You can Download Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants Questions and Answers, 1st PUC Biology Question Bank with Answers, Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Biology Question Bank Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants
1st PUC Biology Respiration in Plants NCERT Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Differentiate between
(a) Respiration and Combustion
Answer:
| Respiration | Combustion |
| (1) It is a biochemical process | It is a physicochemical process |
| (2) It occurs in living cells | It does not occur in living cells |
| (3) ATP is generated | ATP is not generated |
| (4) Enzymes are required | Enzymes are not required |
| (5) It is a biologically controlled process | It is an uncontrolled process |
(b) Glycolysis and Krebs’ cycle
Answer:
| Glycolysis | Krebs’ cycle |
| (1) It is a linear pathway | It is a cyclic pathway |
| (2) It occurs in cell cytoplasm | It occurs in mitochondrial matrix |
| (3) It occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration | It occurs in aerobic respiration |
| (4) It generates 2 NADH2 and 2 ATP molecules on break down of one glucose molecules | It produces 6 NADH2, 2FADH2 and 2 ATP molecules on break down of two acetyl-CoA molecules. |
(c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation
Answer:
| Aerobic respiration | Fermentation |
| (1) Oxygen is used for deriving energy | Fermentation occurs in the absence of oxygen but presence of microbes |
| (2) Occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria |
Occurs in the cytoplasm |
| (3) End products are carbon dioxide and water | End products are ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide |
| (4) Complete oxidation the respiratory substrate takes place | Incomplete oxidation of the respiratory substrate takes place |
| (5) About 36 ATP are produced | Only 2 ATP molecules are produced |
Question 2.
What are respiratory substrates? Name the most common respiratory substrate.
Answer:
The compounds oxidised during the process of respiration are called respiratory substrates. Carbohydrates especially glucose act as respiratory substrates. Fats, proteins and organic acids also act as respiratory substrates.
![]()
Question 3.
Give the schematic representation of glyolysis?
Answer:
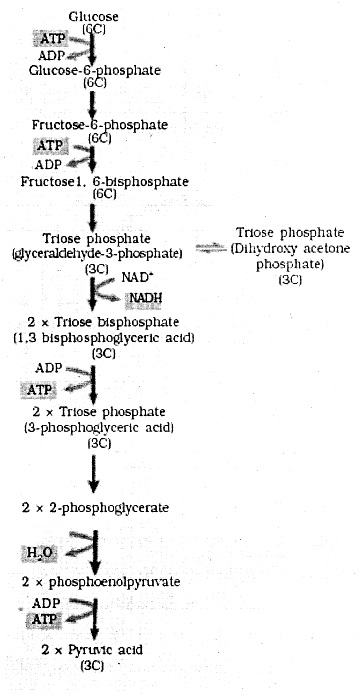
Question 4.
What are the main steps in aerobic respiration? Where does it take place?
Answer:
The major steps in aerobic respiration and the sites where they occur are listed in the given table.
| Step | Site of Occurrence |
| (1) Glycolysis | cytoplasm |
| (2) Krebs cycle | matrix of mitochondria |
| (3) electron transport system | Inner mitochondrial membrane |
| (4) oxidative phosphorylation | F0-F1 particles in the inner mitochondrial membrane. |
Question 5.
Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs’ cycle.
Answer:
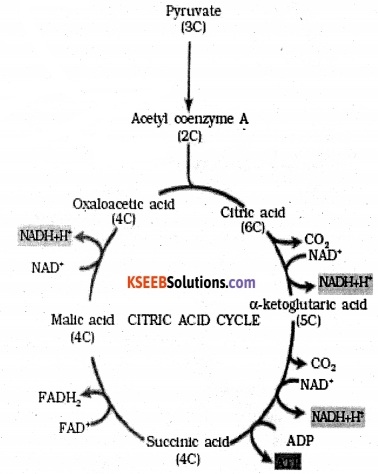
Question 6.
Explain ETS
Answer:
ETS or electron transport system is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It helps in releasing and utilizing the energy stored in NADH + H+ and FADH2 NADH+ H+, which is formed during glycolyis and citric acid cycle, gets oxidized by NADH dehydrogenase. The electrons so generated get transferred to ubiquinone through FMN. In a similar manner, FADH2 generated during citric acid cycle gets transferred to ubiquinone. The electrons from ubiquinone are received by cytochrome bc1, and further get transferred to cytochrome C. The cytochrome C acts as a mobile carrier between complex III and cytochrome C oxidase complex containing cytochrome a and a3, along with copper centres.
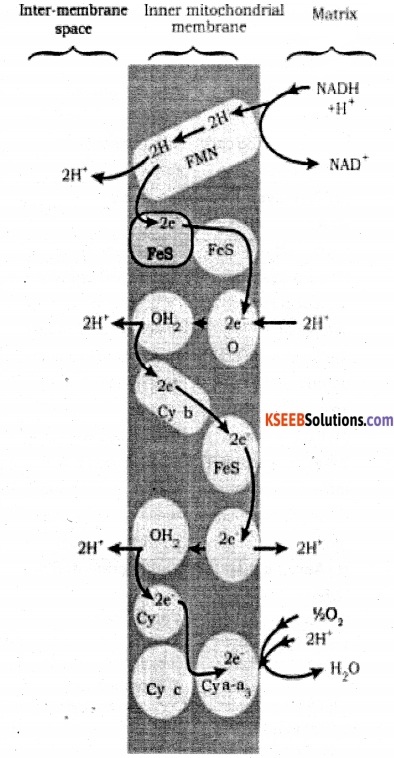
During the transfer of electrons from each complex, the process is accompanied by the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate by the action ATP synthase. The amount of ATP produced depends on the molecule, which has been oxidized.
![]()
Question 7.
Distinguish between the following:
(a) Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration
Answer:
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| (1) It uses oxygen for deriving energy | it occurs in the absence of oxygen |
| (2) It occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria | It occurs in cytoplasm |
| (3) The end products are carbon dioxide & water | The end products are ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide |
| (4) Complete oxidation of the respiratory substrate takes place | Incomplete oxidation of the respiratory substrate takes place. |
| (5) 36-38 ATP molecules lire produced | only 2 ATP molecules are produced |
(b) Glycolysis and Fermentation
Answer:
| Glycolysis | Fermentation |
| (1) Glycolysis occurs during aerobic and anaerobic respiration | Fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration |
| (2) Pyruvic acid is produced as its end product | Ethanol or lactic acid is produced as its end product. |
(c) Glycolysis and Citric acid Cycle
Answer:
| Glycolysis | Citric acid Cycle |
| (1) It is a linear pathway | It is a cyclic pathway |
| (2) It occurs in the cell cytoplasm | It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix |
| (3) It occurs in both aerobic & anaerobic respiration | It occurs in aerobic respiration |
| (4) one glucose molecule breaks down to generate 2 NADH2 & 2 ATP molecules | It produces 6 NADH, 2FADH2 and 2 ATP molecules on breakdown of two acetyl- CoA molecules |
Question 8.
What are the assumptions made during the calculation of net gain of ATP?
Answer:
- It is assumed that various parts of aerobic respiration such as glycolysis, TCA cycle and ETS occur in a sequential and orderly pathway.
- NADH produced during the process of glycolysis enters into mitochondria to undergo oxidative phosphorylation.
- Glucose molecule is assumed to be the only substrate while it is assumed that no other molecule enters the pathway at intermediate stages.
- The intermediates produced during respiration are not utilized in any other process.
Question 9.
Discuss “The respiratory pathway is an amphibolic pathway.”
Answer:
Respiration is generally assumed to be a catabolic process because, during respiration, various substrates are broken down for deriving energy. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose before entering respiratory pathways. Fats get converted into fatty acids and glycerol whereas fatty acids get converted into acetyl CoA before entering the respiration. In a similar manner, proteins are converted into amino acids, which enter respiration after deamination.
During the synthesis of fatty acids, acetyl CoA is withdrawn from the respiratory pathway. Also, in the synthesis of proteins, respiratory substances get withdrawn. Thus, respiration is also involved in anabolism. Therefore, respiration can be termed as.amphibolic pathway as it involves both anabolism and catabolism.
![]()
Question 10.
Define RQ. What Is Its value for fats?
Answer:
Respiratory quotient or respiratory ratio can be defined as the ratio of the volume of to of the volume of CO2 liberated to the volume of the O2 consumed, or; CO2 evolved to the volume of O2 consumed during respiration. The value of respiratory quotient depends on the type of respiratory substrate. Its value is one for carbohydrates. However, it is always less than one for fats as fats consume more oxygen for respiration than carbohydrates.
Question 11.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Answer:
Oxidative phosphorylation is a process in which electron are transferred from electron donors to oxygen which acts as electron acceptor. The oxidation-reduction reactions are involved in the formation of a proton gradient. The main role in oxidative phosphorylation is played by the enzyme ATP synthase. This enzyme complex consists of F0 and F1, components. For every two protons passing through F0-F1, complex, synthesis of one ATP molecule takes place.
Question 12.
What is the significance of the step-wise release of energy in respiration?
Answer:
The process of aerobic respiration is divided into four phases glycolysis, TCA cycle, ETS and oxidative phosphorylation. It is generally assumed that the process of respiration and production of ATP in each phase takes place in a step-wise manner.
The product of one pathway forms the substrate of the other pathway. Various molecules produced during respiration are involved in other biochemical process. The respiratory substrates enter and withdraw from pathway on necessity. Thus, the stepwise release of energy makes the system more efficient in extracting and storing energy.
1st PUC Biology Respiration in Plants Additional Questions and Answers
1st PUC Biology Respiration in Plants One Mark Questions
Question 1.
What is anaerobic respiration? (Oct. 83)
Answer:
Incomplete or partial breakdown of fuel molecules into compounds such as ethyl alcohol, lactic acid in the absence of molecular oxygen.
Question 2.
Name the scientist who was awarded Nobel Prize for the work on respiration. (Oct. 84)
Answer:
Sir Hans Krebs.
Question 3.
What is respiration? (Oct. 86)
Answer:
Oxidative process in which chemically bound energy from complex organic fuel molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is captured in the form of ATP.
Question 4.
What is Fermentation? (Apr. 87, July 2006)
Answer:
Anaerobic respiration carried out by microorganisms.
Question 5.
How many ATP is formed at the end of Kreb’s cycle? (Mar. 89)
Answer:
38.
![]()
Question 6.
Name the site of glycolysis in a ceil. (Oct. 90, 92, July 2006, March 2011)
Answer:
Cytoplasm
Question 7.
Name the products of anaerobic respiration. (Apr. 94)
Answer:
Ethyl alcohol and carbondioxide
Question 8.
Name the coenzyme associated with dehydrogenation of Succinic acid during Krebs cycle. (Apr. 96)
Answer:
NAD.
Question 9.
Name the cell organelle in which Racker’s particles are present. (Apr. 98,2005)
Answer:
Mitochondria
Question 10.
What is alcoholic fermentation? (Apr. 98)
Answer:
Alcoholic fermentation is the process by which yeast cells breakdown glucose into ethyl alcohol and carbon-dioxide under anaerobic conditions.
Question 11.
What is Pasteur effect ? (Apr. 99, 09, Oct. 02, June 2009)
Answer:
When the anaerobic yeast cells adapt to aerobic conditions in the presence of oxygen the outcome is termed Pasteur’s effect.
Question 12.
Define Respiratory quotient? (Oct. 99, 03, Apr. 2005, March 2010)
Answer:
Respiratory quotient is defined as the ratio of the volume of CO2 liberated to the volume of the O2 consumed, or;
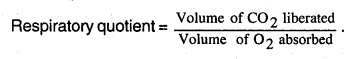
Question 13.
Expand ATP. (Apr. 2000)
Answer:
Adenosine Tri Phosphate
Question 14.
Expand FAD. (Oct. 2000)
Answer:
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide.
Question 15.
What Is lactic acid fermentation? (Oct. 2001)
Answer:
It is the process of fermentation by which lactose found in milk is converted to lactic acid by the action of lactobacillus.
Question 16.
Give the chemical equation of aerobic respiration. (Apr. 2002)
Answer:
C6H12O6+6O2 → 6CO2+6H2O→energy.
Question 17.
How many NADH2 molecules are resulted due to the degradation of one mole of pyruvic acid during Kreb’s Cycle? (Apr. 2003)
Answer:
4.
Question 18.
What are Aerobes?
Answer:
The organisms respire in the presence of O2 are called aerobes.
![]()
Question 19.
Which is the site of Krebs cycle? (Apr. 07)
Answer:
Mitochondrial Matrix.
Question 20.
What are respiratory substrates?
Answer:
The substances present in cell protoplasm which undergo oxidation and generate energy are called respiratory substrates.
Question 21.
Name the three-carbon compound formed during glycolysis.
Answer:
Pyruvate
Question 22.
Name the site of EMP pathway.
Answer:
Cytoplasm
Question 23.
What Is the RQ value for carbohydrate?
Answer:
One / unity (Apr. 2004)
Question 24.
Give reason: (July 2008)
RQ value of glucose is 1.
Answer:
It is because the volume of CO2 evolved is equal to the volume of 02 absorbed.
Question 25.
Give reason: (March 2009)
RQ value of protein is generally less than one.
Answer:
Proteins are Compounds poor in oxygen and require more of external 02 for oxidation hence RQ is less than one.
1st PUC Biology Respiration in Plants Two Marks Questions
Question 1.
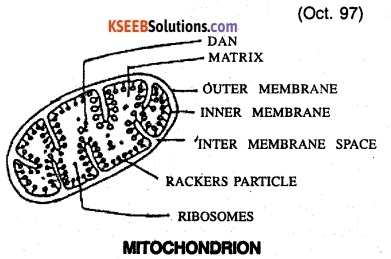
Draw a neat labelled diagram of mitochondria. (Oct. 97)
Answer:
Question 2.
Name any two respiratory substrates and their RQ values. (M.Q.P.)
Answer:
Respiratory substrates.
Carbohydrates with R.Q. = unity
Proteins with R.Q. = 0.7.
Question 3.
Define Aerobic Respiration. Write an equation. (April 99)
Answer:
Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of the respiratory substrate into carbon-di-oxide and water.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Question 4.
What is fermentation ? Give 2 examples of products of fermentation. (Oct. 2000)
Answer:
Anaerobic respiration carried out by microorganisms is called fermentation. The products of fermentation are lactic acid, ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide.
![]()
Question 5.
List our any 2 difference between anaerobic respiration and fermentation. (April 2001)
Answer:
anaerobic respiration:
(1) It is a partial breakdown of the respiratory substrate into alcohol and
C6H12O6 + 2C2H5OH+ 2C2O + energy
(2) The end product of glycolysis is pyruvic acid which yields alcohol & CO2
fermentation:
(1) It is anaerobic respiration carried out by microorganisms![]()
(2) End product of glycolysis is pyruvic acid which can form lactic acid, butyric acid or
alcohol.
Question 6.
What is RQ? Name the apparatus used to measure RQ. (July 2006)
Answer:
The ratio of volumes of CO2 liberated and O2 used during respiration is called respiratory quotient. It is denoted by RQ. The RQ values of different substrates can be measured by Ganong’s respirometer.
Question 7.
Give an overall equation for alcoholic fermentation.
Answer:
![]()
Question 8.
Write any four differences between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
Answer:
Aerobic Respiration
- In this respiratory substrate is completely oxidized.
- It takes place in the presence of molecular O2.
- End products of this process are CO2 and H2O.
- More amount of energy is liberated.
Anaerobic respiration.
- A respiratory substrate is incompletely oxidized.
- It takes place in the absence of molecular O2.
- End products are ethyl alcohol and CO2.
- Less amount of energy is liberated.
Question 9.
Write any two differences between alcoholic fermentation and Lactic acid fermentation.
Answer:
Alcoholic Fermentation
- End products of alcoholic fermentation are ethyl alcohol and CO2.
- This process is carried out by yeast.
Lactic acid Fermentation.
- End product of lactic acid fermentation is lactic acid.
- This process is carried out by lactic acid bacteria present in milk.
Question 10.
What is fermentation? Give the equation for alcoholic fermentation. (Oct. 2004)
Answer:
Anaerobic respiration carried out by microorganisms is called fermentation.
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH+ 2C2O ↑+ energy
1st PUC Biology Respiration in Plants Five Marks Questions
Question 1.
Draw labelled diagram and describe the structure and function of a mitochondrion.
(Apr. 83, 87, Oct. 86)
Answer:
Diagram under Q.1 of two marks.
Mitochondria called powerhouse of the cell are the organelles of cellular respiration. The mitochondria are bounded by a double unit membrane space. The outer membrane is smooth and the inner folded repeatedly into projections called cristae. The central portion of the mitochondrion encloses the matrix.
The matrix side of the inner membrane, including surfaces of cristae are bounded by lollipop like structures called Rackers particles or F0Ft complexes which help in ATP synthesis. Molecules necessary for electron transport are present. The matrix contains highly concentrated mixture of several enzymes Associated with kreb’s cycle! The matrix has DNA, RNA and 70s type of ribosomes.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the conversion of hexose sugar into pyruvic acid during respiration.
OR
Write the schematic representation of glycolysis. (Oct. 84, 96, 97, 99, 03, Apr. 91, 95, 97, 01, 06, July 06, 07, 2010, M.Q.P.)
Answer:
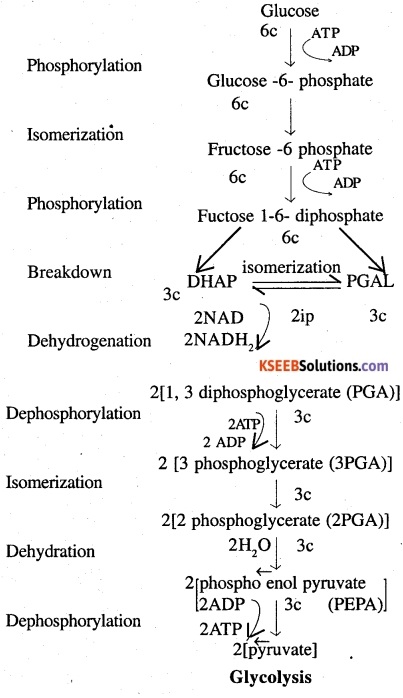
Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid also called EMP pathway after the scientists Embden, Meyerhof and Paranas and is seen in the Cytoplasm. It involves several steps, Glucose in the presence of ATP is converted to glucose 6 phosphate which by isomerisation forms fructose -6- phosphate and by a second phophorylation forms fructose 1-6 diphosphate.
This fructose 1 -6 diphosphate a 6 Carbon compound breaks up into 2 molecules of PGAL and DHAP both being 3 Carbon compounds. Each compound then by phosphorylation and dehydrogenation combine with IP and NAD to yield 1,3 di PGA and NADH2. The di PGA by dephosphorylatoin gives ATP and’3 PGA which by rearrangement produces 2PGA. Dehydration of 2PGA yields phosphoenol pyruvate which by dephosphorylation give pyruvic acid.
One molecule of glucose yields 2 molecules of pyruvic acid.
ATP calculion : ATP used – 2 ATP
ATP synthesised NADH2 formed = 2×3 = 6 ATP
ATP formed = 4 ATP 10 ATP
Net gain = ATP synthesised – ATP used
10-2 = 8 ATP.
Question 3.
Differentiate Respiration from Photosynthesis. (March 1990)
Answer:
(1) Respiration – (a) Photosynthesis
(1) Occurs in all living cells in the cytoplasm and mitochondria.
(a) occurs in cells with chloroplasts.
(2) no segregation into light and dark reactions
(b) Light reactions totally dependent on light.
(3)Starting compounds are C6H12O6 and O2.
(c) Starting materials are CO2 and H2O.
(4)ATP is produced by oxidative phosphorylation.
(d) ATP produced by photo phosphorylation.

Question 4.
Give an account of (Kreb’s cycle) Citric acid cycle. (April 1985, 1988, 1989, 1992, 2000, 2006, Oct. 1991, 1993, 2002, 2004, July 2008)
Or
Write the schematic representation of citric acid cycle with preparatory phase.
(July 2011)
Answer:
Kreb’s cycle or citric acid cycle is second step of respiration and takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. Pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is first converted to acetyl CoA a 2 Carbon compound which in the mitochondrial matrix to initiate Kreb’s cycle.
Condensation: acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate in presence of water to give a tricarboxylic acid citric acid. CoA is released.
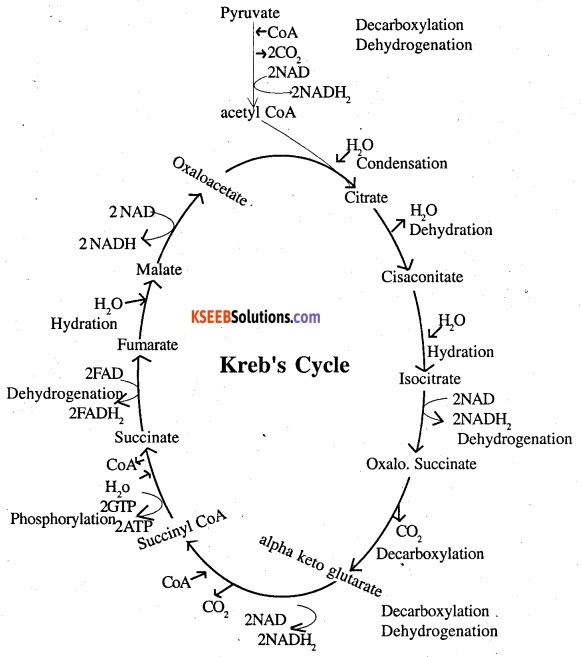
Dehydration and Hydration:
The citric acid then loses a molecule of water to form cis-aconitate which takes up a molecule of water and forms isocitrate.
Dehydrogenation: Isocitrate undergoes dehydrogenation and forms oxalosuccinate. This yields 2 molecules of NADH2.
Decarboxylation: By giving out CO2 – oxalosuccinate is converted to α- ketoglutarate.
Dehydrogenation & decarboxylation: The a- ketoglutarate simultaneously shows dehydrogenation decarboxylation to form succinyl CoA, 2 molecules of CO2, NADH2 are released and CoA is added.
Hydration & Phophorylation: Succinyl CoA in presence of water forms succinate, CoA is released and 2 GTP’s are synthesised which are converted to ATP.
Dehydrogenation: Dehydrogenation of succinate yields Fumarate and 2 molecules of FADHO2 are formed.
Hydration: Fumarate in presence of water yields Malate.
Dehydrogenation: Malateby dehydrogenation gives 2 molecules of NADH2 and is converted to oxaloacetate.
ATP Calculation.
8 NADH2 = 8 × 3 = 24 ATP
2 FADH, = 2 × 2 = 4 ATP
2 GTP =2- = 2ATP
Total =30 ATP
![]()
Question 5.
Describe the mechanism of anaerobic respiration. (Oct. 85, 94)
Answer:
Anaerobic Respiration is the respiration carried out in the absence of oxygen and the fuel molecules are partially broken down.
I Step – glycolysis same as 4,
II step – Anaerobic breakdown of glucose.
Glucose produced during glycolysis is converted to substances like ethyl alchohol and

The pyruvate by decarboxylation form acetaldehyde and by hydrogenation gives ethyl alcohol. The overall equation is
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH+ 2C2O + energy
ATP calculation:
Net gain during glycolysis = 8 ATP
ATP used for (2NADH2) 2×3 =6 ATP
Balance = 2ATP
Question 6.
Define fermentation. Explain the fate of pyruvic acid in Saccharomyces and Lactobacillus
(April 2007, March 2010)
Answer:
Anaerobic breakdown of organic food substances into CO2 ethyl alcohol or lactic acid by the enzymes of some microorganisms is called fermentation. Fate of pyruvic acid in saccharomyces.
In saccharomyces, pyruvate is further oxidized into ethyl alcohol and CO2 yeast converts pyruvate into ethyl alcohol and CO2 in the absence of O2. It is called alcohol or ethanol fermentation.
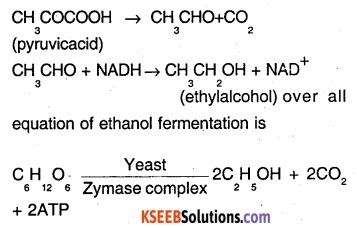
Fate of pyruvate in lactobacillus The lactobacilli of milk convert pyruvate into lactic acid. It is called lactic acid or lactate fermentation.
CH3COCOOH+2NADH → C3H6O3 +2NAD+