You can Download Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Questions and Answers, 1st PUC Biology Question Bank with Answers, Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Biology Question Bank Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
1st PUC Biology Question Bank NCERT Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell?
Answer:
24 hours is the average cell cycle for mammalian cell.
Question 2.
Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Answer:
- Karyokinesis: It is a phase in which division of nucleus into two daughter nuclei occurs. Separation of daughter chromosomes occur in this phase. It consists of four substages namely prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
- Cytokinesis: It refers to division of the cytoplasm resulting in two daughter cells.
Question 3.
Describe the events taking place during interphase.
Answer:
During interphase, the cell prepares for division by undergoing both cell growth and DNA replication in an orderly manner. It’s divided into three-phase.
- G phase: In this phase the cell is metabolically active and continuously grows but does not replicate its DNA.
- S phase /Synthesis): In this phase DNA synthesis or replication takes place. During this time the amount of DNA per cell doubles but the chromosome number remains the same. In animal cells, DNA replication begins in the nucleus and the centrioles duplicate in the cytoplasm.
- G
2 phase: In this phase proteins are synthesised in preparation for mitosis and cell growth continues.
![]()
Question 4.
What is G0(quiescent phase) of cell cycle?
Answer:
Some ceils in adult animals which divide occasionally to replace cells that are lost exit G1 phase to enter an inactive stage called quiescent stage (G0) of the cell cycle. Cells in this stage remain metabolically active but no longer proliferate unless called on to do so by the organism.
Question 5.
Why is mitosis called equational division?
Answer:
The number of chromosomes in the parent and daughter cells is the same in mitosis. Hence it is called equational division.
Question 6.
Name the stage of cell cycle at which one of the following events occur:
1. Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator.
2. Centromere splits and chromatids separate.
3. Pairing between homologous chromosomes takes place.
4. Crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
Answer:
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Zygotene
- Pachytene
Question 7.
Describe the following:
(a) synapsis
(b) bivalent
(c) chiasmata Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
Answer:
(a) Synapsis: In zygotene stage, homologous chromosomes start pairing together and this process is called synapsis
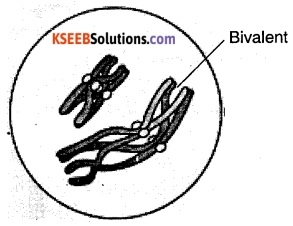
(b) Bivalent: The complex formed by a pair of synapsed homologous chromosome is called a bivalent or a tetrad.
(c) Chiasmata: In diplotene, the dissolution of the synaptonemal complex and the tendency of the recombined homologous chromosome of the bivalents to separate from each other except at the sites of cross overs is recognised. These X-shaped structures are called chiasmata.
Question 8.
How does cytokinesis in plant cells differ from that in animal cells?
Answer:
In animal cell, cytokinesis is achieved by the appearance of a furrow in the plasma membrane. The furrow gradually deepens and ultimately joins in the centre dividing the cell cytoplasm into two.
Due to the presence of cell wall, cytokinesis is different in plants. In plants, wall formation starts in the centre of the cell and grows outward to meet the existing lateral walls. The formation of the new cell wall begins with the formation of a simple precursor, called the cell plate that represents the middle lamella between the walls of two adjacent cells. Organelles like mitochondria and plastids get distributed between the two daughter cells during this process.
Question 9.
Find examples where the four daughter cells from meiosis are equal in size and where they are found unequal in size.
Answer:
- Meiosis forming equal daughter cells – Spermatogenesis
- Meiosis forming unequal daughter cells – Oogenesis.
Question 10.
Distinguish anaphase of mitosis from anaphase I of meiosis
Answer:
| Anaphase of Mitosis | Anaphase I of Meiosis |
| (a) Centromeres are split at this stage and chromatids separate. (b) The chromosomes are large and thin |
(a) Centromeres do not divide at this stage. Homologous chromosomes separate while sister chromatid remains associated at their centromeres. (b) Chromosomes are shorter and thicker |
Question 11.
List the main differences between mitosis and meiosis.
