Students can Download 1st PUC Accountancy Model Question Paper 5 with Answers, Karnataka 1st PUC Accountancy Model Questions with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Accountancy Model Question Paper 5 with Answers
Time: 3.15 minutes
Max. Marks: 100
Instructions:
- All sub-questions of section – A should be answered continuously at one place.
- Provide Working notes wherever necessary.
- 15 minutes of extra time have been allotted for the candidates to read the questions
- Figures in the right hand margin indicate full marks.
Part – A
I. Answer any EIGHT of the following questions. Each carries ONE mark: ( 8 × 1 = 8 )
Question 1.
Accounting begins with (he identification of transactions and ends with the preparation of ________ Statements.
Answer:
Financial
Question 2.
A concept that a business enterprise will not be sold or liquidated in the near future is known as:
(a) Going Concern
(b) Economic Entity
(c) Monetary In it
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Going Concern.
Question 3.
The process of recording transactions in Journal is called ________.
Answer:
Journalising.
![]()
Question 4.
Ledger records transactions in ________.
(a) Chronological order.
(b) Analytical order.
(c) Both a and b above.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Chronological order.
Question 5.
Trial Balance is a Statement (State True or False).
Answer:
True
Question 6.
A bill is drawn an 1-04-2017 for 3 months. Find out the date of Maturity.
Answer:
The maturity date of Bill is 3-6-2017.
Question 7.
How do you treat interest on capital while preparing Profit and loss Account?
Answer:
Interest on capital is debited in profit and loss account.
Question 8.
Why the Statement of Affairs is prepared?
Answer:
To find out capital i.e., both opening as well as closing capital.
![]()
Question 9.
Expand AIS.
Answer:
Accounting Information System.
Question 10.
Give an example for Accounting Software.
Answer:
Tally, ERP.
Section – B
II. Answer any FIVE of the following questions. Each carries TWO marks: ( 5 × 2 = 10 )
Question 11.
Detine Accounting .
Answer:
According to American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), “Accounting is the art of recording, classifying and summarising in a significant manner and in terms of money, transactions and events which are in part at least of a financial character and interpreting the results thereof’.
Question 12.
What is Double Entry System?
Answer:
The system of recording 2 aspects (i.e., debit and credit) of every transaction in the books of accounts is known as double entry system.
Question 13.
State the Rules of Debit and Credit of Assets Account.
Answer:
Debit what comes in and credit what goes out.
![]()
Question 14.
Why the Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared?
Answer:
To reconcile, two Balance i.e.. Balance as per cash book. Balance as per pass book.
Question 15.
Purchase of Machinery for 25,000 has been entered in the Purchases Book. Give the Rectifying Entry.
Answer:

(Being machinery purchased on credit wrongly entered in purchase book know rectified)
Question 16.
Name any two example of ‘Provision’.
Answer:
- Provision for depreciation
- Provision for taxation.
Question 17.
Give an example for Closing Entry.
Answer:

(Being opening stock a/c closed by transferring to debit side of trading account)
![]()
Question 18.
What are the functional components of Computer System?
Answer:
- Input unit
- Central processing unit
- Output unit
Section – C
III. Answer any FOUR of the following questions. Each carries SIX marks : ( 4 × 6 = 24 )
Question 19.
Classify the following Accounts into Assets, Liabilities, Capital, Revenue/Gains & Expenses/Losses:
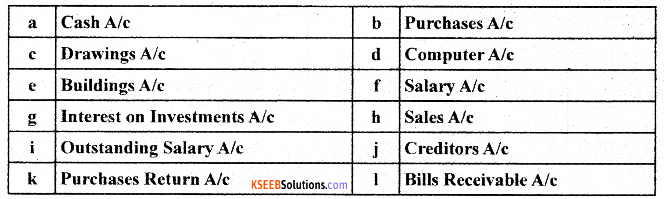
Answer:
Cash a/c – Asset – Real A/c
Purchase a/c – Asset – Real A/c
Computer a/c – liability – personal a/c
Building a/c – Asset – Real a/c
Salary a/c – Expenses – Nominal A/c
Interest on investment a/c – Income – nominal a/c
Sales -a/c Assets – Real a/c
Drawings a/c – Liability – personal a/c
Outstanding salary a/c – Liability a/c
Purchase return a/c – tosses a/c
Bills receivable a/c – Revenue a/c
![]()
Question 20.
