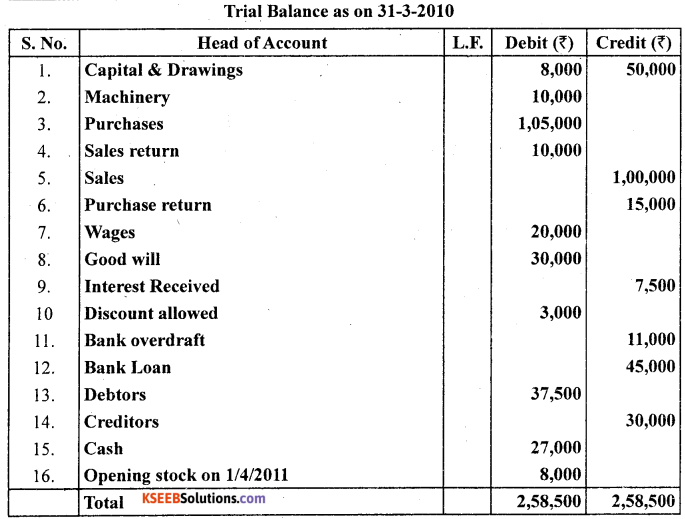
Question 27.
The trial balance of Prakash is prepared as on 30-06-2012 which contains some errors. Prepare the correct Trial balance.
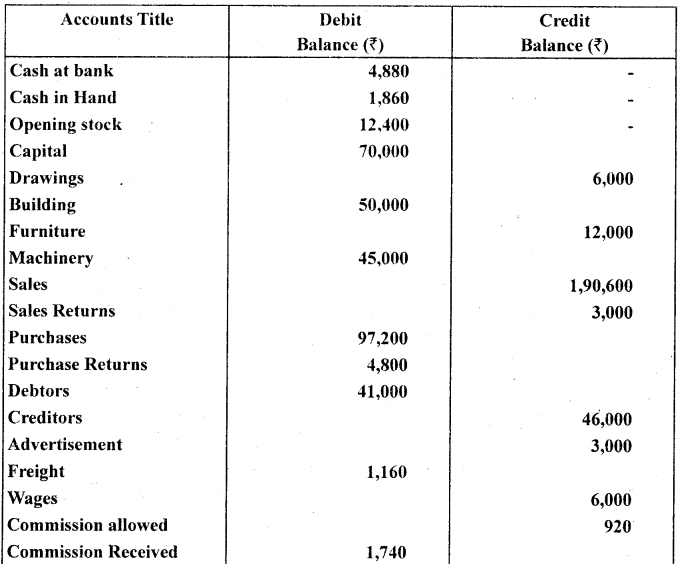
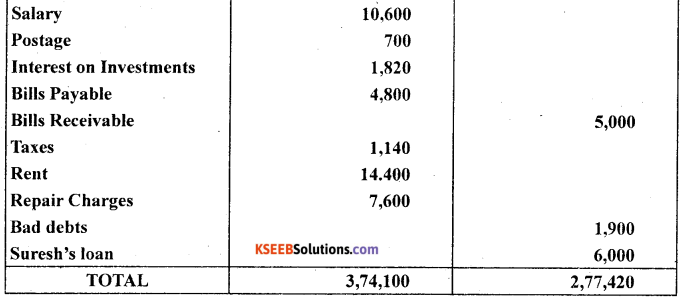
Answer:
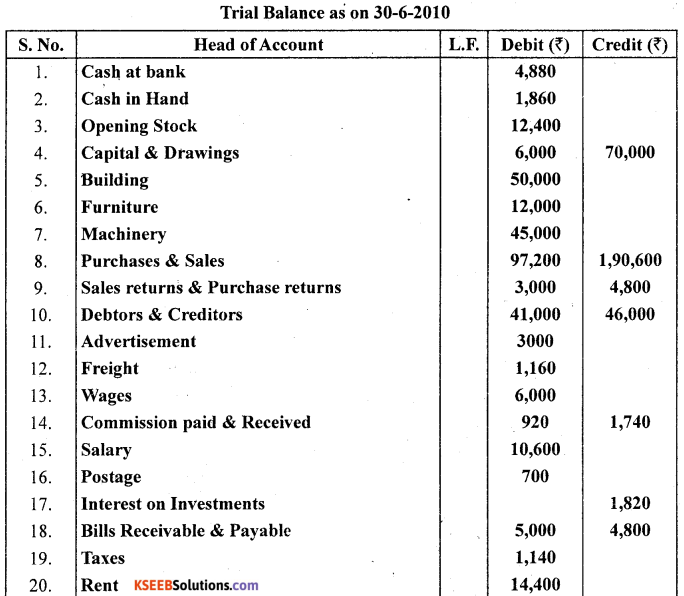

![]()