You can Download Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Questions and Answers, Notes, 2nd PUC Chemistry Question Bank with Answers Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Chemistry Question Bank Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life
2nd PUC Chemistry Chemistry in Everyday Life NCERT Textbook Questions
Question 1.
Why do we need to classify drugs in different ways?
Answer:
The classification of drugs and the reason for classification are as follows:
1. On the basis of pharmacological effect: This classification provides doctor the whole range of drugs available for the treatment of a particular type of problem Hence, such a classification is very useful to doctors.
2. On the basis of drug action: This classification is based on the action of a drug on a particular biochemical process Thus, this classification is important.
3. On the basis of chemical structure: This classification provides the range of drugs sharing common structural features and often having similar pharmacological activity.
4. On the basis of molecular targets: This classification provides medicinal chemists the drugs having the same mechanism of action on targets Hence, is the most useful to medicinal chemists.
Question 2.
Explain the term, target molecules or drug targets as used in medicinal chemistry
Answer:
In medicinal chemistry, drug targets refer to the key molecules involve in certain metabolic pathways that result in specific diseases Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids are example of drug targets.
Drugs are chemical agents designed to inhibit these target molecules by binding with the active sites of the key molecules.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the macromolecules that are chosen as drug targets
Answer:
The macromolecules chosen as drug targets are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids.
Question 4.
Why should not medicines be taken without consulting doctors?
Answer:
A medicine can bind to more than one receptor site, thus a medicine may be toxic for some receptor site Further, in most cases, medicines cause harmful effects when taken in higher dose than recommended As a result, medicines may be poisonours in such cases Hence, medicines should not be taken without consulting doctors.
Question 5.
Define the term chemotherapy
Answer:
The use of chemicals for therapeutic effect is called chemotherapy For example the use of chemicals in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases.
Question 6.
Which forces are involved in holding the drugs to the active site of enzymes?
Answer:
Either of the following forces can be involved in holding drugs to the active sites of enzymes.
- Ionic bonding
- Hydrogen bonding
- Dipole-dipole interaction
- Van der Waals forces
Question 7.
While antacids and antiallergic drugs interfere with the function of histamines, why do these not interfere with the function of each other ?
Answer:
Specific drugs affect particular receptors Antacids and anti-allergic drugs work at different receptors This is the reason why antacids and anti-allergic drugs do not interfere with each others functions, but interfere with the functions of histamines.
Question 8.
Low level of noradrenaline is the cause of depression What type of drugs are needed to cure this problem? Name two drugs
Answer:
Anti-depressant drugs are needed to counteract the effect of depression These drugs inhibit enzymes catalysing the degradation of the neurotransmitters, nor adrenaline As a result, the important neurotransmitters is slowly metabolised and then it can activate its receptor for longer periods of time.
Two anti-depressant drugs are:
- Iproniazid
- Phenelzine
![]()
Question 9.
What is meant by the term ‘broad spectrum antibiotics? Explain
Answer:
Antibiotics that are effective against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria are known as broad spectrum antibiotics, chloramphenicol is a broad spectrum antibiotics.
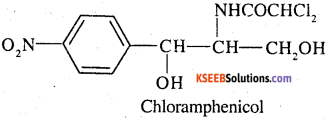
It can be used for the treatment of typhoid, dysentery, acute fever, pneumonia, meningitis, and certain forms of urinary infections Two other broad spectrum antibiotics are vancomycin and ofloxacin Ampicillin and amoxycillin-synthetically modified from penicillin – are also broad spectrum antibiotics
Question 10.
How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants ? Give one example of each
Answer:
Antiseptics and disinfectants are effective against micro-organisms However antiseptics are applied to the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers, and diseased skin surfaces, while disinfectants are applied to inanimate objects such as floors, drainage system, instruments, etc Disinfectants are harmful to the living tissues.
Iodine is an example of a strong antiseptic Tincture of iodine (2-3 percent of solution of iodine in alcohol – water mixture) is applied to wounds 1 percent solution of phenol is used as a disinfectant.
Question 11.
Why are cimetidine and ranitidine better antacids than sodium hydrogen carbonate or magnesium or aluminium hydroxide ?
