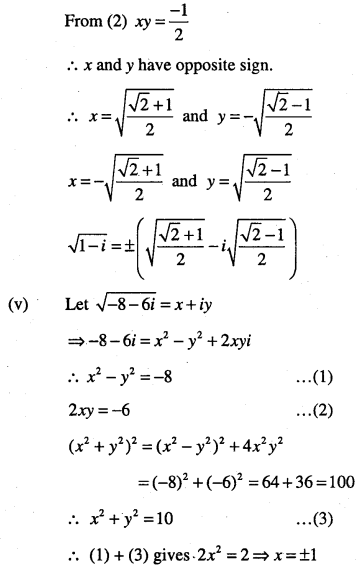Students can Download Maths Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, 1st PUC Maths Question Bank with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Maths Question Bank Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Question 1.
Define a complex number.
Answer :
A number of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers, is defined to be a complex number, where i2 = -1.
Here ‘a’ is called the real part, denoted by Re (z) and ‘b’ is called the imaginary part, denoted by Im (z), of the complex number z = a + ib.
Question 2.
When you say that two complex numbers are equal?
Answer :
Two complex numbers z1 = a + ib and z2 = c + id are equal if a = c and b – d.
Question 3.
Define purely real and purely imaginary numbers.
Answer :
A complex number z is said to be:
- Purely real, if Im(z) = 0,
- Purely imaginary, if Re(z) = 0
![]()
Question 4.
If 4x + i(3x – y) = 3 +i (-6), where x and y are real numbers, then find the values of
x and y.
Answer :
Given 4x + i(3x – y) = 3 + i(-6), Equating the real and the imaginary parts,we get
4x = 3 and 3x – y = -6
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{3}{4} \text { and } y=3\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)+6=\frac{33}{4}\)
Question 5.
Define addition of two complex numbers.
Answer :
Let z1=a + ib and z2=c + id be any two complex numbers. Then addition of z1 and z2 defined as z1 + z2 = (a + c) + i(b + d) which is again a complex number.
Properties of addition of complex numbers:
(i) Closure property: The sum of two complex numbers is always a complex number, i.e., addition is closed in C set of complex numbers.
(ii) Commutative property: For any two complex numbers z1 and z2
we have z1 + z2 = z2 + z1
(iii) Associative properly: For any complex numbers z1,z2 and Z3, we have
\( z_{1}+\left(z_{2}+z_{3}\right)=\left(z_{1}+z_{2}\right)+z_{3}\)
(iv) Existence of additive identity: For any complex number z, we have z + 0 = 0 +-z = z
Thus, 0 is the additive identity for complex numbers.
(v) Existence of additive inverse: Every complex number z-a + ib has -z = (-a) + i(-b) as its additive inverse, as z + (-z) = (-z) + z = 0.
Question 6.
Define difference of two complex numbers.
Answer :
Let z1 and z2 be any two complex numbers. The different z1 – z2 is defined as follows:
z1 – z2 =z1 +(-z2)
Question 7.
Define multiplication numbers.
Answer :
Let z1=a + ib and z2 = c + id be any two complex numbers. Then, the product z1z2 is defined as follows:
z1z2 = (ac – bd) + i(ad + bc)
Properties of product of complex numbers:
- Closure property: The product of two complex numbers is always a complex number.
- Commutative law: For any two complex numbers z1 and z2 we have z1 z2 = z2z1
- Associative law: For any three complex numbers z1 z2 and z3 we have (z1z2)z3=z1(z2z3).
- Existence of multiplicative identity: For every complex number z, we have z . 1 = 1. z = z. Thus, 1 is the multiplicative identity.
- Existence of multiplicative inverse: Let z = a + ib. Then
\(z^{-1}=\frac{1}{z}=\frac{1}{a+i b}=\frac{1}{a+i b} \cdot \frac{a-i b}{a-i b}=\frac{a-i b}{a^{2}+b^{2}} \)
Clearly
\(z \cdot \frac{1}{z}=\frac{1}{z} \cdot z=1\)
Thus, every z = a + ib has its multiplicative inverse, given
\( z^{-1}=\frac{1}{z}=\frac{a}{a^{2}+b^{2}}-\frac{a}{a^{2}+b^{2}} i \quad(z \neq 0)\)
Question 8.
Define division of two complex numbers.
Answer :
Let z1 and z2 be two complex numbers and z2 ≠0.Then \( \frac{z_{1}}{z_{2}} \) is defined by \( \frac{z_{1}}{z_{2}}=z_{1}\left(\frac{1}{z_{2}}\right) \)

Question 9.
Prove the following
(i) \(\left(z_{1}+z_{2}\right)^{2}=z_{1}^{2}+2 z_{1} z_{2}+z_{2}^{2}\)
(ii) \(\left(z_{1}-z_{2}\right)^{2}=z_{1}^{2}-2 z_{1} z_{2}+z_{2}^{2}\)
(iii) \(\left(z_{1}+z_{2}\right)^{3}=z_{1}^{3}+3 z_{1}^{2} z_{2}+3 z_{1} z_{2}^{2}+z_{2}^{3}\)
(iv) \(\left(z_{1}-z_{2}\right)^{3}=z_{1}^{3}-3 z_{1}^{2} z_{2}+3 z_{1} z_{2}^{2}-z_{2}^{3}\)
(v) \(z_{1}^{2}-z_{2}^{2}=\left(z_{1}+z_{2}\right)\left(z_{1}-z_{2}\right) \)
Answer:
(i) We have, (z1 + z2)2 = (z, + z2)(z1 + z2)
= (z1 + z2)z1 + (z1 + z2)z2 (by distributive law)
= z21 + z2z1 +z1z2 + z2 (by distributive law)
\( =z_{1}^{2}+2 z_{1} z_{2}+z_{2}^{2} \quad \ z_{1} z_{2}=z_{2} z_{1}\)
Remaining try yourself.
![]()
Question 10.
Express the following in the form of a+ib
(i) \( (-5 i)\left(\frac{1}{8} i\right)\)
(ii) \((5 i)\left(-\frac{3}{8} i\right)\)
(iii) \((2+i 3)+(-6+i 5)\)
(iv) \((6+3 i)-(2-i)\)
(v) \((2-i)-(6+3 i)\)
(vi) \((3+5 i)(2+6 i)\)
(vii) \(3(7+7 i)+i(7+7 i)\)
(viii) \((1-i)-(-1+6 i)\)
(ix)\(\left(\frac{1}{5}+\frac{2}{5} i\right)-\left(4+\frac{5}{2} i\right)\)
(x)\(\left[\left(\frac{1}{3}+i \frac{7}{3}\right)+\left(4+i \frac{1}{3}\right)\right]-\left(-\frac{4}{3}+i\right) \)
(xi) \(i^{9}+i^{19}\)
(xii)\( i^{-39}\)
(xiii)\((-i)(2 i)\left(-\frac{1}{8} i\right)^{3}\)
(xiv) \((5-3 i)^{3}\)
(xv) \(\left(\frac{1}{3}+3 i\right)^{3}\)
(xvi) \(\left(-2-\frac{1}{3} i\right)^{3}\)
(xvii) \((\mathbf{1}-i)^{4}\)
(xviii) \(\frac{5+\sqrt{2} i}{1-\sqrt{2 i}}\)
(xix) \( \frac{(3+i \sqrt{5})(3-i \sqrt{5})}{(\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{2} i)-(\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2} i)}\)
Answer:
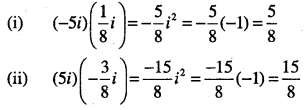

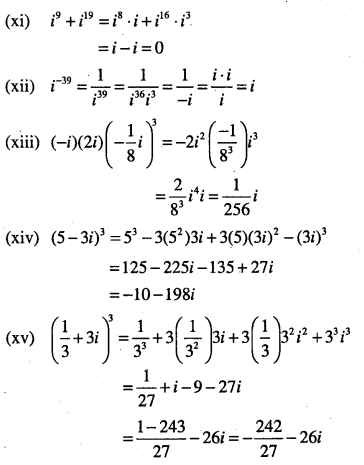
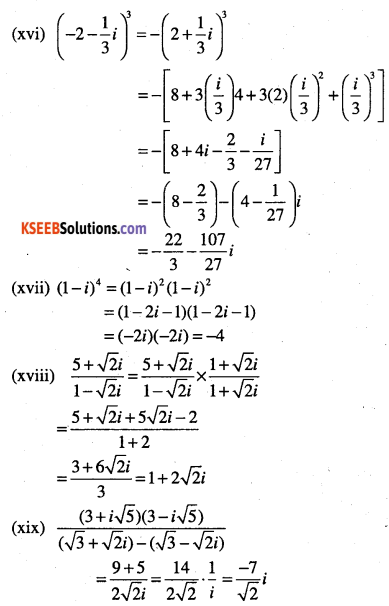
Question 11.
Define modulus of a complex number.
Answer :
Let. z = a + ib be a complex number. Then, the modulus of z, denoted by |z| to be the non-negative real number \(\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}\)
Question 12.
Define conjugate of a complex number.
Answer :
Let z = a + ib be a complex number. Then, the conjugate of complex number z, denoted \(\bar{z} \) as , is the complex number a – ib, i.e., i= a – ib
Question 13.
Write down the modulus of
(i) i
(ii) \( 3+\sqrt{-3}\)
(iii)\((-1-i)^{3}\)
Answer:
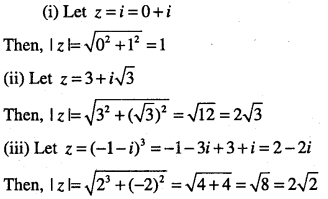
Question 14.
Write down the conjugate of
(i) \((2+\sqrt{-2})\)
(ii) \( i^{3}\)
(iii) \((3-4 i)^{2} \)
Answer:

Question 15.
Find the multiplicative inverse of the following complex numbers:
(i) 2-3i
(ii) 4-3i
(iii) \(\sqrt{5}+3i\)
(iv) \(\sqrt{5}+3i \)
(v) \(-i\)
Answer:

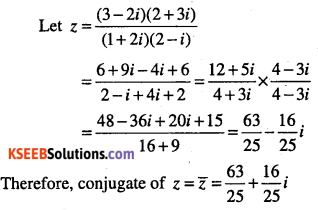
Question 16.
Find the conjugate of \(\frac{(3-2 i)(2+3 i)}{(1+2 i)(2-i)}\)
Answer:
Question 17.
Evaluate:
\( \left[i^{18}+\left(\frac{1}{i}\right)^{25}\right]^{3}\)
Answer:
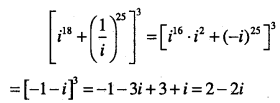
![]()
Question 18.
Reduce \( \left(\frac{1}{1-4 i}-\frac{2}{1+i}\right)\left(\frac{3-4 i}{5+i}\right)\) to the standard form.
Answer:
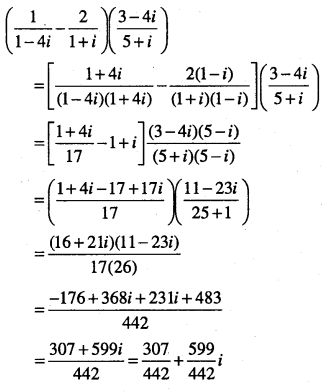
Question 19.
Find the modulus of
\(\frac{1+i}{1-i}-\frac{1-i}{1+i}\)
Answer:
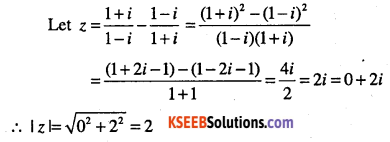
Question 20.
Find the real numbers x and y if (x – iy) (3 + 5i) is the conjugate of -6 – 24i
Answer:


Question 21.
For any two complex numbers Z1 and Z2, prove that
Re(z1z2) = Re(z2) . Re(z2) – Im(z1) . Im(z2)
Answer :
z1=a + ib and z2=c + id
z1z2 = {a + ib)(c + id) = (ac-bd) + i(ad + bc)
∴ Re(z1z2) = ac-bd
= Re(z1).Re(z2)-1m(z1)\m{z2)
![]()
Question 22.
\(\text { If } z_{1}=2-i, z_{2}=1+i, \text { find }\left|\frac{z_{1}+z_{2}+1}{z_{1}-z_{2}+1}\right| \)
Answer:
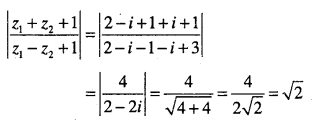
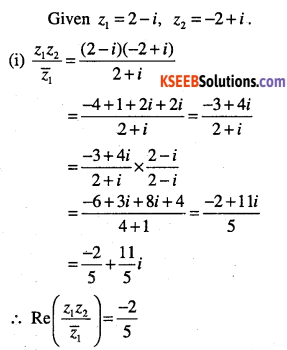
Question 23.
Let z1 = 2 – i, z2 = -2 + i .Find
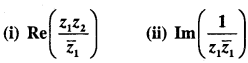
Answer:

Question 24.
If \(x+i y=\frac{a+i b}{a-i b}, \text { prove that } x^{2}+y^{2}=1\)
Answer:

Question 25.
If \(x-i y=\sqrt{\frac{a-i b}{c-i d}}\) Prove that
\(\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)^{2}=\frac{a^{2}+b^{2}}{c^{2}+d^{2}}\)
Answer:

Question 26.
If \(a+i b=\frac{(x+i)^{2}}{2 x^{2}+1}\), Prove that \(a^{2}+b^{2}=\frac{\left(x^{2}+1\right)^{2}}{\left(2 x^{2}+1\right)^{2}}\)
Answer:
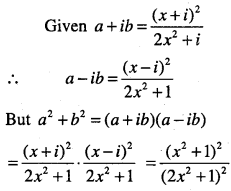
Question 27.
If (x + iy)3 =u + iv, then show that
\(\frac{u}{x}+\frac{v}{y}=4\left(x^{2}-y^{2}\right)\)
Answer:
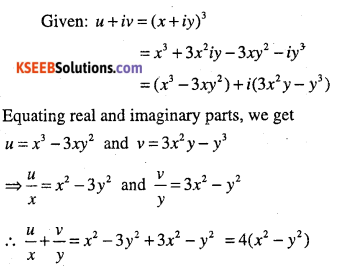
Question 28.
If (a + ib)(c + id){e + if) (g + ih) = A + iB then show that (a2+b2)(c2+d2)(e2+f2) (g2+h2) = A2+B2
Answer:
Given: A + iB = (a + ib)(c + id)(e + if)(g + ih)
∴ A-iB = (a- ib)(c – id)(e – if)(g – ih)
But A2 + B2 = (A + iB)(A – iB)
= (a2 +b2)(c2+d2)(c2+f2)(g2+h2)
![]()
Question 29.
If α and β are different complex numbers with |β|=1 then find
\(\left|\frac{\beta-\alpha}{1-\bar{\alpha} \beta}\right|\)
Answer:
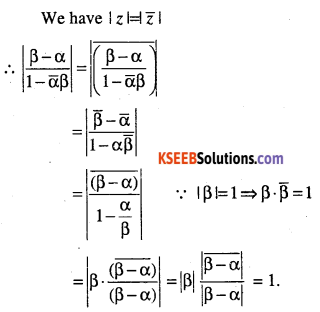
Question 30.
If \(\left(\frac{1+i}{1-i}\right)^{m}=1 \)then find the least positive integral value of m.
Answer:
![]()

Question 31.
Find the number of non-zero integral solutions of the equation \(|1-i|^{x}=2^{x}\)
Answer:

Question 32.
Find real θ such that \(\frac{3+2 i \sin \theta}{1-2 i \sin \theta}\) is purely real
Answer:

Question 33.
Define the polar form of complex number.
Answer:
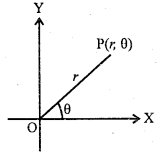
Let the complex number z = x + iy be represented by the point P(x,y) in the complex plane.
Let \(| X O P=\theta \text { and }|O P|=r>0\)
Then
P(r, θ) are called the polar coordinates of P.
where x = rcosθ
y = rsinθ
∴ z = r(cosθ+ i sin θ)
This is called the polar form or trigonometric form or modulus – amplitude form of z.
Keen Eye;
- \( r=\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}=1 z 1 \) is called the modulus of z and 0 is called the argument (or amplitude) of z, written as arg (z) or amp (z).
- The value of such that -π<θ≤n is called principal argument of z.
- To find θ
Case (i):
When z is purely real. Then, it lies on the x-axis.
(i) If x > 0, then θ=0
(ii) If x < 0, then θ = π
Case (ii):
When z is purely imaginary. Then, it lies on the y-axis
(i) \(\text { If } y>0, \text { then } \theta=\frac{\pi}{2}\)
(ii) \(\text { If } y<0, \text { then } \theta=-\frac{\pi}{2}\)
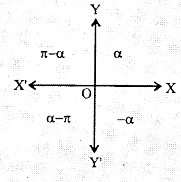
Case(iii):
Let tan α =|tan θ|
\(\text { where } 0<\alpha<\frac{\pi}{2}\)
(i) θ = α, when z lies in I quadrant
(ii) θ – π – α, when z lies in II quadrant
(iii) θ = α – π, when z lies in III quadrant
(iv) θ = -α, when z lies in IV quadrant
Question 34.
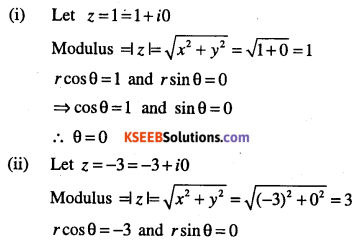
Find the modulus and the arguments of the following:
(i) 1
(ii) -3
(iii) i
(iv) -8i
(v) 1+i
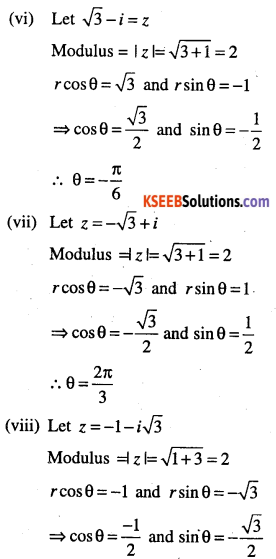
(vi) \(\sqrt{3}-i\)
(vii)\(-\sqrt{3}+i\)
(viii)\(-1-i \sqrt{3}\)
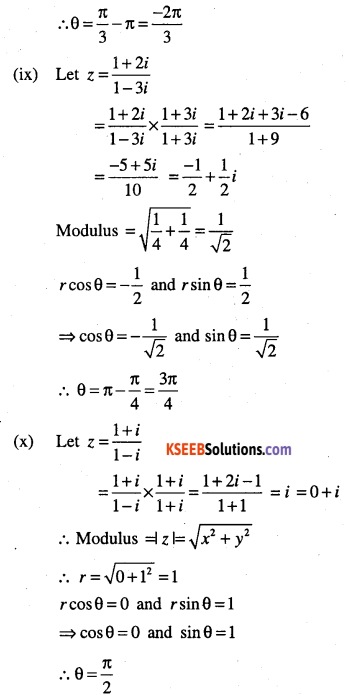
(ix)\(\frac{1+2 i}{1-3 i}\)
(x)\(\frac{1+i}{1-i}\)
(xi) \(\frac{1}{1+i}\)
Answer:

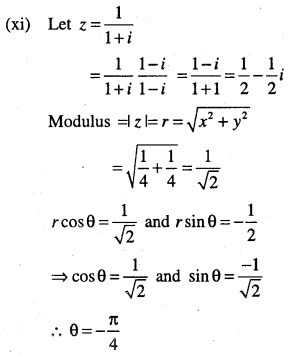
![]()
Question 35.
Convert the Following complex numbers in the polar form:
(i) 1+i
(ii) 1-i
(iii) -1+i
(iv) -1-i
(v) \(\sqrt{3}+i\)
(vi) \(\sqrt{3}-i\)
(vii) \(-\sqrt{3}-i\)
(viii) \(-\sqrt{3}+i\)
(ix) \(1+i \sqrt{3}\)
(x) \(1-i \sqrt{3}\)
(xi) \(-1+i \sqrt{3}\)
(xii) \(-1-i \sqrt{3}\)
(xiii) -3
(xiv) i
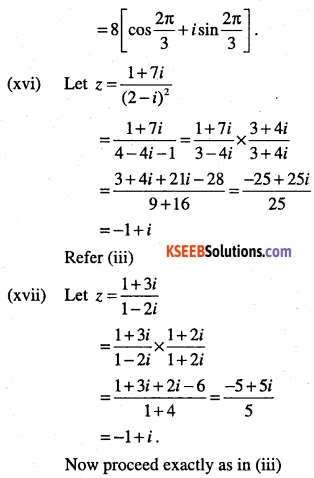
(xv) \(\frac{-16}{1+i \sqrt{3}}\)
(xvi) \(\frac{1+7 i}{(2-i)^{2}}\)
(xvii) \(\frac{1+3 i}{1-2 i}\)
(xviii)
\(\frac{i-1}{\cos \frac{\pi}{3}+i \sin \frac{\pi}{3}}\)
Answer:
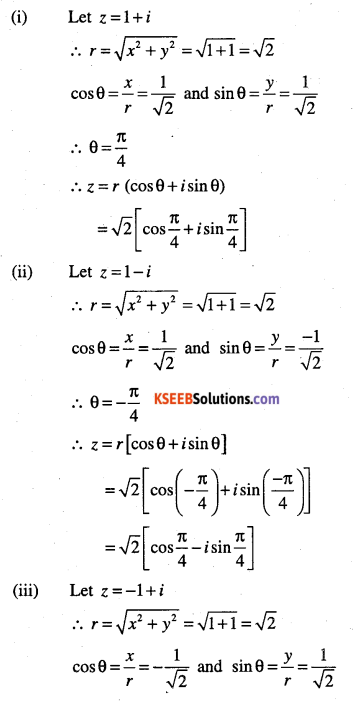

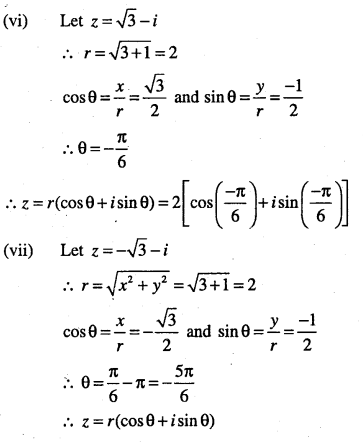

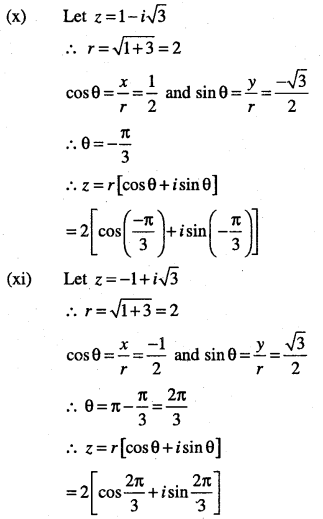
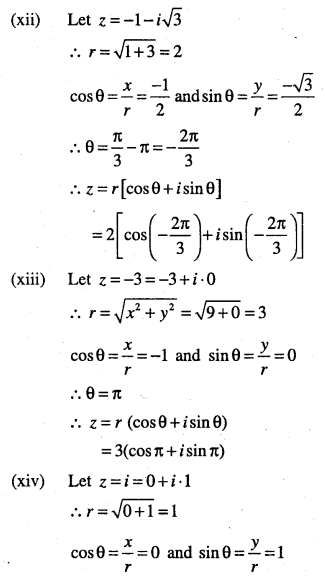

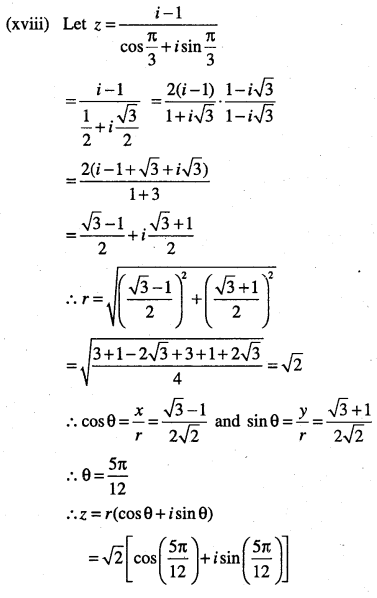
![]()
Question 36.
Keen Eye:
- A polynomial equation has at least one root.
- A polynomial equation of degree V has n roots. Solve each of the following equations:
(i) x2 + 2 = 0
(ii) x2 + 3 = 0
(iii) x2 + x +1 = 0
(iv) 2x2 + x +1 = 0
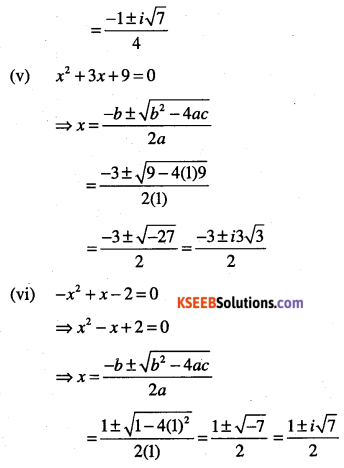
(v) x2 + 3x + 9 = 0
(vi) -x2 + x – 2 = 0
(vii) x2 + 3x + 5 = 0
(viii) x2 – x + 2 = 0
(ix)\(3 x^{2}-4 x+\frac{20}{3}=0\)
(x) \(x^{2}-2 x+\frac{3}{2}=0\)
(xi) 27x2 -10x + 1 = 0
(xii) \(\sqrt{2} x^{2}+x+\sqrt{2}=0\)
(xiii) \(\sqrt{3} x^{2}-\sqrt{2} x+3 \sqrt{3}=0\)
(xiv)\( x^{2}+x+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=0\)
(xv) \(x^{2}+\frac{x}{\sqrt{2}}+1=0\)
Answer:

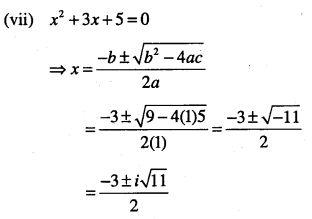
(viii) x2 -x+2=0
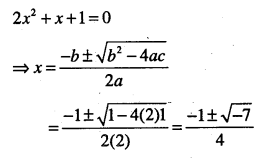
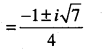

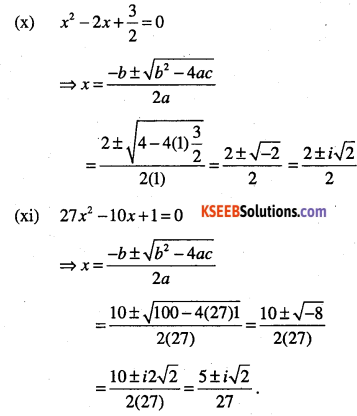
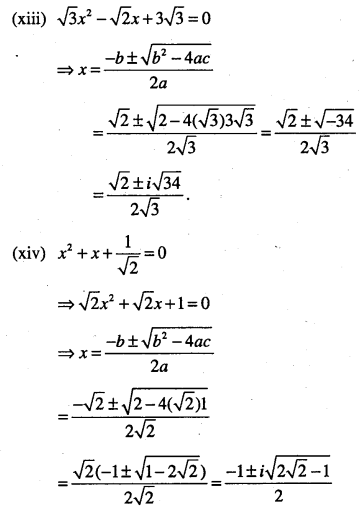
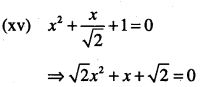
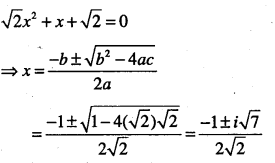
Question 37.
Find the equation roots of the following:
(i) i
(ii) i
(iii) 1+i
(iv) 1-i
(v) -8-6i
(vi)-15-8i
(vii) -7-24i
Answer:
(i)

(ii)
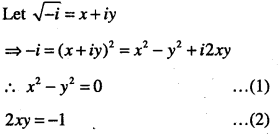

(iii)

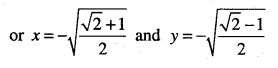
(iv)