Students can Download Basic Maths Exercise 21.2 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, 2nd PUC Basic Maths Question Bank with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Basic Maths Question Bank Chapter 21 Definite Integral and its Applications to Areas Ex 21.2
Part-A
Applications of Areas
2nd PUC Basic Maths Definite Integral and its Applications to Areas Ex 21.2 Two marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Find the area bounded by the curve y = x2, x – axis and the ordinates x = 0, x = 1
Answer:
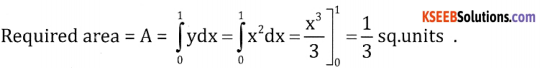
Question 2.
Find the area bounded by the curve y2 = 8x, x – axis and the lines x = 0, x = 2
Answer:
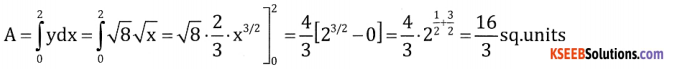
Question 3.
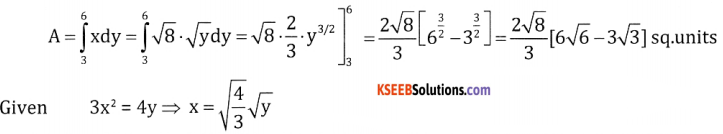
Find the area bounded by the curve x2 = 8y, y-axis and the abscissas y = 3, y = 6
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
Find the area bounded by the curve 3x2 = 4y, y-axis and the lines y = 1, y = 2
Answer:
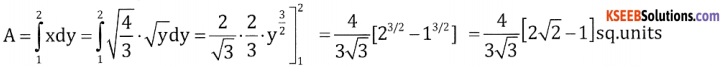
Part- B
2nd PUC Basic Maths Definite Integral and its Applications to Areas Ex 21.2 Five Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Find the area bounded by the parabola y2 = 4ax and its latus rectum.
Answer:
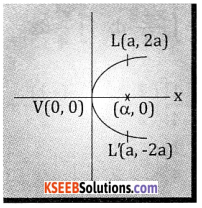

Question 2.
Find the area bounded by the parabola y2 = 4x and x2 = 4y
Answer:
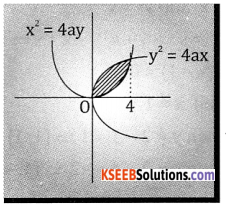
Given
y2 = 4x and x2= 4y
\(\left(\frac{x^{2}}{4}\right)^{2}\) ∵y = \(\frac{x^{2}}{4}\)
\(\frac{x^{4}}{16} = 4 x\)
x4 – 43x = 0
x(x3 – y3) = 0 ⇒ x = 0, x = 4

![]()
Question 3.
Find the area bounded by the curve y2 = 5x and the line y = x
Answer:
y2 = 5x and y = x
x2 – 5x = 0
x(x – 5 ) = 0 ⇒ x = 0 and x = 5
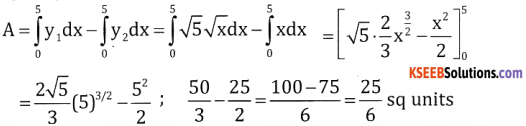
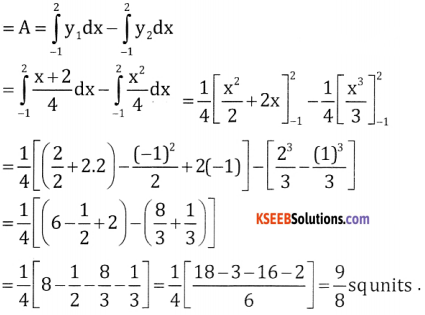
Question 4.
Find the area enclosed between the parabola x2 = 4y and the line x = 4y – 2
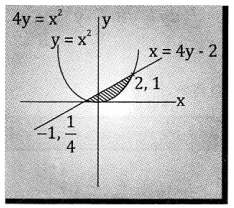
Answer:
Given x2 = 4y and line x = 4y – 2
x = x2 – 2 ∴ 4y = x2
x2 – x – 2 = 0
(x – 2) (x + 1) = 0
⇒ x = 2, y = -l
So when x = 2, y = 1 ⇒ (2, 1)
When x = -1, y = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) ⇒ \(\left(-1, \frac{1}{4}\right)\)
These two points where line meets parabola as we got these values by solving the 2 equations,
So, required area
![]()
Question 5.
Find the area enclosed between the parabola y2 = x and the line x + y = 2
Answer:
Given y = 2 – x and y2 = x
⇒ [2 – x]2 = x ⇒ 4 + x2 – 4x = x ⇒ x2 – 5x + 4 = 0
⇒ (x – 4) (x – 1) = 0
⇒ x = 4 and x = 1
when x = 1 then y = 2 – 1 = 1 ⇒ (1,1)
when x = 4 then y = 2 – 4 = -2 ⇒ (4, -2)

Question 6.
Find the area enclosed between the parabola y2 = 4ax and the line y = mx
Answer:
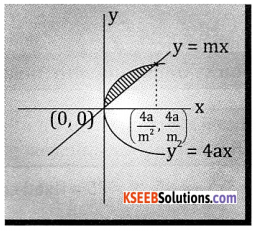
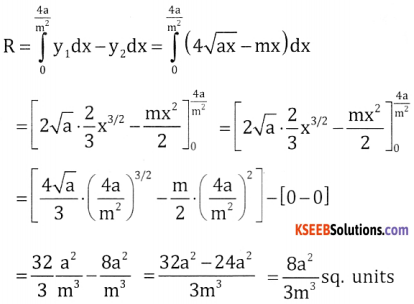
Given y2 = 4ax and line y = mx.
Points where both meet at a \(\left(\frac{4 a}{m^{2}}, \frac{4 a}{m}\right)\) and (0,0)
⇒ y2 = 4ax
m2x2 = 4ax ⇒ x = \(\frac{4 \mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{m}^{2}}\) and y = mx = \(\mathrm{m} \cdot \frac{4 \mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{m}^{2}}=\frac{4 \mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{m}}\)
Required area = Area of y2 = 4ax from 0 to \(\frac{4 \mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{m}^{2}}\) – Area of the line y = mx from 0 to \(\frac{4 \mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{m}^{2}}\)
![]()