Enter the following transactions in an Analytical Petty Cash Book:
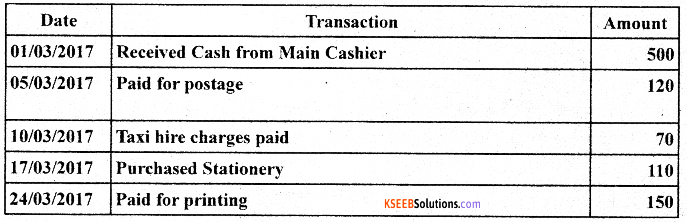
Answer:
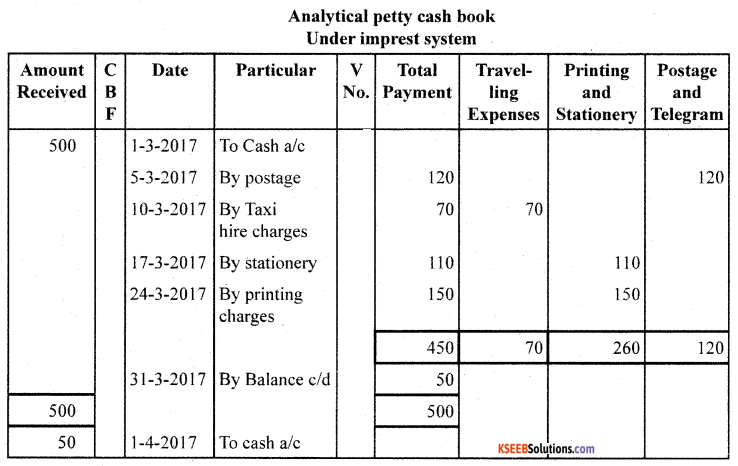
Question 21.
From the following transactions, prepare Purchases Book:

Answer:
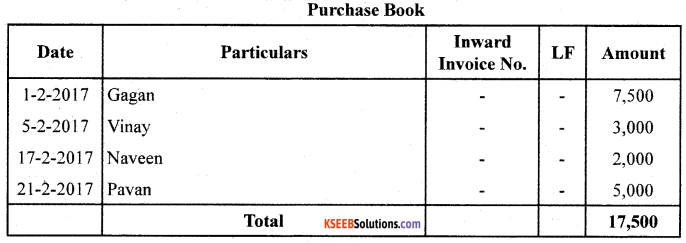
![]()
Question 22.
From the following ledger balances, prepare the Trial Balance as on 31/031/2017:
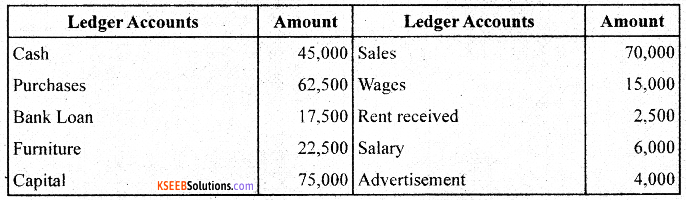
Answer:
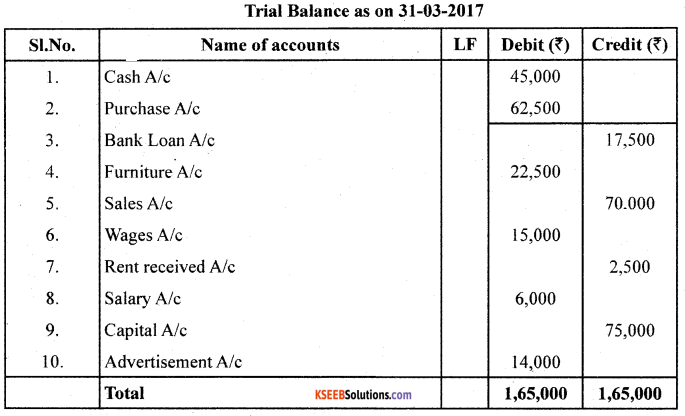
Question 23.
