Students can Download 1st PUC Accountancy Model Question Paper 1 with Answers, Karnataka 1st PUC Accountancy Model Questions with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Political Science Model Question Paper 1 with Answers
Time: 3.15 minutes
Max. Marks: 100
SECTION – A
I. Answer any 8 questions each carries 1 mark. (1 × 8 = 08)
Question 1.
What is accounting?
Answer:
Accounting is an art of recording, classifying, measuring and summarizing in terms of money, of the business transaction.
Question 2.
What is cost concept?
Answer:
An assets acquired by a concern is recorded in the books of accounts at cost called cost concept.
Question 3.
Classify the English system of account.
Answer:
The three types of accounts under English system are:
- Personal account
- Real account
- Nominal account
- Revaluation or valuation account
Question 4.
What are contra entries?
Answer:
A single transaction entering both the side of two or three column cash book called contra entries.
Question 5.
What is Trial balance?
Answer:
Trial balance is the list of all debit and credit balances of accounts taken out from the ledger at a given period.
![]()
Question 6.
What is Bills Payable?
Answer:
A bill which is accepted by a party and for which he has to pay money called bills payable. Bills payable is a liability.
Question 7.
Mention any four items appeared in Trading account debit side.
Answer:
The items appeared in trading a/c debit side are:
- Purchases
- Wages
- Freight charges
- Factory expenses
Question 8.
What is Adjusted closing capital under Single Entry system?
Answer:
Under single entry system adjusted capital means, closing capital adjusted with drawings and additional capital called adjusted capital [Closing capital + Drawings – Additional Capital = Adjusted Capital].
Question 9.
State any two types of computers.
Answer:
The types of computer are:
- Super Computer
- Main Frame Computer
- Mini Computer
- Micro Computer.
![]()
Question 10.
What is computerised accounting system?
Answer:
It is an accounting information system that processes the financial transaction and events as per GAAP.
SECTION – B
II. Answer any 5 questions each carries 2 marks. (2 × 5 = 10)
Question 11.
If accounting information is not clearly presented, which of the qualitative characteristics of accounting is violated?
Answer:
If accounting information is not clearly presented, then the qualitative characteristics like comparability, reliability & understandability are violated.
Question 12.
State the two systems of book-keeping.
Answer:
The two systems of book-keeping are:
- Single entry system of book-keeping.
- Double entry system of book-keeping.
Question 13.
Write the rule of capital a/c under American system.
Answer:
Capital a/c rule, under American system is:
“Debit decrease in capital.
Credit increase in capital”.
![]()
Question 14.
State any one reasons for the difference between cash book balance and pass book balance.
Answer:
The differences between cash and pass book casuse are:
- Cheque deposited into bank but not realised
- Cheque issued to parties but not presented
- Any expenses directly debited by bank book and not in the cash book.
- Any income directly received by bank and not recorded by business.
Question 15.
State any two examples for errors of omission.
Answer:
Examples for omission are:
- Purchase goods from Murthy not recorded in purchase book. It is a omission of original entry.
- Sold goods to Mary recorded in sales book but not posted to ledger. It is a omission of postings.
Question 16.
Why do you prepare final accounts?
Answer:
For knowing the exact financial position and financial result of the concern, final accounts to be prepared.
Question 17.
What is meant by Voucher Entry?
Answer:
Voucher entry is a proof of transaction which is also copy of transaction.
![]()
Question 18.
What is Capital reserve?
Answer:
Capital reserve is created out of Capital profits which is used for writing off capital losses or issue of bonus shares.
SECTION – C
III. Answer any 4 questions each carries 6 marks. (6 × 4 = 24)
Question 19.
What practical difficulties are encountered by a trader due to incompleteness of accounting records?
Answer:
The following are the difficulties that are encountered by a trader due to incompleteness of accounting records:
a. Accuracy of accounts:
Arithmetical accuracy of accounts cannot be ascertained, since proper records of accounts are not maintained. Consequently, Trial Balance cannot be prepared.
b. Encourages fraud:
As the arithmetical accuracy cannot be determined; so, this encourages fraud and provides sufficient scope for bluffing and carelessness.
c. Difficult to ascertain correct profit or loss:
Since all expenses and income are not recorded, true profit or loss cannot be correctly ascertained.
d. Difficult to analyse the true financial position:
As profit or loss cannot be ascertained easily, so the balance sheet cannot be easily prepared. Hence, the absence of balance sheet will not reflect the true financial position of the business.
e. Difficulty in comparison:
Due to the incomplete records and non-availability of previous years data, comparison is not possible. By the same token, comparisons with other firms are also not possible.
f. Unacceptable to tax authorities:
It does not reflect the true and acceptable presentation of expenses and revenues. Hence, these are not acceptable by the tax authorities.
g. Raising funds:
Since analysis of solvency, profitability and liquidity of business cannot be done, it is difficult to raise fund from outside.
![]()
Question 20.
Write a note accrual basis of accounting.
Answer:
The accrual method records income items when they are earned and records deductions when expenses are incurred. Accrual basis of accounting matches revenue to the time period in which they are earned and matches expenses to the time period in which they are incurred.
While it is more complex than cash basis accounting, it provides much more information about the business. The accrual basis allows matching revenue to the expenses incurred in earning them giving more meaningful financial report.
Question 21.
Write the Advantage / Merits of incomplete records system.
Answer:
The important uses/merits of incomplete records are:
- It is a simple and easy method of book – keeping.
- It is less costly, because only few books of accounts are maintained.
- Only personal and cash accounts are main trained.
- It is suitable for small business concern.
- Accounting knowledge is not much required
Question 22.
Explain the disadvantages of Computerized Accounting.
Answer:
Disadvantages of computerized accounting are as follows:
- Extremely high cost is involved in developing, introducing and using the system.
- Special training for personal is required.
- There is dependence on machines.
- There is an inability to check unanticipated errors.
- There are ill-effects on health.
![]()
Question 23.
Calculate gross income from the following information:
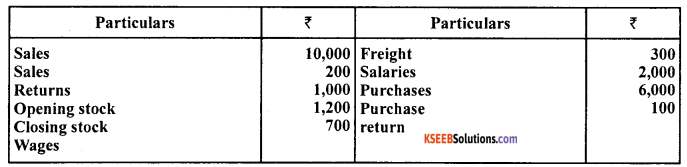
Answer:
Gross income = Net sales – Cost of goods sold
= ₹ 9,800 – ₹ 6,700 = ₹ 3100
Working Notes :
a. Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + Net purchases + wages + freight – Closing stock
= ₹ 1,000 + ₹ 5,900 + ₹ 700 + ₹ 300 – ₹ 1,200
= ₹ 6,700
b. Net sales = Sales – Sales Returns
= ₹ 10,000 – ₹ 200
= ₹ 9,800
c. Net Purchases = Purchase – Purchase returns
= ₹ 6,000 – ₹ 100
= ₹ 5,900 (2+ 1 + 1 + 1)
Question 24.
Enter the following transactions in a simple cash book for the month of Jan 2014. 2014
Jan
1. Amar started business with ₹ 80,000
4. Purchased goods for cash ₹ 40,000
6. Received from Suresh ₹ 20,000
10. Opened an account with Canara Bank by paying in ₹ 5,000
15. Sold goods for cash ₹ 30,000
16. Paid advertising charges ₹ 2,000
20. Purchase office furniture for cash ₹ 35,000
24. Paid for electricity charges ₹ 1,000
28. Paid office rent ₹ 2,000
30. Paid salaries to staff ₹ 6,000
Answer:
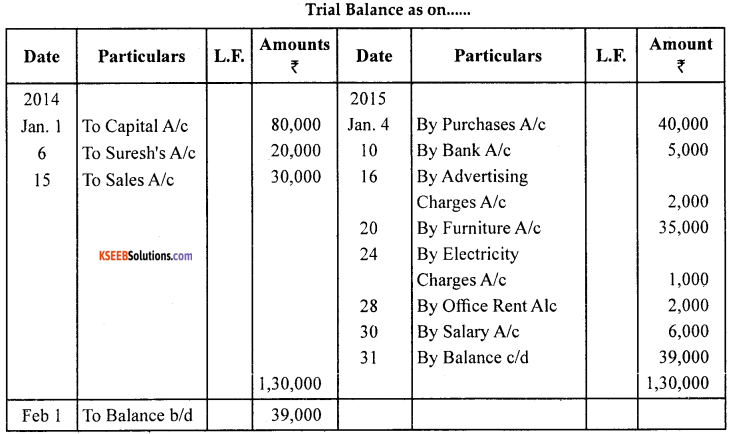
Question 25.
From the following balance prepare a Trial Balance:
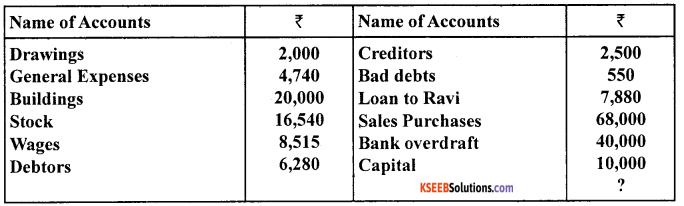
Answer:
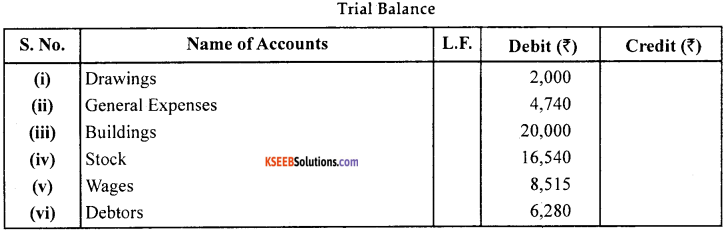

SECTION – D
IV. Answer any 4 questions each carries 12 marks. (12 × 4 = 48)
Question 26.
Journalise the following transactions and open only the personal accounts in the ledger.
Govind started his business with the following :

Answer:
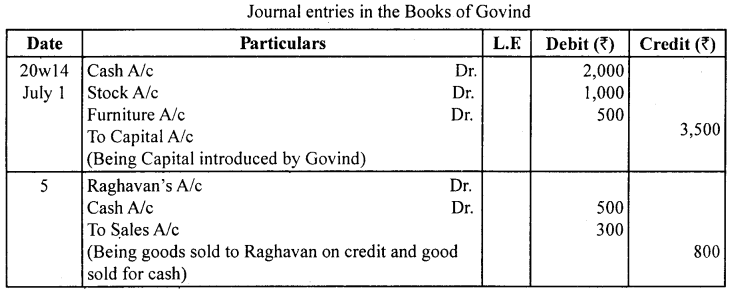
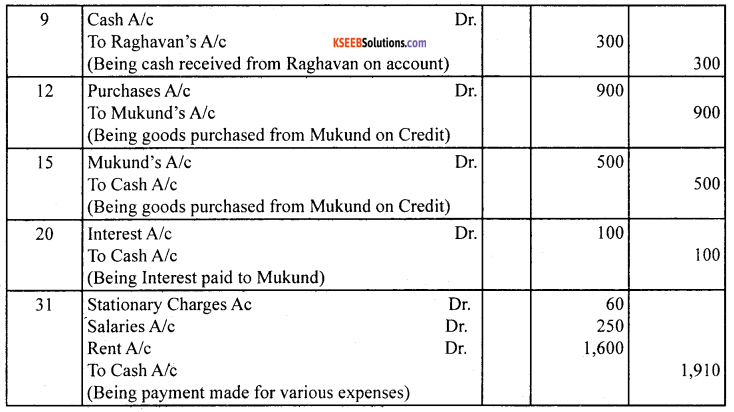
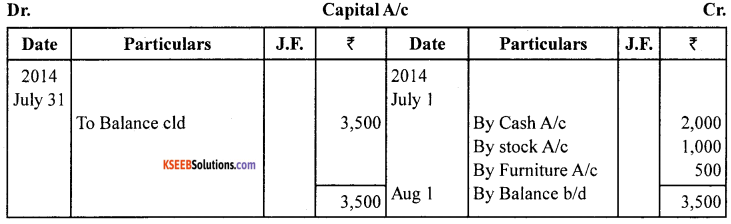
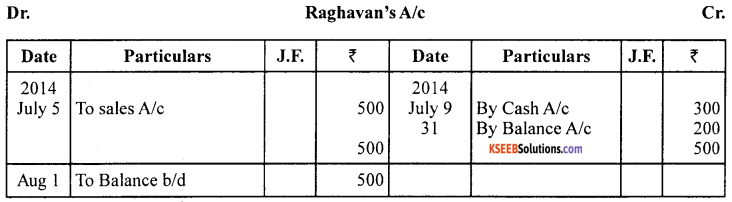
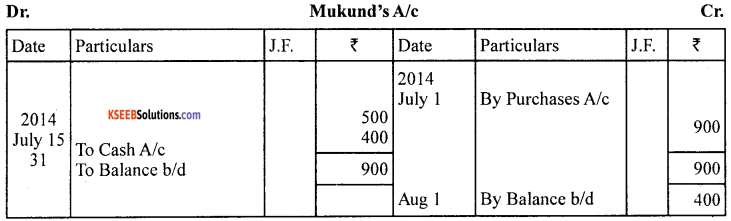
![]()
Question 27.
X sold goods on credit to A/c for ₹ 5,000 on 10.04.2014. On the same date, A accepted a bill drawn by X payable after 3 months. On the due date, the bill is dishonoured by A. Noting charges paid by X amounted to ₹ 200. Pass entries in the books of both the parties.
Answer:
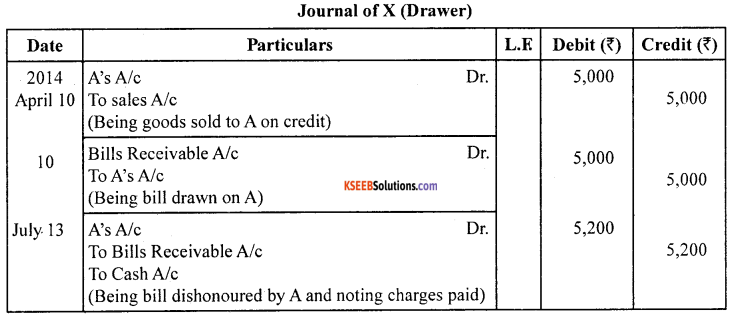
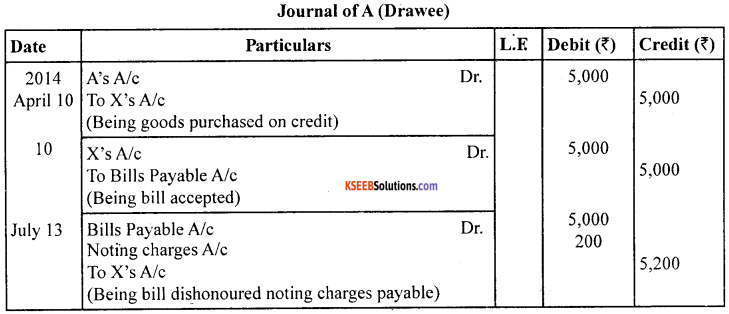
Question 28.
Answer:
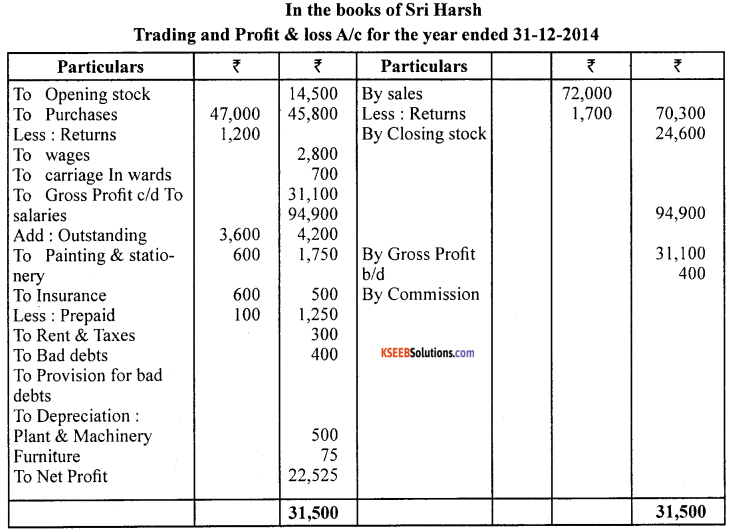
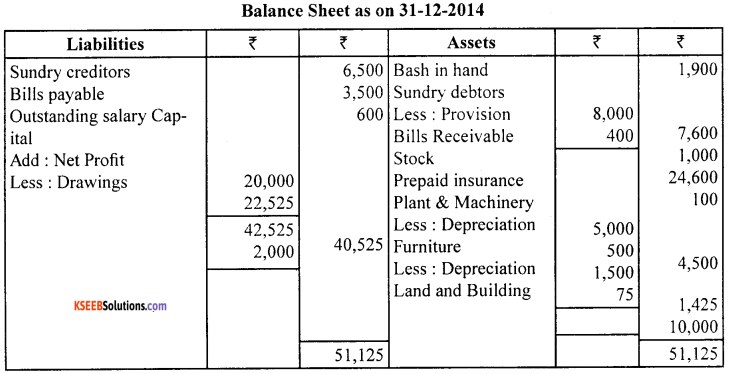
Question 29.
From the following information prepare a statements showing profits for the year ended 31.12.2014 and a revised statement of affairs as on the that date.

During the year drawings amounted to ₹ 1,600 and investment in 6% debentures of ₹ 2,000 on 1.7.2014, which is treated as a business asset. Tools should be written down by 20%.
Answer:
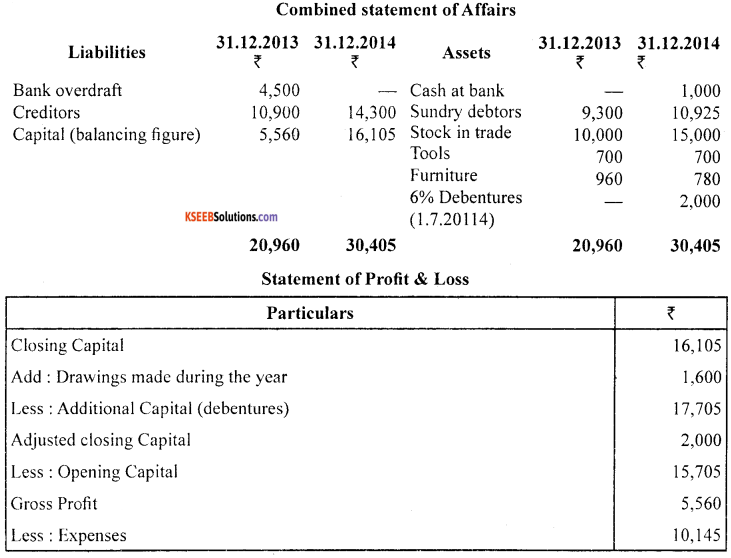
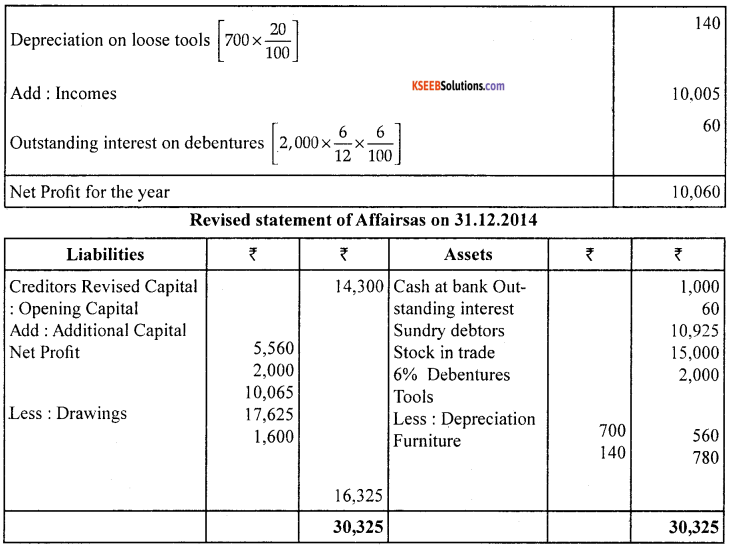
Notes :
1. The amount of debentures ₹ 2,000 is treated as a business asset and also as additional capital introduced during the year.
2. The difference between the opening balance and closing balance of furniture is assumed to be sale of furniture. (4 + 5 + 5)
![]()
Question 30.
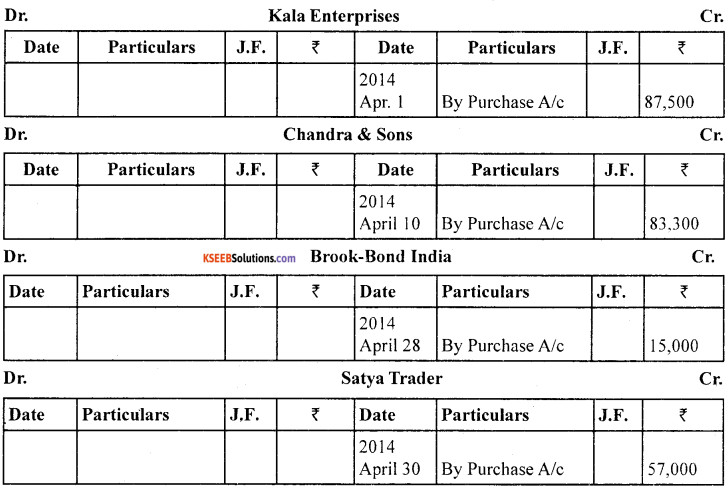
Enter the following transactions in purchases book and post them into ledger accounts.
2014
April 1.
Purchased from Kala Enterprises
100 bags of wheat at ₹ 400 per bag
50 bags of rice at ₹ 500 per
bag 50 bags of sugar at ₹ 450 per bag
April 10.
Bought from M/S Chandra & Sons
200 bags of rice at ₹ 400 per bag
20 bags of sugar at ₹ 400 per bag
Less trade discount at 15%
April 28.
Purchased from Brook-Bond India
100 cases of tea at ₹ 150 per bag
April 30.
Purchased from Satya Traders
100 bags sugar at ₹ 350 per bag
So cases of coffee powder at ₹ 500 per case
Less trade discount at 5%
Answer:
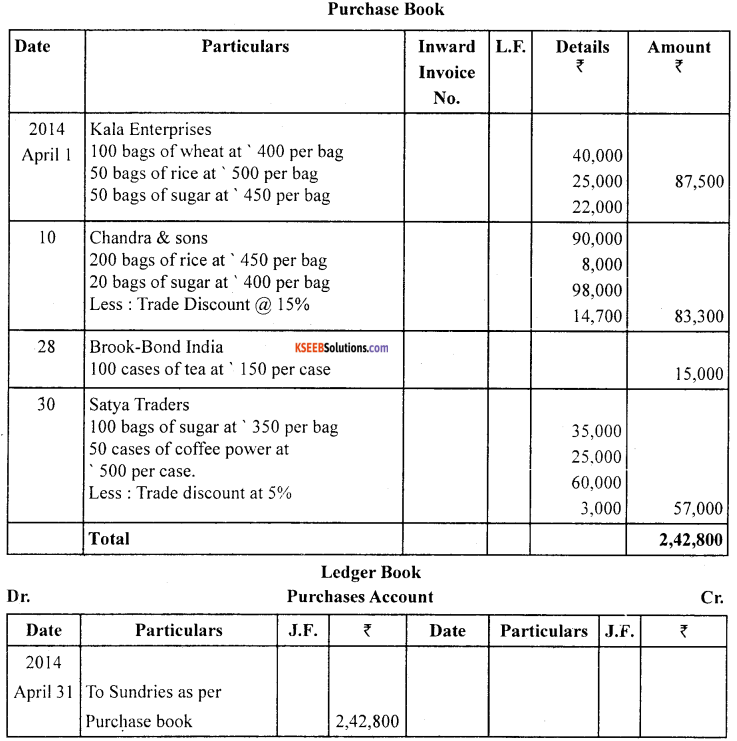
Question 31.
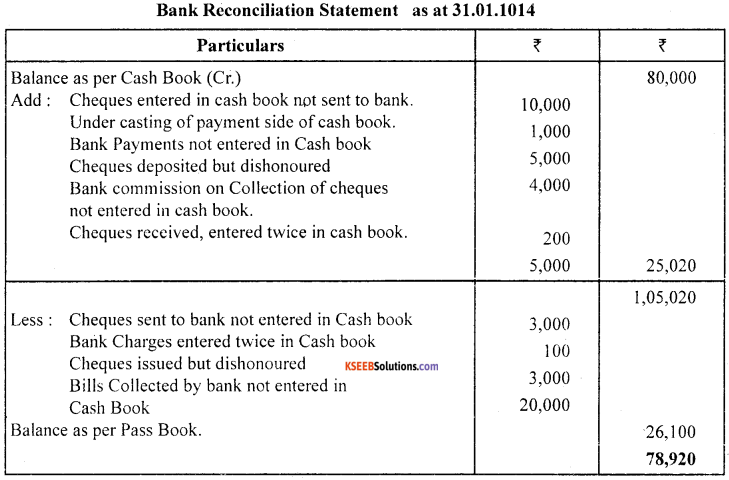
Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement as at 31.01.2014 from the following:
- Balance as per cash book (cr.) ₹ 80,000
- Cheques sent to bank without entering in to cash book ₹ 3,000.
- Cheques entered in cash book but not sent to Bank ₹ 10,000
- Payment side of cash book is undercasts by ₹ 1,000
- As per advice, book payment of ₹ 5,000 omitted in cash book
- Bank charges entered twice in cash book ₹ 100.
- Customer’s cheque of ₹ 4,000 was dishonoured but not entered in cash book.
- Issued cheques of ₹ 3,000 later on dishonoured without an entry in cash book.
- Collection of bill by bank of ₹ 20,000 only appeared in pass Book,
- Cheques sent to bank for collection ₹ 50,000 but passbook collected ₹ 49,980, difference being bank commission.
- Cheques received of ₹ 5,000 entered twice in cash book.
Answer:
![]()
Question 32.
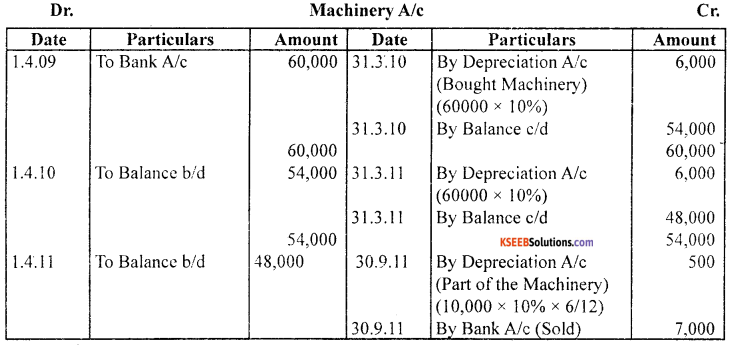
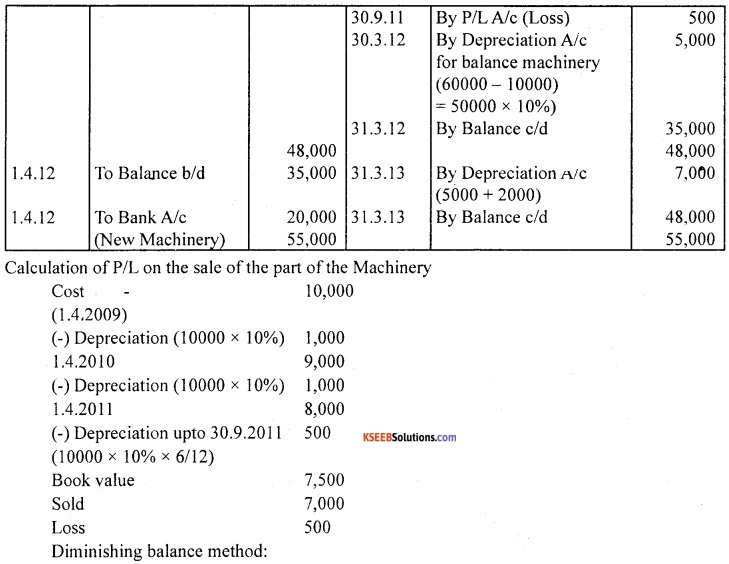
On 01.04.2009, a company purchased Machinery for ₹ 60,000. On 30.09.2011, a part of the Machinery which was purchased on 01.04.2009 costing ₹ 10,000 was sold for ₹ 7,000. On 01.04.2012 new Machinery was purchased for ₹ 20,000. Depreciation was charged at 10% p.a. on straight line method. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year. Show Machinery a/c and Depreciation A/c for the period ending 31.03.2013.
Answer:
SECTION – E
V. Answer any 2 questions each carries 5 marks. (5 × 2 = 10)
Question 33.
Prepare a statement of affairs using five imaginary figures.
Answer:
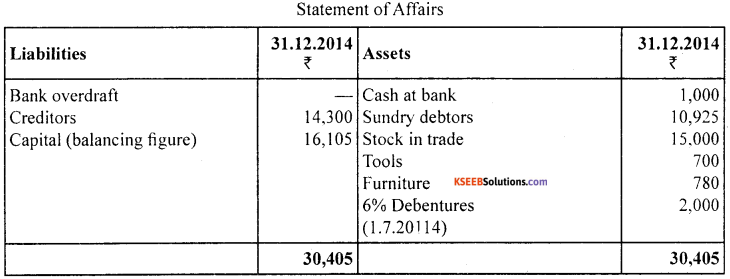
Question 34.
Draft a specimen of an invoice.
Answer:
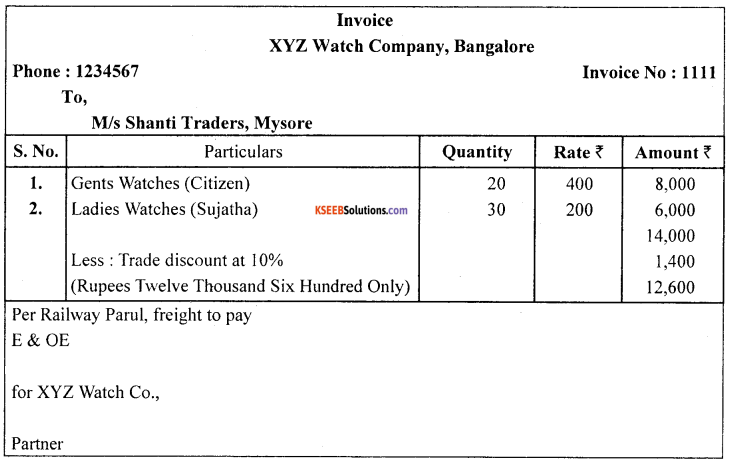
![]()
Question 35.
Prepare a specimen of Bills of Exchange.
Answer:
