You can Download Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals Questions and Answers, 1st PUC Biology Question Bank with Answers, Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Biology Question Bank Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals
1st PUC Biology Structural Organisation in Animals NCERT Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer in one word or one line.
(i) Give the common name of Periplaneta Americana.
Answer:
Cockroach
(ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm?
Answer:
Two
(iii) What is the position of ovaries in cockroach?
Answer:
2 large ovaries are found lying laterally in the 2nd to 6th abdominal segment.
(iv) How many segments are present in the abdomen of cockroach?
Answer:
Ten segments.
(v) Where do you find Malpighian tubules?
Answer:
Malpighian tubules are the main excretory organs of the cockroach.
Question 2.
Answer the following:
(i) What is the function of nephridia?
Answer:
Nephridia is the excretory organ of the earth worm or pheretima.
(ii) How many types of nephridia are found in earthworm based on their location?
Answer:
3 types of nephridia
- Septal nephridia: present on both sides of intersegmental septa of segment 15 to the last that open into intestine.
- Integumentary nephridia: attached to lining of the body wall of segment 3 to the last that open on the body surface.
- Pharyngeal nephridia: present as three paired tufts in the 4th, 5th and 6th segments.
![]()
Question 3.
Draw a labelled diagram of the reproductive organs of an earthworm.
Answer:
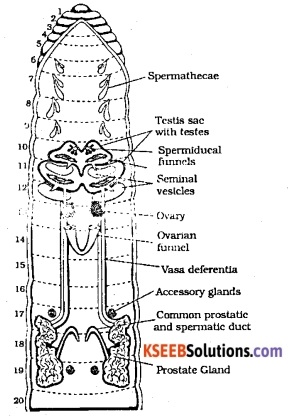
Question 4.
Draw a labelled diagram of alimentary canal of a cockroach.
Answer:
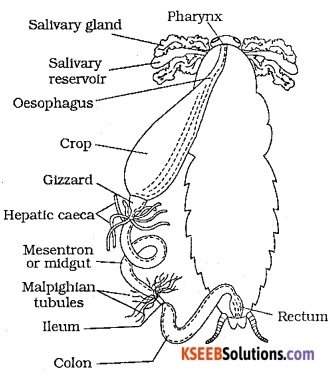
Question 5.
Distinguish between the followings
(a) Prostomium and peristomium
Answer:
Prostomium is the front most part of the earthworm. This is not called a true segment as it doesn’t contain typical organs of an annelida. Peristomium is from where the true segment of the earthworm body starts.
(b) Septal nephridium and pharyngeal nephrldium
Answer:
Septal nephridia, present on both sides of intersegmental septa of segment 15 to the last open into intestine. Pharyngeal nephridia, present as three paired tufts in the 4th, 5th and 6th segments.Both are same structurally and functionally.
Question 6.
What are the cellular components of blood?
Answer:
Red blood cells and white blood cells are the cellular components of blood.
Question 7.
What are the following and where do you find them In animal body.
(a) Chondriocytes
Answer:
Cells of cartilage
(b) Axons
Answer:
Tail like structure of a neuron
(c) Ciliated epithelium
Answer:
Found in the inner lining of bronchioles. Cilia help trap and clear dust foreign particles.
Question 8.
Describe various types of epithelial tissues with the help of labelled diagrams.
Answer:
Epithelial tissues provide covering to the inner and outer lining of various organs. The cells of epithelial tissues are compactly packed with little intercellular matrix.
There are two types of epithelial tissues.
(a) Simple epithelium: Composed of a single layer of cells and functions as a lining for body cavities, ducts and tubes.
(b) Compound epithelium: consists of two or more cell layers and has protective function as it does in our skin. They cover the dry surface of the skin, the moist surface of buccal cavity, pharynx, inner lining of ducts of salivary glands and of pancreatic ducts.
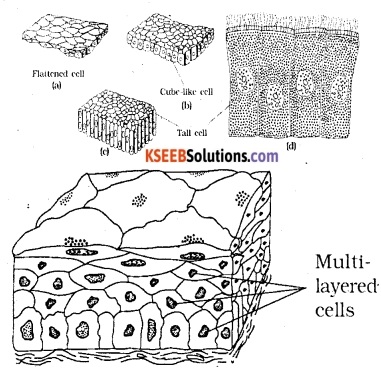
On the basis of structural modification of the cells, simple epithelium is further divided into three types. These are:
(i) Squamous: Made of a single thin layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries. They are found in the walls of blood vessels and air sacs of lungs and are involved in functions like forming a diffusion boundary.
(ii) Cuboidal: Composed of a single layer of cube-like cells. This is commonly found in ducts of glands and tubular parts of nephrons in kidneys and its main functions are secretion and absorption. The epithelium of proximal convoluted tubule of nephron in the kidney has microvilli.
(iii) Columnar: Composed of a single layer of tall and slender cells. Their nuclei are located at the base. Free surface may have microvilli. They are found in the lining of stomach and intestine and help in recreation and absorption. If the columnar or cuboidal cells bear cilia on their free surface they are called ciliated epithelium. Their function is to move particle or mucus in a specific direction over the epithelium. They are mainly present in the inner surface of hollow organs like bronchioles and fallopian tubes.
Question 9.
Distinguish between
(a) Simple epithelium and compound epithelium
Answer:
Simple epithelium is composed of one layer of cells while compound epithelium is composed of more than one layer of cells.
(b) Cardiac muscle and striated muscle
Answer:
Cardiac muscle are present in the cells of heart only. They have contractile property which helps in”the pumping action of the heart. Striated muscles are present near articulatory joints. Their role is to facilitate movement of organs like hands and feet.
(c) Dense regular and dense irregular connective tissues
Answer:
Fibres and fibroblasts are compactly packed in the dense connective tissues. Orientation of fibres show a regular or irregular pattern and are called dense regular and dense irregular tissues.
In dense regular connective tissues, the collagen fibres are present in rows between many parallel bundles of fibres. Tendons, which attach skeletal muscles to bones and ligaments which attach one bone to another are examples of this tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue has fibroblasts and many fibres that are oriented differently. This tissue is present in the skin.
(d) Adipose and blood tissue
Answer:
Adipose tissue is a type of loose connective tissue located mainly beneath the skin. The cells of this tissue are specialised to store fats. The excess of nutrients which are not used immediately are converted into fats and are stored in this tissue. Blood is a fluid connective tissue. The main function of blood is to transport gases, nutrients and waste products in the body.
(e) Simple gland and compound gland
Answer:
Simple gland is composed of single-cell while compound gland is composed of multiple cells.
Question 10.
Mark the odd one in each series:
(a) Areolar tissue; blood; neuron; tendon
Answer:
Neuron is not a connective tissue.
(b) RBC; WBC; platelets; cartilage
Answer:
Cartilage is not part of blood.
(c) Exocrine; endocrine; salivary gland; ligament
Answer:
Ligament is not part of gland.
(d) Maxilla; mandible; labrum; antenna
Answer:
Antenna is not a masticating part of cockroach.
(e) Protonema; mesothorax; metathorax; coxa
Answer:
Coxa is not part of thorax.
![]()
Question 11.
Match the terms in column I with those in column II:
Column I – Column II
(a) Compound eplthellum – (i) Alimentary canal
(b) Compound eye – (ii) Cockroach
(c) Septal nephrldla – (iii) Skin
(d) Open circulatory – (iv) Mosaic vision
(e) Typhiosole – (v) Earthworm
(f) Osteocytes – (vi) Phallomere
(g) Genitalia – (vii) Bone
Answer:
a – (iii)
b – (iv)
c – (y)
d – (ii)
e – (i)
f – (vii)
g – (vi)
Question 12.
Mention briefly about the circulatory system of earthworm
Answer:
Blood vascular system: Pheretima exhibits a closed type of blood vascular system consisting of blood vessels, capillaries and heart. Due to closed circulatory system, blood is confined to the heart and blood vessels. Contractions keep blood circulating in one direction. Smaller blood vessels supply the gut, nerve cord and the body wall. Blood glands are present on the 4th, 5th and 6th segments. They produce blood cells and haemoglobin which is dissolved in blood plasma. Blood cells are phagocytic in nature. Earthworms lack specialised breathing devices. Respiratory exchange occurs through moist body surface into their bloodstream.
Question 13.
Draw a neat diagram of digestive system of frog.
Answer:

Question 14.
Mention the function of the following
(a) Ureters in frog
Answer:
The ureters act is urinogenital duct which opens into the cloaca. In females, the ureters and oviduct open separately in the cloaca.
(b) Malpighian tubules
Answer:
Excretion is performed by un malphigian tubules in cockroaches. Each tubule is lined by glandular and ciliated cells. They absorb nitrogenous waste products and convert them into uric acid which is excreted out through the hindgut.
(c) Body wail an earthworm
Answer:
The body wall of earthworm is covered externally by a thin noncellular cuticle below which is the epidermis, two muscle layers and an innermost coelonic epithelium. The epidermis is made up of a single layer of columnar epithelial cells which contain secretory gland cells.
1st PUC Biology Structural Organisation in Animals Additional Questions and Answers
1st PUC Biology Structural Organisation in Animals One Mark Questions
Question 1.
What do fibroblasts synthesize?
Answer:
Collagen and elastin fibres.
Question 2.
Name two kinds of filaments of microfibrils.
Answer:
Actin and Myosin filaments.
Question 3
Name the functional contractile unit of the muscle.
Answer:
Sarcomere.
Question 4.
Name the type of tissue that is most abundant in animal body.
Answer:
Connective tissue.
Question 5.
Name the tissue which connects muscles to a bone.
Answer:
Tendon
Question 6.
Name one specialised connective tissue.
Answer:
Blood.
Question 7.
Where are blood cells manufactured in the bone?
Answer:
Bone marrow.
Question 8.
What name is given to the cells of cartilage?
Answer:
Chondrocytes
Question 9.
What technical term Is given to bone cells?
Answer:
Osteocytes.
Question 10.
Why are striated muscles called Skeletal muscles?
Answer:
Since striated muscles are attached to the bones, they are called skeletal muscles.
Question 11.
Why are smooth muscles called Involuntary muscles?
Answer:
Smooth muscles are called involuntary muscles because their functioning cannot be controlled by our will
Question 12.
Name the excretory organs of an earthworm.
Answer:
Nephridia.
Question 13.
How does a frog take in water?
Answer:
Frogs take in water through their skin.
Question 14.
How many cranial nerves does a frog have?
Answer:
Ten pairs.
Question 15.
Name the larva of a frog.
Answer:
Tadpole.
Question 16.
Name any 2 species of cockroach?
Answer:
Periplaneta Americana
Blatta Orentalis.
Question 17.
What is an exoskeleton?
Answer:
‘The external body covering of the cock-roach is called Exoskeleton.
Question 18.
What are Malpighian tubules? (Belgaum 2004)
Answer:
The excretory organs of Insects (Cockroach) are called Malphigian tubules.
![]()
Question 19.
What Is a nymph? (Belgaum 2004)
Answer:
The larva of cockroach is called Nymph.
Question 20.
What are mandibles?
Answer:
The jaws of cockroach are called mandibles.
Question 21.
What type of mouth parts are seen in cock-roach? (B’lore South, B’lore North 2004)
Answer:
Mandibulate/ Chewing type.
Question 22.
Why is cockroach called an omnivorous animal? (D.Kannada 2005)
Answer:
Cockroach feeds on all kinds of substances like leather, paper, cloth etc., hence called omnivorous.
Question 23.
What are anal styles? (Tumkur 2005)
Answer:
Anal styles are unsegmented hair like out-growths arising from the end of the abdomen in male cockroach.
Question 24.
Write the scientific name of cockroach.
Answer:
Periplaneta americana (Kolar 2005)
Question 25.
What is tergum? (Mandya 2005)
Answer:
Tergum is a dorsal chitinous plate of the exoskeleton of cockroach.
1st PUC Biology Structural Organisation in Animals Two Marks Questions
Question 1.
What is pscudostratified epithelium? Mention one place where it is located in human body.
Answer:
Psudostratified Epithelium is the epithelial tissue made up of a single layer of columnar cells, but appears two layered because some cells are shorter than others and have their nuclei at different levels. It is located in trachea and bronchi.
Question 2.
Name two proteins produced by fibroblasts. What is their functions?
Answer:
Collagen and Elastin.
These fibrous proteins provide strength, elasticity and flexibility to the tissue.
Question 3.
What are exocrine glands? Name any two secretions of them.
Answer:
The glands which have ducts to pour their secretions into the respective site of action are called exocrine glands, e.g.: Salivary glands secrete saliva into buccal cavity. Liver secretes bile into duodenum.
Question 4.
What are endocrine glands? Name their secretion.
Answer:
The glands which do not have ducts and pour their secretions directly into the blood are called endocrine glans. Their secretions are called hormones.
Question 5.
Differentiate between loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue.
Answer:
| Loose connective tissue | Dense connective tissue |
| The cells and fibres are loosely arranged in the matrix e.g.: Areolar tissue | The cells and fibres are compactly arranged. e.g.: Tendon |
Question 6.
Name the type of connective tissue that serves as a support framework for epithelium.
Mention the cell types in it.
Answer:
Areolar connective tissue serves as a support framework for epithelium. It contains mast cells, macrophages and fibroblasts.
Question 7.
Write four functions of bones.
Answer:
- Provide a place for attachment of muscles and help in movement and locomotion.
- Provide protection to internal organs
- The long-bones of limbs serve the weight-bearing function.
- They act as depot of calcium and phosphorous.
Question 8.
Mention four sites in adult human body, where cartilage is present.
Answer:
- tip of nose
- pinna of ear
- between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column
- joints in the limbs
Question 9.
Differentiate between smooth muscles and cardiac muscles.
Answer:
| Smooth muscles | Cardiae muscles |
| Cells are spindle shaped | Cells are cylindrical |
| striations are absent | striations are present |
| Intercalated discs are absent | Intercalated discs are Present |
| don’t have automatic rtythmicity | have automatic rtrythmicity |
Question 10.
What is the main role of setae in an earthworm? What is their shape? Where are they attached to the body?
Answer:
Setae:-Their principal role is locomotion. They are S-shaped. They are embedded in the epidermal pits in the middle of each segment.
Question 11.
What is meant by cutaneous respiration? Name two group of animal that show it.
Answer:
Respiration by skin is known as cutaneous respiration. Frog and earthworm show that.
Question 12.
What is pulmonary respiration? Name two groups of animal that have it.
Answer:
Respiration by lungs is called pulmonary respiration Reptiles, Mammals have that.
Question 13.
Mention any two differences between male and female cockroaches. (Bijapur, Udupi, Gulbarga 2005)
Answer:
Male cockroach
- The 10th abdominal segment is rounded.
- The terminal abdominal segment has anal styles and anal cerci.
Female Cockroach :
- It is pointed in female.
- Anal styles are absent in females.
![]()
Question 14.
What are spiracles? How are they distributed in cockroach. (B’lore North 2004)
Answer:
Spiracles are the openings of the respiratory system (trachea) in cockroach. There are 10 pairs of spiracles of which two pairs are located in the thorax and eight pairs in the abdomen.
Question 15.
List the mouthparts of Cockroach. (D. Kannada 2006)
Answer:
Labrum, Mandible, hypopharynx, manillary palp (cardo, stipes, lacinia, galea) submentum, mentum, prementum, glossa, paraglossa, labial palp.
1st PUC Biology Structural Organisation in Animals Three Marks Questions
Question 1.
What are the three types of muscle tissue? Write two characteristic points about the structure of each of them.
Answer:
(i) Striated muscles
- Cells are cylindrical and unbranched
- They show alternate dark and light bands called striations.
(ii) Smooth muscles
- cells are spindle-shaped
- Striations are absent
(iii) Cardiac muscles
- Cells are cylindrical and branched
- Striations are faint
Question 2.
Name the fluid connective tissue in our body. What is its matrix called? Name the cell types present in it.
Answer:
Blood is the fluid connective tissue. Its matrix is called plasma cell types in blood.
- Red blood corpuscles
- White blood corpuscles
- Platelets
Question 3.
Write three differences between bone and cartilage.
Answer:
| Bone | Cartilage |
| It is a solid, rigid and strong connective tissue | It is a solid, semi-rigid and flexible connective tissue |
| Occur singly in a lacuna | Occur in clusters of 2 or 3 in each lacuna |
| Matrix is deposited with salts of calcium and phosphorous | No calcium and phosphorous salts are present in the matrix. |
Question 4.
Answer the following:
(i) What is the function of nephridia?
Answer:
Nephridia regulate the volume and composition of the body fluid in the earthworm. They help in the excretion of wastes.
(ii) How many types of nephridia are found in the earthworm, based on their location?
Answer:
Three types of nephridia are found.
Question 5.
Describe the nervous system of an earth-worm.
Answer:
Brain is formed by the fusion of a pair of cerebral ganglia, it lies in the anterior and dorsal part of the third segment. It is connected to two sub-pharyngeal ganglia lying below the pharynx. A double ventral nerve cord runs up to the last segment. Ganglia are segmentally arranged on the nerve cord and they give nerves to the organs of that segment.
Question 6.
Mention the function of the following
(a) Ureters In frog
Answer:
They carry urine from kidneys to cloaca. In males, it also conducts the sperms.
(b) Malphlglan tubules
Answer:
They are the excretory organs of a cockroach. They collect the nitrogenous wastes from the haemolymph and send them into the intestine.
(c) The body wall of earthworm
Answer:
The muscle layers help in locomotion. It has sensory/receptor cells. Mucus is secreted by certain cells of the body wall.
1st PUC Biology Structural Organisation in Animals Five Marks Questions
Question 1.
(i) Draw a labelled diagram of areolar connective tissue.
Answer:

(ii) Where is It found In human body?
Answer:
It is found beneath the skin.
(iii) How does it differ from adipose tissue?
Answer:
| Areolar tissue | Adipose tissue |
| Adipocytes are absent | Adipocytes are present |
| Most cells are present | Mast cells are absent |
| It serves as a support framework for epithelium | It synthesises, stores and metabolises fat. |
Answer in one word or one line.
(i) Give the common name of Periplanata americana
Answer:
Cockroach
(ii) How many spermathecae are found In earthworms?
Answer:
Four pairs.
(iii) What is the position of ovaries in a cockroach?
Answer:
A pair of ovaries extend between 4th and 6th segments.
(iv) How many segments are present in the abdomen of a cockroach?
Answer:
Ten segments
(v) Where do you find Malphigian Tubules?
Answer:
The junction between midgut and hindgut.
Question 3
Draw a neat labelled diagram of the digestive system of cockroach. (B.North, Shimoga, Gulbarga, Belgaum, Chikmagalur 2004, D.Kannada, Hassan, Mysore, Kolar, M.Q.P. 2005, Udupi.06, 08, D.K. 06, 07, 08, Koppala, Tumkur. 05,08, U.Kannada 08, D.K. 2009)
Answer:
The digestive system mainly consists of the foregut, midgut and hindgut. The foregut/stomodium consists of the mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, crop and gizzard. The mouth is situated anteriorly below the labrum and between the mandibles. It leads into the buccal cavity. The hypopharynx lies on the floor of the buccal cavity. The salivary receptacujar duct opens behind the tongue.
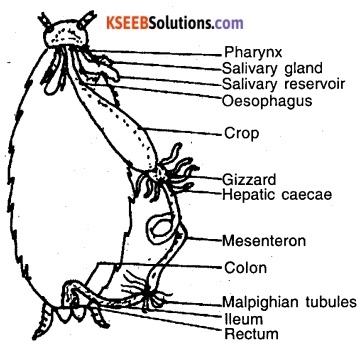
Pharynx is narrow tubular part from where the oesophagus arises. The oeophagus is narrow and connects the buccal cavity to the crop. Crop is thin-walled sac, present in the whole of the thorax and serves as a reservoir for food storage. The midgut/mesenteron is a short narrow tube lined by glandular epithelium. It is the main organ of digestion and absorption. At the junction of gizzard and midgut 6 – 8 short fingerlike hollow tubes arise called hepatic caecae.
The hindgut/proctodaeum is a long tube like structure with 60 – 70 narrow thread like yellow structures called Malpighian tubules. The hindgut is differentiated into an anterior short, narrow ileum, middle long wide coiled colon and a terminal short dilated sac like structure the rectum which opens to the exterior by anus.
![]()
Question 4.
With the help of a neat labelled diagram Explain the nervous system of cockroach. (Bangalore South, Bangalore Rural, Mandya, Mysore, Udupi 2005, D.Kanaada 2011)
Answer:
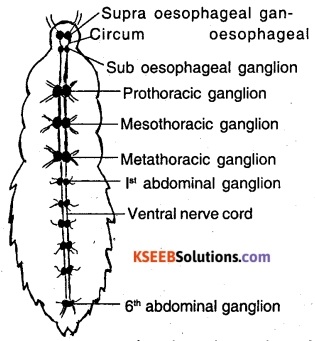
The nervous system of cockroach consists of the central and periphernal systems, The central nervous system is made of ganglia and nerve, cords, whereas the peripheral nervous system is made of nerves arising from the ganglia.
- Supra oesophageal ganglion:- are a pair of ganglia found in the head & form the brain.
- Circum oesophageal Connectives:-These are thick ends of nervous tissue arising from the base of the brain and called commissures.
- Sub oesophageal ganglia:- are a pair of ganglia the oesophagus. They give off several nerves to the mouth parts.
- Ventral nerve end cord segmental ganglia:- The double ventral nerve cord arises from the base of the sub oesophageal ganglia, and runs to the end of the body. There are nine segmental ganglia, of which three pairs are thoracic, six pairs in the abdomen i. e 1st five lie in the first five abdominal segments, the last is large & found farther behind.
- The thoracic ganglia give out nerves to the muscles of legs and wings and abdominal ganglia give out nerves to abdominal muscles, heart, spiracles & reproductive organs.
Question 5.
Explain the mouth parts of Cockroach. (D.Kannada 2007)
Answer:
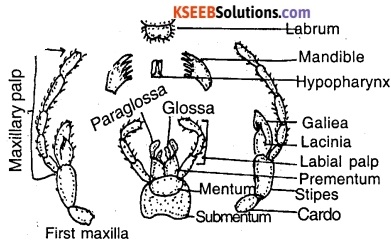
Mouth parts: On the ventral side of the head mouth is present. The appendages surrounding the mouth which are helpful in feeding are called the mouth parts or trophi. The mouth parts of cockroach are chewing and biting type.
The mouth parts of Cockroach includes labrum (upper lip), mandibles, maxillae, labium (lower lip) and hypopharynx (tongue).
(i) Labrum: This is also known as upper lip. It is a small flap like structure which covers the mouth dorsally. The inner surface of the labrum bears taste buds concerned with tasting of the food material.
(ii) Mandibles: The mandibles are a pair of small triangular, stout unjointed sclerotized structures present on either side of the mouth. They have toothed inner edge helps in biting the food materials into small pieces. Hence treated as jaws.
(iii) Maxillae: A pair of maxillae are present beneath the mandibles and treated as additional jaws. Each maxilla is differentiated into a basal segment consisting of cardo and stipes, terminal segment consisting of outer larger part called galea and inner stouter part called lacinia. The outer border of stipes bears long five jointed maxillary palp which is five jointed structure. The maxillae help in holding and pushing the food into the mouth during swallowing.
(iv) Labium: The labium or lower lip lies behind the maxillae. It consists of proximal submentum, middle mentum and distal bilobed prementum. The mentum posses a pair of labial palps. The prementum bears a pair of outer paraglossae and a pair of inner glossae.
(v) Hypopharynx: This is also known as lingua. It represents the tongue of the cockroach. It is a cylindrical and tubular structure present above the labium between maxillae. Common salivary receptacular duct opens at its base.