Compute cost of goods sold for the year 2017:
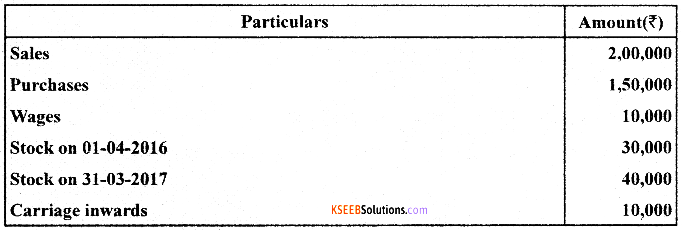
Answer:
Calculation of cost of goods sold for the year 2017:
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + Purchases + Direct expenses – Closing stock
= 30,000 + 1,50,000 + (10,000 + 10,000) – 40,000
= 30,000 + 1,50,000 + 20,000 – 40,000 = 2,00,000 – 40,000
Cost of goods sold = ₹ 1,60,000
Note : Direct expenses includes both wages as well as carriage inwards.
![]()
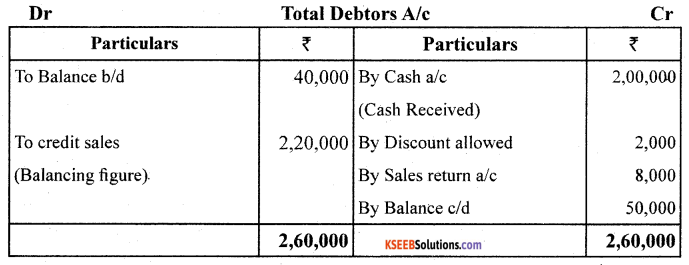
Question 24.
Kind out the Credit Sales by preparing Total Debtors A/c:
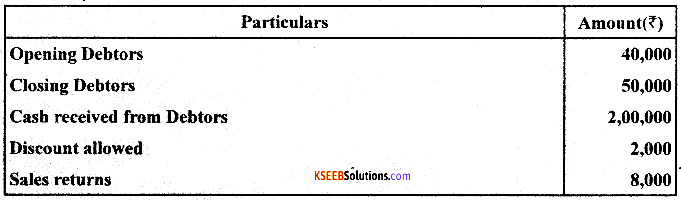
Answer:
Question 25.
Distinguish between Manual Accounting System and Computerised Accounting System.
Answer:
Manual accounting:
- The data recorded under manual accounting are visible.
- The trial of events under can be easily established.
- The data recorded in manual accounting are not subjected to the risk of manipulation.
- The cost of preparing statements and reports under the manual accounting system is high.
- In manual accounting system, accounting data cannot be adjusted to produce various special statement and reports.
Computerised accounting:
- The data stored in computerised accounting (i.e.) in computer) are not visible
- The trial of event cannot be established easily under computerised accounting.
- The data recorded in computerised accounting are subjected to the risk of manipulation.
- The cost of preparing statements and reports under computerised account will be low.
- In computerised accounting system, the accounting data can be easily adjusted to generate various special statement and reports.
