You can Download Chapter 13 Entrepreneurship Development Questions and Answers, Notes, 2nd PUC Business Studies Question Bank with Answers Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Question Bank Chapter 13 Entrepreneurship Development
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development Text Book Exercises
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development Multiple Choice Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Entrepreneurs undertake
(a) Calculated risks
(b) high risks
(c) Low risks
(d) moderate and calculated risks
Answer:
(b) It is generally believed that entrepreneurs take high risks as there is no assured career 10 that and secondly for a higher return the person takes higher risk.
Question 2.
In Economics, which of the following is not a function of the entrepreneur?
(a) Risk-taking
(b) Provision of capital and organisation of production
(c) Innovation
(d) Day-to-day conduct of business
Answer:
(d) Day-to-day conduct of business is not the function of the entrepreneur.
Question 3.
Which of the following statements does not clearly distinguish between entrepreneurship and management?
(a) Entrepreneurs found the business; managers operate it
(b) Entrepreneurs are the owners of their businesses; managers are employees
(c) Entrepreneurs earn profits; managers earn salaries
(d) Entrepreneurship is once for all activity; management is a continuous activity
Answer:
(d) Entrepreneurship is once for all activity, The concept behind this is not clear. Through this point, it is difficult to understand the difference between entrepreneurship and management.
Question 4.
In the roles and functions of the entrepreneur identified by Kilby, which of the following is not an aspect of ’political administration’?
(a) Dealing with public bureaucracy
(b) Managing human relations within the firm
(c) Introducing new production techniques and products
(d) Managing customer and supplier relations
Answer:
(c) Introducing new production techniques and products is not an aspect of political administration. It is come under the ‘Technology’ identified by Kilby.
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following attitudes is not generally associated with successful entrepreneurship?
(a) Investing in R&D
(b) Live your business day-by-day
(c) Innovate and improvise continually
(d) Produce as per customers’requirements
Answer:
(b) Live your business day-by-day is not the attitude associated with successful entrepreneurship.
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development Short Answer Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Clarify the meaning of the terms ‘entrepreneur’, ‘entrepreneurship’ and ‘enterprise’.
Answer:
Entrepreneur: The owner of a business is known as Entrepreneur or we can say that the person who set-up a business. That person is the co-ordinator, organiser of resources and gives shape to the business.
Entrepreneurship: It is the dynamic process of interaction between the person and the environment. It means starting up one’s own business, concerned with strategic decisions of resource allocation and involves huge risk to create value and earn profit.
Enterprise: The output of the entrepreneurship process is known as the Enterprise. It is something attempted to be performed. It provides employment opportunities, professional opportunities and business opportunities which helps in building up the economy of a nation.

Question 2.
Why is entrepreneurship regarded as a creative activity?
Answer:
Entrepreneurship is a creative activity. As an entrepreneur converts raw materials into useful goods and services, it involves creation of value, introduction of new products, discovery of new markets and technologies. Successful entrepreneurs keep focusing on innovative ideas and skills to produce efficient and effective results. Thus, an entrepreneur is innovator and this process is creative.
Question 3.
Entrepreneurs undertake ‘moderate risk’. Elaborate this statement.
Answer:
Entrepreneurs undertake ‘moderate risks’. It implies that an entrepreneur assures various supply of the projects, agrees to pay salaries, wages, rent whether the venture success or not. Secondly, the person who opted a career in entrepreneurship takes a bigger risk as there is no assured payoff. It is said that it is a 50 : 50 situation means loss and profit both are unpredictable.
Success depends upon the observations, calculations of risk, skills and confidence. Risk is not centred to one problem. It involves many issues like fluctuation in price, taste and preference fashion, risk of strikes, lock outs etc. It becomes the essential feature of the entrepreneurship which is to be focused more and more.
![]()
Question 4.
How does entrepreneurship result in increasing the spectrum and scope of economic activities?
Answer:
Development does not mean only the betterment of existing but it means the overall betterment across the geographical, sectoral and technological scope. Entrepreneurship results in diversification of economic activities by creating employment, business opportunities, stabilising the demand and supply factors as underdeveloped countries caught in the vicious cycle of the demand as well as supply side.
