Students can Download 2nd PUC Business Studies Model Question Paper 2 with Answers, Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Model Question Paper 2 with Answers
Time: 3 Hrs 15 Min
Max. Marks: 100
SECTION – A
I. Answer any ten of the following questions in a word or a sentence each.
Each questions carries one mark. (10 × 1 = 10)
Question 1.
State any one dimension of management?
Answer:
Management of work.
Question 2.
Henry fayol was a.
- Social Scientist
- Mining Engineer
- Accountant
- Production Engineer
Answer:
2. Mining Engineer.
Question 3.
What do you mean by business environment? An example for standing plan is
- Budget
- Program
- Project
- Rule
Answer:
4. Rule
Question 4.
State any one importance of planning function?
Answer:
Planning Provides Direction.
![]()
Question 5.
A______________ structure of organisation leads to occupational specialisation.
Answer:
Functional structure.
Question 6.
State the first step in staffing process?
Answer:
Estimating the man power requirements.
Question 7.
Mention any one element of Directing function?
Answer:
Supervision.
Question 8.
State any one limitation of controlling function.
Answer:
Difficulty in setting quantitative standards.
Question 9.
Give the meaning of Business finance.
Answer:
Money required for carrying out business activities is called business finance.
![]()
Question 10.
What is the other name given for secondary capital market?
Answer:
Stock exchange/stock market.
Question 11.
In which year was consumer protection Act passed?
Answer:
Consumer protection Act was passed in the year 1986.
Question 12.
Who is an entrepreneur?
Answer:
The person who set – up his business is called an entrepreneur.
SECTION – B
II. Answer any ten of the following questions in two or three sentences each.
Each question carrier two marks: (10 × 2 = 20)
Question 13.
Mention any two organizational objectives of Management.
Answer:
- Survival
- Profit
Question 14.
What do you mean by mental revolution?
Answer:
Mental revolution involves a change in the attitude of workers and management towards one another from competition to cooperation.
Question 15.
What is Globalisation?
Answer:
Globalization means the integration of the various economies of the world leading towards the emergence of a cohesive global economy.
![]()
Question 16.
What is Policy
Answer:
Policies are general statements that guide thinking towards a particular direction.
Question 17.
Define Organising?
Answer:
According to Henry Fayol,” To organize a business is to provide it with everything, useful to its functioning – raw materials, machines, tools, capital and personnel”.
Question 18.
What is Orientation?
Answer:
It is a process of introducing the new employee in the organization to the existing employees and familiarizing him with the rules and policies of the organization.
Question 19.
What is Directing
Answer:
According to Koontz and O’Donnell, “Direction is the inter-personal aspect of managing by which sub-ordinates are led to under stand and contribute effectively and efficiently to the attainment of enterprise objective.”
![]()
Question 20.
Mention any two modern techniques followed in managerial control process.
Answer:
- Return on Investment
- Ratio Analysis.
Question 21.
What do you understand by financing decisions? Give an example
Answer:
The decision about the quantum of finance to be raised from various long-term sources is known as financing decisions. These long-term sources of capital include debt, equity, preference share capital, and retained earnings. Example for financing decision: Decision about how much funds are to be raised from which source.
Question 22.
What is meant by a depository?
Answer:
A depository keeps securities in electronic form on behalf of the investor.
Question 23.
State any two objectives of Pricing.
Answer:
1. Obtaining Market Share Leadership:
If a firm’s objective is to obtain larger share of the market; it will keep the price of its products at lower levels so that greater number of people are attracted to purchase the products.
2. Surviving in a Competitive Market:
If a firm is facing difficulties in surviving in the market because of intense competition or introduction of a more efficient substitute by a competitor, it may lead to discounting its products or running a promotion campaign to liquidate its stock.
![]()
Question 24.
Give any two reasons to emphasise the importance of consumer protection from the consumer point of view.
Answer:
- Consumer Ignorance
- Unorganized Consumers
SECTION – C
III. Answer any seven of the following questions in 10 – 12 sentences.
Each question carrier 4 Marks: (7 × 4 = 24)
Question 25.
Explain briefly the principles of scientific Management of FW Taylor?
Answer:
Scientific management refers to the use of scientific and standardized tools, methods and trained workers in all organisational activities in order to increase the total production with minimum cost and wastage. Following are the principles of scientific management contributed by FW Taylor.
1. Science not Rule of Thumb:
Taylor was the first person to introduce the method of scientific inquiry into the domain of management practice. He believed that there was only one best method to maximise efficiency i.e., by scientific way. Scientific management includes scientific selection of workers, placement and training, work-study motion study fatigue study, time – study, gradation of equipments and machinery, payment of wages according to work done, etc.
2. Harmony, Not discord:
There should be harmonious relationship between management and workers. Both should realise that each one is important. This avoids class-conflict. To achieve this, Taylor introduced mental revolution. Both management and workers should transform their thoughts in order to achieve harmonious relationship amongst them.
3. Cooperation, Not individualism:
There should be complete cooperation between the labour and the management instead of individualism. Competition should be replaced by cooperation. Both should realise that they need each other. To achieve this fact, the management should consult their employees while taking important decisions.
There should be a two way communication between management and workers. According to Taylor, there should be almost equal division of work and responsibility between workers and management.
4. Development of each and every person to his or her greatest efficiency and prosperity:
Industrial efficiency depends on personnel competencies. According to Taylor, efficiency could be achieved from the beginning i.e., from the time of selection of employees.
Each person must be scientifically selected. Work should be assigned according to his mental and intellectual capabilities Proper training should be given to improve his/her skill. This will contribute to their greatest efficiency and prosperity for both organisation and workers.
![]()
Question 26.
Explain briefly any four features of planning function?
Answer:
The planning function of the management has certain special features. These features are as follows:
a. Planning focuses on achieving objectives:
Organisations are set up with a general purpose in view. Specific goals are set out in the plans along with the activities to be undertaken to achieve the goals. Thus, planning is purposeful. It contributes to the achievement of predetermined goals of an organization.
b. Planning is a primary function of management:
Planning lays down the base for other functions of management. All other managerial functions are performed within the framework of the plans drawn. Thus, planning is referred to as the primary function of management.
c. Planning is pervasive:
Planning is required at all levels of management. It is also o required in all departments of the organization. Planning is not an exclusive function of top management. It is required at every level and in every department. Hence, planning is all pervasive in nature.
d. Planning is continuous:
Plans are prepared for a specific period of time. At the end of that period there is a need for a new plan to be drawn on the basis of new requirements and future conditions. Hence, planning is a continuous process.
Question 27.
Explain briefly the steps in the process of organising function?
Answer:
The following are the steps in the process of organizing:
a. Identification and Division of work:
The process of organizing starts with the identification and division of work. The work is divided into manageable activities so that duplication of work can be avoided. The burden of work can be shared among the employees.
b. Departmentalization:
It refers to the process of grouping the activities of similar nature under same departments. This helps specialization and co-ordination. Departments can be created generally on the following basis:
- On the basis of function
- On the basis of type of product manufactured
- On the basis of territory
c. Assignment of duties:
It is necessary to define the work of different job positions and allocate the work accordingly to various employees. Once departments are formed, it is necessary to assign the work to the employees according to their skill and competencies. It is essential that a balance is created between the nature of the job and the ability of the employee.
d. Establishment of reporting relationships:
Mere allocation of work is not enough. Each individual should know from whom he has to take orders and to whom he is accountable. The establishment of such clear relationship helps to create a hierarchal structure and helps in co-ordination among various departments.
![]()
Question 28.
Explain briefly any four on the job methods of training?
Answer:
On the job-training:
It is a method, where workers learn by doing the work. The following are the important methods of on the job training:
- Apprenticeship training
- Coaching
- Internship training
- Job-rotation
On the job means learning while doing. The following are the popular on the job training methods:
1. Apprenticeship Programmes:
Apprenticeship programmes put the trainee under the guidance of a master worker. These are designed to acquire a higher level of skill. People seeking to enter skilled jobs like plumbers, electricians, etc., are required to undergo apprenticeship training.
2. Coaching:
In this method, the superior guides and instructs the trainee as a coach. The coach or counselor sets mutually agreed upon goals, suggests how to achieve these goals periodically reviews the trainees progress and suggests changes required in behavior and performance. The trainee works directly with a senior manager and the manager takes full responsibility for the trainee’s coaching.
3. Internship training:
It is a joint programme of training in which educational institutions and business firms cooperate. Selected candidates carry on regular studies for the prescribed period. They also work in some factory or office to acquire practical knowledge and skills.
4. Job Rotation:
This kind of training involves shifting the trainee from one department to another or from one job to another. This enables the trainee to gain a broader understanding of all parts of the business and how the organization as a whole functions. Job rotation allows trainees to interact with other employees. When employees are trained by this method, the organization finds it easy at the time of promotions, replacements or transfers.
Question 29.
Explain briefly the importance of controlling process ?
Answer:
A good control system helps an organization in the following ways:
a. Accomplishing organizational goals:
The controlling function measures progress towards the organizational goals and brings to light the deviations, if any, and indicates corrective action. Thus, it guides the organization and keeps it on the right track so that organizational goals might be achieved.
b. Judging accuracy of standards:
A good control system enables management to verify whether the standards set are accurate and objective. An efficient control system keeps a careful check on the changes taking place in the organization and in the environment and helps to review and revise the standards in light of such changes.
c. Making efficient use of resources:
By exercising control, a manager seeks to reduce wastage and spoilage of resources. Each activity is performed in accordance with predetermined standards and norms. This ensures that resources are used in the most effective and efficient manner.
d. Improving employee motivation:
A good control system ensures that employees know well in advance what they are expected to do and what are the standards of performance on the basis of which they will be appraised. It, thus, motivates them and helps them to give better performance.
e. Ensuring order and discipline:
Controlling creates an atmosphere of order discipline in the organization. It helps to minimize dishonest behaviour on the part of the employees by keeping a close check on their activities.
f. Facilitating coordination in action:
Controlling provides direction to all activities and efforts for achieving organizational goals.
![]()
Question 30.
Explain briefly the factors affecting Capital Budgeting Decision?
Answer:
A long-term investment decision is also called as capital budgeting decision. It involves committing the finance on a long-term basis.
The following are certain factors which affect capital budgeting decisions:
1. Cash flows of the project:
When a company takes an investment decision involving huge amount, it expects to generate some cash flows over a period. These cash flows are in the form of a series of cash receipts and payments over the life of an investment. The amount of these cash flows should be carefully analysed before considering a capital budgeting decision.
2. The rate of return:
These calculations are based on the expected returns from each proposal and the assessment of the risk involved.
3. Investment criteria:
The decision to invest in a particular project involves a number of calculations regarding the amount of investment, interest rate, cash flows and rate of return. There are different techniques to evaluate investment’proposals which are known as capital budgeting techniques. These techniques are applied to each proposal before selecting a particular project.
Question 31.
Explain briefly any four functions of stock exchange?
Answer:
Stock Exchange means any body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, constituted for the purpose of assisting, regulating or controlling the business of buying and selling or dealing in securities.
The following are the important functions of the stock exchange:
1. Providing liquidity and marketability to existing securities:
The basic function of a stock exchange is the creation of a continuous market where securities are bought and sold. It gives investors the chance to disinvest and reinvest. This provides both liquidity and easy marketability to already existing securities in the market.
2. Pricing of Securities:
share prices on a stock exchange are determined by the forces of demand and supply. A stock exchange is a mechanism of constant valuation through which the prices of securities are determined. Such a valuation provides important instant information to both buyers and sellers in the market.
3. Safety of Transaction:
The membership of a stock exchange is well regulated and its dealings are well defined according to the existing legal framework. This ensures that the investing public gets a safe and fair deal on the market.
4. Contributes to Economic Growth:
A stock exchange is a market in which existing securities are resold or traded. Through this process of disinvestment and reinvestment, savings get channelized into their most productive investment avenues. This leads to capital formation and economic growth.
Question 32.
Explain any four functions performed by public relations department of an organization.
Answer:
The following are the important functions performed by public relations department of an organization:
1. Press relations:
Information about the organization needs to be presented in a positive manner in the press. The public relations department is in contact with the media to present true facts and a correct picture about the company.
2. Product publicity:
New products require special effort to publicise them and the company has to sponsor such programmes. The public relations department manages the sponsoring of such events like news conferences, seminars, exhibitions etc.
3. Corporate communication:
The image of the organization needs to be promoted through communicating with the public and the employees within the organization. This is generally done with the help of newsletter, annual reports, brochures, articles and audio-visual materials.
4. Lobbying:
The organization has to deal with government officials and different ministers in charge of corporate affairs, industry, finance with respect to policies relating to business and the economy. The public relations department has to be proactive in promoting or decoding regulations that affect their organization.
![]()
Question 33.
Discuss briefly any four differences between selling and marketing
Answer:
| Money Market | Capital Market |
| It is a market where short-term funds are borrowed and lent. | It is a market where long-term funds are borrowed and lent. |
| The participants in the capital market are financial institutions, banks, corporate entities, and foreign investors. | The participants in the money market are RBI, banks, financial institutions, and finance companies. |
| Individuals can take part in the trading of capital market | Individuals cannot directly trade in the money market. |
| The instruments involved for a transaction are treasury bills, calls money, certificate of deposit, commercial papers, commercial bills etc. | The major players are companies, Individual investors, Institutional Investors, foreign investors, banks and financial institutions. |
Question 34.
Explain any four ways in which the objective of consumer protection can be achieved.
Answer:
There are various ways in which the objective of consumer protection can be achieved which are as follows:
1. Self Regulation by Business:
Enlightened business firms realize that it is in their long-term interest to serve the customers well. Socially responsible firms follow ethical standards and practices in dealing with their customers.
2. Business Associations:
The associations of trade, commerce and business like Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce of India and Confederation of Indian Industries have laid down their code of conduct which lay down their guidelines for their members in dealing with the customers.
3. Consumer Awareness:
A consumer who is well informed about his rights, and the reliefs available, would be in a position to raise his voice against any unfair trade practices or any kind of exploitation by the seller.
4. Consumer Organization:
Consumer organizations play an important role in educating consumers about their rights and providing protection to them. They can force business firms to avoid malpractices and exploitation of consumers.
5. Government:
The government can protect the interest of the consumers by enacting various legislations.
SECTION – D
IV. Answer any four of the following questions in 20 – 25 sentences each.
Each question carrier 8 marks: (4 × 8 = 32)
Question 35.
Explain the various functions of Business Management?
Answer:
Management is described as the process of planning, organising, directing and controlling the efforts of organisational members and of using the resources of the organisation to achieve specific goals. Luther Gulick has given a keyword “PODSCORB”.
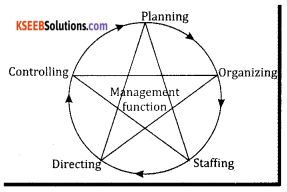
- P → Planning
- 0 → Organising
- S → Staffing
- D → Directing
- Co → Coordination
- R → Reporting and
- B → Budgeting
The most widely accepted classification of management functions is given by Koontz and O’Donnell which includes planning, organizing, staffing, Directing and Controlling.
1. Planning:
Planning is the basic and first function of management. It is the function of determining in advance what is to be done and who is to do it. A plan is a future course of action. Planning implies setting goals in advance and developing a way of achieving them efficiently and effectively. Planning is necessary to ensure proper utilisation of human and non-human resources.
2. Organisaing:
It is the process of bringing together, physical, financial and human resources. It develops productive relationship amongst them for achievement of organisational goals. Organising is the management function of assigning duties, grouping tasks, establishing authority and allocating resources required to carry out a specific plan. Organising as a process involves.
- Identification of activities
- Classification of activities
- Assignment of duties
- Delegation of authority and creation of responsibility
- Coordinating authority and responsibility relationships.
3. Staffing:
It includes finding the right people for the right job. This is also known as the human resource function and has assumed greater importance in the recent years staffing involves.
- Man – power planning
- Recruitment, selection and placement
- Training and Development
- Remuneration
- Performance appraisal
- Promotions and Transfer
4. Directing:
Directing function involves leading, influencing and motivating employees to perform the tasks assigned to them. It is that part of managerial function that actuates the organisational methods to work efficiently for achievement of organisational objectives Directing has the following elements:
- Supervision
- Motivation
- Leadership
- Communication
- Delegation
- Coordination
5. Controlling:
It is the management function of monitoring organisational performance towards the attainment of organisational goals. It implies the measurement of actual performance against the set standards and connecting the deviations if any so as to ensure the achievement of organisations goals. Controlling has the following steps:
- Establishment of standards
- Measurement of actual performance
- Comparison of actual performance with the set standards and finding out deviations if any
- Taking corrective action.
Conclusion:
Theoretically, the management functions can be separated but practically these functions are overlapping in nature. Hence they are inseparable. Each function blends into the other and each function affects the performance of other functions.
![]()
Question 36.
Explain in detail the various dimensions of business environment with examples.
Answer:
Dimensions of business environment include economic, social, technical, logical, political and legal conditions which are considered relevant for decision-making and improving the performance of an enterprise.
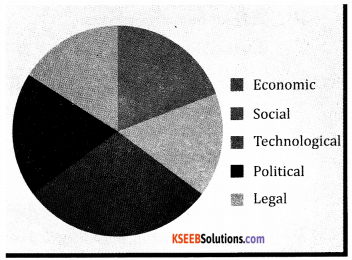
1. Economic Environment:
Interest rates, inflation rates, changes in disposable income of people, stock market indices and the value of rupee are some of the economic factors that can affect management practices in a business enterprise.
2. Social Environment:
The social environment of business include the social forces like customs and traditions, values, social trends, society’s expectations from business, etc. Values refer to concepts that a society holds in high esteem.
In India, individual freedom, social justice, equality of opportunity and national integration are examples of major values cherished by all of us. Social trends present various opportunities and threats to business enterprise.
3. Technological Environment:
This includes forces relating to scientific improvements and innovations which provide new ways of producing goods and services and new methods and techniques of operating a business. This technological advancement creates shifts in demand and also has been responsible for creating new business.
4. Political Environment:
Political environment include political conditions such as general stability and peace in the country and specific attitudes the elected government representatives hold towards business. If political unrest prevails, there may be uncertainty of business activities. Political stability builds up confidence among business people to invest in the long term projects and assist in the growth of the economy.
5. Legal Environment:
Legal environment includes various legislations passed by the Government administrative orders issued by government authorities, court judgements, decisions given by various commissions and agencies at every level of the government – Centre, state or local. An adequate knowledge of rules and regulations framed by the Government is a prerequisite for better business performance.
Question 37.
State the Advantages and disadvantages of Formal Organisation.
Answer:
Formal Organisation refers to the organization structure which is designed by the management to accomplish a particular task. It specifies clearly the boundaries of authority and responsibility and there is a systematic coordination among the various activities to achieve organizational goals.
Advantages of Formal Organisation include:
1. It is easier to fix responsibility since mutual relationships are clearly defined.
2. There is no ambiguity in the role that each member has to play as duties are specified. This also helps in avoiding duplication of effort.
3. Unity of command is maintained through an established chain of command.
4. It leads to effective accomplishment of goals by providing framework for the operations to be performed and ensuring that each employee knows the role he has to play.
5. It provides stability to the organization. This is because behavior of employees can be fairly predicted since there are specific rules to guide them.
Disadvantages of Formal Organisation:
1. The formal communication may lead to procedural delays as the established chain of command has to be followed which increases the time taken for decision making.
2. Poor organization practices may not provide adequate recognition to creative talent, since it does not allow any deviations from rigidly laid down policies.
3. It is difficult to understand alumna relationships in an enterprise as it places more emphasis on structure and work. Hence, the formal organization does not provide a complete picture of how an organization works.
![]()
Question 38.
Explain in detail the staffing process.
Answer:
Following are the steps involved in Staffing Process:
- Estimating the manpower requirements/ Man Power Planning:
- Recruitment
- Selection
- Placement and Orientation
- Training and Development
- Performance appraisal(Evaluation)
- Promotion and Career Planning
- Compensation [Wage and Salary administration}
1. Manpower Planning:
It is the estimation of human resources required by an organization. Its main focus will be on getting right number of qualified people at the right time. While estimating the manpower requirement, the management generally keeps in mind, the available infrastructure including the technology, production schedule, market fluctuation, demand forecasts, etc.
2. Recruitment:
It is the process of finding the candidates for employment and motivating them to apply for the jobs in the organization.
3. Selection:
It is a process of choosing the best candidate from the large pool of applicants. It aims at finding the right person for the right job.
4. Placement:
It is a process of assigning job to the selected candidates. Assigning jobs to employees may involve a new job or different job. it also includes assignment of job to a new employee, transfer, promotion and also demotion of existing employee. Placement involves striking a fit between the requirements of a job and the qualifications of a candidate.
5. Orientation:
It is a process of introducing the selected employee to other employees and familiarizing him with the rules and policies of the organization. This process will help the new entrants to know about their superiors, subordinates, colleagues and about the organization.
6. Training:
Training is the process which is under taken to increase the knowledge and skills of an employee to perform the present job accurately.
7. Development:
It refers to the process of not only building up the skill and abilities for specific purpose, but also the overall competence of managerial executives to undertake more difficult and challenging tasks. Development refers to the training of managers and executives.
8.Performance appraisal (evaluation):
It is the systematic evaluation of the individual with respect to his performance on the job and his potential for development. It is concerned with determining the differences among the employees, working in the organization. It also determines an employee’s worth to the organization.
9. Promotion and career planning:
Promotion is a term usually used for the upward movement of an employee to a higher position with greater responsibilities and higher pay. Promotion requires more knowledge, experience and skills to perform the job.
10. Compensation:
Workers work for wages or salary which can be otherwise known as compensation. The term compensation comprises of cash payments related to wages and salary, bonus, share in the profit, pension etc. A properly developed compensation system enables an employer to attract, obtain, retain and motivate people of required intelligence and qualification in the organization.
Conclusion:
A competent staffing process obtains the most competent person to the organization. Staffing process should be carefully followed to get right man in the right job at the right time and in the right place.
Question 39.
How does Demat system works? Explain.
Answer:
1. A depository participant (DP), either a bank, broker, or financial services company, may be identified.
2. An account opening form and documentation (PAN card details, photograph, and power of attorney) may be completed.
3. The physical certificate is to be given to the DP along with a dematerialisation request form.
4. If shares are applied in a public offer, simple details of DP and Demat account are to be given and the shares on allotment would automatically be credited to the demat account.
5. If shares are to be sold through a broker, the DP is to be instructed to debit the account with the number of shares.
6. The broker then gives instruction to his DP for delivery of the shares, to the stock exchange.
7. The broker then receives payment and pays the person for the shares sold.
8. All these transactions are to be completed within two days, i.e., delivery of shares and payment received from the buyer is on a T+2 basis, settlement period.
![]()
Question 40.
Explain the advantages and limitations of advertising?
Answer:
Advertising is the most commonly used tool of promotion. It is an impersonal from of communication, which is paid for by sponsors to promote some goods or service.
A. Merits of Advertising:
1. Mass Reach:
Advertising is a medium through which a large number of people can be reached over vast geographical area.
2. Enhancing customer satisfaction and confidence:
Advertising creates confidence amongst prospective buyers as they feel more comfortable and assured about the product quality and hence feel more satisfied.
3. Expressiveness:
with the help of computer designs, graphics, etc advertising has developed into one of the most forceful medium of communication. With the special effects created, even simple product and messages look very attractive.
4. Economy:
Advertising is a very economical mode of communication. A large number of people can be reached at a time. Because of its wide reach, the overall cost of advertising gets spread over numerous communication links established. As a result the per unit cost of reach comes low.
B. Limitations of advertising:
1. Less Forceful:
Advertising is an impersonal form of communication. It is less forceful than personal selling as there is no compulsion on the prospects to pay attention to the message.
2. Lack of feedback:
The evaluation of the effectiveness of the advertising message is very difficult as there is no immediate feedback mechanism of the message that is delivered.
3. Inflexibility:
Advertising is less flexible as the message is standardized and cannot be altered according to the requirements of the different customer groups.
4. Low Effectiveness:
As the volume of advertising is getting more and more expanded, it is becoming difficult to make advertising messages heard by the target customers. This affects the effectives of advertising.
C. Objections to Advertising:
1. Adds to cost:
Advertising unnecessarily adds to the cost of product, which is ultimately passed on to the buyers in the form of high prices. The money spent on advertising adds to the cost, which is an important factor in the fixation of the price of a product.
But, advertisement also helps to increase the demand for the product as large number of potential buyer are persuaded to buy more product. Increased demand leads to higher production, which brings in the economies of scale. As a result, the per unit cost of production comes down. This reduces the burden of consumers.
2. Undermines social values:
People argue that advertising undermines social values and promotes materialism. It encourages dissatisfaction among people as they come to known about new products and feel dissatisfied with their present state of affairs.
But, advertisement in fact, helps buyers by informing them about the new products, which may be improvement over the existing products. If the buyers are not informed about these products, they may be using inefficient products.
3. Confuses the buyers:
So many advertisements create confusion among the buyers. All advertisements make similar claims that the buyer gets confused as to which one is true and which product should be purchased. But, the supporters of advertisement argue that buyers can clear their confusion by analyzing the information provided on the advertisements and other sources before taking a decision to purchase a product.
4. Encourages sale of inferior product:
Advertising does not distinguish between superior and inferior products. Hence, it persuades people to buy even inferior products.
But, superiority and inferiority depends on the quality, which is a relative concept. The desired level of quality also depends on the economic status and preferences of the target customers. Hence, advertisements are not solely responsible for the sale of inferior products.
5. Some advertisements are in bad taste:
Another Criticism against advertising is that some advertisements are in bad taste. These show something which is not approved generally by people some advertisement also distort the human relationships.
There can be some chances of misuse of adverting as a tool, which can be properly safeguarded by the low or by developing a code of conduct by the advertisers, for their self regulation.
Conclusion:
Most of the Criticism against advertising are not entirely true. In the changed are economic environment of globalization, advertising is considered as an important tool of marketing. It helps a firm in effectively communicating with its target market, increasing the sale and there by reducing the per-unit cost of production.
It is not a social waste it adds value to the social cause by increasing production and generating more employment opportunities. Hence, advertising is a use and not a waste.
SECTION – E
V. Answer any two of the following questions.
Each question carrier five marks: (2 × 5 = 10)
Question 41.
As a general manager, list out any ten Fayol’s Principles of Management which you would like to adopt in your business organization.
Answer:
- Division of work
- Authority and responsibility
- Discipline
- Unity of Command
- Unity of Direction
- Subordination of individual interest to general interest.
- Remuneration of Employees
- Centralisation and Decentralisation
- Scalar Principle
- Order.
Question 42.
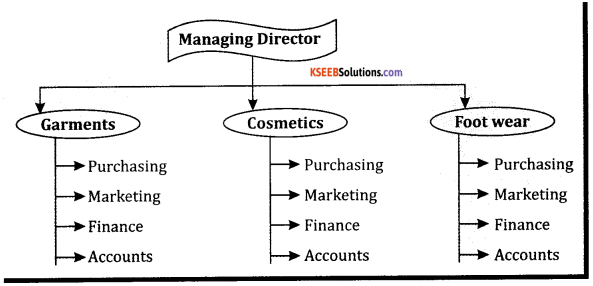
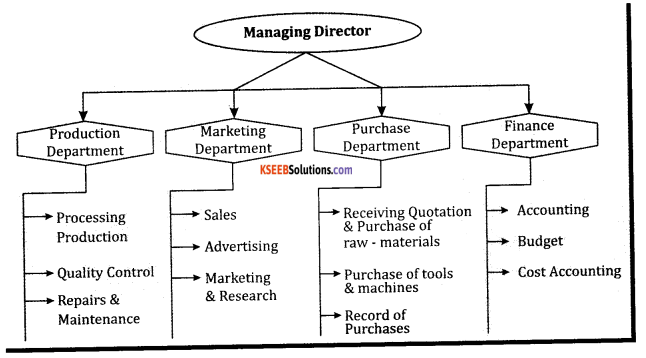
Draw the organisation Chart showing Divisional and Functional Structure.
Answer:
Divisional Chart of an Organisation
Functional Chart of an Organisation
![]()
Question 43.
As a Financial Consultant, give the list of any ten factors which affect the choice of Capital Structure.
Answer:
List of factors that affects the choice of Capital Structure
- Cash flow position
- Interest Coverage Ratio
- Debt Service Coverage Ratio
- Return on Investment
- Cost of debt
- Tax rate
- Cost of Equity
- Flotation Costs
- Risk Considerations
- Flexibility