Section – D
IV. Answer any FOUR of the following questions. Each carries TWELVE marks: ( 4 × 12 = 48 )
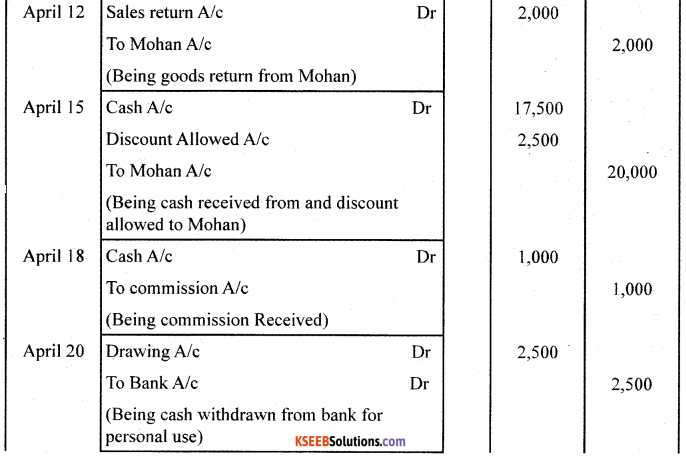
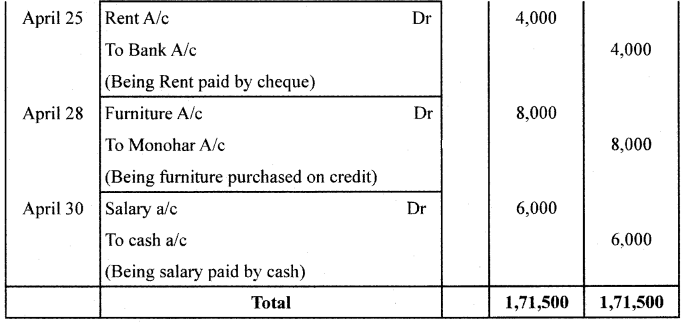
Question 26.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Shri Ganesh:
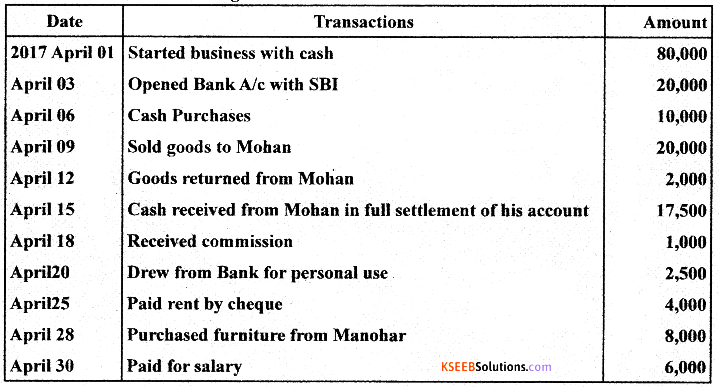
Answer:
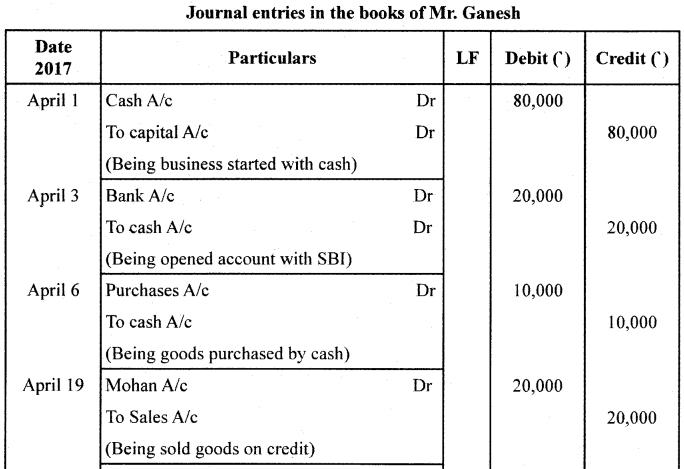
![]()
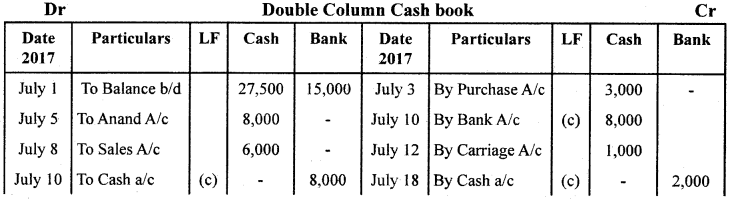
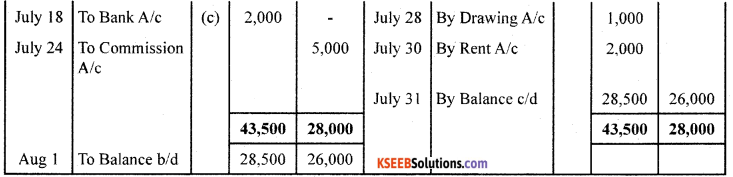
Question 27.