Answer:
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| (a) Mitosis consists of a single division. | (a) Meiosis is a two phase division. |
| (b) Mitosis is an equational division. Daughter cell has same number of chromosome as that of parent cell. | (b) The chromosome number in daughter cell is reduced to half of that in parent cell. |
| (c) Mitosis results in growth. | (c) Meiosis results in reproduction. |
| (d) Mitosis results in two daughter cells. | (d) Meiosis results in four daughter cells. |
| (e) The daughter cells are similar to that of a parent | (e) The daughter cells vary from their parent cell |
| (f) Mitosis occur continuously in somatic cells. | (f) Meiosis occurs in germ cells during garnet genesis. |
| (g) Mitosis is a simple division | (g) Meiosis is a complex division. |
![]()
Question 12.
What is the significance of meiosis?
Answer:
- Conservation of specific chromosome number of each species across generations is achieved by meiosis.
- Due to crossing over, the hereditary characters from male and female parents get mixed. So genetic variability in the population of organisms from one generation to the next occurs which is most important for the process of evolution.
- Gametes are produced by Meiosis.
- Meiosis results in reproduction and is similar among different organisms.
Question 13.
Discuss with your teacher about
(1) haploid insects and lower plants where cell-division occurs, and
(2) some haploid cells in higher plants where cell-division does not occur.
Answer:
- Haploid insect – Honey bee
haploid lower plants – Spirogyra, Riccia. - Male and female gametes.
Question 14.
Can there be mitosis without DNA replication in ‘S’ phase?
Answer:
NO.
Question 15.
Can there be DNA replication without cell division?
Answer:
Generally DNA replication is followed by cell division. But, there can be DNA replication without cell division.
Question 16.
Analyse the events during every stage of cell cycle and notice how the following two parameters change
(i) Number of chromosomes (N) per cell
(ii) Amount of DNA content (C) per cell
Answer:
- Gt Phase: DNA and chromosome content
do not change. - S Phase: Amount of DNA content doubles eg: from ‘2c’ to ‘4c’.
Number of chromosome remains the same. - G2 phase: Amount of DNA is twice that of the original cell.
- M phase: Chromosome number per cell remains the same after M phase. DNA content is same as the original cell.
1st PUC Biology Question Bank Additional Questions and Answers
1st PUC Biology Question Bank One Mark Questions
Question 1.
What is Karyokinesis? (B’lore North 2005)
Answer:
The division of nucleus is called karyokinesis.
Question 2.
What is interphase?
Answer:
The nondividing phase of cell is interphase
Question 3.
Name the synthetic phase of interphase.
Answer:
S phase
Question 5.
Mention the substages of Interphase.
Answer:
G1 stage, ‘S’ stage and G2 stage.
Question 6.
What is Cytokinesis? (B’lore North, Dharwar .04)
Answer:
Division of cytoplasm is called cytokinesis.
![]()
Question 7.
Mention the Substages of Mitosis.
Answer:
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis.
Question 8.
Give two differences between plant and animal cell division.
Answer:
- In-plant cell, Asters are not formed.
In animal cell Asters are formed. - In-plant cell, cytokinesis occurs due to the formation of a cell plate.
In an animal cell, cytokinesis occurs due to the formation of a cleavage furrow.
Question 9
What is Synapsis? (Bijapur, Belgaum, Shimoga 2004)
Answer:
The process of pairing of homologous chromosomes is called Synapsis.
Question 10.
What Is genetic crossing over? (B.North. 04)
Answer:
Exchanges of segments between non sister chromatids of the bivalents is called Genetic crossing over.
Question 11.
What are Chiasmata?
Answer:
The regions where segments of non sister chromatids of the bivalents are exchanged are called chiasmata.
Question 12.
Why mitosis is equational division called?
Answer:
Mitosis is a process of cell division, in which chromosomes are equally distributed into two daughter cells so it is equational division.
Question 13.
Define cell cycle.
Answer:
The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesis the other constituents of the cell and eventually divides into two daughter cells is termed as cell cycle.
Question 14.
What percentage of the duration of cell cycle does interphase last?
Answer:
More than 95%.
Question 15.
What happens during ‘S’ phase In animal cells?
Answer:
During ‘S’ phase in animal cells, DNA replication begins in the nucleus, and the
centriole duplicates in the cytoplasm.
Question 16.
Name the two major types of cell division.
Answer:
Mitosis and meiosis.
Question 17.
What is a metaphase plate?
