You can Download Chapter 9 Financial Management Questions and Answers, Notes, 2nd PUC Business Studies Question Bank with Answers Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Question Bank Chapter 9 Financial Management
2nd PUC Business Studies Financial Management Text Book Exercises
2nd PUC Business Studies Financial Management Objective-Type Questions With Answers
Question 1.
The cheapest source of finance is
(a) debenture
(b) equity share capital
(c) preference share
(d) retained earning
Answer:
(d) Retained earning is the cheapest source of finance.
Question 2.
A decision to acquire a new and modem plant to upgrade an old one is a
(a) financing decision
(b) working capital decision
(c) investment decision
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Investment decision is related to careful selection of assets in which funds will be Invested by firms. Thus, the above case comes under the investment decision.
Question 3.
Other things remaining the same, an increase in the tax rate on corporate profits will
(a) make debt relatively cheaper
(b) make the debt relatively the dearer
(c) have no impact on the cost of debt
(d) we can’t say
Answer:
(a) If the tax rate on corporate profits are increased, it makes debt relatively cheaper
Question 4.
Companies with higher growth pattern are likely to
(a) pay lower dividends
(b) pay higher dividends
(c) dividends are not affected by growth considerations
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Companies who are having a higher growth pattern are likely to pay lower dividends.
Question 5.
Financial leverage is called favourable if
(a) return on investment is lower than the cost of debt
(b) return on investment is higher than the cost of debt
(c ) debt is easily available
(d) if the degree of existing financial leverage is low
Answer:
(b) If ROI is higher than cost of debt, financial leverage in that case is called favourable.
![]()
Question 6.
Higher debt equity ratio ( Debt/Equity ) results in
(a) lower financial risk
(b) higher degree of operating risk
(c) higher degree of financial risk
(d) higher EPS
Answer:
(c) Higher debt equity ratio results in higher degree of financial risk.
Question 7.
Higher working capital usually results in
(a) higher current ratio. higher risk and higher profits
(b) lower current ratio, higher risk and profits.
(c) higher equity, lower risk and lower profits
(d) lower equitably, lower risk and higher profits
Answer:
(a) If the working capital is higher, it results in higher current ratio, higher risk and higher profits.
Question 8.
Current assets are those assets which get converted into cash
(a) within six months
(b) within one year
(c) between one and three years
(d) between three and five years
Answer:
(b) Current assets are those assets which are converted into cash within one year.
Question 9.
Financial planning arrives at
(a) minimising the external borrowing by resorting to equity issues
(b) ensuring that the firm always have significantly more fund than required so that there is no paucity of funds
(c) ensuring that the firm faces neither a shortage nor a glut of unusable funds
(d) doing only what is possible with the funds that the firm has at its disposal
Answer:
(c) Financial planning means deciding how much to spend and on what to spend it ensuring that the firm faces neither a shortage nor a glut of unusable funds.
Question 10.
Higher dividend per share is associated with
(a) high earnings, high cash flows, unstable earnings and higher growth opportunities
(b) high earnings, high cash flows, stable earnings and high growth opportunities
(c) high earnings, high cash flows, stable earnings and lower growth opportunities
(d) high earnings, low cash flows, stable earnings and lower growth opportunities
Answer:
(c) Higher dividend per share includes high earnings, high cash flows, stable earning and lower growth opportunities.
Question 11.
A fixed asset should be financed through
(a) a long term liability
(b) a short term liability
(c) a mix of long and short term liabilities
(d) Not given
Answer:
(a) Fixed assets financed through longterm liability.
Question 12.
Current assets of a business firm should be financed through
(a) current liability only
(b) longterm liability only
(c) both types (i.e., long and short term liabilities)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Current assets are financed through both long and short term liabilities.
2nd PUC Business Studies Financial Management Short Answer Questions With Answers
Question 1.
What is meant by capital structure?
Answer:
Capital structure refers to the mix between owners personal and borrowed funds. It represents the proportion of equity’ and debt.
Capital Structure = (Debt/Equity)
Question 2.
Discuss the two objectives of Financial Planning.
Answer:
Financial Planning strives to achieve the following two objectives
1. To ensure availability of funds whenever these are required: This includes a proper estimation of the funds required for different purposes such as for the purchase of long term assets or to meet day-to-day expenses of business etc.
2. To see that the firm does not raise resources unnecessarily: Excess funding is almost as bad as Inadequate funding. Efficient financial planning ensures that funds are not raised unnecessarily in order to avoid unnecessary addition of cost.
Question 3.
What is ’financial risk’? Why does it arise?
Answer:
It refers to the risk of company not being able to cover its fixed financial costs. The higher level of risks are attached to higher degrees of financial leverage. With the increase in fixed financial costs, the company is also required to raise its operating profit (EBIT) to meet financial charges. If the company cannot cover these financial charges, it can be forced into liquidation.
Question 4.
Define ‘current assets’ and give four examples.
Answer:
Current assets are those assets of the business which can be converted into cash within a period of one year. Cash in hand or at bank, bills receivables, debtors, finished goods inventory are some of the examples of current assets.
![]()
Question 5.
Financial management is based on three broad financial decisions. What are these?
Answer:
Financial management is concerned with the’solution of three major issues relating to the financial operations of a firm corresponding to the three questions of Investment, Financing and Dividend decision. In a financial context, it means the selection of best financing alternative or best investment alternative. The finance function therefore, is concerned with three broad decisions which are as follows
1. Investment Decision: The investment decision relates to how the firm’s funds are invested in different assets.
2. Financing Decisions: This decision is about the quantum of finance to be raised from various long term sources and short term sources. It involves identification of various available sources of finance.
3. Dividend Decision: This decision relates to distribution of dividend.
Dividend is that portion of profit which is distributed to shareholders. The decision involved here is how much of the profit earned by company is to be distributed to the shareholders and how much of it should be retained in the business for meeting investment requirements.
Question 6.
What is the main objective of financial management? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Primary aim of financial management is to maximise shareholders’ wealth, which is referred to as the wealth maximisation concept. The wealth of owners is reflected in the market value of shares. Wealth maximisation means the maximisation of market price of shares.
According to the wealth maximisation objective, financial management must select those decisions which result in value addition, that is to say the benefits from a decision exceed the cost involved. Such value additions increase the market value of the company’s shares and hence result in maximisation of the shareholders’ wealth.
Question 7.
Discuss about working capital affecting both the liquidity as well as profitability of a business.
Answer:
The working capital should neither be more nor less than required. Both these situations are harmful. If the amount of working capital is more than required, it will no doubt increase liquidity but decrease profitability. For instance, if a large amount of cash is kept as working capital, then this excessive cash will remain idle and cause the profitability to fall.
On the contrary, if the amount of cash and other current assets are very little, then lot of difficulties will have to be faced in meeting daily expenses and making payment to the creditors. Thus, optimum amount of both current assets and current liabilities should be determined so that profitability of the business remains intact and there is no fall in liquidity.
2nd PUC Business Studies Financial Management Long Answer Questions With Answers
Question 1.
What is working capital? How is it calculated? Discus five important determinants of working capital requirement.
Answer:
Working capital is that part of total capital which is required to meet day-to-day expenses, to buy raw materials, to pay wages and other expenses of routine nature in the production process or we can say it refers to excess of current assets over current liabilities.
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
Factors affecting working capital requirement are. the following :
1. Nature of business: The basic nature of a business influences the amount of working capital required. A trading organisation usually needs a lower amount of working capital compared to a manufacturing organisation. This is because in trading, there is no processing required. In a manufacturing business, however, raw materials need to be converted into finished goods, which increases the expenditure on raw material, labour and other expenses.
2. Scale of operation: For firms which are operating on a higher scale of operations, the quantum of inventory, debtors required is generally high. Such organisations, therefore, require large amount of working capital as compared to the organisations which operate on a lower scale.
3. Production Cycle: Production cycle is the time span between the receipts of raw materials and their conversion into finished goods. Some businesses have a longer production cycle while some have a shorter one. Working capital requirement is higher in firms with longer processing cycle and lower in firms with shorter processing cycle.
4. Credit Allowed: Different firms allow different credit terms to their customers. A liberal credit policy results in higher amount of debtors, increasing the requirements of working capital.
5. Credit Availed: Just as a firm allows credit to its customers it also may get credit from its suppliers. The more credit a firm avails on its purchases, the working capital requirement is reduced.
![]()
Question 2.
Capital structure decision is essentially optimisation of risk-return relationship. Comment.
Answer:
Capital structure refers to the mix between owners and borrowed funds. It can be calculated as (Debt/Equity).
Debt and equity differ significantly in their cost and riskiness for the firm. Cost of debt is lower than cost of equity for a firm because lender’s risk is lower than equity shareholder’s risk, since lenders earn on assured return and repayment of capital and therefore they should require a lower rate of return.
Debt is cheaper but is more risky for a business because payment of interest and the return of principal is obligatory for the business. Any default in meeting these commitments may force the business to go into liquidation. There is no such compulsion in case of equity’, which is therefore, considered riskless for the business. Higher use of debt increases the fixed financial charges of a business. As a result increased, use of debt increases the financial risk of a business.
Capital structure of a business thus, affects both the profitability and the financial risk. A capital structure will be said to be optimal when the proportion of debt and equity is such that it results in an increase in the value of the equity share.
Question 3.
A capital budgeting decision is capable of changing the financial fortune of a business. Do you agree? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Investment decision can be long term or short term. A long term investment decision is also called a capita! budgeting decision. It involves committing the finance on a long term basis, e.g., making investment in a new machine to replace an existing one or acquiring new fixed assets or opening a new branch etc. These decisions are very crucial for any business. They affect its earning capacity over the long-run.
Assets of a firm, profitability and competitiveness, are all affected by the capital budgeting decisions. Moreover, these decisions normally involve huge amounts of investment and are irreversible except at a huge cost. Therefore, once made, it is almost impossible for a business to wriggle out of such decisions. Therefore, they need to be taken with utmost care. These decisions must be taken by those who understand them comprehensively.
A bad capital budgeting decision normally has the capacity to severely damage the financial fortune of a business.
Question 4.
Explain the factors affecting the dividend decision.
Answer:
Dividend decision relates to distribution of profit to the shareholders and its retention in the business for meeting the future investment requirements.
How much of the profits earned by a company will be distributed as profit and how much will be retained in the business is affected by many factors. Some of the important factors are discussed below.
1. Earnings: Dividends are paid out of current and past year earnings. Therefore, earnings is a major determinant of the decision about dividend.
2. Stability of earnings: Other things remaining the same, a company having stable earning is in a position to declare higher dividends. As against this, a company having unstable earnings is likely to pay a smaller dividend.
3. Growth opportunities: Companies having good growth opportunities retain more money out of their earnings so as to finance the required investment. The dividend in growth companies, is therefore, smaller than that in non-growth companies.
4. Cash flow position: Dividends involve an outflow of cash. A company may be profitable but short on cash. Availability of enough cash in the company is necessary for declaration of dividend by it.
5. Shareholder Preference: If the shareholders in general desire that at least a certain amount should be paid as dividend, the companies are likely to declare the same.
6. Taxation Policy: If tax on dividend is higher it would be better to pay less by way of dividends. As compared to this, higher dividends may be declared if tax rates are relatively lower.
7. Stock Market reaction: For investors, an increase in dividend is a good news and stock prices react positively to it. Similarly a decrease in dividend may have a negative impact on the share prices in the stock market.
8. Access to Capital Market: Large and reputed companies generally have easy access to the capital market and therefore, depend less on retained earnings to finance their growth. These companies tend to pay higher dividends than the smaller companies which have relatively low access to the market.
9. Legal constraints: Certain provisions of the Company’s Act place restrictions on payouts as dividend. Such provisions have to be adhered to, while declaring dividends.
10 Contractual Constraints: While granting loans to a company, sometimes the lender may impose certain restrictions on the payment of dividends in future The companies are required to ensure that the dividends do not violate the terms and conditions of the loan agreement in this regard.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the term ‘Trading on Equity’. Why, when and how it can used by a company?
Answer:
Trading on equity refers to the Increase in profit earned by the equity shareholders due to presence of fixed financial charges. When the rate of earning or Return on Investment (ROI) of a company is higher than the rate of interest on borrowed funds, only then a company should opt for trading on equity. Let us consider the following example.
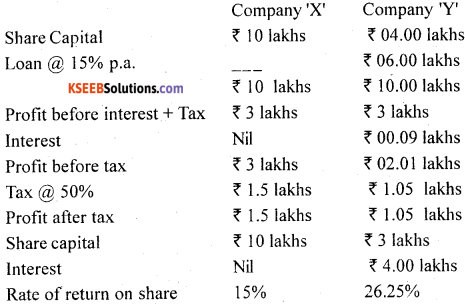
It should be clear from the above example that shareholders of the company ‘X have a higher rate of return than company ‘Y’, due to loan component in the total capital of the company.
2nd PUC Business Studies Financial Management Case Problems
’S’ Limited is manufacturing steel at its plant in India. It is enjoying a buoyant demand for its products as economic growth is about 7% – 8% and the deniand for steel is growing. It is planning to set up a new steel plant to cash on the increased demand it is facing. It is estimated that it will require about ? 5,000 crores to set up and about. ? 500 crores of working capital to start the new plant.
Question 1.
Describe the role and objectives of financial management for this company.
Answer:
Role of Financial Management Financial management is concerned with the proper management of funds. It involves the followin.
- Managerial decisions relating to procurement of long term and short term funds
- Keeping the risk associated with respect to procured funds under control.
- Utilisation of funds in the most productive and effective manner .
- Fixed debt equity ratio and capital.
Objective of Financial Management:
The objective of financial management is maximisation of shareholders’ wealth The investment decision, financial decision and dividend decision help an organisation to achieve its objective In the given situation, S limited envisages growth prospects of steel Industry due to the growing demand. To expand the production capacity, the company needs to invest.
How ever, investment decision will depend on the availability of funds, the financing decision and the dividend decision. However, the company will take those financial decisions which result in value addition. The benefits are more than the cost. This leads to an increase in the market value of the shares of the company.
Question 2.
Explain the importance of having a financial plan for this company. Give an imaginary plan to support your answer.
Answer:
Importance of financial plan for the company is as under.
- Financial Planning ensures provision of adequate funds to meet working capital requirements.
- It brings about a balance between inflow and outflow of funds and ensures liquidity through out the year.
- It solves the problems of shortage and surplus of funds and ensures proper and optimum utilisation of available resources,
- It ensures increased profitability through cost benefit analyses and by avoiding wasteful operations
- It seeks to eliminate waste of funds and provides better financial control.
- It seeks to avail the benefits of trading on equity.
Financial Plan of S Ltd
Total finance required; Fixed capital = ₹ 1,000 crores
Working capital = ₹ 100 crores : Source of finance is 2:1 Ratio i.e..
50% finance collected by issue of shares and 50% by borrowed funds,
Question 3.
What are the factors which will affect the capital structure of this company?
Answer:
Capital structure refers to the proportion in which debt and equity funds are used for financing the operations of a business. A capital structure is said to be optimum when the proportion of debt and equity is such that it results in an increase in the value of shares. The factors that will affect the capital structure of this company are the following:
1. Equity Funds: The composition of equity funds in the capital structure will be governed by the following factors
(a) The requirement of funds of S Limited is for longterm. Hence, equity funds will be more appropriate
(b) There are no financial risks attached to this form of funding
(c) If the stock market is bullish, the company can easily raise funds through issue of equity shares.
(d) If the company already has raised reasonable amount of debt funds, each subsequent borrowing will come at a higher interest rate and will Increase the fixed charges.
2. Debt Funds: The usage and the ratio of debt funds in the capital structure will be governed by factors like these.
(a) The availability of cash flow with the company to meet its fixed financial charges. The purpose is to reduce the financial risk associated with such payments which can further be checked by using debt’ service coverage ratio.
(b) It will provide the benefit of trading on equity and hence will Increase the earning per share of equity shareholders. However, return on Investment ratio will be the guiding principle behind it. The company should opt for trading on equity only when return on investment is more than the fixed charges.
(c) Interest on debt funds is a deductible expense and therefore, will reduce the tax liability
(d) It does not result in dilution of management control.
Question 4.
Keeping in mind that it is a highly capital intensive sector what factors will affect the fixed and working capital ? Give reasons in support of your answer.
Answer:
The working and fixed capital requirement of’S’ Limited will be high due to the following reasons.
- The business is capital intensive and the scale of operation is large.
- Heavy investments are required for building up the production base and for technological upgradation
- In case of steel industry, the major input is iron ore and coal. The ratio of cost of raw material to total cost is very high. Hence, higher will be the need for working capital.
- The longer the operating cycle, the larger is the amount of working capital required as the funds get locked up in the production process for a long period of time.
- Terms of credit for buying and selling of goods, discount allowed to the suppliers and to the customers also determine the quantum of working capital.

2nd PUC Business Studies Financial Management Additional Questions
2nd PUC Business Studies Financial Management One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Name any one basic objective of financial marketing.
Answer:
Profit maximization.
Question 2.
What do you mean by financial decisions?
Answer:
It is concerned with mobilization of finance for the purpose of Investment
Question 3.
Name any one type of capital requirement of an organization.
Answer:
Fixed Capital or Working Capital
Question 4.
What is fixed capital?
Answer:
Fixed capital is refers to investments in long-term assets or fixed assets.
Question 5.
What is working capital?
Answer:
It refers to investments in current assets such as stock of materials, work-in-progress, finished goods, account receivables etc.
Question 6.
State any one factor affecting working capital requirement of a business concern.
Answer:
Nature of business.
Question 7.
State any one factor affecting fixed capital requirement of a business concern.
Answer:
Growth & Expansion prospects.
Question 8.
What is financial Management?
Answer:
It means effective and efficient management of money. It is concerned with planning & controlling of firms’ financial resources.
Question 9.
State any one importance of financial management.
Answer:
Estimating capital requirement. Or Capital Budgeting
Question 10.
State any one objective of financial management.
Answer:
Profit Maximization or Wealth Maximization
Question 11.
State any two importance of financial planning.
Answer:
Tool to face uncertainties, ensures liquidity’
Question 12.
Stat any two features of fixed capital.
Answer:
It is concerned with long term funds, it involves large amount of funds.
Question 13.
Mention any two features of working capital.
Answer:
It is concerned with short term funds, it involves lesser risk.
![]()
2nd PUC Business Studies Financial Management Two Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is financial management?
Answer:
It means effective and efficient management of money It is concerned with planning & controlling of firms financial resources. It mainly deals with the process of procurement and utilization of funds for the business purpose.
Question 2.
Give the meaning of investment decisions.
Answer:
Investment decisions are concerned with how firm’s funds are invested in different assets either long term or short term. The long term investment decisions are also called as Capital Budgeting Decision and the short term inv estment decisions are called as Working Capital Decisions.
Question 3.
Give the meaning of dividend decisions
Answer:
Dividend decisions are concerned with the apportionment of the’firm’s profit. Dividends are the portions of the profit which will be distributed to the share holders. The portion of profit which is undistributed to the share holders are called as retained earnings which will be utilized for expansion and development of the business.
Question 4.
Give the meaning of financing decisions.
Answer:
Financing decisions are concerned with how to raise the funds for business activities from various sources. There are two source of raising fiance to. the business they are Debt and Equity. The owner fund or share holders fund are called equity. The harrowed funds are called debts.
Question 5.
State any two factors affecting working capital requirement of a business concern,
Answer:
1. Nature of business: Trie amount of working capital required basically depends on the nature of the business. Due to the cash nature of the transactions in the business. Some business requires huge working capital and some need little working capital for their operations.
2. Scale of Operations: The requirement of working capital also depends up on the scale of operation. Small Scale needs less working capital when compared to large scale.
Question 6.
State any two factors affecting fixed capital requirement of a business concern.
Answer:
Nature of business: The amount of fixed capital requirement basically depends on the nature of the business. Some business requires huge fixed capital and some need little fixed capital depending on their operations. The need for fixed capital will be more as the concern need to invest on fixed assets like plant, machinery & Buildings etc.
Scale of operation: The scale of operation is the other important determinant of fixed capital requirement of a business. Larger the size and the scale of operations, the greater will be the amount of fixed capital requirement.
Question 7.
What is financial planning?
Answer:
Financial planning is concern with the preparation of a financial blue print of an organization for future operations. Financial planning is the process of determining the objectives, polices, procedure and program to deal with the financial activities of an organization.
Question 8.
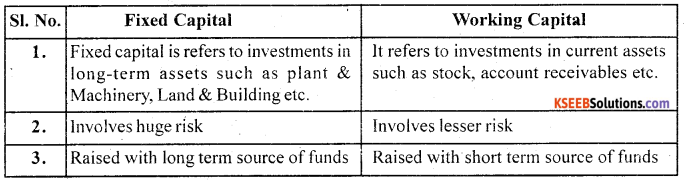
Write the difference between working capital & Fixed capital?
Answer:
![]()
2nd PUC Business Studies Financial Management Four Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Describe the importance of financial management.
Answer:
Estimating capital requirement: Financial Management makes the estimation of both short term & long term financial needs to make the smooth running of a business.
- Short Term Financial Needs: Refers to the financial requirement for a period within one year or financial required to meet day today expense.
- Long Term Financial Needs: Refers to the financial requirements for a period exceeding one year.
Capital budgeting: It refers to the long term funds. Capital can be raised in two ways either debts or Equity. Capital budgeting decides the composition of debt & equity in the long term finance of an organization.
Working capital marketing: Excess of current assets over current liabilities represents the working capital of an organization. To ensure the smooth working of an organization it should have sufficient working capital to meet the day to day needs.
Appraisal of financial performance & financial control: Financial Management provides various financials tools such as Ration analysis, Budgeting, Variance analysis. It helps the management to control the financial activities of the organization.
Making financial decision: Financial Management is concerned with financial decisions relates to the composition of assets. Capital & Investment. Sound financial decisions are made depending on risk & return.
Solution to financial problem: A good financial management helps the top management by providing financial information and also solutions to various financial problems.
Communication of financial performance: It is used to measure profitability & liquidity of the business. The various stakeholders who are keen about the financial performance of the organization are Share holders, Creditors, Investors, Economists, Employees and Government.
Question 2.
What do you mean by financial decisions? Explain in brief the types of financial decisions?
Answer:
Financial decisions are concerned with how to raise the funds for business activities from various sources. There are two source of raising fiance to the business they are Debt and Equity. The owner fund or share holders fund are called equity. The harrowed funds are called debts.
The Financial Management decisions can be broadly classified into:
1. Investment decisions: Investment decisions are concerned with how firm’s funds are invested in different assets either long term or short term. The long term investment decisions are also called as Capital Budgeting Decision and the short term investment decisions are called as Working Capital Decisions.
2. Financing decision: Financing decisions are concerned with how to raise the funds for business activities from various sources. There are two source of raising finance to the business they are Debt and Equity. The owner fund or share holders fund are called equity. The harrowed funds are called debts
3. The dividend decision: Dividend decisions are concerned with the apportionment of the firm’s profit. Dividends are the portions of the profit which will be distributed to the share holders. The portion of profit which is undistributed to the share holders are called as retained earnings which will be utilized for expansion and development of the business.
Question 3.
Explain briefly the importance of financial planning.
Answer:
Financial planning is concern with the preparation of a financial blue print of an organization’s for future operations. Financial planning ensures that enough funds are available at the right time. Financial planning is the process of determining the objectives, polices, procedures to deal with the financial activities of an organization.
Importance of financial planning are:
1. Tool to face uncertainties: Financial planning is a tool to face uncertainties. It helps in forecasting different business situations and develop alternative financial plans to meet the different situations.
2. Ensures liquidity: Financial planning would ensure liquidity of funds throughout the year for meeting various financial commitments and there by create a confidence in the minds of the suppliers who provide funds to the organizations.
3. Ensures adequate funds: Financial planning avoids the situations of both surplus and shortage of funds. Financial planning estimates quantity of the funds required and time when it is required to ensure the optimum fund to achieve the company objective.
4. Elimination of waste: Good financial planning through proper policy and procedures contribute to the elimination of waste of funds and facilitates maximum utilization of the available resources. It also avoids complexity and lack of co ordination among various functions of an organization.
5. Better financial control: An effective financial planning predetermines the desired results and also helps to check the deviation and adopts corrective measure to achieve the desired goals of the organization.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain any five factors which may influence the amount of working capital requirements in a business.
Answer:
1. Nature of business: The amount of working capital requirement basically depends on the nature of the business. Due to the cash nature of the transactions in the business. Some business requires huge working capital and some need little working capital for their operations.
2. Scale of Operations: The requirement of working capital also depends up on the scale of operation. Small Scale operations needs less working capital when compared to large scale operations.
3. Growth & Expansion: As the organizations grows it requires a large amount of working capital in order to meet higher production and sales target. With the growth & expansion the business need more & more working capital to meet the day to day requirement of the organization
4. Business cycle: The amount of working capital required by a concern varies with the changes in the phases of business cycle. During Boom period the demand for the product increases and results in higher working capital requirement. On the other hand during recession and depression demand for the products decreases results in lower working capital requirements.
5. Seasonal factors: The working capital requirement also influenced by the seasonal fluctuation in demand for the products. During peak seasons, the working capital requirement in more due to higher level of activity. On the contrary during lean seasons the requirement of the working capital will be less.
Question 5.
Explain any five factors which may influence the amount of fixed capital requirements in a business?
Answer:
1. Nature of business: The amount of fixed capital requirement basically depends on the nature of the business. Some business requires huge fixed capital and some need little fixed capital depending on their operations. The need for fixed capital will be more as the concern need to invest on fixed assets like plant, machinery & Buildings etc.
2. Scale of operation: The scale of operation is the other important determinant of fixed capital requirement of a business. Larger the size and the scale of operations, the greater will be the amount of fixed capital requirement.
3. Growth & Expansion prospects: Higher growth of organization generally requires higher investment in fixed assets. As the organization as to create higher capacity’ in order to meet the higher demand Suffer
4. Choice of technique of production: An organization may be capital intensive or labor intensive. A capital intensive organization requires higher investment in plant and machinery when compared to labor intensive organization. Thus the requirement of fixed capital for capital intensive organization would be higher.
5. Method of fixed asset acquisition: Organizations purchasing fixed asset on cash basis requires a large amount of fixed capital. Those organizations which acquire fixed assets on hire purchase and installment system requires lesser amount of fixed capital.
Question 6.
Explain any five objectives of financial management.
Answer:
1. Profit maximization: profit can be maximized with proper utilization of organizations resource. The company should earn sufficient profit to reach its expenses, expansion & modification.
2. Wealth maximization: It means the maximization of the market value of shares. The market value of shares is related to three financial decision, viz., investment decision, financial decision, & Dividend decision.
3. Proper estimation of total requirement: It is very important to know the financial requirement to start & run the business. Estimating of financial requirement is done after considering factors such as scale of operation, technology, man power requirements etc.
4. Obtaining funds at minimum cost: The required fund can be mobilized through many sources such as shares, debentures, Bank loan etc. The finance manager must decide about difference & the balance between owned finance & borrowed finance. He must obtain the funds at minimum cost.
5. Proper utilization of finance: Finance must invest in profitable project and care should be taken to ensure that finance is not wasted due to investment in unprofitable project, blocking of finance in inventories & long period of credit.
2nd PUC Business Studies Financial Management Eight Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Describe different objectives of financial management.
Answer:
1. Profit maximization: profit can be maximized with proper utilization of organizations resource. The company should earn sufficient profit to melt its expenses, expansion & modification.
2. Wealth maximization: It means the maximization of the market value of shares. The market value of shares is related to three financial decision, viz., investment decision, financial decision, & Dividend decision.
3. Proper estimation of total requirement: It is very important o know the financial requirement to start & run the business. Estimating of financial requirement is done after considering factors such as scale of operation, technology, man power requirements etc.
4. Obtaining funds at minimum cost: The required fund can be mobilized through many sources such as shares, debentures, Bank loan etc. The finance manager must decide about difference & the balance between owned finance & borrowed finance. He must obtain the funds at minimum cost.
5. Proper utilization of finance: Finance must invest in profitable project and care should be taken to ensure that finance is not wasted due to investment in unprofitable project, blocking of finance in inventories & long period of credit.
6. Maintaining proper cash flow: An organization must have proper cash flow to pay its day-to-day expenses such as purchase of raw material, payment of wages & salaries, rent, electricity bills etc. Healthy Cash flow improves organizational success.
7. Risk minimization: Financial management tries to minimize the risk through creation of reserves to meet unforeseen contingencies. A portion of profits are always kept aside as reserve in order to utilize it for future growth and development.
8. Proper co-ordination: Financial Management works in combination with other areas like production, marketing, personnel etc. thus proper co-ordination with other departments is an important objective of financial management to achieve the organizational goals.
9. Financial control: Finance management should always plan the source of procuring funds & also the applications of funds. Deviation between the planned & actual inflow & outflow of funds should be studied; analyzed & corrective actions should be taken immediately.
10. Creation of goodwill: Financial management should try to create good will for the organization. Financial Management ensures good corporate governance. It will help to create confidence in the minds of the stake holders regarding the financial activities of the organization.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the factors which may influence the amount of fixed capital requirement in a business.
Answer:
1. Nature of business: The amount of fixed capital requirement basically depends on the nature of the business. Some business requires huge fixed capital and some need little fixed capital depending on their operations. The need for fixed capital will be more as the concern need to invest on fixed assets like plant, machinery & Buildings etc.
2. Scale of operation: The scale of operation is the other important determinant of fixed capital requirement of a business. Larger the size and the scale of operations, the greater will be the amount of fixed capital requirement.
3. Growth & Expansion prospects: Higher growth of organization generally requires higher investment in fixed assets. As the organization as to create higher capacity’ in order to meet the higher demand.
4. Choice of technique of production: An organization may be capital intensive or labor intensive. A capital intensive organization requires higher investment in plant and machinery w’hen compared to labor intensive organization. Thus the requirement of fixed capital for capital intensive organization would be higher.
5. Method of fixed asset acquisition: Organizations purchasing fixed asset on cash basis requires a large amount of fixed capital. Those organizations which acquire fixed assets on hire purchase and installment system requires lesser amount of fixed capital.
6. Diversification: Diversification of production or operations is another important factor affecting fixed capital requirement. A concern which chooses to diversify its production requires more fixed capital.
7. Amount of promotion expenses: If a concern has to spend more amounts by way of promotion expenses, cost of raising finance etc then it requires more amount of fixed capital.
8. Level of collaboration: Collaboration refers to the business organizations which share the facilities to each other. It reduces the level of investment in fixed assets for the participating organizations. So the requirement of the fixed capital is less in a collaboration of business.
Question 3.
Explain the importance of financial management.
Answer:
1. Estimating capital requirement: Financial Management makes the estimation of both short term & long term financial needs to make the smooth running of a business.
- Short Term Financial Needs: Refers to the financial requirement for a period within one year or financial required to meet day today expense.
- Long Term Financial Needs: Refers to the financial requirements for a period exceeding one year.
2. Capital budgeting: It refers to the long term funds. Capital can be raised in two ways either debts or Equity’. Capital budgeting decides the composition of debt & equity in the long term finance of an organization.
3. Working capital marketing: Excess of current assets over current liabilities represents the working capital of an organization. To ensure the smooth working of an organization it should have sufficient working capital to meet the day to day needs.
4. Appraisal of financial performance & financial control: Financial Management provides various financials tools such as Ration analysis, Budgeting, Variance analysis. It helps the management to control the financial activities of the organization.
5. Making financial decision: Financial Management is concerned with financial decisions relates to the composition of assets. Capital & Investment. Sound financial decisions are made depending on risk & return.
6. Solution to financial problem: A good financial management helps the top management by providing financial information and also solutions to various financial problems.
7. Communication of financial performance: It is used to measure profitability & liquidity of the business. The various stakeholders who are keen about the financial performance of the organization are Share holders, Creditors, Investors, Economists, Employees and Government.
Question 4.
Explain the importance of financial planning.
Answer:
Tool to face uncertainties: Financial planning is a tool to face uncertainties. It helps in forecasting different business situations and develop alternative financial plans to meet the different situations.
Ensures liquidity: Financial planning would ensure liquidity of funds throughout the year for meeting various financial commitments and there by create a confidence in the minds of the suppliers who provide funds to the organizations.
Ensures adequate funds: Financial planning avoids the situations of both surplus and shortage of funds. Financial planning estimates quantity of the funds required and time when it is required to ensure the optimum fund to achieve the company objective.
Elimination of waste: Good financial planning through proper policy and procedures contribute to the elimination of waste of funds and facilitates maximum utilization of the available resources. It also avoids complexity and lack of co ordination among various functions of an organization.
Better financial control: An effective financial planning predetermines the desired results and also helps to check the deviation and adopts corrective measure to achieve the desired goals of the organization.
Optimum capital structure: Financial planning will contribute to optimum capital structure at minimum cost or it will fix the relative proportion of owned capital & borrowed funds.
Helps in co-ordination: Financial planning helps in coordinating various functions.