From the following; transactions, prepare Double Column Cash Book.

Answer:
Question 28.
From the following information, prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement:

Answer:

Question 29.
On 01/04/2013, Santosh Company Ltd. purchased a Plant costing ₹85,000 and spent ₹15,000 for its erection. On 31/03/2015, the Plant was sold for ₹75,000. On 01/04/2015,a new Plant was purchased for ₹50,000. The firm charges depreciation @ 10% PA under Straight Line Method. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year.
Prepare : 1. Plant A/c and 2. Provision for Depreciation A/c for first 4 years.
Answer:
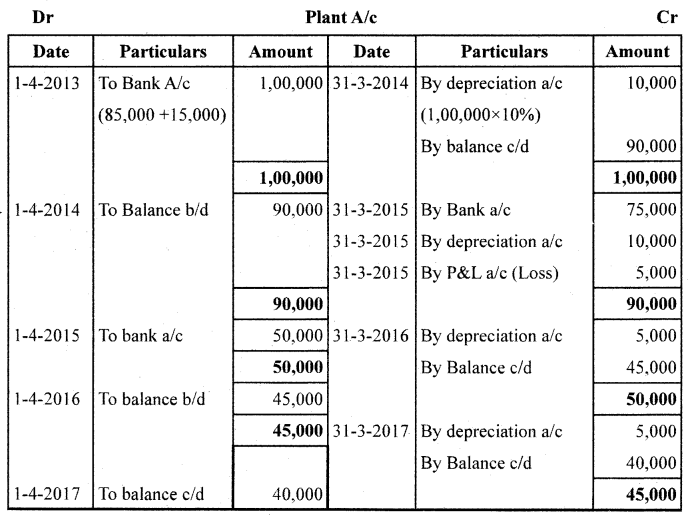
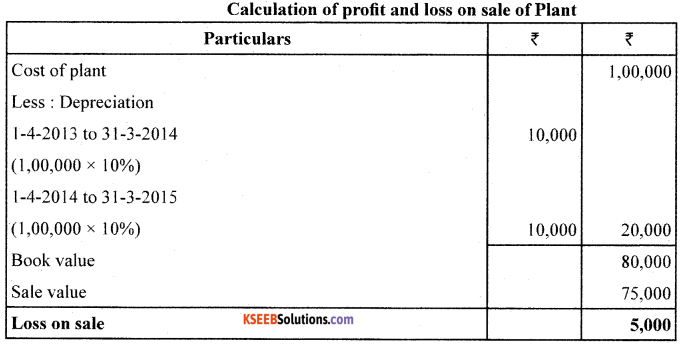
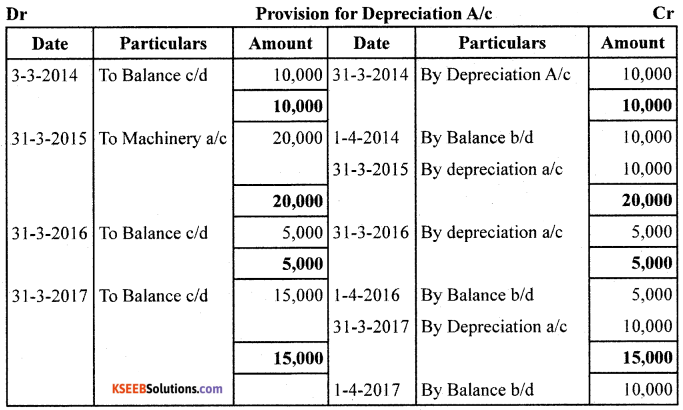
![]()
Question 30.
On 01/04/2017, Prakash drew a Bill on Suresh for ₹50,000 payable after 3 months. Suresh accepted the Bill and returned it to Prakash. On the same dale, Prakash endorsed the Bill to Ramesh: on the above date, the Bill is discounted by Ramesh @ 12% pa. On the due date the Bill is honoured.
Pass the Journal Entries in the books of Prakash, Suresh and Ramesh.
Answer:
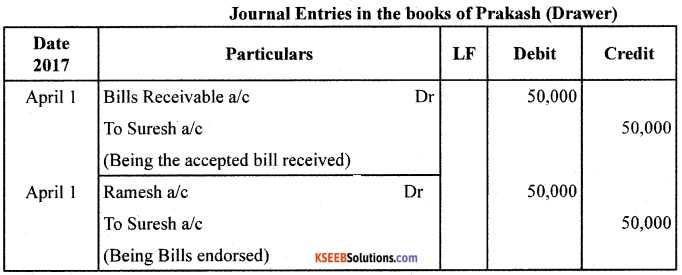
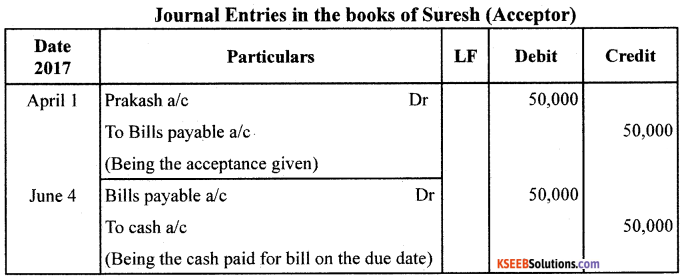
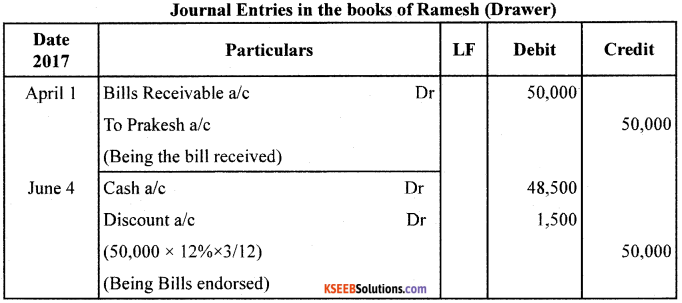
Note : No Journal entry in the books of endorser (Prakash) when the bill is honoured at the date of maturity.
Question 31.
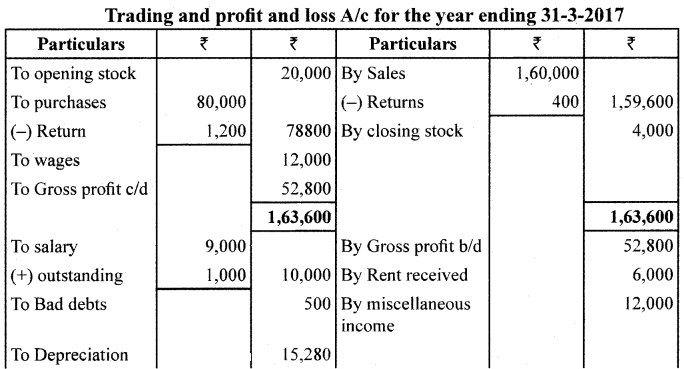
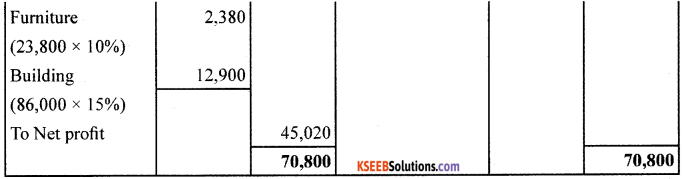
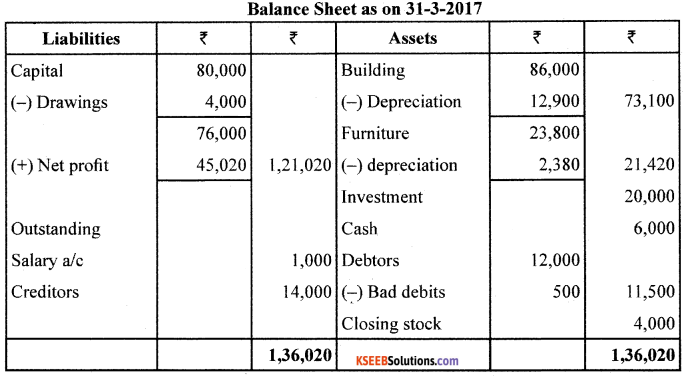
From the following ledger balances and adjustments, prepare Trading A/C, Profit and Loss A/c and Balance Sheet.
