You can Download Chapter 11 Transport, Communication and Trade Questions and Answers, Notes, 2nd PUC Geography Question Bank with Answers Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Geography Question Bank Chapter 11 Transport, Communication and Trade
2nd PUC Geography Transport, Communication and Trade One Mark Questions with Answers
I. Answer the following in a word or a sentence each:
Question 1.
What is Transportation?
Answer:
Transportation refers to the system of carrying persons and goods from one place to another
place.
Question 2.
What do you mean by Communication?
Answer:
Communication refers to exchange of ideas, messages, information from one person to another person.
Question 3.
Which road is at highest altitude in the World?
Answer:
The world’s highest road is Manali -Leh road in the Western Himalayas. It is at an altitude of 4,270 meters.
Question 4.
What is Trade?
Answer:
The process of buying and selling of goods and commadities is called trade.
Question 5.
What is Radio?
Answer:
It is one of the means of communication which sends the information of National and International news, sports, cricket and other kinds of information, etc.
![]()
Question 6.
What is Television?
Answer:
An electronic device that receives television signals and displays them on a screen.
Question 7.
Define Port.
Answer:
A Port is defined as a place of navigable water where ships can shelter for load and unload.
Question 8.
On which river bank Kolkata Port is located?.
Answer:
On the Hoogly river 148 km from the sea.
Question 9.
Name the Satellite launched in November 2013.
Answer:
‘Mangalyann” was launched on 5 November 2013.
Question 10.
Which is the Head quater of Central Railways?
Answer:
Mumbai [CST]
![]()
Question 11.
What is Road transportation.
Answer:
The means of carrying goods and passengers through the motor vehicles from one place to another place.
Question 12.
Expand PMGSY.
Answer:
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY).
Question 13.
Which is the longest National highway in India.
Answer:
The longest National highway is NH-7 from Varanasi to Kanyakumari (2344) km.
Question 14.
Which is first railway line laid in India.
Answer:
The first railway line in India was from Bombay (VT) to Thane a distance of 34 km.
Question 15.
What is the total railway length of India.
Answer:
64,460 km.
![]()
Question 16.
Expand CORE.
Answer:
The central organisation for railway electrification (CORE).
Question 17.
Which is first pipe line in India.
Answer:
India’s first pipeline-Naharkatia to Baruni.
Question 18.
Which is the longest pipeline in India.
Answer:
The Hazira-Bijaipur-Jagdishpur (HBJ) Gas pipeline is one of the longest pipeline of the country (1750 km). ‘
Question 19.
Which is the Milk pipeline in India.
Answer:
A milk pipeline: It is from the Anand dairy to Ahmedabad in Gujarath.
Question 20.
Which is longest inland water way in India.
Answer:
National water way no -1 from Kolkata to Patna through Gahga and its tributaries with a distance of 2510 km.
![]()
Question 21.
Which port is known as Gateway of India.
Answer:
“Mumbai port” is known as Gateway of India.
Question 22.
Name the airports which are called Green Airports of India?
Answer:
Kempegowda International Airport of Bangalore and Hyderabad Airport are called Green Airports of India.
Question 23.
Name the place of first air travelling facility was started in India and when?
Answer:
From Bangalore to Hyderabad by “Deccan Airways” in the year 1946.
Question 24.
Name the first newspaper in India and who introduced it.
Answer:
The newspaper named “Samachar Darpan” introduced by ‘Hicky’s Gazette’ in the year – 1779.
Question 25.
When the first Radio programme was broad casted and where?
Answer:
In the year – 1923 at a place called “Club of Mumbai”.
Question 26.
Which is world’s first artificial Satellite and from where it was launched.
Answer:
“Sputnik-I’, It was launched by the Soviet Union in 1957.
Question 27.
Expand NRSA.
Answer:
National Remote Sensing Agency (NRSA).
![]()
2nd PUC Geography Transport, Communication and Trade Two Marks Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Mention the 3 important Railways gauges?
Answer:
- Broad-Gauge
- Metre – Gauge
- Narrow – Gauge.
Question 2.
Mention any 4 railway zones with their headquarters?
Answer:
- CentralRailway – Mumbai (CST)
- Western Railway – Mumbai (Church gate)
- Southern Railway – Chennai
- Eastern Railway – Kolkata.
Question 3.
Mention the advantages of Radio?
Answer:
- Radio reaches both to the literate and illiterate as well as to people of all ages.
- It creates awakening among the people about the world
- It provides educative value
- The production costs are lower.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the main advantages of Television.
Answer:
- Television educates millions of people through advertisement.
- It is a source of entertainment.
- It makes a personal appeal and transmits the message directly into the home.
- News in different part of the world can be seen within minutes or even seconds.
Question 5.
State two types of Waterways.
Answer:
- Inland water transport
- Ocean transport.
Question 6.
Differentiate between Internal and International airport of India.
Answer:
Internal Airport: The Airways which carries passengers, cargo and mail to different regions of the country and neighbouring countries.
International Airport: The Airways which carries the foreign traffic of passengers and cargo between the countries.
Question 7.
Differentiate between Export and Import trade of India.
Answer:
Export trade of India: Refers to the sale of goods and services by India to other countries of
the world.
Import trade of India: Refers to the buying goods from foreign countries and bringing them to home country.
![]()
Question 8.
Mention the four types of roads in India.
Answer:
- National Highways
- State Highways
- District roads and
- Village roads
Question 9.
State the significance of Air transport in India?
Answer:
- It is very efficient means for speedy transport of people, mail and goods.
- It is very essential on times of peace as well as during emergencies.
Question 10.
Write a short note on Mission Mangalyaan.
Answer:
- The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) informely called Mangalyaan (Sanskrit name for Mars craft) is a mars orbiter launched into Earth orbit.
- On 5th Nov 2013 by (Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) (8) (9) (10) (11).
- It is expected to enter orbit around Mars on 24 Sep 2014.
- The mission is a technology demonstrator project aiming to develop the technologies required for design, planning, management and operation of a Inter planatery mission.
Question 11.
Write any four advantages of Road ways.
Answer:
- Road ways are more flexible, fast, reliable which is capable of providing door to door service.
- It provides employment opportunities.
- It plays a vital role in national and international security.
- In hilly area, roads are the only means of effective transport.
Question 12.
Mention the types of Nagpur Plan road development in India.
Answer:
Nagpur plan has classified the road into 4 categories :
- National highways
- State highways
- District roads and
- Village roads.
Question 13.
Mention the four disadvantages of the railways in India.
Answer:
- The total mileage is still very small considering Indias large area and population.
- Unequal distribution of railway in the country.
- There is an unhealthy competition between the roads and railways.
- Multi-gauges cause inconvenience for transhipment of goods and passengers.
Question 14.
Mention the important international airports of India.
Answer:
- Sahara – Mumbai
- Indira Gandhi International – Delhi
- Subash Chandra Bose – Kolkata
- Anna – Chennai
- Kempegowda international airport – Bangalore
- Rajiv Gandhi international airport – Hyderabad.
Question 15.
Write the advantages of newspaper.
Answer:
- They are available for low cost
- They provide all types of information regarding science and technology, news, articles etc.
- Large number of people can read them.
- They provide a accurate information from different sources.
![]()
Question 16.
Which is the wonder box of 20th century, who invented colour TV and when.
Answer:
‘Television’ is described as the ‘Wonder box’ of 20th century. The first colour television was invented by Hungarian born ‘American Peter Gold Mark in 1940.
2nd PUC Geography Transport, Communication and Trade Five Marks Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Explain the National Highways of India.
Answer:
National Highways : They connect the capitals of the states, Industrial centres and major parts. They are well planned wide roads with two-lane, four-lane and six-lane roads.
- Construction and maintainance is done by the Central Government and National Highways Authority (NHAI).
The total length of the National Highway is about 71,772 km in 2011. They constitute only 2% of the length but they carry over 45% of the road traffic: - The number of National Highways in the country is 235.
Under the National Highways Authority of India, about 14,297 km length of National high way is proposed to be upgraded to four or six lanes in two phases.
* It consists of the following components :
- The Golden Quadrilateral
- The North-South and East-West corridors
- Port connectivity and other projects.
1. The Golden Quadrilateral super Highways Kolkata, Chennai-Mumbai and by six-lane super highway. It has a total length of 5846 kms.
2. East-West corridor :- This project has extended from the North-South corridor linking
between Srinagar (J.K) and Kanyakumari (T.N) and East-West corriders connecting between Silcher (Assam) and Porbandar (Gujarat). The project has a total length of about 7300 km.
3. Port connectivity project:-This project, connect golden quadrilateral roads with 3 major ports (380 km) and other projects (962 km) is in progress.
The longest National Highway is NH-7 from Varanasi to Kanyakumari (2344 km).
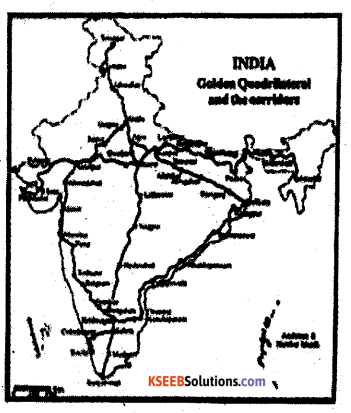
Question 2.
Explain the development of Railways in India.
Answer:
- The first railway line in India was from Bombay (V.T) to Thane, a distance of 34 km, opened on 16th April, 1853.
- It was followed by a railway line in 1856, from Madras to Arkonam (70 km).
- Railway line in 1874 from Kolkata to Raniganj (180 km).
- Then gradually railway lines were constructed to link different parts of the country.
- At the time of Independence, the length of the railway line was 54,96 km.
- During post-Independence period, because of the Five year plans, the Indian railway has recorded spectacular progress.
- There were 43 steam, 4,963 diesel and 3585 electric locomotives 55,065 coaches 2,11,763 wagons.
- The trains moved everyday through more than 7,030 stations.
- On an average they carried 17 million passengers and 2.8 million lakh tones of freight everyday.
- At present all the rail operations in India are managed by Ministry of Indian railways.
- The country’s railways is about 64,460 km of length which is fourth largest railway network in the world and first in Asia.
- It has transported 7651 million passengers and 921 million tonnes of frieght annually.
- The Network operates 28 states and 3 union territories.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain pipelines transport with advantages and disadvantages.
Answer:
- It is most convenient, efficient and cheap mode of transporting products like crude oil and refined products, gas, water and milk.
- At present solid materials are also transported through pipeline after converting them into slurry. .
Advantages of Pipelines :
- Pipelines can be laid through difficult terrain and also through water.
- The initial cost of laying the pipelines is high but the subsequent cost of maintainence and operation is low.
- Pipelines ensure a steady supply and minimizes trans-shipment losses and delays.
- Pipelines operation involves very low consumption of energy and keeps the environment free from pollution.
- Pipeline regions unites industrial regions.
Disadvantages:
- The capacity of pipelines cannot be increased once they are laid.
- The security of pipelines in certain areas and the detection of leakage are difficult.
- The construction of pipelines are expensive.
Question 4.
Explain any two major parts of West coast of India.
Answer:
The major ports located in the west coast of India are (a) Kandla (b) Mumbai.
1. Kandla : It is a tidal port located at Eastern end of Gulf of Kachchh (Gujarat).
- It has a natural harbour and has a vast hinterland, rich in agriculture and animal husbandary.
- Its main exports consists of leather, petroleum products, chemicals, salt, cement, cotton and silk textiles and edible oils.
- The imports include crude oil, potash, fertilizers, machines and synthetic rubber.
2. Mumbai: Mumbai is the biggest, most spacious, natural, well shelter, and capital of the Maharashtra state.
- The port is situated towards the eastern side of Mumbai island which runs in a north-east to south-east direction. ‘
- The length of this port is 20kms and width is 6-10 kms.
- There are 54 berths in its wet dock. This port has become India’s largest oil terminal.
- It has rich hinterland.
- Important items of imports are foodgrains, crude oil, machinery, chemicals, fertilizers ore.
Question 5.
Explain the air transportation of India.
Answer:
- Air transport is the transportation of goods and passengers by means of aeroplane and helicopters.
- It is very efficient means for speedy transport of people, mail & goods.
- It is very essential in times of peace as well as during emergencies.
- The first air travelling facility was started in India between Bangalore and Hyderabad by “Deccan Airways” in the year 1946.
- Indian Airways was nationalized in the year 1953.
- In the year 1996 state airport of Bangalore was declared as an International Airport.
Civil Aviation :- Air transport used for commercial purpose is called civil Aviation.
There are two types of air transport in India namely:
- The Indian Airlines Corporation to operate internal routes.
- Air India International to operate on external routes.
1. The Indian Airlines Corporation :
- Carries passengers cargo and mail to different regions of the country.
- It operates from 55 domestic stations and provides air service to remote areas.
- At present the Indian Airlines Corporation has more than 70 aircrafts.
- It connects all the important places in India & neighbouring countries namely Pakistan,
Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Mynmar and Srilanka.
2. The Air India :
- It carries foreign traffic of passengers and cargo.
- It was established in 1953. –
- It provides services to 97 destinations outside the country.
- It operates 59 stations of which 16 are domestic and 25 international.
- Air India own a fleet of 22 aircrafts.
Question 6.
Briefly explain the importance of satellite communication.
Answer:
Importance^of satellites: Satellites are important to us in many ways.
- They provide us with radio and cable television.
- They allow us to make cellular phone calls from long distances.
- They provide us with a global positioning system (GPS).
- They circle the earth and relay weather conditions and forecasts.
- The government uses them to spy on other countries in order to protect us.
- They are used for space research, which includes sotto satellites that observe the sun and provide us with early warnings of upcoming solar flakes. These solar flakes have been known to knock out various satellite communication links, which allow us to use our credit cards and to use beepers.
- Satellite monitor crops.
![]()
Question 7.
What do you mean by Satellite?
Answer:
A satellite can be defined as a body that orbits the earth or other planet which has been sent from the Earth into space theses are of vital importance to life on earth.
- The 20th century is also known as space age. With the advancement in science and technology artificial satellites has marked a new era in the history of global telecommunication.
- The Geo-stationary satellites are positioned at a height of about 36,000 km in the sky.
- Radio and Television networking over entire India are done through satellite technology. So, it is popularly called as ‘space age communication technique’.
- he world’s first artificial satellite, the sputnik. I was launched by the soviet union in 1957.
- Very recently India has launched a satellite IRS P-2 into the orbit successfully from the country’s space port at Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh.
- Satellite construction and launching is canied out as a part of the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). The ISRO centre is located at Bangalore, the satellite launching centres are located near Hassan in Karnataka.
- National Remote Sensing Agency (NRSA) Hyderabad is responsible for reception, processing of data from remote sensing satellites.
Question 8.
Explain Imports and Exports of India.
Answer:
Imports of India : Imports trade of India refers to buying goods from foreign countries and bringing them to home country.
The main items of Imports of India are :
1. Petroleum crude and products :
- It is the most important materials of Indian.Imports.
- In 2006-2007 India imported rupees 2,58,572 crores worth of crude oil and other petroleum products.
- It contributed 23% of our total imports.
2. Pearls precious and semi precious stones :
India imported rupees 33,881 crores worth of precious stone.
3. Capital goods :
In 2006-2007 India imported rupees 2,51,136 crores worth of capital goods.
4. Fertilizers :
India is a major importer of chemical Fertilizers. It is because the country is agrarian and the Internal production of fertilizers is insufficient. Potash fertilizers are largely imported.
Exports of India : Export trade of India refers to the sale of goods and services by India to other countries of the world.
The main items of our exports are as follows :
- Agricultural and Allied products: Products such as cereals, pulses tobacco, spices, nuts and seeds, oil meals, caster oil etc.
During 2011-2012 exports income is about US dollar 13300.63 million. - Ores and minerals: Export of ores and minerals like Iron ore, Manganese, Micca was estimated at US dollar 4700.29 million during 2011-12.
- Gems and Jewellery: India imports gems and precious stones in their raw form and . exports them after proper cutting and polishing.
- Electronic goods: Items under this group of consists of machinery, iron, steel and other engineering items.
- Petroleum products: Export of petroleum products increased to US dollar 34667.02 million.
Question 9.
Explain the composition and direction of India foreign trade.
Answer:
Composition of Export: Composition of exports refers to the goods that are exported from India to foreign countries.
The export of India may be classified into three types :
- Primary commodities
- Manufacturing goods
- Services.
Direction of India’s exports:
- India’s export of goods to other countries have been increasing significantly since independence.
- Nearly 54% of our exports are made to Asia and other oceanic countries.
- European regions are importing about 21:6% and Americans are importing about 15%.
Composition of India’s Imports:
- Composition of India’s import refers to the various types of goods that are imported from foreign countries to India.
- Today India imports several items like fertilizers, petroleum, crude products and capital goods, organic, chemicals, gold and silver.
Direction of India’s Imports:
- In the beginning India was importing only from few countries including Britain. Now the country is importing from several countries like USA, West Europe, Russia, West Asia.
- India is depending on different countries for different goods. India imports capital goods from Japan, Britain, France and Russia, whereas food products are imported from America and Crude oil from OPEC countries.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain the important inland waterways in India.
Answer:
- The gangas with its tributaries forms the most important inland waterways in India. It is navigable from Kolkata to Patna. It has been declared as the national water way no-1 in 1986. Its length is 2510 km.
- The Brahmaputra is the second important navigable river next to the Gangas. It is navigable from Kolkata to Dibrugh (1280) km. The water way between Satiya and Dhubri (891) km in Assam was declared as a National waterways no-2.
- River of south India are not suitable for navigation. However the deltaic parts of the Godavari (300) km. The Krishna (60 km) and the Mahanadi are useful for.navigation.
- There are some navigable canals, which serve as inland waterways the Buckingham canal (418 km) along the east cost of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu is the longest navigable canal. The Kurnool cuddapah canal in Andhra Pradesh and the some canal in Bihar are also used for inland navigation! ,
- The backwaters and lagoons of Kerala are used for navigation. ‘
Question 11.
Describe the Radio as a communication Media in India.
Answer:
Radio has played an important means of communication in the field of advertising, information, broadcasting local, regional, public opinions, national and international news, sports, cricket etc.
- Radio is more powerful than the press because it gives immediate information throughout the world without loss of time. Radio broadcasting was started in India in the early 1920’s.
- The first programme was broadcasted in 1923 by radio club of Mumbai. The broadcasting service was setup in 1927.
- It was changed to all India Radio (AIR) in 1936. It also came to be known as “Akashvani” from 1957.
- The All India radio has at present 213 Radio stations these includes 114 regional stations, 77 local stations 14 relay centers.
Advantages:
- Radio reaches both to the literate and illiterate as well as to people of all ages.
- It creates awakening among the people about the worls.
- It provides educated values.
- The productions costs are lower.
- Radio is the only mass media that people use while driving, cleaning, moving etc.
Disadvantages:
- Radio is brief, It cannot be very descriptive.
- Its scope is limited.
- It is one way communication.
- It is confined to the control of government.
Question 12.
Briefly explain about the television in India.
Answer:
An electronic device that receives television signals and displays them on a screen.
- Television can offer video clips of events that show the audience what happened in the accompanying story.
- The television coverage covers events at all times of the day.
- Television broadcasting was first started by the government of India under the name of Doordarshan (DD) in Delhi on Sep – 1959.
- Today, Television coverage is provided by Doordarshan to about 90 percent of India’s population in India.
Advantages:
- It is the most effective medium to deliver information to large number of people very quickly.
- News in different part of the world can be seen with in minutes or even seconds.
- Television educates millions of people through advertisement. ,
- It is a source of entertainment.
- It makes a personal appeal and transmits the message directly into the home.
- It exhibits the persons giving the message.
Disadvantages:
- It is a sort of time – consuming, people waste time in watching.
- Television is a health hazard to people, especially to children.
- Television also braodcasts some inappropriate programmes.
- It is very costly, so it can be used only to a limited extent.
- It requires lot of concentration, attention of the people.
![]()