Answer:
Antacids such as sodium hydrogen carbonate, magnesium hydroxide, and aluminium hydroxide work by neutralising the excess hydrochloric acid present in the stomach However, the root cause for the release of excess acid remains untreated.
Cimetidine and ranitidine are better antacids as they control the root cause of acidity These drugs prevent the interaction of histamine with the receptors present in the stomach walls Consequently there is a decrease in the amount of acid release by the stomach This is why cimetidine and ranitidine are better antacids than sodium hydrogen carbonate, magnesium hydroxide, and aluminium hydroxide.
Question 12.
Name a substance which can be used as an antiseptic as well as disinfectant
Answer:
Phenol can be used as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant 0.2 percent solution of phenol is used as an antiseptic, while 1 percent of its solution is used as a disinfectant.
![]()
Question 13.
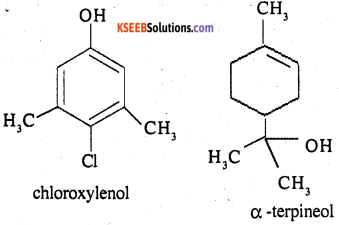
What are the main constituents of dettol?
Answer:
The main constituents of dettol are chloroxylenol and α -terpineol
Question 14.
What is tincture of iodine? What is its use?
Answer:
Tincture of iodine is a 2-3 percent solution of iodine in alcohol-water mixture It is applied to wounds as an antiseptic.
Question 15.
What are food preservatives ?
Answer:
Food preservatives are chemicals that prevent food from spoilage due to microbial growth Table salt, sugar, vegetable oil, sodium benzoate (C6H3 COONa), and salts of propanoic acid are some examples of food preservatives.
Question 16.
Why is use of aspartame limited to cold foods and drinks?
Answer:
Aspartame becomes unstable at cooking temperature This is the reason why its use is limited to cold foods and drinks.
Question 17.
What are artificial sweetening agents ? Give two examples
Answer:
Artificial sweetening agents that sweeten food However, unlike natural sweeteners, they do not add calories to our body They do not harm the human body Some artificial sweeteners are aspartame, saccharin, sucralose, and alitame.
Question 18.
Name the sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient
Answer:
Artificial sweetening agents such as saccharin, alitame, and aspartame can be used in preparing sweets for diabetic patients.
Question 19.
What problem arises in using alitame as artificial sweetener ?
Answer:
Alitame is a high potency sweetener It is difficult to control the sweetness of food while using alitame as an artificial sweetener.
Question 20.
How are synthetic detergents better than soaps?
Answer:
Soaps work in soft water, they are not effective in hard water In contrast synthetic detergents work both in soft water and hard water Therefore, synthetic detergents are better than soaps.
Question 21.
Explain the following terms with suitable examples
(i) cationic detergents
(ii) anionic detergents and
(iii) non-ionic detergents
Answer:
(i) Cationic detergents:
Cationic detergents are quarternary ammonium salts of acetates, chlorides, bromides This are called cationic detergents because the
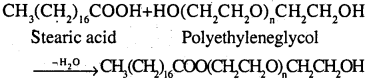
![]()
Question 22.
What are biodegradable and non- biodegradable detergents ? Give one example of each
Explain the cleansing action of soaps
Answer:
Detergents that can be degraded by bacteria are called biodegradable detergents Such detergents have straight hydrocarbon chains For example: Sodium Lauryl sulphate.
Detergents that cannot be degraded have highly branched hydrocarbon chains For example: Sodium – 4- (1, 3, 5,7 – tetra methyl octyl) benzene sulphonate.
Soap molecules form micelles around an oil droplet (dirt) in such a way that the hydrophobic parts of the stearate ions attach themselves to the oil droplet and the hydrophilic parts project outside the oil droplet Due to the polar nature of the hydrophilic parts, the stearate ions (along with the dirt) are pulled into water, thereby removing the dirt from the cloth.
Question 23.
Why do soaps not work in hard water?
Answer:
Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain fatty acids Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions When soaps are dissolved in hard water, these ions displace sodium or potassium from their salts and form insoluble calcium or magnesium salts of fatty acids The insoluble salts separate as scum.
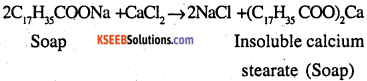
this is the reason why soaps do not work in hard water.
Question 24.
Can you use soaps and synthetic detergents to check the hardness of water?
Answer:
Soaps get precipitated in hard water, but not in soft water Therefore, soaps can be used for checking the hardness of water However, synthetic detergents do not get precipitated either cationic part of these detergents contains a long hydrocarbon chain and a positive charge on the N atom
For example:
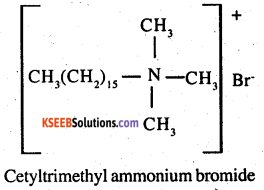
1. Anionic detergents: Anionic detergents are of two types
(a) Sodium alkyl sulphates: These detergents are sodium salts of long chain alcohols, they are prepared by first treating these alcohols with concentrated sulphuric acid and then with sodium hydroxide Examples of these detergents include sodium lauryl sulphate (C11H23CH2OSO3 Na+) and sodium stearyl sulphate (C17H35CH2OSO3 Na+)
(b) Sodium alkyl benzene sulphonates: These detergents are sodium salts of long chain alkyl benzene sulphonic acids They are prepared by Friedd-crafts alkylation of benzene with long chain alkyl halides or alkenes The obtained product is first treated with concentrated sulphuric acid and then with in sodium hydroxide Sodium 4 – (1 – dodecy) benzene sulphonate (SDS) is an example of anionic detergents.
2. Non-ionic detergents Molecules of these detergents do not contain any ions These detergents are esters of alcohols having high molecular mass They are obtained by reacting polyethylene glycol and stearic acid.
Question 25.
If water contains dissolved calcium hydrogen carbonate, out of soaps and synthetic detergents which one will you use for cleaning clothes?
Answer:
Synthetic detergents are preferred for cleaning clothes When soaps are dissolved in water containing calcium ions, these ions form insoluble salts that are of no further use, however when synthetic detergents are dissolved in water containing calcium ions, these ions from soluble salts that act as cleaning agents.
Question 26.
Label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts in the following compounds
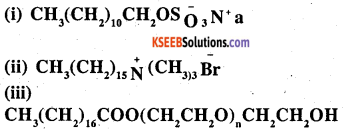
Answer:
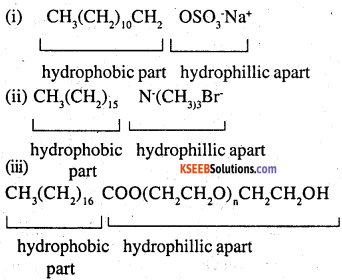
![]()
Question 27.
Sleeping pills are recommended by doctors to the patients suffering from sleeplessness but it is not advisable to make its dose without consultation with the doctor, Why?
Answer:
Most drugs when taken in doses higher than recommended may carry harmful effects and sometimes, may even lead to death Hence, a doctor should always be consulted before taking any medicine.
Question 28.
With reference to which classification has the statement, “ranitidine is an antacid” been given?
Answer:
The given statement refers to the classification of pharmacological effects of the drug This is because any drug that is used to counteract the effects of excess acid in the stomach is called an antacid.
Question 29.
Why do we require artificial sweetening agents
Answer:
A large number of people are suffering from diseases such as diabetes and obesity These people cannot take normal sugar ie sucrose as it is harmful for them Therefore artificial sweetening agents that do not add to the caloric intake of a person are required, Saccharin, aspartame, and ulitame are a few examples of artificial sweeteners.
Question 30.
Write the chemical equation for preparing sodium soap from glyceryl oleate and glyceryl palmitate Structural formulas of these compounds are given below
1. (C15H31COO)3C3H5 – Glyceryl Palmitate
2. (C17H33COO)3C3H5 – Glyceryl oleate
Answer:
1.
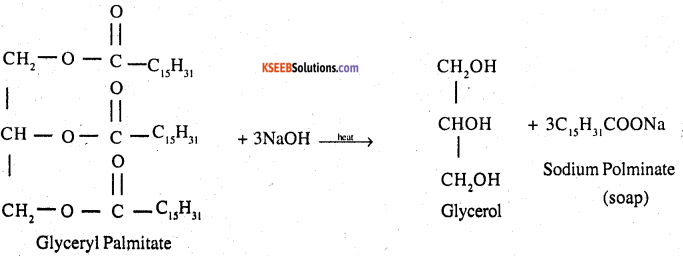
2.
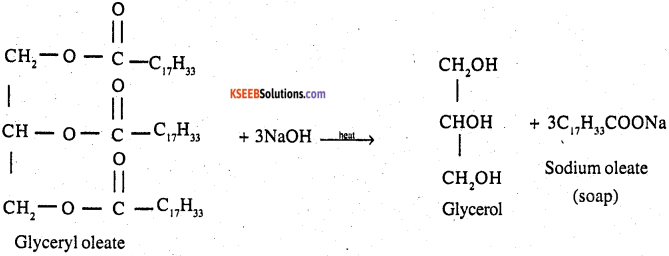
Question 32.
Following type of non-ionic detergents are present in liquid detergents, emulsifying agents and wetting agents Label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts in the molecule Identify the functional group (s) present in the molecule
Answer:
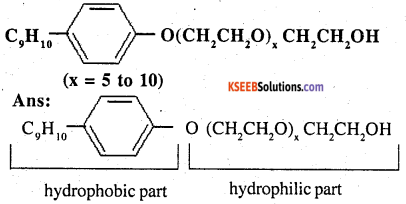
Functional groups present in the molecule are:
- Ether, and
- primary alcoholic group.
2nd PUC Chemistry Chemistry in Everyday Life Additional Questions
Question 1.
In order to wash clothes with water containing dissolved calcium hydrogen carbonate, which cleaning agent will you prefer and why: Soaps or synthetic detergents? Give one advantage of soaps – over synthetic detergents
Answer:
Water containing calcium hydrogen carbonate is hard water Detergents are preferred over soaps for cleaning clothes in hard water because calcium salts of detergents are soluble in water while calcium salts of soaps are insoluble As a result, lot of soap is wasted
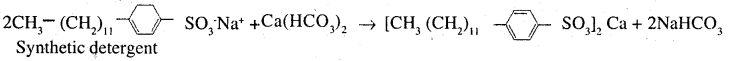
Disadvantage of using detergents: Soaps are biodegradable while detergents having branched hydrocarbon chains are not biodegradable and hence cause water pollution in rivers and waterways.
![]()
Question 2.
Account for following
(i) Aspirin drug helps in prevention of heart attack
Answer:
Most of the heart attacks are due to blood clotting in the coronary arteries Aspirin helps to make the blood thinner and thus prevents the formation of blood clots in the coronary arteries thereby preventing heart attacks.
Question 3.
What are antihistamine? Give two examples
Answer:
Antihistamines are drugs which either reduce or inhabit the action of histamine in the body thereby preventing allergy Two important antihistamines are brompheniramine and terfenadine
Mode of action: Histamines interact with the binding sites of receptor in the body to produce allergy Antihistamines compete with histamines for these binding sites of receptor and thus do not allow histamine to produce allergy.
Question 4.
How does aspirin act as analgesic?
Answer:
Aspirin inhibits the synthesis of erostaglandis which stimulate inflammation of the tissue and cause pain.
Question 5.
What are barbiturates? To which class of drugs do they belong?
Answer:
55 derivatives of barbituric acid are called barbiturates They belong to class of tranquilizers.
Question 6.
What is salvarsan? To which class of drugs do they belong?
Answer:
Salvarsan is an antimicrobial agent It is used for the treatment of disease called syphillis
Question 7.
Give one example of artificial sweetner used by diabetic patients
Answer:
Saccharin (in form of sodium salt) is taken as artificial sweetner by diabetic patients.
![]()
Question 8.
Define a tranquilizer
Answer:
Tranquilizers are drugs which act on central nervous system to help in reducing anxiety.
Question 9.
What is the nature of an antacid?
Answer:
Substances which reduce the release of excess HCl by preventing the interaction of histamine with the receptors present in the stomach wall are called antacids Examples cimetidine and ranitidine.
Question 10.
Which alkaloid is used for
1. hypertension
2. malaria fever?
Answer:
1. Reserpine
2. Quinine