Students can download Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Important Questions, KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Question 1.
What happens in each of the following situations when:
- Milk is left at room temperature during summers.
- An iron tawa/pan/nail is left exposed to humid atmosphere.
- Grapes get fermented.
- Food is cooked.
- Food gets digested in our body.
- We respire?
Answer:
1. When milk is left at room temperature during summer season, the milk undergoes chemical change. The sugar present in milk is converted into an acid. This chemical change spoils the milk.
2. When an iron material such as a nail is left exposed to humid atmosphere, the iron undergoes oxidation (a chemical change) and begins to rust. A new substance called iron oxide is formed.
3. When grapes get fermented, the sugar present in grapes undergoes chemical change and a new substance such as alcohol is formed.
4. When food is cooked, the components present in food undergo chemical change resulting in the formation of new substances.
5. When food gets digested in our body, the various constituents of food will undergo chemical change and are broken down into simpler substances. For example, carbohydrates present in the food we consume changes into glucose during the process of digestion.
6. When we respire, the food present in the body cells will undergo chemical change. This process produces energy and carbon dioxide.
All the reactions above involve chemical changes and in each of the changes, one or more new substances are formed.
![]()
Question 2.
How do you show the formation of magnesium oxide from magnesium?
Answer:
Clean a magnesium ribbon about 2 cm long by rubbing it with sandpaper. Hold it with a pair of tongs. Heat it using a spirit lamp. Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame and changes into a white powder.
Collect this powder in a watch-glass. The ash-like powder so formed is magnesium oxide. Burning of magnesium is a chemical reaction. During this process, magnesium combined with oxygen to form magnesium oxide.
Question 3.
Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air while preparing magnesium oxide?
Answer:
When magnesium ribbon is exposed to moist air, a layer of magnesium oxide is formed on its surface. This hinders the process of burning. This is why magnesium ribbon must be cleaned with sand paper before heating it while preparing magnesium oxide.
Question 4.
Explain the reaction between lead nitrate solution and potassium iodide.
Answer:
Take lead nitrate solution in a test tube. Add potassium iodide into it and shake well. We observe the formation of a new yellow solid substance called lead iodide. During this process, another new substance called potassium nitrate is also formed.
This compound remains in solution. The reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide is a chemical change that results in the formation of new substances.
Question 5.
Explain the reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric acid.
Answer:
Take a few pieces of zinc granules in a small conical flask. Pour dilute sulphuric acid into the flask. The reaction begins immediately forming zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas. This is an example of a chemical change because new substances are formed during this reaction.
Question 6.
What is a chemical change? Give two examples of chemical changes in daily life.
Answer:
Any change in a substance or substances that results in the formation of one or more new substances is called a chemical change. Burning of fuels, respiration, rusting of iron etc., are examples of chemical change.
Question 7.
Describe the reaction between calcium oxide and water.
Answer:
Take a small amount of calcium oxide (quick lime) in a beaker. Slowly add water to it. A vigorous reaction takes place and the beaker becomes wanner. This is a chemical reaction during which calcium hydroxide is formed along with the liberation of heat.
Thus we may say that water reacts with calcium oxide forming calcium hydroxide along with the liberation of heat.
![]()
Question 8.
What changes can be generally observed during a chemical reaction?
Answer:
One or more of the following changes are generally observed during a chemical reaction:
- change in state
- change in colour
- evolution of a gas
- change in temperature.
Question 9.
What are reactants and products of a chemical reaction? Explain with an example.
Answer:
The substance or the substances that take part in a chemical reaction are called reactants. The substance or the substances formed during a chemical reaction are called products.
For example, lead nitrate reacts with potassium iodide forming lead iodide and potassium nitrate. In this reaction, the starting materials namely lead nitrate and potassium iodide are the reactants. The substances that are formed during the reaction namely lead iodide and potassium nitrate are the products.
Question 10.
What is a chemical equation?
Answer:
The representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and formulae of the substances involved in it, wherein the reactants are written on the left-hand side and the products on the right-hand side is called a chemical equation.
Question 11.
What is the simplest way of representing a chemical reaction?
Answer:
A chemical reaction is represented in the simplest manner using a word equation.
Question 12.
What is a word equation in Chemistry? Explain with an example.
Answer:
A chemical reaction that is represented by writing the complete names of the reactants and products rather than their symbols or formulae is known as a word equation. It is simply a chemical equation written in words.
In a word equation, the names of the reactants are written on the left hand side and the names of the products are written on the right hand side. The reactants and products are separated by an arrow directed to the right (towards the products).
In case the reaction has more than one reactant, + sign is put between the reactants. This sign on the reactants’ side indicates ‘reacts with’ or ‘combines with’. Similarly, + sign is put between the products when there is more than one product. Here the + sign indicates ‘and’. The arrow sign indicates ‘produces’ or ‘yields’.