Thus, it helps to overcome from this situation. GOP originates from Industry and services increases. Entrepreneurs through their decisions to divert from the stale sectors and invest in green field sectors, bring a virtual transformation of the economy from underdeveloped to developed status. Thus, we can say entrepreneurship results in increasing the spectrum and scope of economic activities.
Question 5.
Describe briefly the role of achievement motivation in entrepreneurship.
Answer:
Entrepreneurial motivation is important to learn, as different individuals are motivated differ-ently and for the success of an enterprise. The following needs are to be focused to motivate an entrepreneur
1. Need for Achievement: It implies a desire to accomplish something. In order to ac-complish the task, one can use the creativity, talent, organise physical resources, explore and use opportunities, overcome from the obstacles and attain a high standard.
2. Need for Power: It is the concern with influencing people or the behaviour of others moving in the same direction to attain the objectives. Need for power means authority required to control the activities of an enterprise.
3. Need for Affiliation, people to conform: It implies among other things, a tendency of the to the wishes and norms of those whom they value. Entrepreneurs are believed to be Iowan affiliation buy they should focus and trace the elements of affiliation for the successful career and for the development of standardised goods and services for others.
4. Need for Autonomy: It means a desire for independence and being responsible and accountable to oneself rather than some external authority for performance-: Everybody needs freedom to some extent as it is very difficult to take orders and work all the time as per the boss.
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development Long Answer Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Describe briefly the steps involved in starting a new business.
Answer:
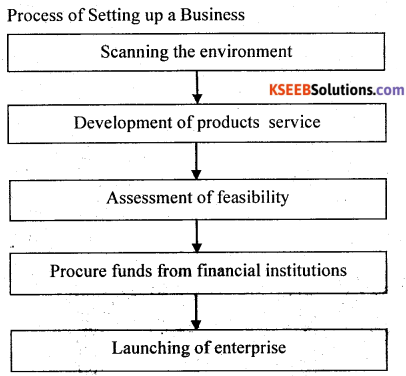
Setting up and running of business unit is a very crucial decision which is taken by an entrepreneur. They perform several functions like assembling inputs, market analysis, sales strategy, risk factors financial analysis and many more. But in order to start a new business following steps are to be taken
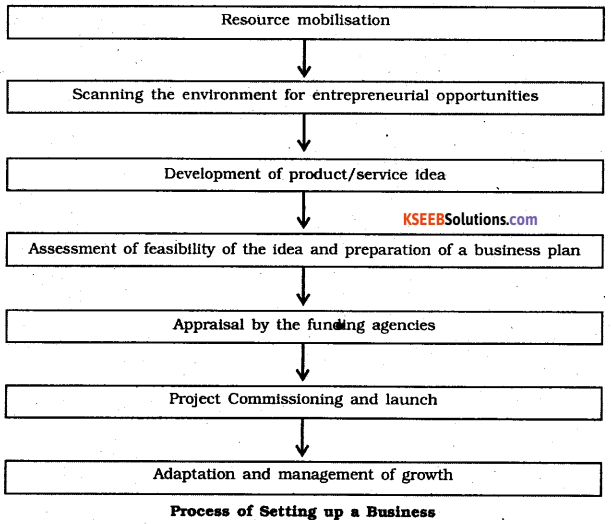
1. Scanning the Environment: The complete awareness and understanding of business environment Is known as Environment scanning An entrepreneur scan business opportunities and risks involved. After the analysis, they use these opportunities and market them in a much better way.
2. Development of Product: It is the second step after scanning the environment, an entrepreneur starts assessing scarce resources, assembling inputs and starts the production of goods and services.
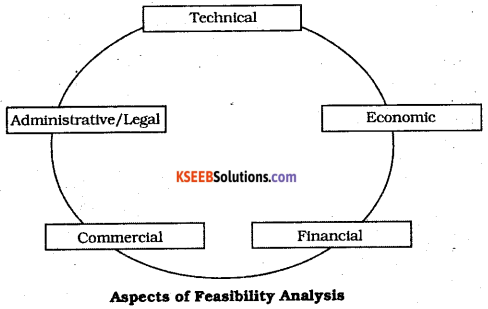
3. Feasibility Analysis: It refers to the analysis which helps in knowing the practical possibility. An entrepreneur starts looking at the feasibility like technical feasibility. This helps in knowing that the idea should be converted into reality using available technology, Similarly, economic feasibility helps in knowing the cost involved in production and after selling whether it will earn profit or not. The business plan starts after the feasibility report.
4. Funding Agencies: Finance is the backbone for the business activity. An entrepreneur needs finance to carry on the business that is why they prepare business plan which is to be submitted before the financial institutions and if satisfied they fund the project.
5. Establishing an Enterprise: After getting the fund, an entrepreneur have to take legal permission and clearance from various agencies in order to establish an enterprise.
![]()
Question 2.
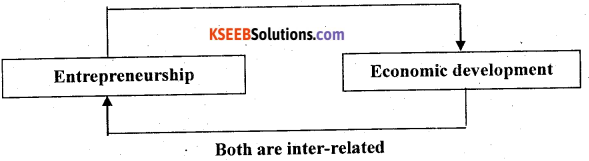
Examine the nature of relationship between entrepreneurship and economic development.
Answer:
There is a mutual relationship between economic development and entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship development leads to economic development of the country fey contributing in GOP and process of economic development which gives an opportunity for expansion and growth. Following points explain the relationship between economic development and entrepreneurship
1. Contfdarting to Gross Domestic Product (GOP): Income is generated in the process of production. Entrepreneurs generate income via organisation of production, it results in incwMttteg the value of GOPdirecdy
2. Capital Formation: Entrepreneurs use their own funds and encourage various investment opportunities to invest in companies. This leads to capital formation.
3. Generation of Employment: Every new business gives the opportunity of employment to the people with different abilities, skills and qualifications. It becomes a source of livelihood to those who neither have the capital to earn interest nor have the land to earn rent.
4. Improves Economic Efficiency Entrepreneurs improve economic efficiency by improving the process, reducing waste, increasing yield and bringing in technical progress. In this way, entrepreneurship results in economic development. On the other hand, economic development provides following opportunities for the growth and expansion of enterprise.
(a) Well developed financial in the economy
(b) Opportunities to raise and avail funds from various financial institutions.
(c) Lower rate of interest and moderate inflation.
(d) Availability of factors of production. ‘
Question 3.
Clarify how motivation and abilities impact on individuals decision to choose entre-preneurship as a career.
Answer:
Motivation and ability can positively reinforce each other. Persons having abilities search for the exposure and focus to start a new business. They take decisions logically with the personal courage and strive hard to acquire the necessary competencies to realise their dreams. Following competencies contribute towards effective performance and success
- Entrepreneur must take initiative to set up an enterprise.
- Recognise the opportunities and grab them as early as possible.
- Must strive for success.
- They must collect important informations.
- Entrepreneurs must set up quality standards.
- Must be committed towards the completion of task.
- Concern for conservation of time, money and effort.
- Entrepreneurs must have the ability to do product planning.
- Must have the ability to diagnose the problems and take required steps to solve them.
- Entrepreneurs must be confident.
- Conveying one’s vision and convincing others of its values.
- They seek the support of others.
- Provide leadership.
- Ensuring the progress of venture,
- Concern for employee’s welfare.
On the other hand, motivation is required to understand because entrepreneur’s objective is profit maximisation and it can only be achieved when employees are motivated in such a manner that fulfillment of enterprise’s objective may also lead to satisfy employees basic needs. In this way, entrepreneurship career proves to be a success for an individual motivation and ability both goes hand to hand.
![]()
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development Application Question
Anshuman was a very industrious sales executive with a small herbal cosmetic manufacturer. He earned a good salary and commission on the business he brought for the firm and had very good command over the Delhi market for which he had virtually become indispensable. He was aware of the enviable position he held in the firm and thought aloud “The key to success in any business is the sale of its products. The beginning and end of the business cycle is nothing but sale and ‘other* people working in the factory to manufacture products are mere cogs in the business machine set in motion by sales people. So, why carry this burden and get only a tiny share of the prosperity of the firm? Instead others enjoying the fruits of my labour,
Question 1
why should I not start my own business?” Should Anshuman take a leap? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Anshuman was a good industrious sales executive with a small herbal cosmetics. As per my opinion, Yes, he should start his own business as he is experienced, has a very good command over the market. He can market the products very well, maintain good relations with customers. He is good in marketing management. Thus, he can produce goods as per the customers’ needs, use effective promotional techniques and take care of customers.
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development Case Problems Studies
Inspiring Feat: Daily wage Labourer turns Entrepreneur
A landless woman from Bihar has been nominated among the top 25 farmers in Asia by a Mexican website.
Forty five years old Lalmuni Devi was a daily wage labourer when she decided to take destiny into her own hands and transformed herself into a successful mushroom farmer. Today she manages to make Rs. 12,000 every year for an investment of only Rs 600.
Her feat finds mention on a Mexican website that has grouped her as the top 25 inspirational farmers in its photo gallery.
“1 am a poor woman. I thought that mushroom farming would profit henceforth I started it. Now, I can earn a living for my family”, said Lalmuni Devi.
Successful Enterprise
The success story has caught on with many women in the Azadpur village on the outskirts of Patna.
“It is effortless farming, which we can even do in our village. Working in the scorching heat is very tiring. Mushroom farming generates more profit”, said Urmila Devi.
Lalmuni and other landless women have been encouraged by the Indian Council for Agriculture Research to take up mushroom farming.
It is to help the poorest of the poor through alternative livelihood support system. For that we have chosen a village where people have no land and they have to share croppers”, said Dr AR Khan, Principal Scientist, ICAR,Patna.
Lalmuni’s efforts have paved the way for many other landless women to take up mushroom farming and earn a livelihood for their family with little effort.
Question 1.
What inspiring feat did Lalmuni Devi perform? Elaborate.
Answer:
A forty five years old woman Lalmuni Devi from Bihar was a daily wage labourer, then she decided to transform herself by starting mushroom farming. This step proved an inspirational feat and she was among the top 25 farmers in Asia by a Mexican website.
Question 2.
Do you feel that you can also become an entrepreneur?
Answer:
Lalmuni efforts have paved the way for others. Similarly, we can also become an entrepreneur and for that we should have following qualities
- Initiate the business
- Grab the opportunities
- High quality work
- Have a concern for employee’s welfare
- Risk taking abilities
Question 3.
What qualities of entrepreneur did Lalmuni Devi exhibit?
Answer:
In the given case, Lalmuni have following qualities v
- She decided to transform herself into an entrepreneur,
- She recognised the opportunity and grabbed it.
- She managed her activities efficiently and effectively.
- She was a chaser and faced the difficulties calmly.
- She was self confident.
- She took the required steps to solve the problems.
Question 4.
What are the benefits and risks of becoming an Entrepreneur? How can you guard against the risks? What (Teachers should highlight the qualities of an entrepreneur and motivate students to do so. Help that.
Answer:
Benefits of an entrepreneur
- They are the owner of the business,
- No worries of job, compensation and reward
- They earn profit.
- They have full authority to take decisions.
Risks of an Entrepreneur
- Market risk
- Financial risk
- Risk in product planning
- Risk of Innovative technologies
In order to safeguard from the risk, an entrepreneur should analyse the market well, study about the innovative technologies, prepare the business plan so that financial institutions grant the fund, adopt the best ideas for product planning.
![]()
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development Additional Questions
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is Entrepreneurship?
Answer:
Entrepreneurship is the process of setting up one’s own business as distinct from pursuing any other economic activity.
Question 2.
What is need for achievement (N-Ach.).
Answer:
Need for Achievement (N-Ach.): Need for achievement implies a desire to accomplish something difficult. To master, manipulate, or organise physical objects, human beings or ideas.
Question 3.
Write a need for power (N-Pow).
Answer:
Need for Power (N-Pow): Need for Power is the concern for influencing people or the behaviour of others for moving in the chosen direction and attaining the envisioned objectives.
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development Two Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write a note as entrepreneural values and attitudes.
Answer:
While explaining human behaviour, one often comes across the terms values and attitudes. Rather than attempting to distinguish between these two terms, it would be sufficient to say here that taken together, entrepreneurial values and attitudes refer to the behavioural choices individuals make for success in entrepreneurship.
The word choice is important, as there are alternative ways of behaving too. In entrepreneurship, a host of behavioural tendencies or orientations have been reported as having a bearing on success.
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development Four Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the concept of Entrepreneurship.
Answer:
The concept of entrepreneurship: entrepreneurship is regarded as one of the four major factors of production, the other three being land, labour and capital. It is derived from French origin, the term ‘entrepreneurship’ (derived from the word ‘entreprende’ meaning ‘to undertake’) pertained not to economics, but to undertaking of military expeditions. So is true of many terms in management (a course of action to beat the competition, the ‘enemy’) and logistics The term ‘entrepreneur’ was first introduced in economics by the early 18th century French economist Richard Cantillon.
He defined the entrepreneur as the “agent who buys means of production at certain prices in order to sell the produce at uncertain prices in the future”In abroader sense it can define entrepreneurship as a systematic, purposeful and creative activity of identifying a need, mobilising resources and organising production with a view to delivering value to the customers, returns for the investors and profits for the self in accordance with the risks and uncertainties associated with business.
Question 2.
Explain the characteristics of entrepreneurship.
Answer:
Characteristics of entrepreneurship :
1. Systematic Activity: Entrepreneurship is a systematic, step-by-step and purposeful activity. It has certain temperamental, skill and other knowledge and competency requirements that can be acquired, learnt and developed, both by formal educational and vocational training as well as by observation and work experience.
2. Lawful and Purposeful Activity: The object of entrepreneurship is lawful business.
3. Innovation: From the point of view of the firm, innovation may be cost saving or revenue enhancing, Entrepreneurship is creative in the sense that it involves creation of value.
4. Organisation of Production: Production, implying creation of form, place, time personal utility, requires the combined utilisation of diverse factors of production, land, labour, capital and technology. Entrepreneur, in response to a perceived business opportunity mobilises these resources into a productive enterprise or firm.
5. Risk-taking: As the entrepreneur contracts for an assured supply of the various inputs for his project, the risk of paying them off whether or not the venture succeeds.
It is generally believed that entrepreneurs take high risks.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the Functions of enterepreneurs.
Answer:
Functions of enterepreneurs in relation to economic development.
1. Contribution to GDP: Increase in the Gross Domestic Product or GDP is the most common definition of economic development.
2. Capital Formation: The entrepreneurial decision, in effect, is an investment decision that augments the productive capacity of the economy and hence results in capital formation.
3. Generation of Employment: Every new business is a source of employment to people with different abilities, skills and qualifications. As such entrepreneurship becomes a source of employees.
4. Generation of Business Opportunities for Others: Every new business creates . opportunities for the suppliers of inputs (this is referred to as backward linkages) and the marketers of the output.
5. Improvement in Economic Efficiency: You are aware that efficiency means to have greater output’ from the same input. Entrepreneurs improve economic efficiency by,
a. Improving processes, reducing wastes, increasing yield ,and,
b. Bringing about technical progress, that is, by altering labour-capital ratios.
6. Increasing the Spectrum and Scope of Economic Activities: Development does not merely mean ‘more’ and ‘better’ of the existing, it also and more crucially means diversification of economic activities- across the geographic, sectoral and technological scope.
7. Impact on Local Communities: Entrepreneurship, in its natural habitat, that is, small business is a great leveler. As there are no entry barriers in terms of educational qualifications, entrepreneurship is an even more attractive career option for such marginalised groups.
8. Fostering the Spirit of Exploration, Experimentation and Daring: Economic development, among other things, requires breaking away from the shackles of traditions and beliefs that restrict growth.
Question 4.
Explain Role of entrepreneurs in relation to their enterprise.
Answer:
Role of entrepreneurs in relation to their enterprise. Opportunity Scouting: Entrepreneurial opportunities have to be actively searched for. One may rely on personal observation, discovery or invention. Personal/professional contacts/ networks and experience or may also help in identifying business opportunities.
Identification of Specific Product Offering: While the environment scan leads to the discovery of more generalised business opportunities, there is a need to zero in on to a specific product or service idea.
Feasibility Analysis: The product offering idea must be technically feasible, that is it should be possible with the available technology to convert the idea into a reality.
Question 5.
Explain the process of entrepreneurship development.
Answer:
The process of entrepreneurship development:
Question 6.
Explain the process of business plan.
Answer:
- Executive Summary
- Business/industry background
- Product/service to be offered
- Market Analysis
- Sales and marketing strategy
- Production / operations strategy
- Management
- Risk factors.