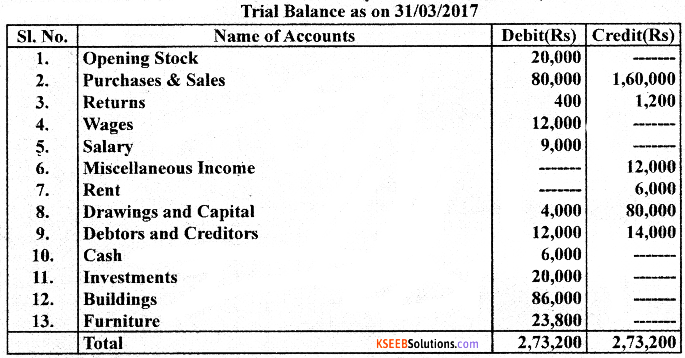
Adjustments:
1. Closing Stock was valued at ? 4,000.
2. Depreciate furniture by 10% pa. and building by 15% pa.
3. Bad Debts written off?500.
4. Salary Outstanding ? 1.000
Answer:
![]()
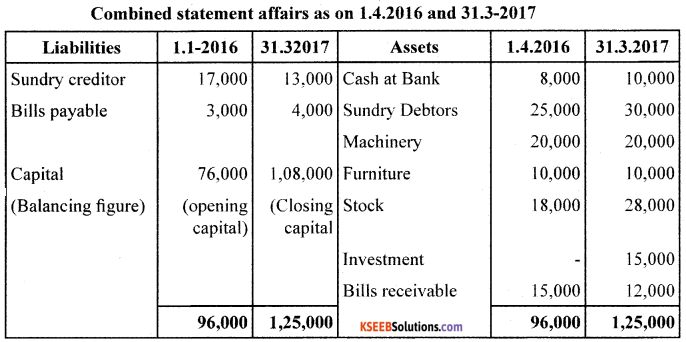
Question 32.
Anand keeps his hooks under Single Entry System : From the following information, prepare Statement of Profit and loss and Revised Statement of Affairs as on 31/03/2017.
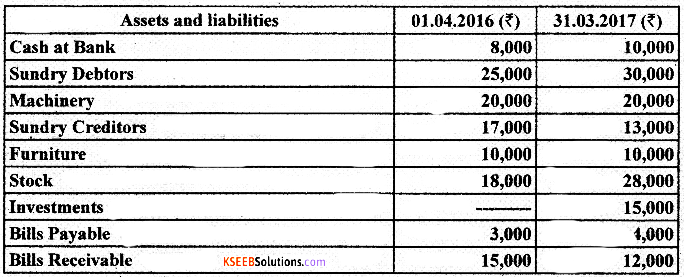
During the year, Anand withdrew ₹10,000 for his personal use and introduced a further capital of ₹7,500.
Adjustments:
1. Depreciate Machinery by 10% pa & Furniture by 12% pa.
2. Provide for Bad and Doubtful Debts @5% on Sundry Debtors
3. Prepaid Insurance ₹500.
4. Legal Expenses due but not paid ₹1,000.
Answer:
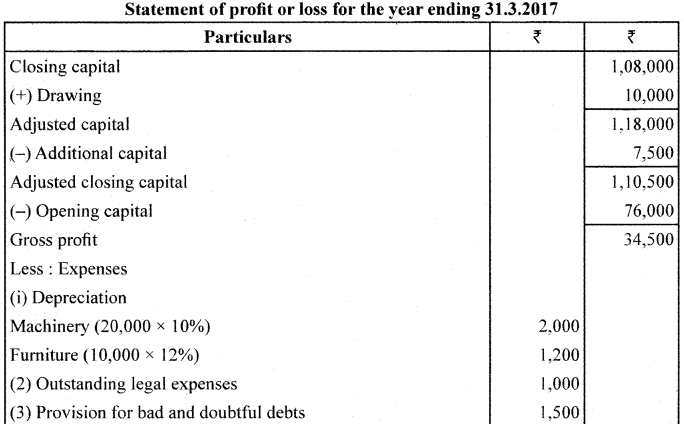

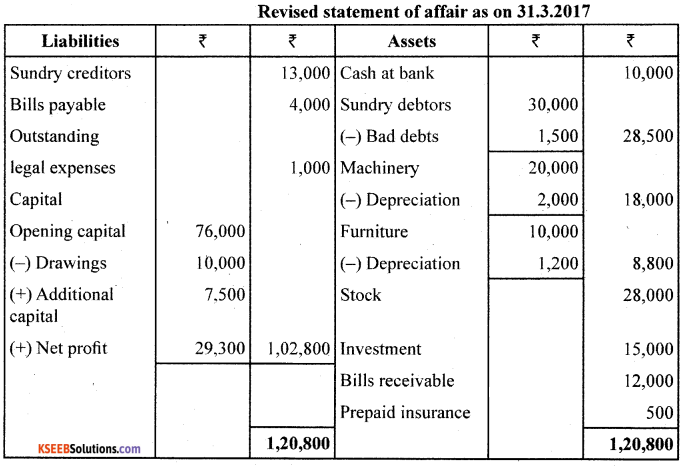
Section – E ( Practical Oriented Questions)
V. Answer any TWO of the following questions. Each carries FIVE marks: ( 2 × 5 = 10 )
Question 33.
Write the Accounting Equation for each item and find the missing figure:
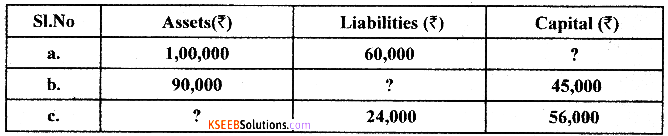
Answer:
(a) Assets – Liabilities + Capital
1,00,000 = 60,000 + Capital
Capital = 100000 – 60000
Capital = ₹ 40,000
(b) Formula to find out liability
Capital Assets – Capital = Liability
90,000 – 45,000 = ₹45,000
Liability = ₹ 45,000
Formula to find out capital : Capital = Assets – liabilities
(c) Formula to find out assets
Assets = Liabilities + capital = 24,000 + 56,000
Assets = ₹ 80,000
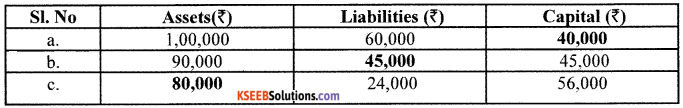
![]()
Question 34.
Prepare Machinery A/c for two years with imaginary figures under. Written Down Value Method.
Answer:
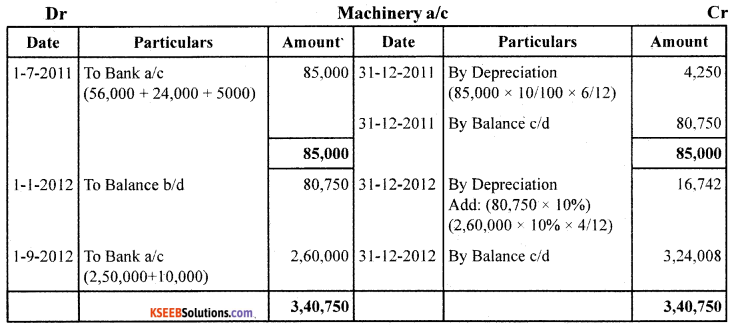
![]()
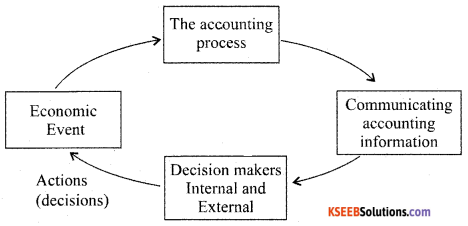
Question 35.
Draw a diagram of Accounting process.
Answer: