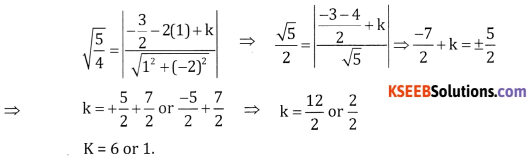Students can Download Basic Maths Exercise 15.3 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, 2nd PUC Basic Maths Question Bank with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Basic Maths Question Bank Chapter 15 Circles Ex 15.3
Part – A
2nd PUC Basic Maths Circles Ex 15.3 One Mark Questions and Answers
1. Show that the circle.
Question 1.
x2 + y2 – 8x + 2y + 16 = 0 touches x= axis.
Answer:
Given g = -4, f = 1, & C = 16

Question 2.
x2 + y2 – 4x + 4y + 4 = 0 touches x-axis.
Answer:
Here g = -2, C = 4
Here (-2)2 = 4 ⇒ g2 = C
∴ The circle touches x-axis.
Question 3.
x2 + y2 + 8x + 6y + 9 = 0 touches y = axis.
Answer:
Here f = 3 & C = 9
& f2 = C ⇒ (3)2 = 9
⇒ Circle touches y-axis.
![]()
Question 4.
x2 + y2 – x + 4y + 4 = 0 touches y-axis.
Answer:
Here f= 2 & C = 4
& f2 = C ⇒ (2)2 = 4
⇒ Circle0 touches y-axis
Question 5.
Show that the circle x2 + y2 + 4x – 3y + 4 = 0 touches x- axis.
Answer:
Here g = 2 & C = 4
g2 = C ⇒ (2)2 = 4
⇒ Circle touches x-axis.
Question 6.
Show that the circle x2 + y2 – 3x + 8y + 16 = 0 touches y – axis.
Answer:
Here f = 4, C = 16 & f2 = C
⇒ (4)2 = 16 .
∴ Circle touches y-axis.
Part – B
2nd PUC Basic Maths Circles Ex 15.3 Two Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Find the length of the chord of the circle x2 + y2 – 6x + 4y + 5 = 0 intercepted by x-axis.
Answer:
Centre of given circle = (3,-2), c = 5
Length of chord intercepted by x – axis = 2\(\sqrt{g^{2}-c}\) = 2\(\sqrt{9-5}\) = 2\(\sqrt{4}\) = 2.2 = 4 units.
Question 2.
Find the length of the chord of the circle x2 + y2 – 6x + 15y – 16 = 0 intercepted by the y-axis.
Answer:
centre = \(\left(3, \frac{-15}{2}\right)\) & C = -16
Length of the chord intercepted by y – axis = 2\(\sqrt{f^{2}-c}\) = 2\(\sqrt{\left(\frac{15}{2}\right)^{2}+16}\)
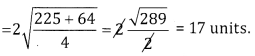
Question 3.
Find the length of the chord of the circle x2 + y2 + 3x – 2 = 0 intercepted by y-axis.
Answer:
Centre = \(\left(-\frac{3}{2}, 0\right)\) c = -2
Length of the chord by y – axis = 2\(\sqrt{f^{2}-c}\) = 2\(\sqrt{0+2}\) = 2\(\sqrt{2}\) units.
![]()
Question 4.
Find the length of the chord of the circle x2 + y2 + 3x – y – 6 = 0 intercepted by the y-axis.
Answer:
Centre = \(\left(-\frac{3}{2}, \frac{1}{2}\right)\) c = -6
Length of the chord by axis = 2 \(\sqrt{f^{2}-c}\) = 2\(\sqrt{\frac{1}{4}+6}\) = 2\(\sqrt{\frac{25}{4}}\) = 5 units
Question 5.
Find the length of the chord of the circle x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y – 12 = 0 and x + 4y – 6 = 0.
Answer:
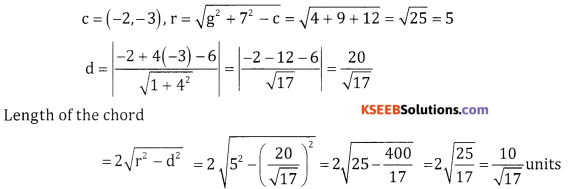
Question 6.
Find the length of the chord intercepted by the circle x2 + y2 – 8x – 6y – 6 = 0 and the line x – 7 y – 8 = 0.
Answer:
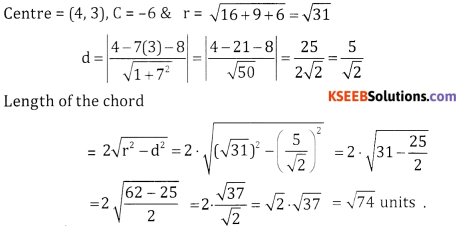
Question 7.
Find the length of the chord intercepted by the circle x2 + y2 – 6x – 2y + 5 = 0 and the line x – y + 1 = 0.
Answer:
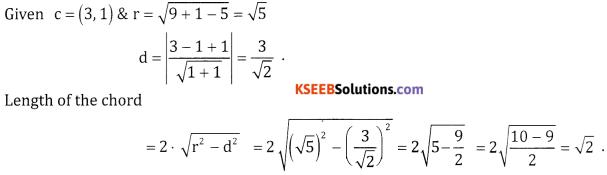
Question 8.
Prove that the length of the chord x + 2y = 5 of the circle x2 + y2 = 9 is 4 units.
Answer:
Length of the chord intercepted by x – axis = 2\(\sqrt{g^{2}-c}\)
Here g = 5, f = -3, c = 9
∴ Length = \(2 \cdot \sqrt{25-9}=2 \sqrt{16}\)
= 2(4) = 8 units
Hence proved.
Centre of the given circle = (0,0), r = 3 units line = x + 2y – 5 = 0
\(d=\left|\frac{0+2(0)-5}{\sqrt{1^{2}+2^{2}}}\right|=\frac{5}{\sqrt{5}}=\sqrt{5}\)
∴ Length of the chord = \(2 \cdot \sqrt{r^{2}-d^{2}}\)
\(=2 \cdot \sqrt{(3)^{2}-(\sqrt{5})^{2}}=2 \sqrt{9-5}=2.2=4 \text { units. }\)
Hence proved.
![]()
Part – C
2nd PUC Basic Maths Circles Ex 15.3 Five Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Show that the line 3x + 4y + 7 = 0 touches the circle x2 + y2 – 4x – 6y – 12 = 0 and find the point of contact.
Answer:
Given centre = (2, 3) and r = \(\sqrt{4+9+12}\) = \(\sqrt{25}\) = 5
If the length of the perpendicular is equal to radius of the circle than the line touches the circle
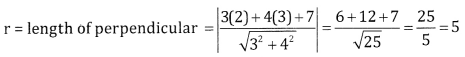
∴ The line 3x + 4y + 7 touches the circle
Any line perpendicular to 3x + 4y + 7 = 0 is of the form 4x – 3y + k = 0
It passes through (2,3) ∴ 8 – 9 + k = 0 ⇒ k = 1
∴ The line is 4x – 3y + 1 = 0
Point of contact is the intersection of 3x + 4y + 7 = 0 and 4x – 3y + 1 = 0
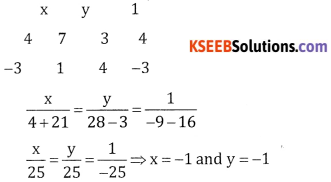
∴ The point of contact is (-1,-1)
Question 2.
Find k if the line 3x + y + k = 0 touches the circle x2 + y2 – 2x – 4y – 5 = 0.
Answer:
Given C = (1, 2) C = -5
Radius = Length of the perpendicular from (1, 2) to 3x + y + k = 0.
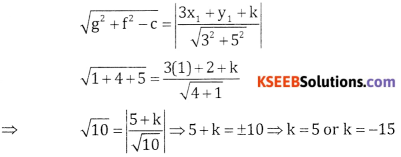
![]()
Question 3.
Find k if the 2x + y + k = 0 touches the circle x2 + y2 + 6x + 2y + 5 = 0.
Answer:
Hence centre = (-3,-1), c = 5
\(r=\sqrt{g^{2}+f^{2}+c}=\sqrt{9+1-5}=\sqrt{5}\)
r = length of the perpendicular from (-3,-1) to the line 2x + y + k = 0
\(r=\sqrt{g^{2}+f^{2}+c}=\sqrt{9+1-5}=\sqrt{5}\)
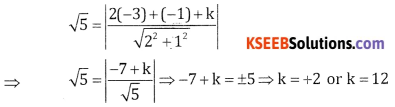
Question 4.
Find k if the line 4x – y + k = 0 touches the circle x2 + y2 + 4x – 8y + 3 = 0.
Answer:
Here centre = (-2,4), r = \(\sqrt{4+16-3}\) = \(\sqrt{17}\)
radius = length of perpendicular from (-2, 4) to the line 4x – y + k = 0
∴ \(\sqrt{17}\) = \(\left|\frac{4(-2)-4+k}{\sqrt{16+1}}\right|\)
-12 + k = ±\((\sqrt{17})^{2}\) ⇒ -12 + K = ±17 ⇒ k = 28 or -5
Question 5.
Find k such that the line x – 2y + k = 0 touches the circle x2 + y2 + 3x – 2y + 2 = 0.
Answer:
Here centre \(\left(-\frac{3}{2}, 1\right)\), \(r=\sqrt{\frac{9}{4}+1-2}=\sqrt{\frac{5}{4}}\)
r = length of perpendicular from \(\left(-\frac{3}{2},-1\right)\) to the line x – 2y + k = 0