- Funds required
- Return on and off investments and exit routes
- Use of the sales proceeds
- Financial summaries
- Appendices, e.g., Reports on Market Survey
Financial Statements, Track Record etc.
![]()
2nd PUC Business Studies Entrepreneurship Development Eight Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write a note as Entrepreneural Competecies.
Answer:
Every opportunity and successful performance of every role and function has a competence requirement. Its true of entrepreneurship as well, entitled ‘Cash OR KASH?’
The term ‘competence’ refers to a composite of knowledge, skills and a host of psychosocial attributes in a person that mark his/her effectiveness for a task. The phrase ‘composite’ is crucial.
EDI has identified a set of 15 competencies that contribute toward entrepreneurial performance and success. These are briefly stated hereunder.
- Initiative: Acting out of choice rather than compulsion, taking the lead rather than waiting for others to start.
- Sees and Acts on Opportunities: A mindset where one is trained to look for business opportunities from everyday experiences. Recall ‘oranges’ example.
- Persistence: A ‘never say die’ attitude, not giving up easily, striving continuously until success is achieved.
- Information seeking: Knowing and knowing who knows, consulting experts, reading relevant material and an overall openness to ideas and information.
- Concern for High Quality of Work: Attention to details and observance of established standards and norms.
- Commitment to Work Contract: Taking personal pains to complete a task as scheduled.
- Efficiency Orientation: Concern for conservation of time, money and effort.
- Systematic Planning: Breaking up the complex whole into parts, close examination of the parts and inferring about the whole.
- Problem-solving: Observing the symptoms, diagnosing and curing.
- Self-confidence: Not being afraid of the risks associated with business and relying on one’s capabilities to successfully manage these.
- Assertiveness: Conveying emphatically one’s vision and convincing others of its value.
- Persuasion: Eliciting support of others in the venture.
- Use of Influence Strategies: Providing leadership.
- Monitoring: Ensuring the progress of the venture as planned.
- Concern for Employee Welfare: Believing in employee well being as the key to competitiveness and success and initiating programmes of employee welfare.
Question 5.
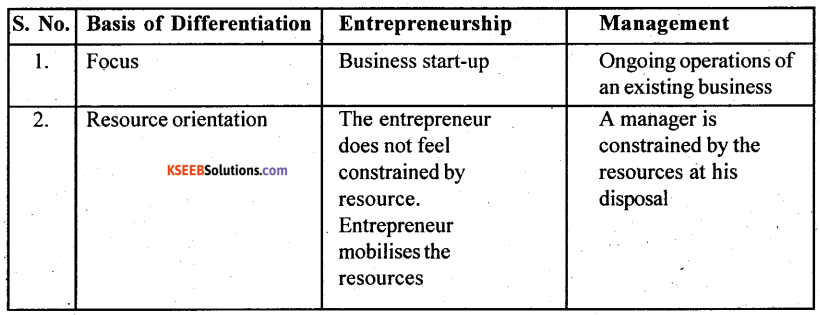
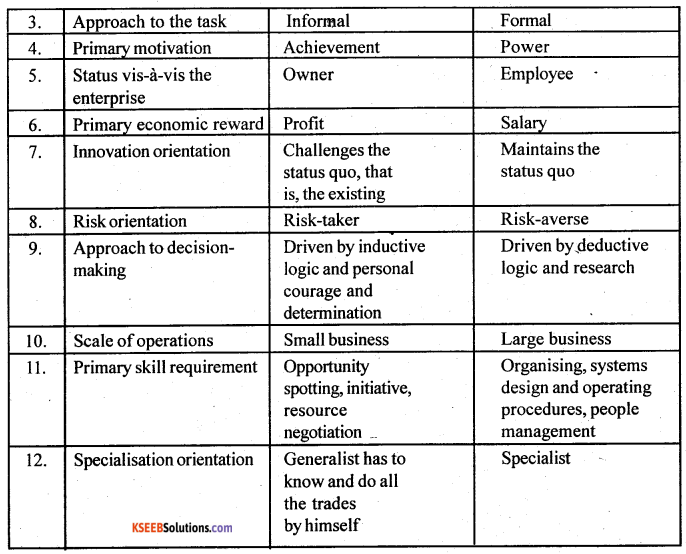
Differences enterpreruship and manageent.
Answer: