Students can Download 2nd PUC Chemistry Model Question Paper 2 with Answers, Karnataka 2nd PUC Chemistry Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Chemistry Model Question Paper 2 with Answers
Time: 3 Hrs 15 Min
Max. Marks: 70
Part-A
I. Answer all of the following. (Each question carries 1 mark) (10 × 1 = 10)
Question 1.
At a given temperature and pressure nitrogen gas is more soluble in water than Helium gas. Which one of them has higher value of KH?
Answer:
Helium gas.
Question 2.
On mixing equal volumes of acetone and ethanol, what type of deviation from Raoult’s law is expected?
Answer:
Positive deviation
Question 3.
What happens to molar conductivity when one mole of KCL dissolved in one liter is diluted to five liters?
Answer:
Increases
Question 4.
What happens to the half life period for a first order reaction, if the initial concentration of the reactants is increased?
Answer:
No change
![]()
Question 5.
Name the process usually employed for the purification of Nickel.
Answer:
Mond’s process
Question 6.
Identify the product ‘A’ in the following reaction
XeF6 + 3H2O → A + 6HF
Answer:
XeO3
Question 7.
How many moles of AgCl will be precipitated when an excess of AgNO3 solution is added to one molar solution of [CrCl (H2O)5] Cl2?
Answer:
2 moles
Question 8.
Name the organic product formed when chlorobenzene is treated with sodium in dry ether.
Answer:
Diphenyl
Question 9.

Name the above reaction.
Answer:
Rosenmund reduction
Question 10.
Deficiency of which vitamin causes the disease pernicious anaemia?
Answer:
Vitamin-B12
Part-B
II. Answer any FIVE of the following. (Each question carries 2 marks) (5 × 2 = 10)
Question 11.
What is meant by the term co-ordination number in solids? What is the co-ordination number in a face centered cubic close packing structure?
Answer:
The number of nearest neighbours of a particle in solids is called Co-ordination number.
C.No.of FCC structure – 12
Question 12.
State Faraday’s first law of electrolysis. For the electrode reaction Zn2+ + 2e– → Zn(s), What quantity of electricity in coulombs required to deposit one mole of zinc.
Answer:
Faraday’s I – law states that “The amount of chemical reaction which occurs at any electrode during electrolysis by a current is directly proportional to the quanting of electricity passed through the electrolyte.
To deposit one mole of zinc;
2 × 96500 = 1,93,000 C of electricity is required.
![]()
Question 13.
A reaction is first order with respect to the reactant A and second order with respect to the reactant B in a reaction A + B → product.
i) Write the differential rate equation.
Answer:
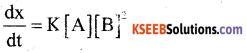
ii) How is the rate of the reaction affected on increasing the concentration of B by two times?
Answer:
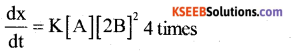
Question 14.
Give any two differences between lanthanoids and actinoids.
Answer:
Lanthanoids:
- 4f – orbital s s progressively filled
- Magnetic properties are complex
Actinoids:
- 5f – orbital is progressively filled
- Magnetic properties are more complex
Question 15.
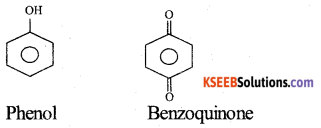
Name the product formed when phenol is treated with acidified solution of Na2Cr2O7. Give equation.
Answer:
Benzoquinone
Question 16.
Identify A and B in the following reaction:
Answer:
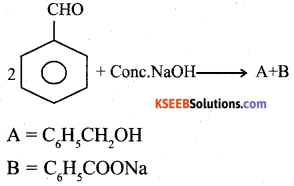
Question 17.
What is the role of these as food additives?
1. Sodium benzoate
Answer:
Sodium benzoate – Food preservation
2. Aspartame
Answer:
Aspartame – Artificial sweetening agent.
![]()
Question 18.
Explain saponification of oils/fats with equation.
Answer:
When oils / Fats are heated with NaOH, Soaps are formed. This reaction is known as saponification.
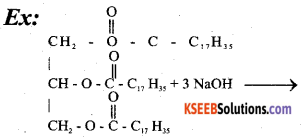
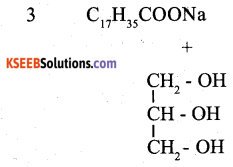
Part-C
III Answer Any FIVE of the following. (Each question carries three marks) (5 × 3 = 15)
Question 19.
Describe the three steps involved in the leaching of bauxite to get pure Alumina (equations not expected). (3)
Answer:
1. The bauxite ore contains silica (SiO2) Iron oxide (Fe2O3) and titanium dioxide (TiO2) as inpurities. Bauxite in concentrated by digesting the powdered ore in a concentrated solution of NaOH at 473 – 523K and 35 bar pressure. Al2O3 dissolves in alkali and is leached as sodium aluminate leaving impurities behind.
2. The solution of Sodium aluminate is filtered cooled and neutralised by passing CO2 gas and hydrated Al2O3 is precipitated by seeding.
3. Hydrated alumina is filtereds dried and heated to get pure alumina (Al2O3).
Question 20.
Write the equations involved in the preparation of nitric acid by Ostwald’s process by maintaining the reaction conditions. (3)
Answer:
![]()
Step – 2 : 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
Step – 3 : 3NO2(g) + H2O(1) → 2HNO3(aq) + NO(g)
Question 21.
Complete the following equations:
a) CH4 + 2O2 →
Answer:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 +2H2O
b) 2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O →
Answer:
2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO2-4 + 4H+
![]()
Answer:
![]()
![]()
Question 22.
a) Which is the strongest acid among the hydrogen halides? Give one reason [X = F, Cl, Br, I].
Answer:
HI
Because HI has least bond dissociation energy or Least electronegativity value.
b) Write the structure of Chloric acid (HClO3). 1
Answer:
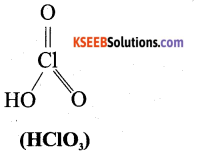
Question 23.
Give reason (one each) for the following: (3)
a) Transition metals are good catalytic agent.
Answer:
- They exhibit variable oxidation states.
- They have incompletely filled d-orbitals.
- They have more surface area
b) Second ionisation enthalpy of copper is very high.
Answer:
Because due to the disruption of stable d10 configuration of Cu+ ion. Considerable loss of exchange energy.
c) The spin only magnetic moment of SC3+ is zero (Z = 21).
Answer:
SC3+ has d0 configuration and lence no ‘d’ electrons. So r = 0
i.e In SC3+ ion, no unpaired e-s present and hence µ = 0
Question 24.
Write the equations involved in the preparation of Potassium Dichromate from Chromite ore. (3)
Answer:
- 4FeCr2O4 + 8Na2 CO3 +7O2 → 8Na2 CrO4 + 2 Fe2O3 + 8CO2
- 2Na2 CrO4 + 2H+ → Na2Cr2O7 + 2Na+ + H2O
- Na2Cr2O7 + 2Kcl → K2Cr2O7 + 2Nacl
Question 25.
With the help of Valence bond theory account for hybridisation, geometry and magnetic property of [Ni(CN)4]2- complex ion [Z for Ni = 28]. (3)
Answer:
E.C of Ni = 28 = [Ar] 3d84S2
E.C of Ni2+ = [Ar] 3d8 4S0
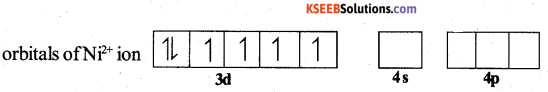
When strong ligand, CN– approaches the Ni2+ ion, pairing of electrons takes place in 3d – orbital against Hund’S rule.
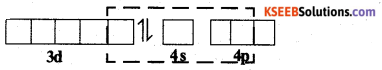
Ni2+ can undergo dsp2 hybridisation. The four hybrid orbitals then overlap with orbitals of four CN– ligands.
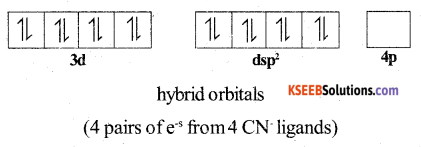
Thus the complex has square planar structure. It has no unpaired e-s and hence it is diamagnetic.
![]()
Question 26.
a) For the given complex.
[Co (NH3)5Br]SO4, write the IUPAC name and its ionisation isomer. (2)
Answer:
Penta ammine bromido cobalt (111) sulphate [CO (NH3)5SO4]Br
b) Which set of d-orbitals of metal ion/atom experience more repulsion in octahedral field created by the ligand? (1)
Answer:
eg or dx2 – y2 and dz2
Part – D
IV. Answer Any THREE of the following. Each question carries 5 marks. (3 × 5 = 15)
Question 27.
a) Calculate the packing efficiency in a unit cell of Cubic Close Packing (CCP) structure. (4)
Answer:
In a FCC unit cell the edge length is ‘a’ and radius of the particle is ‘r’. Then
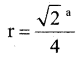
and four particles are present in an unit cell.

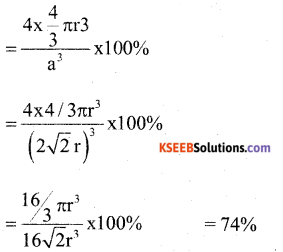
b) Name the crystal defect which lowers the density in an ionic crystal. (1)
Answer:
Schottky defect
Question 28.
a) A solution containing 18g of non-volatile non-electrolyte solute is dissolved in 200 g of water freezes at 272.07K. Calculate the molecular mass of solute. Given: Kf = 1.86 K kg/mol. freezing point of water = 273 K. 3
Answer:
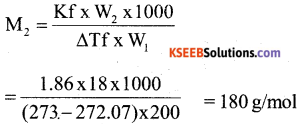
b) Define isotonic solution. What happens when the blood cell is dipped in a solution containing more than normal saline concentration? (2)
Answer:
Two solutions having same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called shrinks Isotonic solutions.
![]()
Question 29.
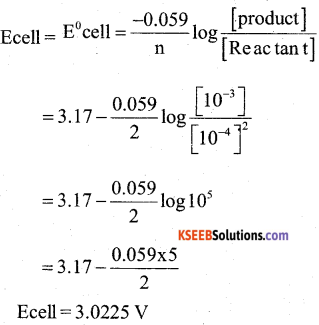
a) Calculate the EMF of the cell for the reaction
Mg(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → +Mg2+(aq) + 2Ag(S)
Given : E0Mg2+ / Mg = -2.37V
E0Ag+ / Ag = -0.80V
[Mg2+] = 0.001M; [Ag+] = 0.0001 M
log 105 = 5 (4)
Answer:
ECell = Eright – Eleft
= 0.80 – (-2.37 V)
= 3.17 V
b)
What are fuel cells? (1)
Answer:
A galvanic cell that are designed to convert the energy of fuel like hydrogen methane, methanol etc into electrical energy are called fuel cells.
Question 30.
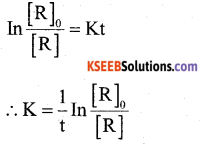
a) Derive integrated rate equation for the first order reaction. (3)
Answer:
The rate ofreaction is directly proportional to the first power of the concentration of the reactant ‘R’.
Consider a first order reaction
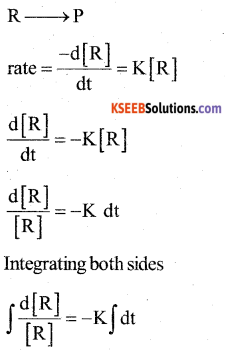
In [R] = -K t +1 (1)
Where I → Integration constant
To find I, whent = 0, [R] = [R]0
In [R]0 = -K × 0 +1
I = In [R]0
Substituting in equ (1) we get
In [R]0 – In [R] = Kt
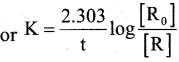
![]()
b) According to collision theory, what are the two factors that lead to effective collisions? (2)
Answer:
- Activation energy / Threshold energy
- Proper orientation of the colloidal particles.
Question 31.
a) Write any two differences between physisorption and chemisorption. (2)
Answer:
Physisorption
- It is caused by intermolecular vander waal’s process
- It is not specific in nature
- It is reversible
Chemisorption
- It is caused by chemical bonds
- It is highly specific in nature
- It is irreversible
b) Name the phenomenon/effect for the following:
1. Colloidal particles are in zig-zag motion. (1)
Answer:
Brownian movement
2. When an electrical potential is applied across two platinum electrodes dipping in a colloidal solution, particles move towards one or the other electrodes. 1
Answer:
Electrophoresis / Catephoresis
3. Scattering of light by colloidal soil
Answer:
Tyndall effect
Part-D
V Answer Any FOUR of the following. (Each question carries 5 marks) (4 × 5 = 20)
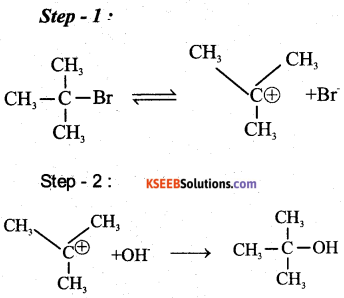
Question 32.
a) Write equations for the steps in SN1 mechanism of the conversion of tert. butyl bromide into tert. butyl alcohol (2)
b) Identify the products A, B and C in the following equation
Answer:
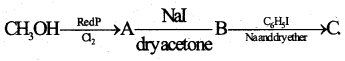
A = EH3CI
B = CH3I
C = C6H5CH3
![]()
Question 33.
a) Write the mechanism of acid catalysed dehydration of ethanol to ethene. (3)
Answer:
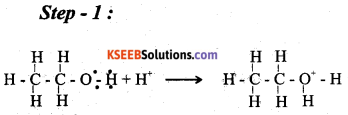
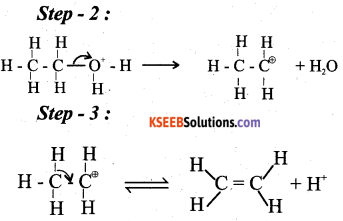
b) Explain Williamson’s reaction. Write the general equation. (2)
Answer:
When alkyl halide is allowed to react with sodium alkoxide ether is formed.
R – X + R – ONa → R – 0 – R + NaX
Question 34.
a) Write the organic compound formed in the following equations.
Answer:
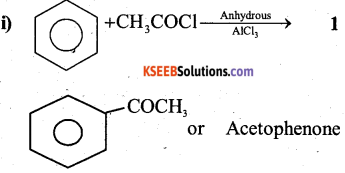
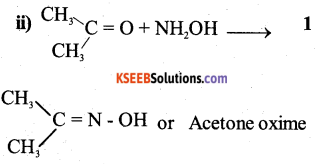
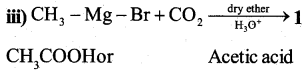
b) Explain HVZ (Hell – Volhard – Zelinsky) reaction with equation. (2)
Answer:
Carboxylic acid having an α -hydrogen are halogenated at α -position on treatment with Cl2/ Br2 in the presence of Red P to give α -halo carboxylic acid.
This reaction is known as HVZ reaction.
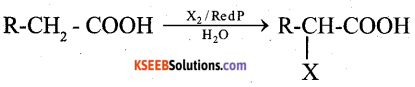
Question 35.
a) Identify the reactant ‘A’ in the following reaction: (1)
Answer:
A + 2R – X → R4N+X–
R2NH or 20 amine
b) Explain Hoffmann’s bromamide degradation reaction for the preparation of methanamine. (2)
Answer:
When an amide is treated with bromine in aqueous or alcoholic solution of NaOH, primary amine is formed.
Ex: CH3CONH2 + 4NaOH + Br2 → CH3 NH2 + Na2CO3 + 2NaBr + H2O
c) Which is more basic among aqueous solutions of aniline and ammonia? Give one reason. (2)
Answer:
Ammonia:
Because NH2 group is directly attached directly to the benzene ring and the unshared electron pair on nitrogen atom in conjugated with benzene ring. Hence less available for protonation
![]()
Question 36.
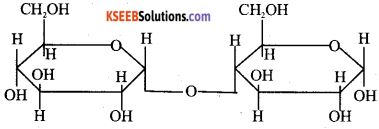
a) Write Haworth structure for
Answer:
b) What is meant by denaturation of proteins? Which level of structure remains intact during denaturation of globular protein? (2)
Answer:
When protein in native form is subjected to physical change like change in temperature or chemical change protein loses its biological activity is called denaturation. Primary structure
c) Name the base present only in DNA but not in RNA. (1)
Answer:
Thymine
Question 37.
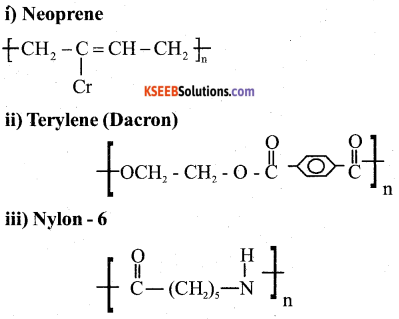
a) Write the partial structure of (3)
Answer:
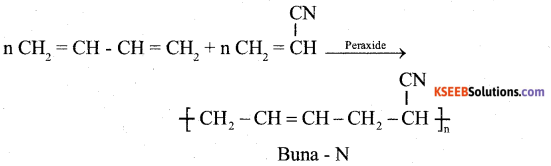
b) Explain the preparation of Buna-N with equation. (2)
Answer:
When 1,3 – butadiene and aclylonitrite is treated in the presence of peroxide to get Buna -N