Students can Download 2nd PUC Geography Previous Year Question Paper June 2017, Karnataka 2nd PUC Geography Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Geography Previous Year Question Paper March 2017
Time: 3 Hrs 15 Min
Max. Marks: 100
Section – A
I. Answer the following questions in one sentence each: ( 10 × 1 = 10 )
Question 1.
Who is called the Father of Human Geography?
Answer:
Friedrich Ratzel.
Question 2.
Expand H.D.I.
Answer:
Human development index
Question 3.
What is mining?
Answer:
Mining refers to the Extraction of the minerals from the Earth such as Iron ore, Manganese, Gold, Coal, Diamond and Petroleum.
Question 4.
What is transportation?
Answer:
Transport is the means of carrying Goods Passengers from one place to other by Human. Animals and different kinds of vehicles.
Question 5.
What is settlement?
Answer:
Settlement means the places inhabited by people permanently in village, a town or a city is called Settlement.
Question 6.
Name the state recorded highest literacy rate of India.
Answer:
The state recorded as highest literacy rate of India is Kerala with 93.9 1%.
Question 7.
What is the name Bhakra reservoir?
Answer:
Govind Sagar
Question 8.
Mention one important beverage crops of India.
Answer:
Tea and Coffee are important Beverage crops of India.
Question 9.
Which mineral is called “Black Diamond”?
Answer:
Coal
Question 10.
Expand GP.S.
Answer:
missing
Section – B
II. Answer any 10 of the following questions in 2 to 3 sentences each: ( 10 × 2 = 20 )
Question 11.
Mention any two different techniques of mining?
Answer:
The diflìrent technique of Mining are:
- Open Cast mining
- Underground mining
- Shaft mining.
Question 12.
What are the different types of fishing?
Answer:
The different types of Fishing are:
- Fresh water fishing
- Coastal fishing and
- Open sea fishing.
Question 13.
Give two examples of educational towns.
Answer:
- Mysore
- Dharwad.
Question 14.
What are the two types of migration?
Answer:
- Internal migration
- International migration
Question 15.
Name the varieties of wheat in India.
Answer:
- Bread wheat
- Macaroni wheat
- Emmer wheat
- Indian dwarf wheat.
Question 16.
Mention the types of coal.
Answer:
The types of coal arc;
- Anthracite
- lignite
- Bituminous
- Peat.
Question 17.
Name the two important gold producing regions of India.
Answer:
- Hutti gold field in Raichur districts and Bellary gold field in Tumkur in Karnataka.
- Ramagiri in Ananthpur district and Jonnagiri in Kurnool in Andhra Pradesh.
Question 18.
Name the places where software technology parks are located in Karnataka.
Answer:
- Bangalore
- Mysore
- Udupi
- Hubli
Question 19.
Mention the three important railway gauges.
Answer:
- Broad – Gauge
- Metre – Gauge
- Narrow – Gauge.
Question 20.
State the two types of water ways.
Answer:
- Inland water transport
- Ocean transport.
Question 21.
What are the types of pollution?
Answer:
The types of Pollutions are :-
- Air pollution
- Water pollution.
- Land pollution
- Noise pollution.
Question 22.
What are the causes of air pollution?
Answer:
- Increased use of varieties of fuels such as coal, petrol and diesal.
- Increase in emission of Toxic Gases from Industrial activities into the Atomosphere.
- Mining activities release dust in the air.
- Important Pollutants are oxides of sulpher and nitrogen, hydro carbons, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide lead and asbestos.
Section – C
III. Answer any eight of the following questions in 25 to 30 sentences each: ( 5 × 8 = 40 )
Question 23.
Explain the importance of human geography.
Answer:
Importance of Human Geography:
- It clarifies the societies and cultures in different locations.
- The great diversity reflects through the fashion life.
- Which realizes carrying capacity of the Earth.
- It helps us to understand circumstances affecting people and nation.
- It is helpful to the planners, administrations, Industrialists and others.
Question 24.
What is human development? Discuss the measurement of human development.
Answer:
Meaning of Human development :
Human development is “development that enlarges people’s choice and improves their lives”. Standard of living & where people can live meaningful lives. Such as healthy, able to develop their talent. Participate in the activities of society etc.
Measurements of Human Development:
Human development is measured with –
- The Human development Index.
- The Human poverty Index,
1. The Human development index: It is measured in three dimensions.
- Health: Good health results of higher life expectancy means the people have a greater chance of living longer and health.
- Education: Based on the literacy rate development and status of a persons decides.
- Decent standard of living: It is measured in terms of purchasing power (in US dollars).
2. The Human poverty index: It measures the short fall in human development in following indices.
- The probability of not surviving till the age of 40.
- The adult illiteracy rate.
- The number of people who are not able drink pure water.
- The number of small children who are under weight.
Question 25.
What is demographic cycle? Explain the stages of demographic cycle.
Answer:
Demographic cycle is the process of population transformation from the countries of high birth rate and high death rates to low birth rate & low death rate countries.
Stages of Demographic cycle:
- First stage: High birth rate and high death is found when the country is economically most backward, so the population remains stationary. India was in the stage till 1920.
- Second stage (Early expanding): It begins with the declining of death rate while the birth rate ramins unchanged. These changes due to the advancement of science & technology, basic health care and education etc. At present many developing countries of Asia & Africa are in this stage.
- Third stage (Late expanding): Death rate declines and birth rate begins to fall due to access of contraceptives, urbanization, an increase in the status and women education etc India appears to be this stage.
- Fourth stage (Low stationary): It is characterized with low birth rate and low death rate. Growth is stationary due to changing life style, high obesity and many diseases are caused in this stage. Japan. Sweden, Belgium Denmark & Switzerland are in this stage.
- Fifth stage( Declining): Population begins to decline or birth rate is lower than death rate. East European countries like Germany and Hungary and North European countries like Sweden. Norway are now in this stage.
Question 26.
Describe the importance of the pipelines.
Answer:
- It is most convenient, efficient and cheap mode of transporting products like crude oil and refined products, gas, water and milk.
- At present solid materials are also transported through pipeline after converting them into slurry.
Advantages of Pipelines :
- Pipelines can be laid through difficult terrain and also through water.
- The initial cost of laying the pipelines is high but the subsequent cost of maintenance and operation is low.
- Pipelines ensure a steady supply and minimize trans-shipment losses and delays.
- Pipelines operation involves very low consumption of energy and keeps the environment free from pollution.
- Pipeline regions unites industrial regions.
Disadvantages:
- The capacity of pipelines cannot be increased once they are laid.
- The security of pipelines in certain areas and the detection of leakage arc difficult.
- The construction of pipelines are expensive.
Question 27.
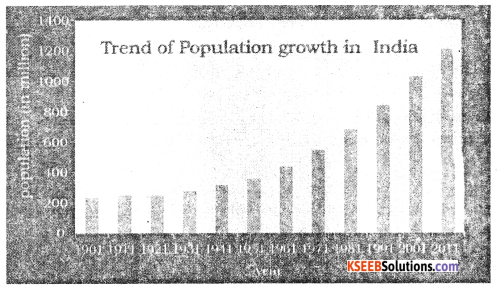
Explain the trend of population growth in India.
Answer:
The Population growth in India between 1 90 I and 2u 11 can be divided into four stages as follows
- 1901 – 1921 Stagnant population growth.
- 1921 – 1951 Steady growth.
- 1951 – 1961 Rapid high growth.
- 1981 – 2011 High growth with definite signs of slowing down.
1. In the first stage : In this decade, population growth was naturally curbed with the outbreak of Plague. Cholera. Malaria, influenza and other epidemics. Thus the decade considered as the great divide in the history of Indian Census.
2. In the second stage : The population can be considered as moderate The population growing from about 251 million (1921) to 361 million (1951), an increase of about 110 million. The main reason was decline in death rate due to control if epidemics like Plague. Cholera etc.
3. The third stage : is very important, because of the growth rate of population very high. The Population grew from 361 million (1951) to 686 (198!). an increase of about 325 million. The growth has been very rapid after independence. The government of India was implemented man Socio-Economical Programs in all sectors.
4. The fourth stage : It completely differs from other three stages, Here the trend of growth rate of population is gradually slowing down. We can easily justify that the period from 1981 to 2011 is referred to as a high growth with definite signs of slowing down.
Question 28.
Discuss the factors affected on human development index in India.
Answer:
Factors influencing on HDI of India are discussed below:
1. Birth and Death Rate : Declining of birth rate has been much slower than that of the death rate. This results in rapid increase of population. It affects on slow economic growth of the country. It is the main cause for declining of human development index.
2. Life Expectancy : Life Expectancy has gone up 65.77 years for males 67.95 years females respectively in 2011-12. This is due to the consequence of the expansion of food security and medical facilities. It helps to raise the HDI in the country.
3. Food and Nutrition : According to the 2011 Global Hunger Index (GHI) report, India has 15th rank among the leading countries with hunger situation.
- The World Bank estimates that India is one of the highest-ranking countries in the Vor1d for the number of children suffering from malnutrition.
- It is adversely affecting the Human development.
4. Literacy : Education is the key for socio-economic progress. The Indian literacy rate grew to 74.04% in 2011 from 12% at the end of the British rule in 1947. The large proportion of illiterate females is another reason for the low literacy rate in India. Due to this there is decline in the Human development Index of the country.
Question 29.
Discuss the important features and aims of Damodar Valley Project.
Answer:
The main aims of the project are flood control, Promotion of irrigation, Generating Hydro Electricity, Navigation, Afforestation, Prevents Soil erosion, Inland fishing and recreation facilities.
Its features are as follows :
Damodar and its tributaries –
It comprises four Dams, three Hydel Power stations one barrage and three thermal power stations.
1. Tilaiya Dam :
This dam has been constructed on Barakar river a tributary of Damodar.
- Its gross storage capacity is 395 million cubic metres.
- Two power stations of 200KW each have been set up here. The dam provides irrigation facilities to 40,000 hectares.
2. Konar Dani :
- It has been constructed on Konar river.
- Its gross storage capacity is 337 million cubic metres, Its provides irrigation facilities to 1.4 Lakh hectares.
3. Maothon Dam :
It has been constructed on Barakar river.
Question 30.
Give an account of the production and distribution of rice in India.
Answer:
Rice Cultivation is widely distributed in India. Its cultivation is concentrated in River valleys, deltas, flood plains, low lying coastal areas of North-Eastern & Southern India etc are important rice growing areas.
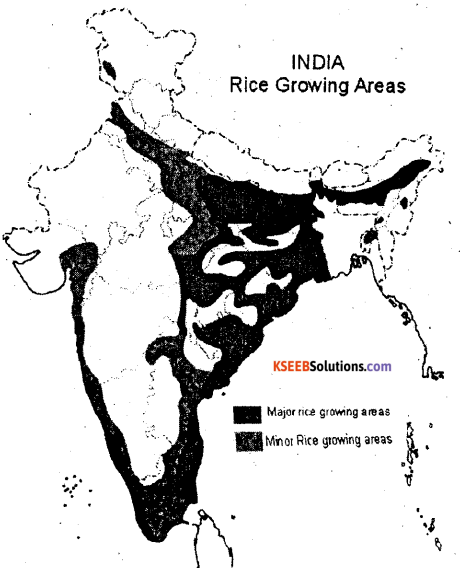
1. West Bengal :West Bengal is the largest producer of rice in India
- About three fourth of the Total state’s cropped area is under the rice cultivations
- Rice is growing in three seasons. They are called in different names.
(i) Aus (ii) Aman and (iii) Boro, Mediñipur, Bardhaman 24 Parganas, Bankura & Cochbehar are important rice-producing districts in the state West Bengal producer 14.2% under total production of Rice in India.
2. Uttar Pradesh : This is second largest producer of rice in India.
- The rice cultivated area is concentrated in Gorakhpur, Basti, Varanasi, Allahabad, Shaharanpur, Azamgarh & Shajahanpur etc are important districts & major rice growing areas.
- Uttar Pradesh produces 13.44% f Rice under total production of Rice in India.
3. Andhra Pradesh : It is the third largest producer of rice iñ India.
- The delta of Godavari -Krishna & coastal plains are suitable for rice cultivation in the state.
- It contributes 12.35 % of Rice under total production of rice in India.
4. Punjab : Punjab is the fourth largest producer of rice in India.
- Amritsar, Patiala, Ropar, Firozepur districts are the major produces of rice in Punjab.
- Its share 10.11 % under total production of Rice in India.
5. Bihar: Bthar is fifth leading producer of rice in India. ,
- Gaya, Rohtas, Bhajpur, Darbhanga, Champaran, Purenea, Bhagalpur & Patna districts.
- It produces 6.90% under total output of rice in india.
6. TamilNadu: It is the sixth largest producer of rice in India.
- Tirunelveli, Tiruchirapalli, Salem, Madhural, Coimbatore.
- Its production is 6.61% under total production of total Rice in India.
7. Chattisgarh: It is the important producer of rice in country.
- Bastar, Bilaspur, Durg, Sarguja, Raipur, Raigarh & Janjgir are the main rice producing districts.
- Its production is 5.78% under total production of Rice in India.
8. Karnataka : Karnataka has rapid progress in rice cultivation during last few years. The important rice producing districts are Raichur, Davangere, Mysore, Bellary, Shimoga, Mandhya & Koppal.
Its production is 3.87% under total production of Rice.
Production of rice : India is the second largest producer of rice in the world next to the China. It produceses 104.3 million tonnes of rice during 2011-12, it accounts for 22% of the worlds production. Now India is self sufficient in rice production.
Question 31.
Explain the distribution and production of iron ore in India.
Answer:
India is endowed with fairly abundant reserves of iron ore. The estimated iron ore reserves were about 25 billion tonnes in the year 2012-2013.
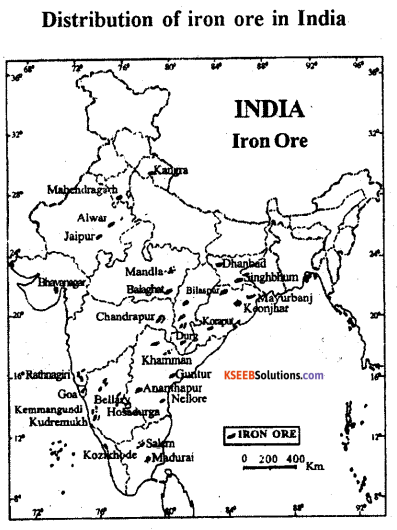
Odisha :
- It is a largest producer and accounts for about 47 percent of the total iron ore in India. Most of the deposits of iron ore in the state occur in Sundargarh, Mayurbhanj, Cuttack, Sambalapur, Keonjhar and Koraput districts.
- Chattisgarh : It produce over 21 percent of the total production of iron ore in india.
- Chattisgarh is thé second largest producer of iron bre in the country. Iron ore producing areas are Bailadila in Bastar, Dhalli Rajhara in Durga and Jabalpur districts.
- Jharkhand: This state ranks third in the production of iron ore in India. It contributes nearly 13 percent of the total production areasar Budhäburu, Kotamatiburu and Rajoriburu in Singhbhum districts.
- Karnataka: Karnataka produces only 4 percent of the iron ore production in India. But it has vast deposits of Harmatite as well as magnetite iron ore in Bababudan hills in Chickmangalur district, Sandur and Hospet area of Bellary district.
- Others : In Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, \Vest Bengal etc produce small quantity of iron ore.
Production :
- India ¡s the fourth largest produces of iron ore in the world.
- The total production of iron ore is 167 million tonnes in 2011-12 and 143 million tonnes in 2012-2013.
- It is decreased by 19 percent as compared to previous year.
Question 32.
Mention the importance of cement industry development in India.
Answer:
Importance : The ‘Cement’ is the name given to the mixture of limestone, clay, silica and gypsum. This is essential for all types of construction activities.
- Cement is essential for the development of all types of infrastructure facilities such as roads, bridge, dams, buldings canals etc.
- The production and consumption of cement is an indicator of the progress of a nation.
- It is the fundamental requirement for the development of major economic sectors such as agriculture, industry, transportation, trade etc.
- India is not olny one of the major cement producing countries of the world, at the same time, it is one of the largest cement consumer as well as exporter.
Development : The first cement plant was established by South Indian Industries at Ranipet near Chennai in 1904.
- During 1914-16 two more cement plants were established at Katni in Madhya Pradesh & Lakheri of Rajasthan.
- In 1934, 10 out of 11 existing companies merged together & established Associated
Cernent Company Ltd., (ACC) by 1947. - At present (2010) there are 153 large cement plants with a total production of 219.51 million tonnes. Besides the country have more than 99 mini cement plants with an installed capacity of 11.10 mmt. it the last three decades the country has emerged as the second largest cement producing country of the world.
Question 33.
Explain any two major ports of west coast of India.
Answer:
The major ports located in the vcst coast of India are
- Kandla
- Mumbai.
1. Kandla: It is a tidal port located at Eastern end of Gulf of Kachclih (Gujarat).
- It has a natural harbour and has a vast hinterland, rich in agriculture and animal husbandry.
- Its main exports consists of leather, petroleum products, chemicals, salt, cement, cotton and silk textiles and edible oils.
- The imports include crude oil, potash, fertilizers, machines and synthetic rubber.
2. Mumbal: Mumbai is the biggest, most spacious, natural, well shelter, and capital of the Maharashtra state.
- The port is situated towards the eastern side of Mumbai island which runs in a north-east to south-east direction.
- The length of this port is 2Okms and width is 6-10 kms.
- There are 54 berths in its wet dock. This port has become India’s largest oil terminal.
- It has rich hinterland.
- Important items of imports are food grains, crude oil, machinery, chemicals, fertilizers sand transport equipment.
- The main items of exports are cotton textiles oilseeds, hides and skins,iron and manganese ore.
Question 34.
Discuss any six problems of people living in slums.
Answer:
- Slums arc in environmentally unsuited and degraded area. Houses in slums are decaying, poor hygienic conditions, poor ventilation.
- Lack of basic amentities like drinking water, light and toilet facilities.
- They are overcrowded having narrow street pattern prone to serious hazards from fire.
- People living in slums are poor. Thorefore problems are common.
- They are the undernourished, prone to different types of diseases and illness.
- They can not afford to give proper education to their children.
- The Poverty makes them valnerable to drug abuse alcoholism, crime, vandalism and ultimately they face social exclusion.
Section – D
IV. Answer any one of the following questions : ( 1 × 10 = 10 )
Question 35.
Describe the occurrence, production and distribution of crude oil in India.
Answer:
- In India petroleum was discovered in 1860.
- Another important achievement was the discover of oil in the Digboi area in 1889.
- The government of India contituted a separate Directorate of Oil and Natural Gas
Commission (ONGC) on August 1956, Oil India Ltd., (OIL) on Febraur 1959.
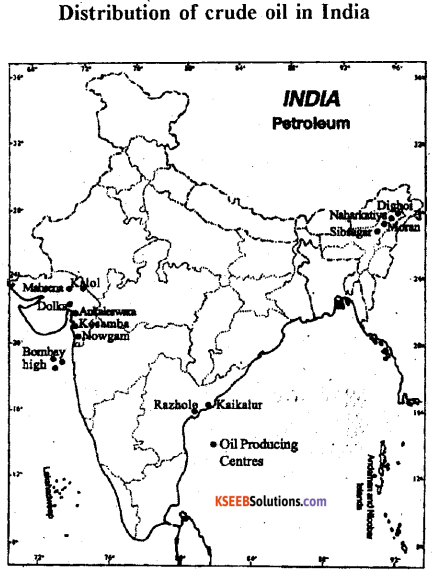
1. Bombay High : This is the largest oil producing area contributing 42.7 percent of the total
crude oil output of the country.
- It is found in coat of Maharashtra about 176 km of the North-West Mumbai.
- It is known as “Sagar Samrat”.
2. Assam :
- In india the petroleum was first dicovered at Makum (Assam) in 1867. The first oil well was drilled at Digboi.
- It contributes about 13.2% of the oil production in the country.
- Major oil fields of Assam state are the Digboi, Naharkatiya, Rudrasagar, Sibsagar and Hugrini.
3. Gujarat: It contributes 15.2% of Petroleum production in India.
Ankaleshwar and Cambay are the main oil fields, Kolob, Nangaon etc.
4. The Eastern Coast Oil field : The basin and deltas of the Godavari, the Krishna of Andhra Pradesh and the Cauvery river of Tamil Nádu holds great potential of oil and natural gas production.
5. Others : Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan etc
Production :
- The total production of Petroleum in India was 380.9 lakh tonnes in 2011-12.
- India is not a significant producer of Petroleum in the world.
- Recently the domestic crude oil production has increased. This is because of the constant efforts made by ONGC and Oil India Ltd.
Question 36.
Discuss the factors which influence on the location of the industries.
Answer:
Some Important factors are:
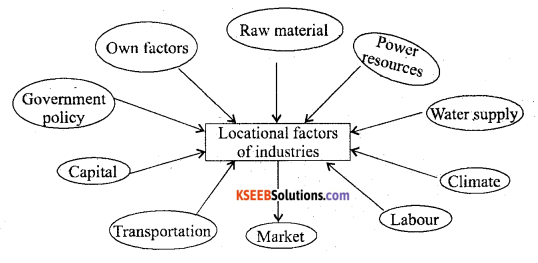
- Raw materials :- Industries are set up close to or in the regions where raw materials is available.
- Power Resources :- Power is essential for running the machinery of industries and influences much on the industrial location.
- Water supply :- Large quantities of water essential for the processing of raw materials or for cooling purposes. Therefore industries are usually localizednear rivers or lakes.
- Climate :- Industries are influenced by climate. For example Cotton textile industry requires humid climate.
- Labour :- Cheap and efficient labour is required to work in the industries.
- Market :- Nearness to market is essential for quick marketing of manufactured goods.
- Transportation :- It is necessary to carry raw materials to the factories and to carry finished products to the markets as well.
- Capital :-. Development of Indust es requires large capital investment.
- Government :- GoverRment must have favourable policies such as tax exemptions electricity and sites at concessional rates, subsidies, rail-link, improved roads etc.
Section – E
V. Answer any two of the following. ( 2 × 10 = 20 )
Question 37.
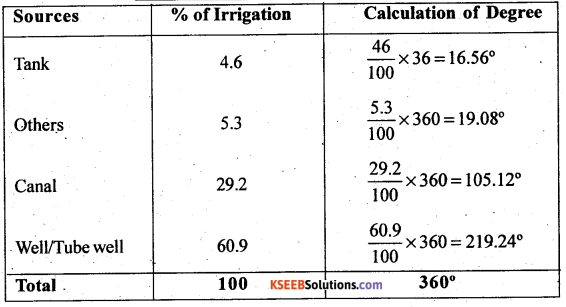
Construct a Pie-Diagram by using.data given in the table. India : Sources of Irrigation – 2011
Answer:
| Sources | % of irrigation |
| Canal | 29.2 |
| Well/Tube well | 60.9 |
| Tank | 4.6 |
| Others | 5.3 |
| Total | 100 |
Question 38.
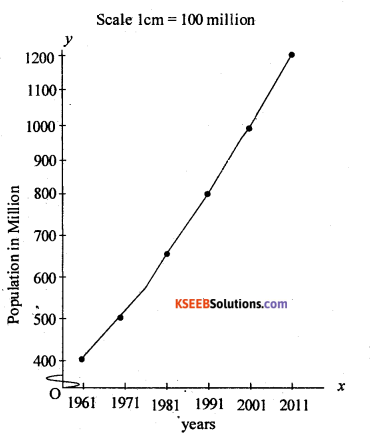
Construct a line graph by using in following data.
Growth of Population in India – 1961 –
| Year |
Population in million |
| 1961 | 439 |
| 1971 | 548 |
| 1981 | 683 |
| 1991 | 843 |
| 2001 | 1026 |
| 2011 | 1210 |
Answer:
Question 39.
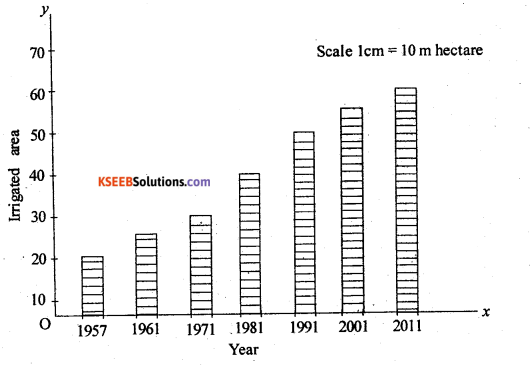
Construct a simple bar diagram to represent the data given in the table. India : Decade-Wise Total Irrigated Area (in Million hectares)
| Year |
Irrigated Area |
| 1951 | 20.85 |
| 1961 | 24.66 |
| 1971 | 3 1.10 |
| 1981 | 38.72 |
| 1991 | 47.80 |
| 2001 | 54.65 |
| 2011 | 57.00 |
Answer:
For Blind Students Only
Answer any two of the following questions: ( 2× 10 = 20 )
Question 40.
(a) What are the effects of globalization?
Answer:
There are Positive effects and Negative effects:
1. Positive effects: Industry has brought in huge amount of foreign investments into the industry & they has boosted the economy quite significantly.
- This has helped to provide employment to many people in the country.
- This has helped to make the Indian Industry more technologically advanced.
- It helps to reduce poverty in the country.
2. Negative effects :
The Negative effects of globalization on Indian industry are that it is increased computation
in the Indian market between the foreign companies and domestic companies.
- The foreign goods being better than the India goods, the consumer preffered to by the foreign goods. This reduced the amount of profit of the Indian industry companies. Its effects are more on pharmaceutical, manufacturing, chemical & the steel industries.
- The coming up technology in number of labour required decreased and this resulted in many people being removed from their jobs.
(b) What is satellite communication?
Answer:
Importance of satellites: Satellites are important to us in many ways.
- They provide us with radio and cable television.
- They allow us to make cellular phone calls from long distances.
- They provide us with a global positioning system (GPS).
- They circle the earth and relay weather conditions and forecasts.
- The government uses them to spy on other countries in order to protect us
- They are used for space research, which includes sotto satellites that observe the sun and provide us with early warnings of upcoming solar flakes. These solar flakes have been known to knock out various satellite communication links, which allow us to use our credit cards and to use beepers.
- Satellite monitor crops.
(c) Explain the sources of data.
Answer:
Meaning – The data which are collected for the first time by a researcher or groups of researchers, institution or organizations are called Primary sources of data.
Types of Primary data collection:
1. Through Personal interview : Personal interviews are the most commonly used method of collecting data, because the interviewer has the opportunity of explaing the study and answering any question, here the researcher gets direct information from the respondents.
2. By Personal observations: It refers to the collection of data or information by individual or group of individuals, through direct observations in the field.
3. By Questionnaire : The most common method used in surverys is the Questionnaire. In this method, simple questions and their possible answers are written on a plain paper, and the respondents have to tick mark the possible answers from given choices.
4. Others methods :
- Telephone interview : In this method, the researcher/interviewer can collect the information over the telephone.
- Measuring properties : In this method, the data about properties of soil and water collected directly from the field by measuring their characteristics using soil and water quality kit.
Types of Secondary sources of data :-
1. Publishçd sources – There are 5 types
- International publications : In this publications year books, monographs and reports are published by different agencies of the united nations.
- Government publication : These publications comprise the census of India published by officë of the register general of India.
- Semi Government publication : In this category thc publications and reports of corporations, boards, urban development authórities etc …
- Private publication : The research reports, surveys, year-books and monographs are published.
- Newspapers and Periodicals : The daily news papers and periodicals or magazines are easily accessible.
2. Unpublished sources – There are 3 types.
- Government Documents : The reportš, papers, findings, monographs and documents are prepared and maintained as unpublished records at different levels of Government.
- Government Records : The corporations, boards, district councils and civil departmènts prepare and maintain the periodical reports and the develópnient plans.
- Private Documents : The companies, trade unions, different political and non-political organizations and resident welfare associations arc having unpublished reports and records.