Karnataka 1st PUC Business Studies Question Bank Chapter 4 Business Services
You can Download Chapter 4 Business Services Questions and Answers, Notes, 1st PUC Business Studies Question Bank with Answers Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
1st PUC Business Studies Business Services Textual Questions and Answers
1st PUC Business Studies Business Services Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
DTH services are provided by
a. Transport companies
b. Banks
c. Cellular companies
d. None of the above
Answer:
c. Cellular companies
Question 2.
The benefits of public warehousing includes
a. Control
b. Flexibility
c. Dealer relationship
d. None of the above
Answer:
b. Flexibility
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following is not a function of insurance?
a. Risk sharing
b. Assist in capital formation
c. Lending of funds
d. None of the above
Answer:
c. Lending of funds
Question 4.
Which of the following is not applicable in the life insurance contract?
a. Conditional contract
b. Unilaterl contract
c. Lending of funds
d. None of the above
Answer:
c. Lending of funds
Question 5.
CWC stands for
a. Central water commission
b. Central warehousing commission
c. Central warehousing corporation
d. Central water corporation
Answer:
c. Central warehousing corporation
![]()
1st PUC Business Studies 4 Business Services Multiple Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define services and goods.
Answer:
Services are essentially intangible activities which are separately identifiable and provide satisfaction of wants. We cannot kept it in stock. Their purchase does not result in the ownership of anything physical. Services involve an interaction to be realized between the service provider and the consumer.
A good is a physical product capable of being delivered to a purchaser and involves the transfer of ownership from seller to customer. Goods also refer to commodities or items of all types, except services, involved in trade or commerce.
Question 2.
What is e-banking? What are the advantages of e-banking?
Answer:
The growth of internet and e-commerce is dramatically changing every day, with the model World Wide Web and e-commerce the world is transforming into a digital global village. In simple terms, internet banking means any user with a PC and a browser can get connected to the banks website to perform the banking functions and avail the bank’s services; e-banking refers to electronic banking or banking using electronic media.
Thus, e-banking is a service provided by banks that enables a customer to conduct banking transactions, such as checking accounts, applying for loans or paying bills over the internet using a personal computer, mobile telephone or handheld computer, e-banking includes a range of services like Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT), Automated Teller Machine (ATM), Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), Credit Cards, and Electronic or Digital Cash.
Advantages of e-banking
- e-banking provides 24 hours, 365 days a year services to the customers of the bank.
- It lowers the transaction cost.
- It inculcates a sense of financial discipline and promotes transparency.
- It reduces the load on bank branches.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a note on various telecom services available for enhancing business.
Answer:
There are various type of telecom services which facilitate business. These include
(i) Cellular Mobile Services
These include all types of mobile telecom services including voice and non-voice messages, data services and PCO services utilizing any type of network equipment within their service area.
(ii) Radio Paging Services
Radio Paging Service is a means of transmitting information to persons even when they have mobile. It is an affordable one way information broadcasting solution which includes tone only, numeric only and alpha/numeric paging.
(iii) Fixed Line Services
These include all types of fixed services including voice and non-voice messages and data services used to establish linkages for long distance traffic utilizing any type of network equipment connected through fiber optic cables.
(iv) Cable Services
These include linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation to operate media services which are essentially one way entertainment related services.
(v) VSAT Services
VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminal) is a satellite-based communications service which is highly flexible, uninterrupted and reliable communication solution for applications such as newspapers-on-line and tele-education in both urban and rural areas.
(vi) DTH Services
DTH (Direct to Home) is a satellite based media service provided by cellular companies. One can receive media services directly through a satellite with the help of a small dish antenna and a set top box.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain briefly the principles of insurance with suitable examples.
Answer:
The specific principles of a valid insurance contract consist of the following:
(i) Utmost Good Faith
A contract of insurance is a contract of uberrimae fidei i.e., a contract found on utmost good faith. It is the duty of the insured to voluntarily make full, accurate disclosure of all facts, material to the risk being proposed and the insurer to make clear all the terms and conditions in the insurance contract, e.g., if any person has taken a life insurance , policy by hiding the fact that he is a cancer patient and later on if he dies because of cancer then insurance company can refuse to pay the compensation as the fact was hidden by the insured.
(ii) Insurable Interest
The insured must have an insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance. Insurable interest means some pecuniary interest in the subject matter of the insurance contract. The insured must have an interest in the preservation of the thing or life insured, e.g.,. If a person has taken the loan against the security of a factory premises then the lender can take fire insurance policy of that factory without being the owner of the factory because he has financial interest in the factory premises.
(iii) Indemnity
According to it, the insurer undertakes to put the insured in the same position that he occupied immediately before the loss due to happening of the event insured against. The principle of indemnity is not applicable to life insurance, e.g., A person insured a car for 2.5 lakh against damage or an accident case. Due to accident he suffered a loss of 1.5 lakh, then the insurance company will compensate him 1.5 lakh only not the policy amount i.e., 2.5 lakh as the purpose behind it is to compensate not to make profit.
(iv) Contribution
Under this principle, an insurer who has paid a claim under insurance has the right to call upon other liable insurers to contribute for the loss of payment, e.g., A person gets his house insured against fire for e.g., 1 lakh with insurer A and for 50000 with insurer B. A loss of 75000 occurred. Then A is liable to pay 50000 and B is liable to pay 25000.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain warehousing and its functions.
Answer:
Warehousing was initially viewed as a provision of static unit for keeping and storing goods in a scientific and systematic manner so as to maintain their original quality, value and usefulness but now it is viewed as a logistical service provider of the right quantity, at the right place, in the right time, in the right physical form at the right cost.
Functions of Warehousing
(i) Consolidation
The warehouse receives and consolidates materials/goods from different production plants and dispatches the same to a particular customer on a single transportation shipment.
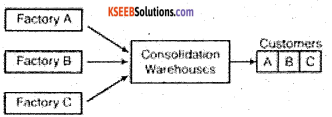
(ii) Break the Bulk
The warehouse divides the bulk quantity of goods received from the production plants into smaller quantities and then transported according to the requirements of clients to their places of business.

(iii) Stock Piling
Goods or raw materials which are not required immediately for sale or manufacturing 1 are stored in warehouses to be made available to business depending on customers demand. This type of warehouse is also known as the storehouse of surplus goods.
(iv) Value Added Services
Provision of value added services such as in transit mixing, packaging and labeling is also a function of modern warehousing.
(v) Price Stabilization
Warehousing performs the function of stabilizing prices by adjusting the supply of goods according to demand. Financing Warehouse owners provide loans to the 1 owners on security of goods and further supply goods on credit terms to customers. The warehouse keepers issue a receipt when goods are kept in warehouse. This receipt can be used as security to get loans from banks and owners. In this way it also helps i in financing.
![]()
1st PUC Business Studies Business Services Multiple Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are services? Explain their distinct characteristics?
Answer:
Services are essentially intangible activities which are separately identifiable and provide satisfaction of wants. Their purchase does not result in the ownership of anything physical. Services involve an interaction to be realized between the service provider and the consumer.
There are five distinct characteristics of services as discussed below:
(i) Intangibility
Services are intangible, i.e., they cannot be touched. They can only be experienced and hence the quality of the service cannot be determined before consumption. Therefore, the service providers consciously work on creating a desired service so that the customer has a favorable experience, e.g., service in a restaurant should be a favorable experience for customer to visit again.
(ii) Inconsistency
Services have to be performed exclusively each time according to different consumer demands as there is no standard tangible product on offer. Hence inconsistency is an important characteristic of services. Service providers need to modify their offer to closely meet the requirements of the customers, e.g., services provided by nationalized banks are quite different from the banking services provided by private banks.
(iii) Inseparability
Activities of production and consumption are performed simultaneously in. case of services which makes the production and consumption of services seem to be inseparable as services have to be consumed as and when they are produced, e.g., we cannot separate the medical services provided by a doctor.
(iv) Absence of Inventory
Services are intangible and perishable and hence cannot be stored for future use. This implies that the supply needs to be managed according to demand as the service has to be performed as and when the customer asks for it. e.g., a medicine, can be stored but the medical care will be experienced only when the doctor provides it.
(v) Involvement
Participation of the customer in the service delivery process is an important characteristic of services as the customer has the opportunity to get the services modified according to his/her specific requirements, e.g., cinema halls are providing services.to watch movie but the customer has to visit to the hall to experience the movie in cinema hall.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the functions of Commercial Banks with an example of each.
Answer:
Banks perform a variety of functions including the basic or primary functions and the agency or general utility functions as discussed below:
(i) Accepting Deposits
Banks accept deposits and pay interest on them as these deposits form the basis of loans given by banks. These deposits are generally taken through current account, savings account and fixed deposits. Current account and savings accounts deposits can be withdrawn at any time without any prior notice while fixed deposits are time deposits of fixed maturity. Higher rate of interest is paid on fixed deposits as compared to the savings accounts.
(ii) Lending of Funds
Second major function of commercial banks is to provide loans and advances to individuals and businesses out of the money received through deposits. These advances can be made in the form of overdrafts, cash credits, discounting trade bills, term loans, consumer credits and other miscellaneous advances.
(iii) Cheque Facility
Banks collect the cheques of their customers drawn on other banks. The cheque is a developed credit instrument for the withdrawal of deposits which serves as a convenient and inexpensive medium of exchange.
There are two types of cheques mainly:
- bearer cheques, which are encashable immediately at bank counters and
- crossed cheques which are to be deposited only in the payees account.
(iv) Remittance of Funds
Commercial banks provide the facility of fund transfer from one place to another, on account of the interconnectivity of branches. The transfer of funds is administered by using bank drafts, pay orders or mail transfers on which the bank charges a nominal commission. The bank issues a draft for the amount on its own branches at other – places or other banks at those places. The payee can present the draft on the drawee bank at his place and collect the amount.
(v) Allied Services
In addition to above functions, banks also provide allied services such as bill payments, locker facilities, underwriting services. Banks also perform other services like opening demat and trading accounts of customers for buying and selling of shares and debentures on instructions and other personal services like payment of insurance premium, collection of dividend etc.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a detailed note on various facilities offered by Indian Postal Department.
Answer:
Indian post and telegraph department provides various postal services across India. For providing these services the whole country has been divided into 22 postal circles. These circles manage the functioning of the various head post offices, sub-post offices and branch post offices. There are 154149 post offices and 564701 letter boxes ’processing 1575 crore mails every year.
The various facilities provided by postal department are broadly categorized into:
(i) Financial Facilities
Post Office Savings Bank is the largest retail bank having 150000 plus branches. Financial facilities are provided through the post office’s savings schemes like Public Provident Fund (PPF), Kisan Vikas Patra, and National Saving Certificates apart from retail banking functions of monthly income schemes, recurring deposits, savings account, time deposits and money order facility.
(ii) Mail Facilities
Mail services consist of parcel facilities that is transmission of articles from one place to another; registration facility to provide security of the transmitted articles and insurance facility to provide insurance cover for all risks in the course of transmission by post.
(iii) Allied Facilities
- Greeting Post Indian post offers a beautiful and varied range of greeting cards for every occasion.
- Media Post Indian corporate can use media post which is an innovative and effective vehicle to advertise their brand through postcards, envelopes, aerogram, telegrams, and also through letter boxes.
- Direct Post It is for direct advertising which can be both addressed as well as unaddressed.
- International Money Transfer Indian post has a collaboration with Western Union financial services, USA, which enables remittance of money from 185 countries to India.
- Passport Facilities Indian post has a unique partnership with the ministry of external affairs for facilitating the process of passport application.
- Speed Post Indian post has over 1000 destinations covered under the speed post facility in India and links with 97 major countries across the globe.
- e-bill Post It is the latest offering of the Indian post and telegraph department to collect bill payment across the counter for BSNL and Bharti Airtel
![]()
Question 4.
Describe various types of insurance and examine the nature of risks protected by each type of insurance.
Answer:
Insurance may be classified as follows:
(i) Life Insurance
A life insurance policy protects against the uncertainty of life though its scope has now widened to suit the various insurance needs of an individual like disability insurance, health/medical insurance, annuity insurance and life insurance proper. Life insurance may be defined as a contract in which the insurer in consideration of a certain premium, agrees to pay to the assured, or to the person for whose benefit the policy is taken, the assured sum of money, on the happening of a specified event, contingent on the human life or at the expiry of certain period.
There are various types of life insurance policies like
- Whole Life Policy
- Endowment Life Assurance Policy
- Joint Life Policy
- Annuity Policy
- Children’s Endowment Policy
(ii) Fire Insurance.
Fire insurance is a contract whereby the insurer, in consideration of the premium paid, undertakes to make good any loss or damage caused by fire during a specified period up to the amount specified in the policy. The fire insurance policy is generally taken for a period of one year after which it is to be renewed from time to time. A claim for loss by fire is considered valid only if it satisfies the following two conditions
(a) There must be actual loss.
(b) Fire must be accidental and non-intentional-. The risk covered by a fire insurance contract is the loss resulting from fire which is the proximate cause of the loss. If damage is caused due to overheating without ignition, it is not regarded as a fire loss within the meaning of fire insurance and the loss cannot be claimed from the insurer.
(iii) Marine Insurance
A marine insurance contract is an agreement whereby the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured in the manner and to the extent thereby agreed against marine losses. Marine insurance provides protection against loss by marine perils or perils of the sea.
There are three things involved in marine insurance:
(a) Ship or Hull Insurance
Since the ship is exposed to many dangers at sea, the insurance policy is for indemnifying the insured for losses caused by damage to the ship.
(b) Cargo Insurance
An insurance policy can be issued to cover against the risks to cargo while being transported by ship. These risks may be at port i.e., risk of theft, lost goods or on voyage etc.
(c) Freight Insurance
Shipping company is insured under freight insurance for reimbursing the loss of freight to the shipping company if the cargo does not reach the destination due to damage or loss in transit.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain in detail the warehousing services.
Answer:
Warehousing was initially viewed as a provision of static unit for keeping and storing goods in a scientific and systematic manner so as to maintain their original quality, value and usefulness but now it is viewed as a logistical service that is making available the right quantity, at the right place, in the right time, in the right physical form at the right cost. The various warehousing services are as follows:
(i) Consolidation
‘The warehouse receives and consolidates materials/goods from different production plants and dispatches the same to a particular customer on a single transportation shipment’.
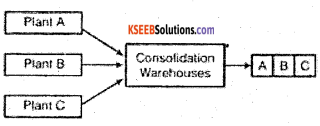
(ii) Break the Bulk
The warehouse divides the bulk quantity of goods received from the production plants into smaller quantities to be transported according to the requirements of clients to their places of business.
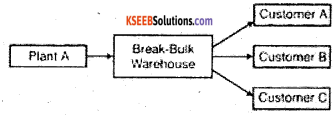
(iii) Stock Piling
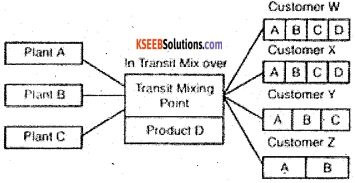
Goods or raw materials which are not required immediately for sale or manufacturing are stored in warehouses to be made available to business depending on customers demand. Agricultural products also need to be stored and released in lots as they are harvested at specific times in a year but are needed for consumption throughout the year.
(iv) Value Added Services Provision of value added services such as in transit mixing, packaging and labeling is also a function of modern warehousing. Goods sometimes need to be opened and repackaged and labeled again at the time of inspection by prospective buyers. Another function of modern warehouses is to grade goods according to quantity and divide goods in smaller lots.
(iv) Price Stabilization
Warehousing performs the function of stabilizing prices by adjusting the supply of goods according to demand. Thus, prices are controlled from falling when supply is increasing and demand is slack and from rising in the reverse situation. Financing Warehouse owners provide loans to the owners on security of goods and further supply goods on credit terms to customers.
1st PUC Business Studies Business Services Multiple Additional Questions And Answers
1st PUC Business Studies Business Services Multiple Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Legal staff, computer operators and accountants are examples of services of
A. government sector
B. private non-profit sector
C. manufacturing sector
D. business sector
Answer:
D. business sector
Question 2.
Hospitals, loan agencies, postal services and schools are examples of services of
A. government sector
B. private non-profit sector
C. manufacturing sector
D. business sector
Answer:
B. private non-profit sector
Question 3.
Act of specific performance offered by one party to another and tangible in nature is classified as
A. service Byproduct
B. product
C. co-branding
D. None of above
Answer:
B. product
Question 4.
Churches, museums and charities are examples of services of
A. government sector
B. private non-profit sector
C. manufacturing sector
D. business sector
Answer:
A. government sector
![]()
Question 5.
Banks, hotels, airlines, law firms and insurance companies are example of services of
A. government sector
B. private non-profit sector
C. manufacturing sector
D. business sector
Answer:
A. government sector
Question 6.
Category of products that come with warranty offered at time of product buying and expires at some specific date is an example of
A. augmented product
B. actual product
C. actual ownership
D. tangible products
Answer:
C. actual ownership
Question 7.
Product support services are part of
A. actual product
B. augmented product
C. differentiation
D. competitive strategy
Answer:
A. actual product
Question 8.
Products that customers buy after careful comparison on price and quality are called
A. specialty products
B. less specialty products
C. shopping products
D. unsought products
Answer:
A. specialty products
Question 9.
Buying of products such as ‘laundry detergents’ is an example of
A. shopping services
B. less sought services
C. convenient products
D. specialty products
Answer:
B. less sought services
![]()
Question 10.
Industry installations and equipment are classified in group of
A. capital items
B. specialty industrial products
C. supplies and services
D. augmented industrial products
Answer:
D. augmented industrial products
1st PUC Business Studies Business Services Multiple Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give two examples of e-banking.
Answer:
The two examples of e-banking are:
- ATMs
- Debit Cards.
Question 2.
What is bank overdraft?
Answer:
An overdraft is a financial arrangement, under which a current account holders in permitted by the bank to overdraw his account, i.e., to draw more than the amount standing to his credit, up to and agreed limit.
![]()
Question 3.
What is cash credit?
Answer:
A cash credit is financial arrangement under which a borrower is allowed and advanced under a separate account call cash credit account.
Question 4.
Define banking.
Answer:
According to this definition, baking means the acceptance of deposits from the public, allowing of withdrawals of such deposits by cheques, drafts, and orders or otherwise, and utilisation of deposits in hand, for the purpose of lending on investment, and also performance of a number of the other activates called subsidiary services.
Question 5.
Define the term ’bank’.
Answer:
It is very difficult to define the term ‘Bank’ precisely on account of the numerous activities performed by a bank. Yet several authorities have defined this term.
Question 6.
Name the largest commercial bank of India.
Answer:
State Bank of India.
Question 7.
Name the central bank of our country.
Answer:
Reserve Bank of India, which is the central bank of our country.
![]()
Question 8.
Name the type of insurance where in insurable interest need not exist when the policy is taken.
Answer:
Marine Insurance.
Question 9.
In which type of insurance insurable interest must exist only at the time of insurance?
Answer:
Life Insurance.
Question 10.
In which type of insurance insurable interest much exist both at the time of insurance and at the time of loss?
Answer:
Fire Insurance.
Question 11.
Give the full form of DTH.
Answer:
Direct to Home services.
Question 12.
Defines services.
Answer:
According to J. Lethinen defined services as “an activity or series of activities which take place in interactions with a contact person or a physical machine and which provides consumer satisfaction”.
![]()
Question 13.
What is ATM?
Answer:
An automated teller machine or automatic teller machine, popularly called the cash machine or any time money, is an electronic machine installed by a commercial bank and operated by the customer himself, to withdraw money and to make other financial transactions.
Question 14.
Name four types of banks.
Answer:
The four types of banks are:
- Commercial Banks
- Agricultural Banks
- Exchange Banks
- Industrial Banks
Question 15.
What is health insurance?
Answer:
Health insurance is a type of insurance which provides insurance cover for financial loss associated with illness and injuries.
Question 16.
Differentiate between insurance and assurance.
Answer:
The one difference between insurance and assurance.
- Insurance: Insurance is a contract between insurer and insured.
- Assurance: Assurance is a contract between assurer and insured.
![]()
Question 17.
Define the term bank.
Answer:
It is very difficult to define the term ‘Bank’ precisely on account of the numerous activities performed by a bank. Yet several authorities have defined this term.
Question 18.
Name the various types of banks.
Answer:
Banks are classified into six categories. They are:
- Commercial Banks or Deposit Banks
- Industrial Banks or investment Banks
- Agricultural Banks
- Exchange Banks.
- Saving Banks
- Central Bank
Question 19.
What is central bank?
Answer:
A central bank is the highest baking and monetary institution of a country. In other words, it is the leader of all other banking and monetary institutions found in a country. As it occupies a central position in the banking structure of a county, it is called the Central Bank.
Question 20.
What do you understand by discounting of bills?
Answer:
Discounting bill is a financial accommodation, in which bank purchase the bill of exchange that matured in short period from .a known customer and pays him or credits his account with the amount equal to the value of bill minus the discount for unexpired period for bill.
![]()
Question 21.
State any two agency functions of a commercial bank.
Answer:
The important agency services rendered by a baker are as follows:
- Banks collect money on behalf of customers understanding instructions.
- Banks make payments on behalf of customers.
Question 22.
State any two general utility services of a bank.
Answer:
The two general utility services of a bank are:
- Banks accept valuables and documents for safe custody.
- Banks dear as referees.
Question 23.
Give any three secondary factions of commercial banks.
Answer:
The three secondary factions of commercial banks are:
- Banks collect money on behalf of customers understanding instructions.
- Banks make payments on behalf of customers.
- Banks accept valuables and documents for safe custody.
Question 24.
Define insurance.
Answer:
In the words of Thomson, “Insurance is a provision which a prudent man makes against fortuitous or inevitable contingencies, loss or misfortunes. It is a form of spreading risks”.
![]()
Question 25.
What is insurable interest?
Answer:
The insured is said to have an insurable interest in the subject-matter of insurance, if he likely to gain by its existence or safety, and lose by its destruction.
Question 26.
What is subrogation?
Answer:
The principle of subrogation is an extension of the principle of indemnity. This principle appliers to all contracts insurance other than life insurance and personal accident insurance.
Question 27.
Define causa proxima.
Answer:
Causa Proxima or proximate cause has been defined as “the actual efficient cause that sets in motion a train of events which brings about a result, without the intervention of any force started and working actively from a new and independent source”.
Question 28.
Define the principle of utmost good faith.
Answer:
According to the principle of utmost good faith, the assured is bound to observe complete good faith and disclose all the material facts know to him, relating to his like. If the assured fails to disclose any material facts known to him, the contract can be avoided by the assurer.
![]()
Question 29.
What is double insurance?
Answer:
When the same subject-matter is insured with two or more insurers to cover the same risk, it is called “Double Insurance”.
Question 30.
What is surrender value?
Answer:
The money paid by the insurer to the insured, when the insured surrenders his policy, is called Surrender Value of the policy.
Question 31.
What is re-insurance?
Answer:
The insurer with whom the risk is re-insured is called the re-insurer. It should be noted that the contract of re-insurance is between two insurers only.
Question 32.
Distinguish between double insurance and re-insurance.
Answer:
Differences between Double insurance and Re-insurance:
| Double insurance | Re-insurance |
| 1. Double insurance represents two or more insurance contracts between the insured and tow or more insurers. | 1. Re-insurance is a contract between the original insurer and the re-insurer. |
| 2. In the case of double insurance, there is no re-distribution of risk by the insurer. | 2. In the case or re-insurance, there is re-distribution of risk by the original insurer. |
![]()
Question 33.
Distinguish between whole life policy and endowment life policy.
Answer:
Differences whole life policy and endowment life policy:
| Whole life policy | Endowment life policy |
| 1. In the case of an endowment policy, the period of the policy is definite or fixed. | 1. In the case of a whole-life policy, the period of the policy is indefinite. |
| 2. The rate of premium for an endowment policy is more | 2. The rate of premium for a whole-life policy is less. |
![]()
Question 34.
What is average policy in fire insurance?
Answer:
This is a policy under which the average clause is included. Under this policy, the insurer is required to bear only a ratable proportion of the actual loss to the property.
Question 35.
What are mail services?
Answer:
Mail services refer to the services rendered by post offices for written communication.
Question 36.
What types of financial services are offered by postal department?
Answer:
The many types financial services are offered by postal department are:
- Monthly income scheme
- Recurring deposit account
- Time deposit, etc.
Question 37.
What is DTII service?
Answer:
Cellular companies offer their satellite-based media service. A small dish -antenna and a set top box are needed to receive the service through multiple channels. The service can be viewed on television. It avoids dependence on the services offered by the cable network service provider.
![]()
Question 38.
What do you mean by VS AT service?
Answer:
Very small aperture terminal service is satellites based communication service used’ to provide innovation applications, such as tele-medicine, newspapers on line, market rates and tele-eduction. This is an uninterrupted service and is better than land based services.
Question 39.
What is credit card?
Answer:
A credit card is an instrument which provides instantaneous facilities to its holder to purchase goods or services for business establishments enrolled as members of the credit card system.
Question 40.
What is debit card?
Answer:
A debit card is also a payment card. It is used to obtain cash, goods or services automatically, debiting the payments to the card holder’s bank account instantly upto the credit balance which exists in the customer’s bank account.
![]()
1st PUC Business Studies Business Services Multiple Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between goods and services.
Answer:
Difference between Goods and Services:
- Goods are objects or things, whereas services are efforts, activities or performances.
- Goods can be transferred from one place to another, whereas services cannot be transferred from the point of sale to the point of use.
- Goods can be stored for later sale or use, whereas services cannot be stored for later sale or use.
- Goods can be standardized. But services can hardly be standardized.
- In case of goods, the customers can evaluate their quality in advance. On the other hand, in the case of services, customers cannot evaluate their quality in advance.
Question 2.
Distinguish between current account and savings bank account.
Answer:
Differences between current accounts and savings bank accounts:
| Current Accounts | Savings Bank Accounts |
| 1. The minimum deposit required for opening current accounts is more. | 1. The minimum deposit required for opening savings bank accounts is less. |
| 2. In the case of current accounts, there are no restrictions on withdrawals. | 2. In the case of savings bank accounts, there are restrictions on withdrawals. |
| 3. Current account holders can get overdraft facilities. | 3. Savings bank account holders cannot get overdraft facilities. |
| 4. Generally, no interest is allowed on current deposits. | 4. Fair interest is allowed on savings bank deposits. |
| 5. Current accounts are operated only by cheques. | 5. Savings bank accounts can be operated either by cheques or by special withdrawal forms accompanied db by pass books. |
![]()
Question 3.
Explain in features of business services.
Answer:
The features of business services are:
- Business services refer to services used by business enterprises.
- Business enterprises for carrying on their activities.
- Examples of business services are banking, insurance, transportation, warehousing, communication, and advertising. Etc.
- Business services cannot obtain their ownership, as there is no transfer of ownership.
- Business services are very helpful to peoples.
Question 4.
Distinguish between life insurance and general insurance.
Answer:
Differences between life insurance and general insurance
| Life Insurance | General Insurance |
| 1. A general insurance policy cannot be surrendered by the inured. | 1. A life insurance policy can be surrendered by the insured. |
| 2. Double insurance is not common in general insurance. | 2. Double insurance is common in life insurance. |
| 3. General insurance is only a protection against actual loss. | 3. Life insurance is combination of both protection against risk and a provision for savings or investment. |
| 4. In general insurance, there may or may not be a claim. | 4. In life insurance, there will be a claim always. |
| 5. There is the possibility of over-insurance or under-insurance in general insurance. | 5. There is no question of over or under insurance in life insurance. |
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the different types of telecom services.
Answer:
There are many types of telecom services. They are:
1. Fixed line services: Fixed line services include use of fixed services to establish linkage for long distance traffic., Under this type, voice and non-voice messages and data are exchanged. Network equipment connected through fiber optical cables are used for this purpose.
2. Radio paging services: Radio paging service is one-way information services to transmit information to persons who are mobile.
3. Cable services: Cable service’s are linkages and switched services available within a licensed area of operation. Cable series are essentially entertainment services.
4. Cellular Mobile services: Cellular mobile services include all types of mobile telecom series for voice and nonvoice massages, data and PCO.
5. Direct to Home (DTH) Service: Cellular companies offer their satellite-based media service. A small dish -antenna and a set top box are needed to receive the service through multiple channels. The service can be viewed on television. It avoids dependence on the services offered by the cable network service provider.
6. VSAT Services: Very small aperture terminal service is satellites based communication service used to provide innovation applications, such as telemedicine, newspapers on line, market rates and tele-eduction. This is an uninterrupted service and is better than land based services.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the functions of commercial banks.
Answer:
The functions of banks can be classified into two categories. They are:
- Principal of primary functions.
- Subsidiary or secondary functions.
Primary Functions:
The primary functions of banks are:
- Receiving of deposits.
- Lending of funds.
1. Receiving of Deposits:
The main types of deposits received by them are:
- Current deposits.
- Savings bank deposits.
- Fixed deposits or term deposits.
- Recurring deposits or cumulative deposits.
2. Lending of funds:
Lending of funds constitutes the main business of commercial banks. Banks lend funds to the public by way of:
- Loans
- Overdrafts
- Cash credits
- Discounting of Bills
Subsidiary or Secondary functions: Apart from the main functions of accepting deposits and granting advances, a banker also performs a number of other functions. Such services are called the subsidiary functions or secondary, supplementary or ancillary services.
The Subsidiary services of a banker may be classified into two classes, viz.
- Agency services
- Miscellaneous or general utility services.
Question 7.
Explain the concept and terms of e-banking.
Answer:
The concept and terms of e-banking are:
- Provision of round -the clock access to banking facilities is an essential feature of e-banking.
- E-banking is conduct of banking operation globally. In other words, e-banking is anywhere banking.
- E-banking is essentially performance of banking operations through electronic means or tools.
- E-banking ensures large number of satisfied customers for a bank, and thereby, contributes to higher rate of retention of existing customers for a bank.
- E-banking is provision of banking products and services by banks through the extensive use of information technology without direct recourse to the bank by customers.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the function of insurance.
Answer:
Functions of Insurance:
a. Diffusion of risk: Insurance may not be able to avoid uncertainties associated with life in general and business in particular.
b. Encouragement of savings: Insurance not only provides protection against risks but also a number of other incentives which encourage people to insure.
c. Prevention of losses: Insurance companies’ help in prevention of losses, as they join hands with those institutions with are engaged in loss-prevention measures.
d. Taking care of social problems: One of the important functions of insurance is to provide solution to social problems.
e. Providing capital or funds for investment: Insurance provides not only protection but also capital to the society. Usually, accumulated funds through savings in the form of insurance premium are invested in economic development plans or productivity projects.
f. Providing protection: The main function of insurcen isto provides protection against the risk of loss. The insurance policy covers the risk of loss.
g. Promotion efficiency and motivation: Insurance has contributed a greatly in the advancement of industry and trade. The large-scale industrial and commercial orgaisations that exist today are the result of various services provided by insurance companies.
![]()
Question 9.
Explain the importance of insurance.
Answer:
The importance of insurance are:
- It is a contract for compensation losses.
- Payment is made to the insured, as per the terms of the agreement, in the event of loss.
- It is contract of utmost good faith.
- The occurrence of the loss is accidental.
- It helps in shifting and sharing risk.
Question 10.
Explain the various types of life insurance policies.
Answer:
The most important types of Insurance:
1. Life Insurance: Insurance is a provision which a prudent man makes against fortuitous or inevitable contingencies, loss or misfortunes. It is a form of spreading risks
Types of life insurance policies:
- Whole life policy or ordinary life policy
- Endowment policy
2. Fire insurance: Fire insurance is a contact under which the insurer undertakes to indemnify or compensate the insured for actual loss caused to him by the destruction or damage of the insured property by fire in return for a consideration called the premium.
3. Marine insurance: Marine insurance is a contract between two parties under which one party agrees to compensate the other party against the loss arising from certain Marin risks in consideration of a certain payment.
4. Health insurance: Health insurance is a type of insurance which provides insurance cover for financial loss associated with illness and injuries.
![]()
Question 11.
Explain the various types of fire insurance policies.
Answer:
Kinds of fire insurance policies:
- Valued policy: This is a policy in which the value of the property insured is agreed upon at the time of taking out the policy.
- Average policy: This is a policy under which the average clause in included. Under this policy, the insurer is required to bear only a ratable proportion of the actual loss to the property.
- Specific policy: This is a policy under which a specific amount is insured on a specified property.
- Floating policy: This is a type of policy under which properties found id different localities are covered by one policy.
- Comprehensive policy: Comprehensive policy is a type of fire policy issued to cover such risks as fire, explosion, lighting, thunder, civil commotion.
- Blanket Policy: Blanket policy is a type of the insurance policy issued to cover all assets, fixed as well as current assets, of the insured under one insurance policy.
- Consequential policy: Consequential loss policy is a type of fire insurance policy issued to indemnify the insured against the loss of profit caused by any interruption o business by fire.
- Reinstatement or replacement policy: This is a policy under which the Reinstatement or replacement Clause is inserted.
![]()
Question 12.
Explain the various types of marine insurance policies.
Answer:
Kinds of Marine Policies:
- Valued policy: This is a policy in which the agreed value of the subject -matter of insurance is stated at the time of taking out of the policy.
- Unvalued Policy or Open Policy: This is a policy in which the agreed value of the subject -matter of insurance is not stated at the time of taking out the policy.
- Time Policy: This is policy in which the subject -matter is insured for definite period of time, generally, not exceeding one year.
- Voyage Policy: This is policy in which the subject -matter is insured for a specific voyage from one point to another, e.g., fire Chennai to London.
- Wager Policy or Honour Policy: This is a policy under which insurance is affected without the insured having any insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance.
- Floating Policy or Open Cover: This is a policy in which no mention is made of the ship or the cargo, but only the round sum insured is mentioned at the time of taking out the policy.
- Mixed Policy: This is a policy in which the subject -matter is insured for specific voyage and for definite period of time.
![]()
Question 13.
Explain the various mail services and financial services provided by post offices.
Answer:
Post offices render two types of services. They are:
I. Mail services: mail services refer to the services rendered by post offices for written communication.
Types of Mail Services:
- Register post: In this case, when a letter is posted, the post office issues a receipt to the sender of the letter.
- Express parcel post or service: Express parcel post is postal service which seeks to provide a reliable and time-bound parcel service through surface transport.
- Speed post: Speed post service is a postal service under which letters, documents and parcels are delivered to the addresses within a given time frame.
- E-post: E-post is a postal service which enables people to send and receive messages or scanned image through e-mail from post offices in the country.
- Instant money order (IMO): instant money order is an online domestic money . transmission service intended for a market clientele requiring money remittance.
- E-money order (EMO): Electronic money order or e-money order is a system that a facilitates remittance of money order electronically.
II. Financial services or facilities: Post office provides various types of financial services. They are:
- Monthly income scheme: Monthly income scheme is a financial service provided by the post office.
- Recurring deposit account: This account can be opened by an individual, jointly by two adults and by a guardian on behalf of minor r minor of the age of 10 year or more.
- Time deposit: A time deposit account can be opened by an individual. It can also be opened by two adults jointly. It can be even opened by minor of 10 years or above or by guardian on behalf of the minor.
- Post office savings bank account: Savings bank account in a post office is a popular post savings account Any individual can open a savings bank account in a post office. Cheque facility is available on savings bank account.
- Senior citizens savings scheme, 2004: The tenure of this scheme is 5 years, which can be extended by 3 years. The investment under this scheme is not transferable to others.
- NSNCS: NSCs are certificates issued by the Government of India and are available at all post offices. The duration of NSN is 5 years and 10 years.
- Public provident funds: Public provident funds are operated by SBI, scheduled banks and also by post offices.
![]()
Question 14.
Explain the different components of e-banking.
Answer:
There are different components of e-banking:
1. Mobile Banking: Mobile banking refers to conduct of banking operations on mobile phones. In other words, mobile banking means banking operations that are done through mobile phone while a person is on the move. Service is available only to an existing customer of the bank availing internet banking services. Mobile banking is available for the individual customers.
2. Telephone Banking or Phone Banking: Telephone banking refers to the delivery of banking and financial services to the customer of a bank through the medium of telephone. In other words, telephone banking is a form of e-banking under which a customer can obtain the necessary information of dialing a telephone number specified in advance. Telephone banking is a secure, fast and convenient way to obtain a range of banking services.
3. Internet Banking: Internet Banking refers to provision of banking services by banking to its customers through its website. Internet baking enables the customers to have every banking activity which a customer could do over a bank counter with comforts from his office or home. Internet banking helps the banks to raise huge deposits from the NRIS.
4. Home Banking: Use of personal computers at home for conducting their banking operations with their banks is called home banking. Use of personal computer at home or in office by customer for handling his bank account is one of the main features of home banking.
5. Debit Cards: A debit card is also a payment card. It is used to obtain cash, goods or services automatically, debiting the payments to the card holder’s bank account instantly upto the credit balance which exists in the customer’s bank account. There is no need to carry cash, its use is less complicated than using a cheque.
6. Credit Cards: A credit card is an instrument which provides instantaneous facilities to its holder to purchase goods or services for business establishments enrolled as members of the credit card system.
7. ATMs: An automated teller machine or automatic teller machine, popularly called the cash machine or any time money, is an electronic machine installed by a commercial bank and operated by the customer himself, to withdraw money and to make other financial transactions. ATMs can be installed at any place, at the bank premises or at important places like railway station, bus station, shopping centers, etc.
8. EFT: The electronic funds transfer scheme is scheme of the Reserve Bank of India. Electronic funds transfer is a system by which cheqes, pay-in-slips and other financial papers are replaced by computer controlled invisible and immediate transfer of funds from one account to another.
9. Core .Banking: Core banking or centralized banking is the process which is completed in centralized environment. That is, under this process, the information relating to customers account is stored in the Central Server of the Bank that is available to all the net- worked branches of the bank.
![]()