You can Download Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Questions and Answers, 2nd PUC Biology Question Bank with Answers, Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Question Bank Chapter 7 Evolution
2nd PUC Biology Evolution NCERT Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain antibiotic resistance observed in bacteria in light of Darwinian selection theory.
Answer:
Penicillin when discovered was used as antibiotic against all bacteria. Soon many of these became resistant. This is because alleles of resistance which are already present in bacteria are of no importance in absence of antibiotics. Adjustment to change in environment due to genetic variation is adaptation.
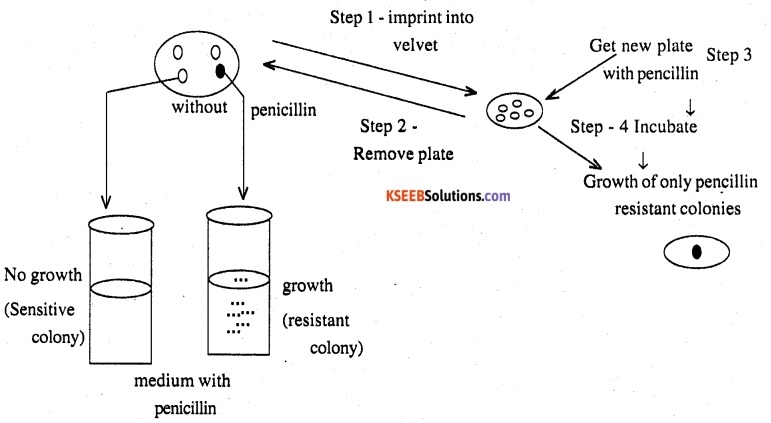
Question 2.
Find out from newspapers and popular science articles any new fossil discoveries or controversies about evolution.
Answer:
- Fossil of small terrestrial dinosour with feathers covering limbs and body. (Archaeopteryx lithdgraphia)
- Mesohippus – intermediate horse size of goat with 3 toes on each foot and molar teeth had serration.
Question 3.
Attempt giving a clear definition of the term species.
Answer:
Species is a morphologically distinct and reproductively isolated one or more natural populations of individuals which resemble one another closely and interbreed freely amongst themselves.
![]()
Question 4.
Try to trace the various components of human evolution (hint: brain size and function, skeletal structure, dietary preference, etc.)
Answer:

Question 5.
Find out through internet and popular science articles whether animals other than man has self-consciousness.
Answer:
Please do survey in internet.
Question 6.
List 10 modern-day animals and using the internet resources link it to a corresponding
ancient fossil. Name both.
Answer:
Please do survey in internet.
Question 7.
Practise drawing various animals and plants.
Answer:
Please practice drawing.
Question 8.
Describe one example of adaptive radiation.
Answer:
Adaptive radiation – Formation of different species from a common ancestor with new species adapting to different geological niches.
Example: Darwin’s finches is Galapagos island have wolves from mainland finches. They underwent changes is shape, size of beaks, food habit, feathers.
Question 9.
Can we call human evolution as adaptive radiation?
Answer:
No, because parent species of homosapiens have evolved by progressive evolution
(Homo habilis —Homoerectus lineage)
Question 10.
Using various resources such as your school Library or the internet and discussions with your teacher, trace the evolutionary stages of any .one animal say horse.
Answer:
E.g.: Horse – See text book diagram
2nd PUC Biology Evolution Additional Questions and Answers
2nd PUC Biology Evolution One Mark Questions
Question 1.
What is abiogenesis?
Answer:
It is the process of the appearance of first form of life slowly from non living molecules.
Question 2.
What are fossils?
Answer:
Fossils are the remnants or traces of ancient organism that lived in the past.
Or
Fossils are the organnic relies of the past which serve as evidences in tracing biological evolution.
Question 3.
What is evolutionary biology?
Answer:
The science which deals with the study of history of life forms on earth.
Question 4.
Define analogous organs. (CBSE 93,94,2007)
Answer:
The organs which performs the same function but differ in their origin and structures are called analogous organs.
![]()
Question 5.
Define homologons organs.
Answer:
The organs which have similar embryonic origin but they perform the different functions.
Question 6.
What is paleontology?
Answer:
It is the branch of science that deals with fossils.
Question 7.
Define homology.
Answer:
Homology refers to the similarities in the fundamental anatomy and embryology of organs of different groups of plants and animals.
Question 8.
Name any two vertebrate body parts that are homologous to human forelimbs.
(CBSE 2008)
Answer:
Wings of birds, flippers of whale forelimbs of cheetah, wings of bats.
Question 9.
What is analogy?
Answer:
It refers to structurally different organs evolving for the same function in different group of plants and animals.
Question 10.
Mention the type of evolution that has brought similarity as seen in potato tuber and sweet potato.
Answer:
Convergent evolution.
Question 11.
Why are the wings of a butterfly and of a bat called analogous? (CBSE 1996, 2009)
Answer:
They are of different embryonic origin but similar function.
Question 12.
Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of cucurbit are analogous or homologous.
Or
Wings of bird and forelimbs of horse are homologons or analogous
Or
Flippers of penguin and dolphin are analogous or Homologies.
What type of evolution has brought similarity in these cases? (CBSE 1992, Delhi 2009, Foreign 2009)
Answer:
- All these are homologous.
- Divergent type evolution has brought these similarity.
Question 13.
Give 2 examples of evolution due to anthropogenic activities.
Answer:
DDT resistance in mosquitoes and Antibiotic resistance in microbes.
Question 14.
What kind of evidence is afforded by Darwin’s finches in support of orgaine evolution? (CBSE 1991)
Answer:
Adaptive radiation i.e. All these finches evolved from common ancestor but they diverge in various directions.
Question 15.
Name the fossil animal which serves as a connecting link believers reptiles and birds. (CBSE 1995)
Answer:
Archeopteryx – fossil bird.
Question 16.
Define ontogenetic law.
Answer:
Ontogeny recapitulates phytogeny.
![]()
Question 17.
Name the placental mammal corresponding to the Austrian “Spotted cuscus” and Tasmanian “tiger cat”. Which have evolved as a result of convergent evolution (CBSE 2008)
Answer:
Lemur and Bobcat.
Question 18.
As per Hugo deVries, what is the cause of speciation? (Delhi 2008, CBSE 1995)
Answer:
Mutation. (Single step large mutation)
Question 19.
What is meant by genelic equilibrium.
Answer:
When allele frequencies in a population are stable, the allele frequency of a population remains constant. It is called as genetic equilibrium, i.e. the sum total of all the allelic frequency is one.
Question 20.
Define evolution as per Hardy Weinberg.
Answer:
As per Hardy Weinberg, change of frequency of alleles in a population would be considered as evolution i.e. distubance in the genetic equilibrium.
Question 21.
What is meant by gene pool?
Answer:
The sum total of all the genes pooled by the members of a population.
Question 22.
What is meant by gene flow?
Answer:
Changes in the gene pool of population when there is continuous migration of organisms between them i.e. it refers to the addition or loss of genes.
Question 23.
Name the immediate ancestor of lycopods .
Answer:
Zosterophyllum.
Question 24.
Define natural selection?
Answer:
Natural selection is the process in which heritable variations that enable better survival, are enabled to produce and leave behind a greater number of progeny.
Question 25.
Darwin’s theory is known as “Theory of Natural selection”. How is Lamark theory know as? (CBSE 1995)
Answer:
Theory of inheritance of acquired characters.
Question 26.
Define the term “reproductive isolation”.
Answer:
If the population of 2 different species whether they are isolated or not, cannot be enter bread to produce offspring.
Question 27.
Define genetic drift.
Answer:
Random changes in the allelic frequencies of a population, occurring only by chance events, constitute genetic drift.
Question 28.
Name the group of animals that evolved into amphibian.
Answer:
Lobe-fins evolved into amphibian.
Question 29.
Mention the key concepts about the mechanism of biological evolution/ speciation according to
(a) Devries and
(b) Darwin (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
(a) De Vries – Mutation
(b) Darwin – Natural selection and branching decent.
2nd PUC Biology Evolution Two Marks Questions
Question 1.
Describe the theory of abiogenesis.
Answer:
According to this theory, the first form of life arose slowly through evolutionary forces from non living molecules.
- The reducing atmosphere and high temperature favoured the formation of diverse organic compounds from inorganic molecules.
- Then the first noncellular forms of life i.e. self duplicating molecules like RNA evolved.
Question 2.
Write the names of two dinosaurs that lived early in the geological history and two that lived later.
Answer:
- Lived early in the geological history:- Brachyosaurus and Stegosaurus
- Lived later:- Triceratops and Tyrannosaurus.
Question 3.
Amongst pea tendrils, opuntia spines, lemon thorns and cucurbit tendrils. Which ones are homologous structures? Why do you call them homologous? (CBSE 1999)
Answer:
- Pea tendrils and opuntia spines are homologous.
- Lemon thorm and cucurbit tendrils are homologous.
Reason:
- Pea tendrils and Opuntia spines are modified leaves (same orign) but perform different functions.
- Lemon thorns and cucurbit tendrils are modified stems. Both arise from axillary position. Both perform different functions.
Question 4.
Name one organ analogous to the wings of bird. Why are they both analogous. Can you include wings of bat also with them under the same category? Give reason. (CBSE 1997)
Answer:
Wings of insects and birds are analogous because both perform the sante function but have the dissimilar structured and origin. The wings of insects are modified outgrowth of the body without having bones, whereas wings of birds are modified fore limbs.
The wings of bat cannot be put under the same category. This became the wings of bat and birds are homologous organ.
![]()
Question 5.
Given below are the names of 2 pairs of limbs. Categorize them into homologous and analogous organs, give reason.
(i) Human arm and fore leg of cow
(ii) Bat’s wing and Grass hopper’s wing. (CBSE 1999)
Answer:
(i) Human arm and fore leg of cow are homologous organs because they are built upon the same fundamental plan (pentadactyl pattern) but they perform different functions as grasping in man and locomotion in cow.
(ii) Bat’s wing and grass hopper’s wing are analogous organs because they perform the same function bat differ in their origin and structure. Wings of bats are modified fore limbs where as grasshoppers wings are modified outgrowth of the body wall.
Question 6.
Give 2 examples each of analogy and homology in plants. (Hots)
Answer:
Analogy:
- Tubers of sweet potato and potato
- Tendrils of pea and cucurbits.
Homology:
- Tendrils of cucurbit and lemon thorn
- Tendrils of Pea and Spines of opuntia
Question 7.
How do Darwin’s finches illustrate adaptive radiation? (AI2008)
Answer:
Darwin finches are varieties of small black birds found in the Galapagos islands. They all must have evolved in the island itself. From the original seed eating birds, many other forms evolved, with altered beak enabling them to become insectivorous and vulgarian habits. This process of evolution of different species in the same geographical area starting with one spices and radiated to other areas is called adaptive radiation.
Question 8.
Define adaptive radiation with 2 eggs. (Hots)
Answer:
Adaptive radiation is defined as the process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from single species and radiated to other habitats.
Example:
- Australian marsupials, each different from the other, have evolved from an ancestral stock.
- Darwin’s finches – from the original seed eating stock insectivores and vegetarian birds have evolved.
Question 9.
State Hardy – Wein berg principle of genetic equilibrium knowing that genetic drift disturbs this equilibrium. Mention what does this disturbance in genetic equilibrium lead to?
Answer:
Hardy Weinberg principle states that allele frequencies in a population are stable and remain constant from generation to generation.
- Genetic drift refers to a change in allele frequencies of a population acquiring by chance.
- Such a change in allele frequency may be so different that the population becomes a different species.
- The original drifted population is called founder and the effect is called founder effect.
2nd PUC Biology Evolution Three Marks Questions
Question 1.
Whose theory was put to test by Miller Urey and what was the theory? How did their experiment proved the abiotic origin of life on earth?
Answer:
Oparin and Haldane proposed that the first life form could have come from the „ nonliving organic molecules like RNA, protein etc.
- The orgaine molecules must have been produced by chemical evolution, i.e. formation of divers organic molecules from inorganic constituents.
- The condition, of the earth that favoured chemical origin were
(i) very high temperature
(ii) volcanic storms
(iii) Reducing atmosphere that contained methane, ammonia and water vapour.
- Energy must have been produced by U-V radiation and lightning.
- Analysis of the products of their experiment showed the presence of amino acids which help to form proteins.
Question 2.
Give a brief account as how evolution has taken pleace from the time the non cellular aggregate of giant molecules turned into cells.
Answer:
The first formed cells were anaerobic heterotrophs. But slowly some of these cells developed coloured proteins, that could release oxygen, in a process that could have been similar to the light reactions of photosynthesis. As oxygen started coming into the atmospheres is as the atmosphere started becoming an oxidising one, new formes of life could not arise from nonliving organic molecules.
The organisms started becoming aerobic and autotrophic. The single celled organism slowly became multicellular form, where some became autotrophic while many remained heterotrophic. Plants like bryophytes were the first to invade land, followed by reptiles among animals.
![]()
Question 3.
Differentiate between natural selection and artificial selection.
Answer:
| Natural selection | Artificial selection |
| (a) It is the process occurring in nature over a number of generations to increase the number of fit individuals in a population. (b) The characters/ adaptationsare advantageous to the organism. |
(a) It is the process practised by man over a number of generations, to select organisms with better qualities. (b) The characters are advantageous human. |
Question 4.
(i) The study of fossils support evolution of organism. Discuss?
(ii) Describe convergent evolution with an example each from animals and plants.
Answer:
(i) By the careful analyses of the distribution of fossils in the different strata of rocks gives the time of the history of the earth the study showed that life form varied over time, some were simple and those in the superfluid layers resembled modern organism. Some fossils indicate connecting links i.e. they share features of two groups of organisms indicating the evolution of one group into the other.
(ii) Convergent evolution refers to the evolutionary process of selection of similar adaptive features in different groups of organisms in a similar habitat towards the same function.
- It is the similar habilat that has resulted in selection of similar structures.
- Analogous structures that are not anatomically similar but perform the same functions result from convergent evolution. Examples: Wings of butterfly and wings of birds.
Question 5.
How is genetic drift differ from gene migration?
Answer:
| Genetic drift | Gene migration |
| Random changes in the allele frequencies of a population occurring only by chance events constitute genetic drift. | It refers to the change in allele frequencies of a given population when individuals ‘ migrate into the population or leave the population. |
Question 6
(a) Name the largest dinosaurs and mention any two characteristic features.
(b) How did Darwin explain the existence of different varieties of finches on Galapagos Islands?
Answer:
(a) Tyrannosaurus rex was the largest dinosaur it was near about 20 feet in height. It had huge fearsome dagger-like teeth
(b) Darwin explained that all the verities evolved on the island itself from the original seed-eating birds, many other forms with altered beaks arose some others became insectivorous while remained the vegetarian flinches. Such process of evolution of different species in a given geographied area, starting from a point and literally radiating to other habitats, is called adaptive radiation.
Question 7.
Explain Landmark’s theory of evolution with example.
Answer:
According to Lamarck, evolution of life forms had occurred, drives by use and disease of organs. This theory as known as theory of inheritance of acquired characters. He gave the examples of giraffes, who in an attempt to forage leaves on tall trees had to stretch their neck. As they passed this acquired character to the next generations giraffe slowly over the years, came to acquire tons necks.
![]()
Question 8.
How does the shift in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium leads to founder effect. (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
A shift in Hardy – Weinberg equilibrium is caused by factors like gene migration, gametic drift, mutation etc. Gene migration refers to a change in the gene frequencies of the populations, when a section of a population migrates to another place and population.
If gene migration occurs a number of times there would be a gene flow. i.e. new genes/ alleles are added to the new population while they are lost from the original population.
Genetic drift refers to change in allele/ gene frequency at random or that occurs due to some chance event. Some times, the change in allele frequency is so different in the new sample of population that they become different species. The original drifted population becomes the founder and the effect produced is called founder effect.