Answer:
The plane of alignment of the chromosomes at metaphase is referred to as the metaphase plate.
Question 18.
When do the centromeres of chromosomes divide in a cell of the root tip?
Answer:
During anaphase of mitosis.
Question 19.
Name the stage of mitosis, when chromosomes start their poleward movement.
Answer:
Anaphase.
Question 20.
When does the nucleolus reappear during mitosis?
Answer:
Telophase.
Question 21.
What is a cell plate?
Answer:
The formation of the new cell wall begins with the formation of a simple precursor, called the cell plate that represents the middle lamella between the walls of two adjacent cells.
Question 22.
Define meiosis.
Answer:
The specialized kind of cell division that reduces the chromosome member by half resulting in the production of haploid daughter cells is called meiosis.
Question 23.
What indicates the beginning of diplotene?
Answer:
The beginning of diplotene is recognised by the dissolution of the synaptonemal complex and the tendency of the recombined homologous chromosomes to separate from each other.
Question 24.
Name the last state of prophase I and what marks this stage?
Answer:
Diakinesis is the last stage of prophase I and it is marked by the terminalisation of chiasmata.
Question 25.
When does the actual reduction in the number of chromosomes take place during meiosis?
Answer:
Anaphase I.
![]()
Question 26.
What is Interkinesis?
Answer:
The stage between the two meiotic divisions (Meiosis I and Meiosis II) is called interkinesis.
Question 27.
Name the stage of all division to study the chromosome morphology.
Answer:
Metaphase.
1st PUC Biology Question Bank Two Marks Questions
Question 1.
Write the significance of Mitosis / Meiosis. (Udupi 2006, D.Kannada 2010)
Answer:
Significance of Mitosis:
- Distribution of equal number of chromosomes to the daughter cells maintains a constant chromosome number.
- Mitosis increases number of cells so it contributes to growth.
Significance of Meiosis :
- Meiosis brings genetic crossing over and random distribution of paternal and maternal chromosomes to daughter cells.
- Recombination produces variations and variations are the sources of organic evolution.
Question 2.
Name any four stages of prophase of meiosis (M.Q.P., Mandya. 05)
Answer:
Leptotene, Zygotene
Pachytene, Diplotene & Diakinesis.
Question 3.
Bring out any four differences between mitosis and miosis. (Hassan. 05, D.K. 2008)
Answer:
- Mitosis is seen in somatic cells, whereas Meiosis is seen in germ cells.
- Mitosis is an equational division, whereas Meiosis is a reductional division.
- In mitosis no crossing over, whereas in miosis crossing over between nonsister chromatids is seen.
- In mitosis one cell produces two cells with same chromosome number, whereas In meiosis one cell produces four haploid cells
Question 4.
Write any 2 differences between Mitosis and Meiosis.
Answer:
- Mitosis consists single nuclear divisions.
Meiosis consists of two nuclear divisions. - In mitosis crossing over is absent.
In Meiosis crossing over is present.
Question 5.
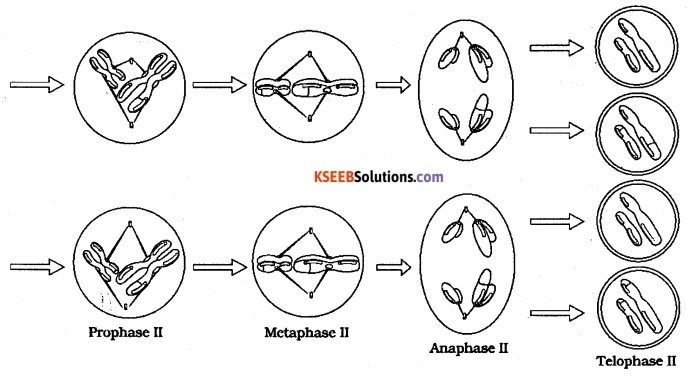
Mention the substages of Meiosis
Answer:
- Proohase II
- Metaphase II
- Anaphase II
- Telophase II
- cytokinesis.
Question 6.
Define Ceil Cycle. Mention two main stages of Ceil Cycle.
Answer:
The series of events occurring in a growing cell that occurs between the formation of cell and its division into daughter cells is called cell cycle. Two main stages are Interphase and M. Phase.
![]()
Question 7.
Mention the differences between G and G2 phase of Interphase.
Answer:
| G1 phase | G2 phase |
| (a) It is the first substage of interphase that follows cytokinesis
(b) The Cell is metabolically active and contiguously grows but does not replicate its DNA. (c) Certain cells may stop dividing and enter G0 phase |
(a) It is the last substage of interphase which is followed by M-phase
(b) Proteins are synthesized in preparation for mitosis while cell growth continues (c) All cells entering G2 phase continue with the M-phase |
Question 8.
What are kinetochores? What is their function?
Answer:
Kinetochores are small disc-shaped structures at the surface of centromeres. They serve as the binding site for the spindle fibres to the centromeres of chromosomes.
Question 9.
Mention the significance of mitosis.
Answer:
- In multicellular organisms, growth of the body is due to mitotic division of cells.
- Replacement of worn-out cells and repair of the damaged cells is by mitosis.
- In unicellular organisms, mitosis results in asexual reproduction of cells.
- In plants, vegetative propagation involves only mitotic divisions.
Question 10.
What is crossing over? Name the enzyme responsible for it.
Answer:
Crossing over is defined as the exchange of equivalent segments between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes and exchange of genetic material between them. The enzyme responsible for crossing over is recombinase.
Question 11.
Mention the events that occur during diakinesis.
Answer:
During diakinesis there is terminalisation of chiasmata. The chromosomes are fully condensed and the meiotic spindle is assembled to prepare the homologous chromosomes for separation. The nucleolus disappears and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
Question 12.
Mention the key features of metaphase in mitosis.
Answer:
- Spindle fibres attach to kinetochores of chromosomes
- Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator and get aligned along with metaphase plate through spindle fibres to both poles.
Question 13.
What is syncytium? Give an example.
Answer:
In some organisms karyokinesis is not followed by cytokinesis as a result of which multinucleate condition arises leading to the formation of syncytium.
E.g: liquid endosperm in coconut.
Question 14.
How does metaphase I differ from metaphase?
| Metaphase I | Metaphase II |
| (a) The homologous pairs of chromosomes are arranged in two rows near the centre of the spindles.
(b) There no metaphasic plate formed (c) The arms of the chromosomes are at spindle fibres |
(a) Centromeres of all the chromosomes are arranged in a single row at the centre of the spindles
(b) A metaphasic plate is formed (c) The arms of the chromosomes are parallel to the fibres. |
Question 15.
Name the four substages of prophase I.
Answer:
- Leptotene
- Zygotene
- Pachytene
- diplotene
1st PUC Biology Question Bank Three Marks Questions
Question 1.
Describe the events in the prophase of animal cells.
Answer:
- Chromosomal material condenses to form compact mitotic chromosomes.
- Chromosomes are seen to be composed of two chromatids attached together at the centromere.
- The centrioles formed in interphase start moving to the opposite poles of the cell.
- Initiation of the assembly of mitotic spindle, the microtubules, the proteinaceous components of the cell cytoplasm help in the process.
- By the end of prophase, the nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
Question 2.
Describe’ he events in the telophase of mitosis.
Answer:
Telophase is the final stage of mitosis. The events that happen in telophase are:-
- Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identity is lost as discrete elements.
- Nuclear envelop assembles around the chromosome cluster.
- Nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER reform.
Question 3.
Define cytokinesis. How is it accomplished in animal and plant cells?
Answer:
The process by which the cytoplasm of the cell divides resulting in the formation of two daughter nuclei is called cytokinesis.
In an animal cell, this is achieved by the appearance of a furrow in the plasma membrane. The furrow gradually deepens and ultimately joins in the centre dividing the cell cytoplasm into two.
In-plant cells, wall formation starts in the centre of the cell and grows outward to meet the existing lateral walls. The formation of a new cell wall begins with the formation of a simple precursor, called the cell plate that represents the middle lamella between the walls to two adjacent cells.
![]()
Question 4.
Diagrammatically show the stages of Meiosis I.
Answer:
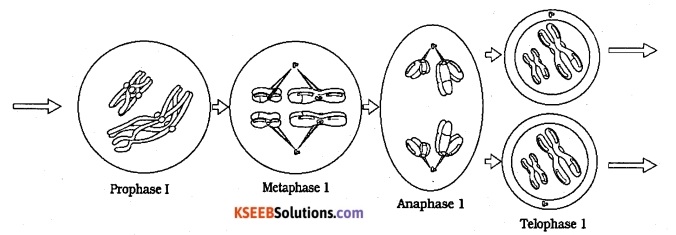
Question 5.
Diagrammatically shows the stages of Meiosis I.
Answer:
1st PUC Biology Question Bank Five Marks Questions
Question 1.
Explain Anaphase and Telophase of Mitosis
Answer:
Anaphase:
- Centromere of each chromosomes splits. So that chromatids separate.
- The separated chromatids along with the centromeres get pulled to the opposite poles. Such movement of chromatids takes place by the shortening of chromosomal fibres. The Anaphasic chromosomes appear V, L, J or I shaped.
Telophase:
- Condensed chromosomes begin to decondense, become thin and produce the chromatin network.
- Spindle fibers, asters, disappear.
- Nucle I membrane, nucleoli are formed. So at the end cell consists two nuclei one at each pole
Question 2.
With neat labelled diagrams explain Meiosis I (Gulbarga, Belgaum, B.South 04, D.K. 07)
Answer:
The first meiotic division is reductional division so that two haploid cells are formed.
Meiosis I consists I Karyokinesis I: It has following stages;
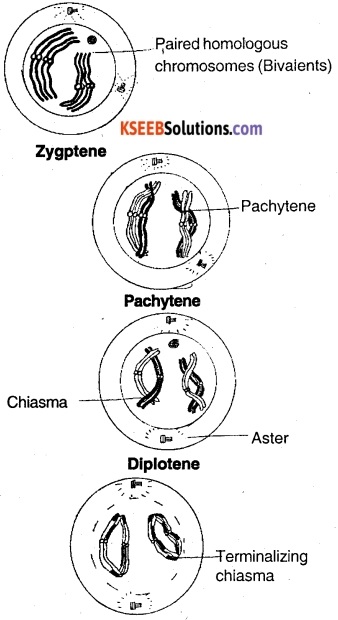
A. Prophase:
It lasts for a long period and studied under the following substages.
(Shimoga. 06)
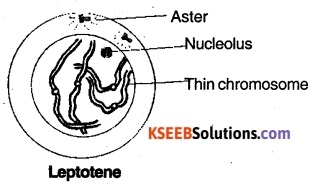
(a) Leptotene following are the characteristic of leptotene –
Chromosomes are long, thin and they are double-stranded each chromosome appear as a string of beads. Such beads are called chromomeres.
(b) Zygotene
- Homologous chromosomes come to lie side by side, closely applied at every point this process of pairing is called Synapsis.
- Each pair is called bivalent and each bivalent consists of 2 chromatids, so-called tetrad.
- The two chromatids of the same chromosome are called sister chromatids and chromatids belonging to two different chromosomes are called non-sister chromatids.
(c) Pachytene :
- Two non-sister chromatids of each tetrad get coiled around each other and exchanges segments
- This process is called genetic crossing over. It results in recombination of genes. Crossing over takes place by breaking and reunion of chromatids.
- The points where exchanges have occurred appear X – shaped structure. It is called chiasmata.
(d) Dipiotene
- Chromosomes are more condensed
- The attraction between homologous chromosomes disappear, but repulsion begins.
- Repulsion produces chain like 8 – shaped or o shaped bivalents.
- Repulsion results in terminalization of chiasmata and finally disappear.
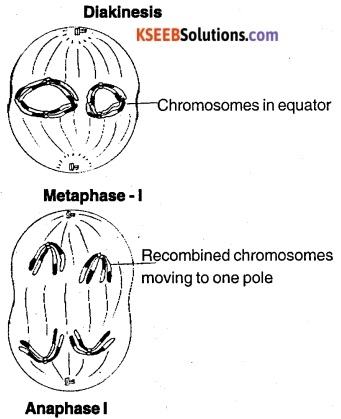
(e) Diakinesis:
Nucleolus disappear, nuclear membranae disappears and each bivalent shows four chromatids.
(B) Metaphase
(i) Paired chromosomes ar-range at the equatorial plane of the spindle and spindle fibres become attached to the centromeres of each chromosome.
(C) Anaphase
Spindle fibres contract so bivalent move towards the opposite poles of the spindle. The separated chromosomes are called univalents. The two centromeres of a homologous pair move towards the opposite poles along with the chromosomes.
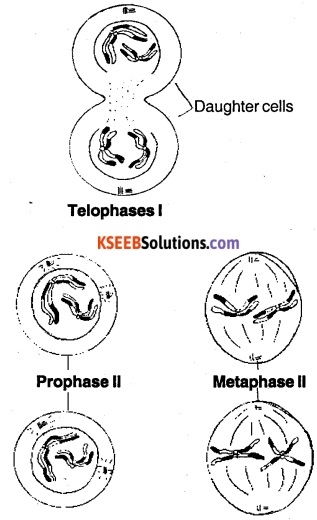
(D) Telophase :
- Chromosomes reach at the poles. They uncoil and become thin and long thread-like.
- Nuclear membrane and Nucleoli reappear:
- Cytokinesis I
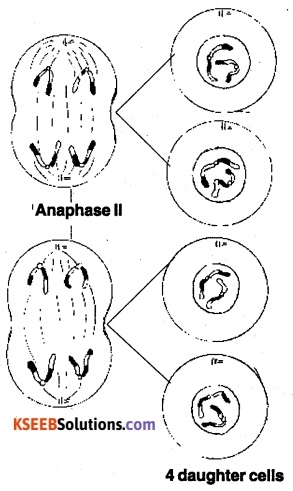
- A constriction develops in the middle of the cell which becomes deep and cytoplasm is divided into two equal parts.
Question 3.
With neat labelled diagrams explain Mitosis In an Animal Cell. (Shimoga, Chikmagalore, Dharwar, Bijapur 2004, B’Iore North, Tumkur, Kolar, Mandya 2005)
Ans:
There are two process.They are
(1) Karyokinesis.
(2) Cytokinesis
(1) Karyokiriesis: It is divided into following sub-stages.
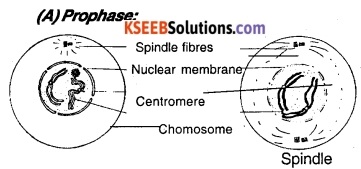
- The duplicated chromosomes undergo condensation (become Short and thick).
- Each chromosome has two chromatids and remains attached to each other at the region of the centromere.
- Centrioles are duplicated and begin to move towards the other pole of the cell.
- Aster begins to appear around each centriole.
- Spindle fibers begin to appear.
- Nuclear membranes and Nucleolus disappear.
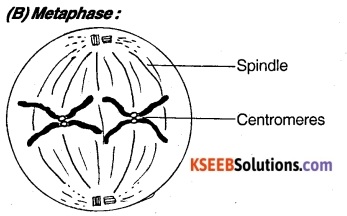
- Spindle fibres are completely formed.
- Chromosomes are highly condensed and they arrange at the equator.
- Spindle fibre attached to the centromere and arms project in a different direction.
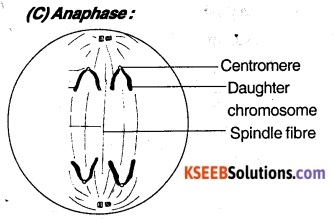
The spindle fibers become short and two chromatids of each chromosome separate and move away from the equator to the opposite poles. The moving chromosome exhibit different shapes like V or J shape.
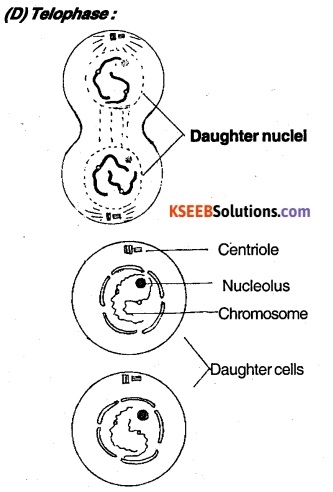
The daughter chromosomes arrived at the poles start uncoiling become thin. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear around the chromosome at each pole. Spindle fibres disappear.
(ii) Cytokinesis: A furrow develops in the middle of the cell which depends at the centre and divides cytoplasm into two equal parts.
Question 4.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Metaphase chromosome and explain any four parts.
Answer:
1) Karyokiriesis: It is divided into following sub-stages.
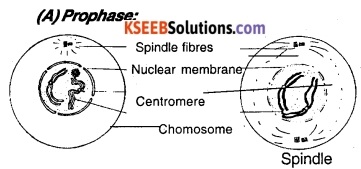
- The duplicated chromosomes undergo condensation (become Short and thick).
- Each chromosome has two chromatids and remains attached to each other at the region of the centromere.
- Centrioles are duplicated and begin to move towards the other pole of the cell.
- Aster begins to appear around each centriole.
- Spindle fibers begin to appear.
- Nuclear membranes and Nucleolus disappear.
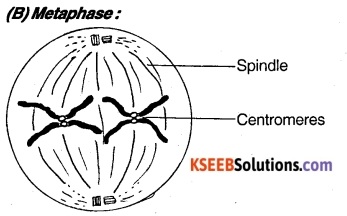
- Spindle fibres are completely formed.
- Chromosomes are highly condensed and they arrange at the equator.
- Spindle fibre attached to the centromere and arms project in a different direction.
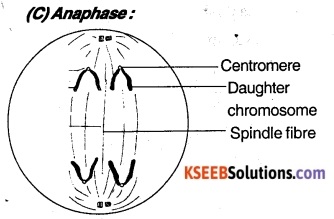
The spindle fibers become short and two chromatids of each chromosome separate and move away from the equator to the opposite poles. The moving chromosome exhibit different shapes like V or J shape.
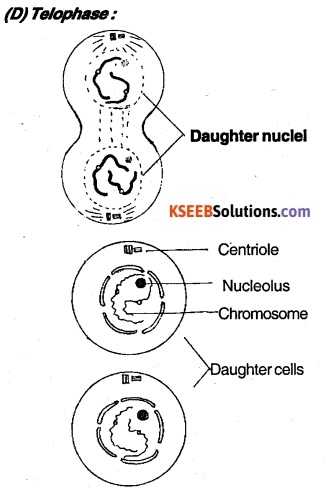
The daughter chromosomes arrived at the poles start uncoiling become thin. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear around the chromosome at each pole. Spindle fibres disappear.
(ii) Cytokinesis: A furrow develops in the middle of the cell which depends at the centre and divides cytoplasm into two equal parts.
Question 5.
Describe Zygotene and Pachytene stage of Meiosis. (D. Kannada 2009)
Answer:
Zygotene
- Homologous chromosomes come to lie side by side, closely applied at every point this process of pairing is called Synapsis.
- Each pair is called bivalent and each bivalent consists of 2 chromatids, so-called tetrad.
- The two chromatids of the same chromosome are called sister chromatids and chromatids belonging to two different chromosomes are called non-sister chromatids.
Pachytene :
- Two non-sister chromatids of each tetrad get coiled around each other and exchanges segments
- This process is called genetic crossing over. It results in recombination of genes. Crossing over takes place by breaking and reunion of chromatids.
- The points where exchanges have occurred appear X – shaped structure. It is called chiasmata.
![]()
Question 6.
When does each of the following occur in mitosis?
(1) The nuclear membrane reappears
(2) The chromosomes are the thickest and shortest
(3) Centromere divides into two
(4) Chromosomes begin to coil
(5) The nuclear membrane disappears
Answer:
- Telophase.
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Prophase
- Prophase.
Question 7.
Give the specific scientific term for the following:
(a) The period between two successive mitotic divisions
(b) Process of all division by which chromosome member is halved.
(c) Nuclear division in mitosis
(d) Phase in cell cycle when proteins and RNA are synthesized
(e) The point at which two sister chromatids are held together.
Answer:
(a) Interphase
(b) Meiosis
(c) Karyokinesis
(d) Interphase
(e) Centromere.
Question 8.
March the following:
(a) Protein Synthesis – (i) Meiosis
(b) Equational division – (ii) Zygotene
(c) Reductlonal division – (iii) G2 phase
(d) Synaptonemal complex – (iv) diplotene
(e) Chlasmata – (v) Mitosis
Answer:
(a) – (iii)
(b) – (v)
(c) – (i)
(d) – (ii)
(e) – (iv)