Consider the reaction between zinc and dilute hydrochloric acid. During this reaction, zinc chloride and hydrogen gas are formed. This can be represented by a word equation as follows:

![]()
Question 13.
What does the arrow in a chemical equation indicate? What does a chemical equation represent?
Answer:
The arrow in a chemical reaction indicates the direction of the reaction. A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction.
Question 14.
Distinguish between a skeletal equation and a balanced equation.
Answer:
1. Skeletal equation:
A chemical equation in which the number of atoms of different elements is not equal on the two sides of the equation is called an unbalanced chemical equation. It is also called skeletal equation.
2. Balanced equation:
A chemical equation in which the number of atoms of different elements is equal on the two sides of the equation is called a balanced chemical equation.
Question 15.
What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Answer:
A balanced chemical equation is one in which the total number of atoms of each element are equal on both sides of the equation. A chemical equation is balanced so that the numbers of atoms of each type involved in a chemical reaction are the same on the reactant and product sides of the equation.
A balanced chemical equation satisfies the law of conservation of mass, i.e., the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products.
![]()
Question 16.
Write the steps involved in writing a balanced chemical equation.
Answer:
Step 1:
Know the reactants and products of the given chemical reaction and write down the word equation for the reaction. Note that the reactants must be written on the left hand side while the products must be written on the right hand side.
Step 2:
The second step is to write the skeletal equation. Write down the symbol and formula of each of the reactants and products.
Step 3:
Enclose the formula of each reactant and product in separate boxes and do not change the formula or the subscripts of anything inside the boxes while balancing the equation.
Step 4:
List the number of atoms of different elements on LHS (reactants) and RHS (products) separately.
Step 5:
Start balancing with the compound (either on the reactants side or on the products side) that contains the maximum number of atoms. After choosing the compound, select the element that has the maximum number of atoms. To balance the atoms, put a small whole number coefficient before the formula of the compound.
Step 6:
Balance all the elements one by one similarly. Check for the correctness of the balanced equation by counting and comparing the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation.
Step 7:
Write the physical state of each of the reactants and products.
![]()
Question 17.
Iron reacts with water (steam) forming iron oxide and hydrogen gas. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
Answer:
Step 1:
Let us write the word equation:
Iron + Water → Iron oxide + Hydrogen
Step 2:
Let us write the skeletal equation for the reaction using symbols and formulae:
Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
Step 3:
Let us put all the formulae/symbols in separate boxes.
![]()
Step 4:
Let us list the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation:
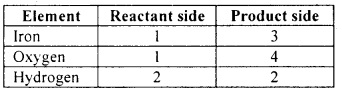
Step 5:
We shall start with the compound having the highest number of atoms namely iron oxide. In this compound, let us start with oxygen as the number of oxygen atoms is highest in the compound.
There are four oxygen atoms in iron oxide on the RHS. However, there is only one oxygen atom on the LHS. To balance this, we shall put 4 as the coefficient for water (H2O).
Now let us balance the iron atoms. This can be done by putting 3 as the coefficient for Fe on the LHS. Now let us balance the hydrogen atoms. This is done by putting 4 as the coefficient for H2 on the RHS. Now the equation becomes 3 Fe + 4 H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 H2
![]()
Step 6:
Let us now check for the correctness of the balance by comparing the number of atoms on either side of the equation.
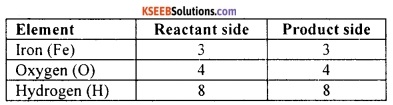
Step 7:
Since each type of atom is balanced on both sides, the equation is balanced. Let us now mention the physical state of each of the reactants and products.
The gaseous, liquid, aqueous and solid states of reactants and products are represented by the notations (g), (l), (aq) and (s), respectively. The word aqueous (aq) is written if the reactant or product is present as a solution in water.
3 Fe (s) + 4 H2O (g) → Fe3O4 (s) + 4 H2 (g)
Note that the symbol (g) is used with H2O to indicate that in this reaction water is used in the form of steam.
![]()
Question 18.
Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions:
- Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
- Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
- Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen.
Answer:
- H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2 HCl (g)
- 3 BaCl2 (aq) + Al2(SO4)3 (aq) → 3 BaSO4 (s) + 2 AlCl3 (aq)
- 2 Na (s) + 2 H2O (l) → 2 NaOH (aq) + H2 (g).
Question 19.
Write balanced chemical equations with symbols for the following reactions:
- Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
- Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Answer:
1. Barium chloride + Sodium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Sodium chloride
BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2 NaCl (aq)
2. Sodium hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid → Sodium chloride + Water
NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
![]()
Question 20.
Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them:
- Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
- Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
- Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
- Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Answer:
1. Hydrogen + Nitrogen → Ammonia
3 H2 (g) + N2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g)
2. Hydrogen sulphide + Oxygen → Water + Sulphur dioxide
2 H2S (g) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 H2O (l) + 2 SO2 (g)
3. Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
3 BaCl2(s) + Al2(SO4)3 (s) → 3 BaSO4 (s) + 2 AlCl3 (s)
4. Potassium + Water → Potassium hydroxide + Hydrogen
2 K (s) + 2 H2O (l) → 2 KOH (aq) + H2 (g)
Question 21.
Balance the following chemical equations:
- HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
- NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
- NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
- BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl.
Answer:
- 2 HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2 H2O
- 2 NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2 H2O
- NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
- BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2 HCl.
![]()
Question 22.
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
- Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium carbonate + Water
- Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver
- Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper
- Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride.
Answer:
- Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 (g) → CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l)
- Zn (s) + 2 AgNO3 (aq) → Zn(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 Ag (s)
- 2Al (s) + 3 CuCl2 (aq) → 2 AlCl3 (aq) + 3 Cu (s)
- BaCl2 (aq) + K2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (aq) + 2 KCl (aq)
Question 23.
A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for white washing.
- Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
- Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in (i) above with water.
Answer:
- The substance ‘X’ is known as calcium oxide (quick lime). Its formula is CaO.
- Calcium oxide reacts with water forming calcium hydroxide.
Calcium oxide + Water → Calcium hydroxide
CaO (s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq)
Question 24.
List the various types of chemical reactions.
Answer:
The different types of chemical reactions are:
- Chemical combination
- Chemical decomposition
- Chemical displacement
- Double displacement.
![]()
Question 25.
What are exothermic and endothermic chemical reactions? Give an example each.
Answer:
1. Exothermic reactions:
Those chemical reactions during which heat is released are known as exothermic chemical reactions.
E.g.: Burning of fuels and respiration are examples of exothermic reactions.
2. Endothermic reactions:
Those chemical reactions during which heat is absorbed are known as endothermic reactions.
E.g.: Reaction between nitrogen and oxygen that results in nitric oxide is an example of an endothermic reaction.
Question 26.
What is meant by chemical combination or combination reaction? Give an example.
Answer:
A chemical reaction in which two or more substances (reactants) chemically combine to form a product is called chemical combination. It is also called combination reaction.
E.g.: Magnesium on heating bums in air forming magnesium oxide. This is a combination reaction.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO.
Question 27.
Explain the reaction that occurs when calcium oxide is made to react with water. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. What type of chemical reaction is this? Why is it called an exothermic reaction?
Answer:
Take a small amount of calcium oxide (quick lime) in a beaker. Slowly add water to this. Touch the beaker. The beaker will have become warmer. During this reaction, calcium oxide reacts with water forming calcium hydroxide. This reaction also releases heat. This reaction can be represented by the following equation:
CaO (s) + H2O(l) (Quick lime) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) (Slaked lime) + Heat.
In this reaction two substances are combining chemically forming a single compound. This is an example of chemical combination. The reaction above produces heat. Therefore, it is an exothermic reaction.
![]()
Question 28.
Distinguish between quick lime and slaked lime.
Answer:
Quick lime is the common name of a compound called calcium oxide. Its molecular formula is CaO. Slaked lime is the common name of a chemical compound called calcium hydroxide. Its molecular formula is Ca(OH)2.
Question 29.
Why do walls appear shiny two to three days after they are white washed with calcium hydroxide? Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Answer:
Walls are white washed with calcium hydroxide. Calcium hydroxide slowly reacts with carbon dioxide present in air forming calcium carbonate. Calcium carbonate gives shiny finish to the walls. The reaction that occurs here can be represented by the following equation:
Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 (g) → CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l).
Question 30.
Represent the reaction involving burning of coal by a balanced chemical equation. What type of chemical reaction is this? Why? Why is this reaction called an exothermic reaction?
Answer:
Coal, on heating, combines with oxygen present in air, forming carbon dioxide. This reaction also releases plenty of heat.
C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + Heat
In this reaction two chemical substances combine to form a single compound. Therefore, this is an instance of chemical combination reaction. This reaction releases heat. Therefore, it is an exothermic reaction.
![]()
Question 31.
Why is respiration considered an exothermic reaction? Explain.
Answer:
During respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen forming carbon dioxide and water.
C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2 (aq) → 6CO2 (aq) + 6H2O (l) + energy
This reaction also releases heat. This is why respiration is considered an exothermic reaction.
Question 32.
Hydrogen combines with oxygen to form water. What type of reaction is this? Why? Write a balanced chemical equation to represent this reaction.
Answer:
In the reaction above, two substances namely hydrogen and oxygen chemically combine to form a single compound namely water. Therefore, this is a case of chemical combination. The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
Question 33.
What is meant by decomposition reaction? Explain with an example.
Answer:
A chemical reaction in which a single compound breaks up into two or more products is called a decomposition reaction. It is also called chemical decomposition.
For example, ferrous sulphate decomposes on heating forming anhydrous ferrous sulphate and water. Anhydrous ferrous sulphate on further heating decomposes to form ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide. In this reaction, there are two decomposition reactions. The first one is:
FeSO4.7H2O (Ferrous sulphate crystals) (s) → FeSO4 (Anhydrous ferrous sulphate) (s) + 7H2O
Anhydrous ferrous sulphate on further heating decomposes to give the following reaction:
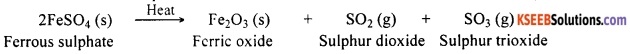
![]()
Question 34.
Describe an experiment to show the decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals. What are the products forrtied during the reaction?
Answer:
Take about 2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals in a dry boiling tube. Note the green colour of the ferrous sulphate crystals. Heat the boiling tube over a flame using a spirit lamp. Observe the changes.
Now the green ferrous sulphate changes its colour on losing water present in its crystal and forms anhydrous ferrous sulphate. On further heating, ferrous sulphate decomposes to form a reddish brown residue. This is ferric oxide. Gases with a characteristic smell are also produced during the reaction. The products formed in this reaction are ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide.
Question 35.
Suma took a pale green substance A in a test tube and heated it over the flame of a burner. A brown coloured residue B was formed along with the evolution of two gases with burning smell of sulphur. Identify A and B. Write the chemical reaction involved.
Answer:
Substance A is ferrous sulphate (FeSO4). Two gases, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide evolved.
Substance B is ferric oxide (Fe2O3).
The reaction involve is

Question 36.
Explain the thermal decomposition of lead nitrate. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. Why is this reaction called decomposition reaction?
OR
Which coloured fumes are obtained when lead nitrate is heated? Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. Name the type of this chemical reaction.
OR
Name the brown fumes liberated when lead nitrate is heated. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
Answer:
Take about 2 g of lead nitrate powder in a boiling tube. Hold the boiling tube with a pair of tongs and heat it over a flame using a spirit lamp. Now, brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide are produced. A yellow residue remains in the boiling tube. This is lead oxide. This reaction can be represented by the following equation:

In this reaction, a single compound breaks down chemically forming three new substances (products). Hence, it is called decomposition reaction.
![]()
Question 37.
Limestone on heating decomposes to form quick lime and carbon dioxide. Represent this reaction by a balanced chemical equation.
Answer:
The chemical name of limestone is calcium carbonate. This compound on heating decomposes to give calcium oxide (quick lime) and carbon dioxide.

Question 38.
Draw a neat, labelled diagram to show the electrolytic decomposition of water.
OR
Draw the diagram of the apparatus used to show that water is a compound of hydrogen and oxygen. Label the following parts:
- The part where oxygen is collected.
- The part where hydrogen is collected.
Answer:
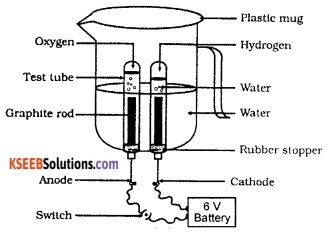
Question 39.
Describe an experiment to show the electrolytic decomposition of water. Write a suitable balanced equation for the reaction.
Answer:
Take a plastic mug and drill two holes at its base. Fit a rubber stopper in each of these holes. Insert carbon (graphite) electrodes in these rubber stoppers. Connect the electrodes to a 6-volt battery. Fill the mug with water such that the electrodes get fully immersed. Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to the water to make it conducting.
Invert a test tube filled with water over each of the two carbon electrodes. Switch on the current and leave the apparatus undisturbed for some time. Now, water decomposes to form hydrogen and oxygen.
Hydrogen gets collected in the test tube inverted over the cathode while the oxygen gets collected in the test tube inverted over the anode. It is also found that the volume of hydrogen is twice the volume of oxygen. This reaction is represented by the following equation:
2 H2O (l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g).
![]()
Question 40.
During the electrolytic decomposition of water, why is the amount of sas collected in one of the test tubes double of the amount collected in the other? Name this eas.
Answer:
In water, hydrogen and oxygen are present in the ratio 2:1 by volume. During decomposition, hydrogen and oxygen are produced in the same ratio. Therefore, the amount of gas in one of the test tubes is double the amount collected in the other. The gas present in higher volume is hydrogen and the other gas is oxygen.
Question 41.
What is photo-decomposition? Give an example.
Answer:
The decomposition of a chemical compound in presence of light is known as photo-decomposition. For example, silver chloride decomposes in presence of sunlight into silver and chlorine.
Question 42.
Silver chloride decomposes in the presence of sunlight. How do you show this? Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
Answer:
Take about 2 g of silver chloride in a china dish. Place this china dish in sunlight for some time. Observe the changes. The white crystals of silver chloride turn grey in sunlight. In the presence of sunlight, silver chloride decomposes into silver and chlorine.
2AgCl(s) → 2Ag (s) + Cl2 (g)
![]()
Question 43.
Silver chloride is usually stored in dark coloured bottles. Give reason.
Answer:
Silver chloride decomposes into silver and chlorine when exposed to light. In order to prevent photo-decomposition, silver chloride is stored in dark coloured bottles.
Question 44.
Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of
- heat
- light and
- electricity.
Answer:
1. CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
In the reaction above, energy for decomposition is supplied in the form of heat.
2. 2AgCl (s) → 2Ag (s) + Cl2 (g)
In the reaction above, energy for decomposition is supplied in the form of sunlight.
3. 2H2O (l) → 2H2 (g)+ O2 (g)
In the reaction above, energy for decomposition is supplied in the form of electricity.
![]()
Question 45.
Identify the reactant which is oxidized and that which is reduced in the following chemical
reaction: CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O.
Answer:
In this chemical reaction, the reactant that is reduced is CuO and the reactant that is oxidised is H2.
Question 46.
Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
In decomposition reaction a single substance decomposes to form two or more substances. This is the exact opposite of combination reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product. This is why composition reactions are called the opposite of combination reactions.
General equation for a combination reaction: A + B → AB.
General equation for a decomposition reaction: AB → A + B.
Question 47.
What is meant by displacement reaction? Give an example.
Answer:
A chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound is known as a displacement reaction.
For example, iron is more reactive than copper. Therefore, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution.
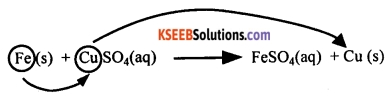
Question 48.
Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Answer:
Copper sulphate solution is blue in colour. When an iron nail is dipped in a solution of copper
sulphate, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate and forms iron sulphate. Iron sulphate is greenish. Therefore, the colour of copper solution changes to green when an iron nail is dipped in it.
![]()
Question 49.
Describe a simple experiment to show that a more active element displaces a less active element from the solution of its compound. Represent this reaction by a suitable equation.
Answer:
Take two iron nails and clean them by rubbing with sand paper. Take about 10 mL of copper sulphate solution in a test tube. Tie one of the nails with a thread and carefully immerse it inside the copper sulphate solution. Keep the other nail for comparison. After about 15-20 minutes, take out the nail from the copper sulphate solution.
A brownish substance is formed on the iron nail and the solution will have turned greenish. In this reaction, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate. The brownish colour on the iron nail is due to the deposition of displaced copper. The greenish colour of the solution is due to the formation of iron sulphate.
Iron + Copper sulphate → Iron sulphate + Copper
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
This experiment shows that iron is more reactive than copper.
Question 50.
Give an example of a double displacement reaction.
Answer:
Zinc is a more reactive element than copper. Zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate solution. The reaction is represented by the following equation:
Zinc + Copper sulphate → Zinc sulphate + Copper
Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
Question 51.
Describe the reaction between lead and copper chloride solution. What type of reaction is this? Between lead and copper, which is more reactive? Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
Answer:
When a lead rod is dipped in a solution of copper chloride, lead displaces copper from copper chloride. During this reaction lead chloride and copper are formed as products. This is a displacement reaction.
Between lead and copper, lead is more reactive. This is why lead displaces copper from copper chloride solution.
The reaction above is represented by the following equation:
Lead + Copper chloride → Lead chloride + Copper
Pb (s) + CuCl2 (aq) → PbCl2 (aq) + Cu(s)
![]()
Question 52.
Zinc liberates hydrogen gas when it reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid whereas copper does not. Explain why.
Answer:
Zinc is chemically more reactive than hydrogen. Therefore, zinc can displace hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid. However, copper is less reactive than hydrogen. Therefore, copper cannot displace hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid.
Question 53.
What is meant by double displacement reaction? Give an example.
Answer:
A chemical reaction in which the two reactant compounds exchange their positive ions to form two new compounds is known as a double displacement reaction.
For example, silver nitrate reacts with sodium chloride forming silver chloride and sodium nitrate. Silver nitrate + Sodium chloride → Silver chloride + Sodium nitrate.
AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) → AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq).
Question 54.
Describe an experiment to show double displacement reaction.
Answer:
Take about 3 mL of sodium sulphate solution in a test tube. Add about 3 mL of barium chloride solution to it. Shake well to ensure proper mixing of the two solutions. Soon we observe the formation of a white substance, which is insoluble in water.
This insoluble substance formed is known as a precipitate. This is barium sulphate. Another product formed during this reaction is sodium chloride. In this reaction, the chloride ion present in barium chloride and sulphate ion in sodium sulphate are exchanged to form two new compounds. This is an instance of double displacement reaction.
Sodium sulphate + Barium chloride → Barium sulphate + Sodium chloride
Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (aq)
![]()
Question 55.
In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal Write down the reaction involved.
Answer:
Silver nitrate + Copper → Copper nitrate + Silver
2AgNO3 (aq) + Cu (s) → Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (s)
Question 56.
What is a precipitation reaction? Give an example.
Answer:
An insoluble substance formed during a chemical reaction is called a precipitate. Any reaction that produces a precipitate can be called a precipitation reaction. It is represented by a downward arrow (↓).
For example, sodium sulphate reacts with barium chloride to form barium sulphate and sodium chloride. Here barium chloride is a precipitate. Therefore, this reaction is a precipitation reaction.
Question 57.
When the solutions of lead (II) nitrate and potassium iodide are mixed,
- What is the colour of the precipitate formed? Name the compound precipitated,
- Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction,
- Is this also a double displacement reaction?
Answer:
1. When lead nitrate and potassium iodide are mixed, a yellow precipitate is formed.’ The compound formed in the form of a precipitate is lead iodide (PbI2).
2. Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) → PbI2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq).
3. Yes, this reaction is a double displacement reaction.
![]()
Question 58.
What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
When a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its salt solution, then it is called displacement reaction. When there is an exchange of ions between the reactants to produce new substances, it is called double displacement reaction.
In a displacement reaction one displacement takes place, while in a double displacement reaction two displacements take place.
Example for a displacement reaction:
Mg (s) + 2HCl (aq) → MgCl2 + H2 (g).
Example for a double displacement reaction:
2KBr (aq) + BaI2 (aq) → 2KI (aq) + BaBr2 (aq).
Question 59.
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case:
- Potassium bromide (aa) + Barium iodide (aa) → Potassium iodide (aq) + Barium bromide(s).
- Zinc carbonate (s) → Zinc oxide (s) + Carbon dioxide (g)
- Hydroeen fg) + Chlorine (fg) → Hydrogen chloride (s)
- Magnesium (s) + Hydrochloric acid (aq) → Magnesium chloride (aq) + Hydrogen (s).
OR
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following chemical reactions:
- Potassium bromide reacts with Barium iodide.
- Zinc carbonate is heated.
Answer:
1. 2KBr (aq) + BaI2 (aq) → 2KI (aq) + BaBr2 (aq).
This is a double displacement reaction.
2. ZnCO3 (s) → ZnO (s) + CO2 (g).
This is a decomposition reaction.
3. H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl (g).
This is a combination reaction.
4. Mg (s) + 2HCl (aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g).
This is a displacement reaction.
![]()
Question 60.
Balance the following chemical equations and identify the type of chemical reaction:
- Mg (s) + Cl2 (g) → MgCl2 (s)
- HgO (s) → Hg (l) + O2 (g)
- Na (s) + S (s) → Na2S (s)
- TiCl4 (l) + Mg (s) → Ti (s) +MgCl2(s)
- CaO (s) + SiO2 (s) → CaSiO3 (s)
- H2O2 (l) → H2O (l) + O2 (g).
Answer:
1. Mg (s) + Cl2 (g) → MgCl2 (s).
This reaction is a chemical combination.
2. 2 HgO (s) → 2 Hg (l) + O2 (g).
This reaction is a chemical decomposition.
3. 2 Na (s) + S (s) → Na2S (s).
This reaction is a chemical combination.
4. TiCl4 (l) + Mg (s) → Ti (s) + MgCl2 (s).
This reaction is a chemical displacement.
5. CaO (s) + SiO2 (s) → CaSiO3 (s).
This reaction is a chemical combination.
6. H2O2 (l) → H2O (l) + O2 (g).
This reaction is a chemical decomposition.
![]()
Question 61.
What is oxidation and reduction? Give an example for each.
OR
Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each:
- Oxidation,
- Reduction.
Answer:
1. Oxidation:
A chemical reaction that involves gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen is known as oxidation.
E.g.: Consider the reaction in which magnesium ribbon burns in air forming magnesium oxide.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
In this reaction, oxygen is added to magnesium and therefore, magnesium is oxidized. This is an example of oxidation.
2. Reduction:
A chemical reaction that involves gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen is known as reduction.
E.g.: Zinc oxide reacts with carbon forming zinc and carbon monoxide.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
In this reaction, oxygen is removed from zinc oxide. Therefore, zinc oxide is reduced to zinc. This is a reduction reaction.
![]()
Question 62.
How do you show the oxidation of a metal into its metal oxide?
Answer:
Take about 1 g of copper powder in a china dish. Heat the china dish. The surface of copper powder becomes dark due to the formation of black copper (II) oxide. In this reaction, oxygen is added to copper and copper oxide is formed. We say that copper is oxidised to copper oxide.
2CU + O2 → 2CuO.
Question 63.
A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Write the name of the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Answer:
The shiny brown coloured element is the copper metal (Cu). When heated in air, copper reacts with the atmospheric oxygen to form a black coloured compound called copper oxide.
2Cu (s) + O2 (g) → 2CuO (s).
Question 64.
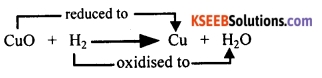
What happens when hydrogen is passed over hot copper (II) oxide? What type of reaction is this? Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
Answer:
If hydrogen gas is passed over heated copper (II) oxide (CuO), the black coating on the surface turns brown. During this reaction, oxygen is removed from copper oxide. Therefore, this is a reduction reaction. This is represented by the following equation:
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O.
![]()
Question 65.
Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions:
- 4 Na(s) + O2 → 2 Na2O(s)
- CuO(s) + H2 (g) → Cu(s) + H2O (l).
Answer:
- In this reaction oxygen is added to sodium. Therefore, sodium is oxidised to sodium oxide. This is an example of oxidation reaction.
- In this reaction, oxygen is removed from copper oxide. Therefore, copper oxide is reduced to copper. This is an example of reduction reaction.
Question 66.
What are redox reactions? Explain with an example.
Answer:
A chemical reaction between two substances in which one substance is oxidized and the other reduced is known as reduction-oxidation reaction. Such reactions are also called redox reactions.
E.g.: Consider the reaction between zinc oxide and carbon. During this process, zinc and carbon monoxide is formed.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO.
In the reaction above, oxygen is removed from zinc oxide and oxygen is added to carbon. Therefore, zinc oxide is getting reduced to zinc while carbon is getting oxidised to carbon monoxide. This is an example of a redox reaction where one of the reactants is oxidised while the other is reduced.
![]()
Question 67.
When hydrogen is passed over hot copper oxide, we get copper and water. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. State the substance that is being oxidised and the one that is getting reduced.
Answer:
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is: CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O.
In the reaction above, copper oxide is losing oxygen. Therefore, CuO is reduced to copper. Oxygen is being added to hydrogen. Therefore, hydrogen is oxidised to water.
Question 68.
Why is the following reaction called a redox reaction:
MnO2 + 4 HCl → MnCl2 + 2 H2O + Cl2? Explain.
Answer:
In the reaction above, HCl loses hydrogen and forms chlorine. Thus, HCl is oxidised to Cl2 whereas MnO2 loses oxygen and is reduced to MnCl2. In this reaction, one of the reactants is getting oxidised while the other is being reduced. Therefore, this reaction is called a redox reaction.
Question 69.
What is corrosion? Give two examples. What is corrosion due to?
Answer:
The process of slow eating up of metals due to reaction with atmospheric gases such as oxygen, water vapour, carbon dioxide etc., is known as corrosion.
When silver is exposed to atmospheric air, a black coating appears on silver. This is an instance of corrosion. Similarly, when copper is exposed to atmospheric air, a green coating appears on its surface. This is another instance of corrosion. Most instances of corrosion are due to oxidation.
![]()
Question 70.
Which is the most common form of corrosion? Give a chemical equation to represent the reaction involved in this case.
Answer:
The most common form of corrosion is rusting of iron. When iron articles are exposed to moist air, the surface of iron turns brown due to the formation of a flaky substance called rust. This is nothing but hydrated ferric oxide. Iron reacts with atmospheric oxygen in presence of water vapour to form ferric oxide (rust).
4 Fe + 3 O2 + 2 H2O → 2 Fe2O3.H2O
Question 71.
What is rancidity? Why does it occur?
Answer:
The oxidation of oils and fats present in food substances resulting in bad smell or bad taste that makes the food unsuitable for consumption is known as rancidity.
Rancidity occurs due to the oxidation of fats and oils present in food due to exposure to atmospheric air.
Question 72.
How can rancidity of food materials be prevented?
Answer:
- Keeping the food substances in air-free containers (vacuum packing),
- Adding anti-oxidants, or
- Replacing air inside the containers with nitrogen can prevent rancidity. These measures help to reduce the oxidation of fats and oils present in food.
Question 73.
Oil and fat-containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Answer:
Food items containing oil and fat become rancid when exposed to air, which gives the food an unpleasant smell and taste. In order to prevent rancidity, food items are flushed with nitrogen. Nitrogen does not react with oils or fats. Therefore, rancidity is prevented.
![]()
Question 74.
Which substances get oxidized in rancidity of food?
Answer:
The fats and oils present in food get oxidized when food turns rancid.
Question 75.
Which substance is flushed in bags of potato chips to prevent rancidity?
Answer:
In order to prevent rancidity, chips bags are flushed with nitrogen gas.
Question 76.
Explain the disadvantages of corrosion.
Answer:
Corrosion causes damage to car bodies, bridges, iron railings, ships and to all objects made of metals, especially those made of iron. Corrosion of iron is a serious problem. Every year an enormous amount of money is spent to replace damaged iron or for the maintenance of iron structures.
Question 77.
Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Answer:
Iron articles get rusted when exposed to moist air forming a brownish compound called iron (III) oxide. When iron articles are painted, their surface does not come in contact with moisture and air. Therefore rusting does not occur.
![]()
Fill In The Blanks
1. A compound of calcium used for white washing walls is Calcium hydroxide
2. The chemical name of rust is Iron oxide
3. The number of products in a combination reaction is one
4. A chemical reaction in which an atom, molecule or ion loses oxygen is called reduction
5. The chemical name of quick lime is Calcium oxide
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following is not a physical change?
(A) Boiling of water to give water vapour
(B) Melting of ice to give water
(C) Dissolution of salt in water
(D) Combustion of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)
Answer:
(D) Combustion of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)
Question 2.
Which of the statements about the reaction below arc correct:
2PbO (s) + C (s) → 2Pb (s) + CO2 (g) ?
(i) Lead is getting reduced.
(ii) Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised.
(iii) Carbon is getting oxidised.
(iv) Lead oxide is getting reduced.
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (i) and (iii)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(D) (iii) and (iv)
![]()
Question 3.
Electrolysis of water is a decomposition reaction. The mole ratio of hydrogen and oxygen gases liberated during electrolysis of water is
(A) 1:1
(B) 2:1
(C) 4:1
(D) 1:2
Answer:
(B) 2:1
Question 4.
Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The reaction above is an example of a
(A) Combination reaction.
(B) Double displacement reaction.
(C) Decomposition reaction.
(D) Displacement reaction.
Answer:
(D) Displacement reaction.
Question 5.
What happens when carbon dioxide is passed in limewater?
(A) Limewater turns red because of formation of permanganate.
(B) Limewater turns milky because of formation of calcium carbonate.
(C) Limewater turns, milky because of formation of water.
(D) Limewater turns red, because of formation of copper sulphate.
Answer:
(B) Limewater turns milky because of formation of calcium carbonate.
![]()
Question 6.
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings?
(A) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(B) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(C) No reaction takes place.
(D) Iron salt and water are produced.
Answer:
(A) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
Question 7.
Which of the following is an endothermic reaction?
(i) Dilution of sulphuric acid
(ii) Sublimation of dry ice
(iii) Condensation of water vapour
(iv) Evaporation of water.
(A) (i) and (iii)
(B) (ii) only
(C) (iii) only
(D) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(D) (ii) and (iv)
Question 8.
The product formed when ferrous sulphate is heated is
(A) Ferric oxide
(B) Sulphur dioxide
(C) Sulphur trioxide
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
![]()
Question 9.
A compound formed when lead metal reacts with a solution of copper chloride is
(A) No reaction takes place
(B) Copper chloride
(C) Lead chloride
(D) Copper-lead chloride
Answer:
(C) Lead chloride
Question 10.
What happens when copper metal is dipped in a solution of zinc sulphate?
(A) Copper sulphate is formed
(B) Oxygen gas is formed
(C) Zinc metal is separated
(D) No reaction takes place
Answer:
(D) No reaction takes place
Question 11.
Which of the following products is formed when calcium oxide reacts with water?
(A) Slaked lime
(B) Carbon dioxide
(C) Calcium oxide
(D) Oxygen gas.
Answer:
(A) Slaked lime
Question 12.
Rancidity of food substances can be prevented by
(A) Keeping food items in the open
(B) Adding antioxidants in food
(C) Adding more oxygen to food
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(B) Adding antioxidants in food
![]()
Question 13.
The substance that is oxidised in the following chemical reaction is
MnO2 + 4 HCl → MnCl2 + 2 H2O + Cl2
(A) HCl
(B) MnO2
(C) MnCl2
(D) H2O
Answer:
(A) HCl