Students can Download 2nd PUC Physics Model Question Paper 2 with Answers, Karnataka 2nd PUC Physics Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Physics Model Question Paper 2 with Answers
Time: 3 Hrs 15 Min
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- All parts are compulsory.
- Answers without relevant diagram/figure/circuit wherever necessary will not cany any marks
- Direct answers to the Numerical problems without detailed solutions will not carry any marks.
Part – A
I. Answer all the following questions ( 10 × 1 = 10 )
Question 1.
Write the SI unit of Electric field.
Answer:
Newton per coulomb (N/C)
Question 2.
When will the magnetic force on a movi¬ng charge be maximum in a mag notified?
Answer:
F = qVBsinθ , If θ = 90° (Fm – qυB)
The magnetic force is maximum only when moving charge is ⊥r to field.
Question 3.
Where on the Earth’s surface is the magnetic dip zero?
Answer:
At equator, dip is zero
Question 4.
State Curie’s law in magnetism.
Answer:
The magnetic susceptability of a para magnetic substance varies inversely to its absolute temperature(T).
i.e x α \(\frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{T}}\) (x = \(\frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{T}}\))
![]()
Question 5.
What is the significance of Lenz’s law?
Answer:
Law of conservation of energy.
Question 6.
Write the formula for Malus law.
Answer:
i = i0cos2θ
Where I → is intensity of the light transmitted by the analyser.
I0 → is intensity of the light incident on the analyser.
θ → is angle between the pass axes of the analyser & polariser.
Question 7.
What is the ratio of the nuclear densities of two nuclei having mass numbers in the ratio 1:3?
Answer:
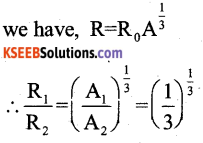
Nuclear density is independent of mass number & is approximately constant.
Hence \(\frac{P_{1}}{P_{2}}\) = 1
Question 8.
Define current amplification factor in a common – emitter mode of transistor.
Answer:
It is defined as the ratio of change in collector current ( ΔIc )to the change in base current (ΔIb) at constant collector emitter voltage (VCE) when the transistor is in active state
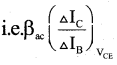
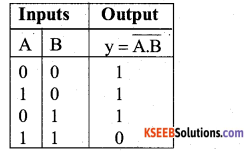
Question 9.
Write the truth table of NAND gate.
Truth table of NAND gate
Question 10.
Why sky wave propagation is not possi¬ble for waves having frequency more than 30 MHz?
Answer:
The sky wave range is short & it is used in short wave broad cast service.
Part – B
II. Answer anyfive ofthe following questions. ( 5 × 3 = 15 )
Question 11.
Sketch the electric lines of force due to a point charge q. If i) q<0 and ii) q>0
Answer:
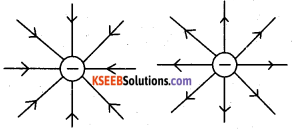
Question 12.
A galvanometer having a coil of resistance 12 Ω gives full scale deflection for a current of 4 mA. How can it be converted into a voltmeter of range 0 to 24V?
Answer:
Given G = 12 Ω, Ig = 4 x 10-3A. V = 24V
We have,
\(\mathrm{R}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{B}}}-\mathrm{G}\)
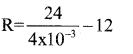
R = 5988Ω
A resistance of 5988 Ω must be connected in series with galvanometer.
![]()
Question 13.
Distinguish between paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances.
Answer:
| Paramagnetic substances | Ferromagnetic Substances |
| 1. Paramagnetics are feebly attracted by magnets. | 1. They are strongly attracted by magnets. |
| 2. Magnetic permeability is slightly greater than one i.e. Mr>1 | 2. Relative permeability is greater than 1000 |
| 3. Magnetic susceptability is low & positive. | 3. Magnetic susceptability is +ve & large. |
Question 14.
What is meant by Self Inductance and Mutual Inductance?
Answer:
- The phenomena in which an emf is induced in a coil due to change of current through the same coil is known as self-induction.
- The phenomena in which an emf is induced in one coil due to change of current is the neighbouring coil is called mutual induction
Question 15.
What are electromagnetic waves? Write the expression for the velocity of electro magnetic waves in terms of permittivity and magnetic permeability of free space.
Answer:
The waves in which there are a sinusoidal variation of electric & magnetic field vectors at right angles to each other & also right angle to the direction of propagation of the wave is called e.m waves.
∴ The expression for velocity of e.m. wave is
\(C=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu_{0} \varepsilon_{0}}}\) Where µ0 → is permeability of free
space, ε0 → is the permittivity of free space.
Question 16.
Write the relation between the path difference and wavelength of light wave used for constructive and destructive interference of light.
Answer:
a) For constructive interference
∴ Path difference = 2n\(\frac{\lambda}{2}\) = nλ
Wheve λ → is wave length of light used
n → 0, 1, 2,
b) For destructive interference :
∴ Path difference = (2n+l)\(\frac{\lambda}{2}\)
Wheve λ → is wave length of light used n → 0, 1, 2,………
Question 17.
Define :
i) photoelectric work function
ii) electron volt (ev)
i) Photoelectric work fraction : the minimum energy required to remove an electron from the metal surface is called work function, i.e. w = hV0
Where h → is planck’s constant
V0 → is threshold frequency
ii) Electron volt is the kinetic energy gained by an electron when it is accelerated through a potential difference of 1 volt.
i.e. lev = 1.602 × 10-19J.
Question 18.
Draw the block diagram of a AM receiver.
Answer:
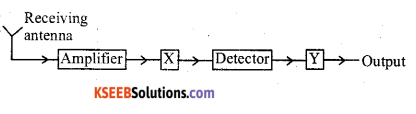
x → Intermediate frequency stage
y → power amplifier
Part – C
III. Answer any five of the following questions. ( 2 × 5 = 10 )
Question 19.
Derive an expression for potential energy of a system of two charges in the absence of external electric field.
![]()
Consider 2 point charges q1 & q2 are separated by a distance ‘r’ are as sho in the fig.
∴ The change q1 is bringing from ∞ to given point A, No work done i.e. w1= 0 |||ly the charge q2 is bringing from ∞ to given point ‘B’ against us field q2
∴work is done it is given by
i.e. w2 = vq2

Question 20.
Arrive at an expression for drift velocity.

Controller a metalic conductor is connected to a battery
Let \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}} \rightarrow\) is E.f. setup inside the conductor
m → is mass of electom
e → charge of free elector
Vd → is drift velovity
τ → is ralaxation time
the force experienced by an electron in the field is given by \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}=-\mathrm{e} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}\)
-Ve sign shows that divertion of \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}\) & \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}\) are in apposite each other
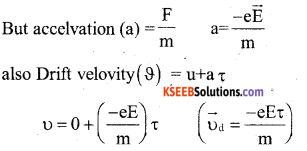
![]()
Question 21.
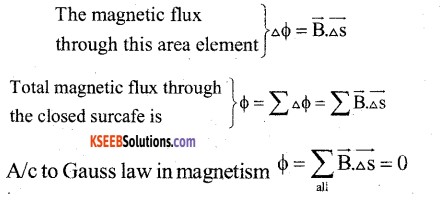
State and explain Gauss law in magnetism.
Answer:
The net magnetic flux through any closed surface is always zero
\(\sum \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathrm{As}}=0\)
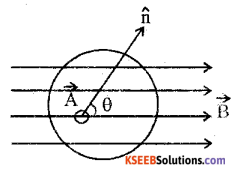
consider a closed surface
S in a uniform
\(\mathrm{M} . \mathrm{F} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}\) Let \(\overrightarrow{\Delta \mathrm{S}}\)
be a small area element of this surface with \(\hat{n}\)
along its normal
Question 22.
Derive the expression for motional emf induced in a conductor moving in a uniform magnetic field.
Answer:
Consider a straight metallic rod PQ of length ‘t’ placed in a uniform M.F. \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}\). The rod is moved with a velocity \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}\) is a direction ⊥r to
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}\) Let the rod moved through a distance ‘x’ in time‘t’ them the area covered by the rod is A= 1 xx The magnetic flux linked with the rod is
Φ = B.A Φ = B1x
∴ The included emf in the rod is
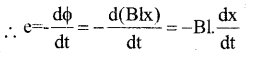
Motional emf (e – Blv)
∴ \(\mathrm{v}=\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{dt}}\)
Question 23.
With a diagram, explain the working of a transformer.
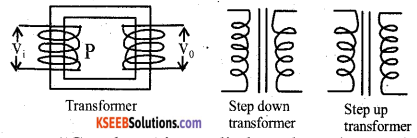
Answer:
AC voltage is applied to the primary, it creates a varying M.F. & hence a changing magnetic flux in the core. Since the secondary coil is magnetically coupled, due to the mutual induction the changing flux causes induced emf in it. Thus, the power is transferred from primary to secondary.
Question 24.
What is total internal reflection? Mention two applications of optical fibres.
Answer:
The phenomena of complete reflection of light at the interface of two optical media when a ray of light travelling in denser medium is called total internal reflection.
- Optical fibre are used in telecommunication
- It is used to measure rate of flow of blood.
Question 25.
What are the matter waves? Write the expression for De – Broglie wavelength of a particle and explain the terms.
Answer:
The waves associated with material particles in motion is called matter waves. The expression for de Broglie wavelength is \(\lambda=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{mv}}\)
where
h → is Planck’s constant
m → is mass of moving particle
v → is the velocity of moving particle.
Question 26.
Write three differences between n-type and p-type semiconductors.
Answer:
P – type S.C.
- It is a semiconductor doped with trivalent impurities.
- Majority charge carriers are holes
- The impurit atom is called acceptor impurity.
n-type S.c
- It is a semiconductor doped with pentavalent impurities.
- Majority charge carriers are electron
- The impurity atom is called Sonar impurity
Part – D
IV. Answer any two of the following questions ( 2 × 5 = 10 )
Question 27.
Derive an expression for the electric field at a point due to an infinitely long thin charged straight wire using Gauss law.
Answer:
Consider an infinitely long thin straight wive with uniform linear charge q density λ. Let P be a point at ⊥r distance r from the wire.
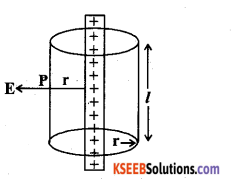
To calculate the E.F \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}\) at P, imagine a cylindrical Gaussian surface.
∴ The surface area of the] curved part S = 2πrl
Total charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface q = λl
Electric fliix through the end Surfaces of the cylinder is Φ = 0
Electric flux through the curved Surfaces of the cylinder is Φ2 = Ecosθ.s
Φ2 = EX1X2πrl
The total electric flux Φ = Φ1 + Φ2
Φ = 0 + E2πrl, Φ2= 2πrlE …………… 1
A/C to Gauss law,

from (a) and (2)
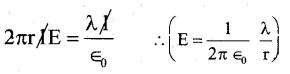
Question 28.
Obtain the bridge balanced condition of Wheatstone’s bridge network by applying Kirchhoff’s rules.
Answer:
Wheatstone’s bridge is a device used to determine unknown resistance.
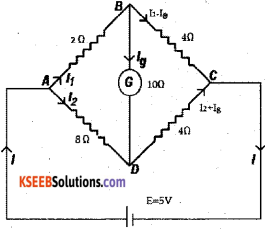
It resistances R1, R2, R3 & R4 a galvanometer of resistance G & a battery with key. Let I is the math current & splits into branch current I1 & I2 respectively
i.e. I = I1 +I2
At B, I1 = I3+ Ig………….(1)
A + D, I2 = 4 + Ig ………. (2)
Apply KVL to the mesh ABDA
I1R1 + igG – I2R2 = o ………….. (3)
to the mesh BCDB
I3R3 – I4R4– IgG = 0 ……………… (4)
The wheatstones bridge is said to be balanced
when no current flowing throught the galvano
meter i.e. Ig 0 ∴ eqn (1) is I1 = I3
eqn(2)is I2 = I4
eqn (3) is I1R1 – I2R2 = 0
∴ I1R1 = I2R2 …………. (5)
eqn (4) is I3R3 – I2R2
∴I3R3 = I4R4 …………………. (6)
![]()
Question 29.
Two straight parallel conductors are placed at certain distance in free space. The direction of current in both the conductors is same. Find the magnitude and direction of the force between them. Hence define ampere.
Answer:
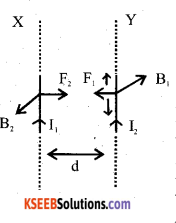
Consider two infinitely long straight parallel condu ctors x & y carrying a current I1 & I2 respectively. Let d is the ⊥r distance between them.
Let I1 is the current flowing through x conductor, it produces a M.F. (B1)
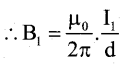
Now the conductor Y carrying current I2 in the M.F.B, it experiences a mehanical force of length 1 is
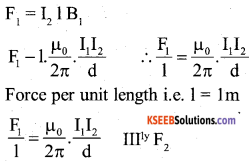
The direction of force can be obtained using ampere’s left-hand rule.
∴ The force bn. two ||le conductors carrying currents in the same direction is attractive. ||ly the force bn two ||le conductors carrying current in opposite direction is repulsive.
Definition of ampere If I1 = I2 = IA, d=lm them F = 2 × 10-7N.
Ampere is the steady current which when flowing through each of 2 infinitely long straight ||le conductors placed in the air at a distance of lm produces a force of 2 × 10-7 N/m.
V. Answer any two of the following question ( 2 × 5 = 10 )
Question 30.
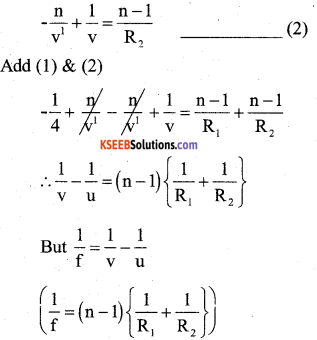
Derive Lens Maker’s formula for a con vex lens.
Answer:
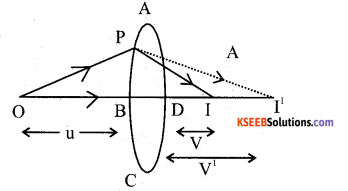
Consider a thin convex lens of focal length f & R.I (n) placed in air as shown in fig let R1 & R2 → are the of curvatur of the surfaces ABC & ADC of the respectively.
o → Luminous point object on the principle axis.
A ray op invident at p, after refraction, emerges along QI & meet at I on the principal axis.
Image formution takes place in two stages. (1) Refraction at the surface ABC In the observe of ADC, the refracted ray is meet at I1, then

(2) Refraction at the surface ADC the image I1 acts as a virtual object to form a real image at a distance V, then
Question 31.
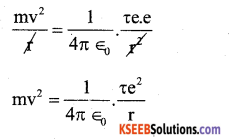
Assuming the expression for radius of the orbit, derive an expression for total energy of an electron in hydrogen atom.
Answer:
Consider an electron of mass m, charge, e revoking around the nucleus of radius of r. The charge on the nucleus + Te.
∴ T.E = KE + P.E
T. E = K + U ………… (1)
For circulation
Centripetal force = Electrostate force bn nucleus & electron.
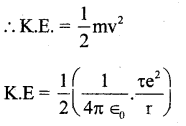
The Potential energy of the electron is the field o nucleus is

![]()
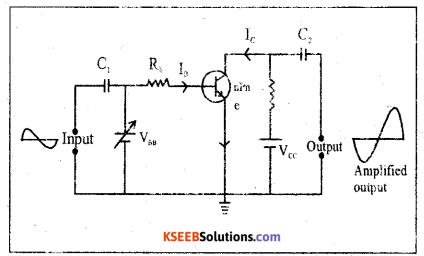
Question 32.
With the help of circuit diagram, explain the working of NPN transistor as a common emitter amplifier.
Answer:
The circuit diagram of a CE amplifier using NPN transistor is as shown m fit. The input circuit is forward biased & the output circuit is reverse biased when the ac input signal to be amplified is fed to the base-emitter circuit. The output voltage V0 varies in accordance with the relation, V0=VCE =Vcc – IcRc, These variations is the collector voltage VCE uppers as amplified output.
During the -t-ve half cycle of ac input signal the forward base of emitter as junction increase Due to this base current IB increase & hence collector current IC increases. As a result of this ICRC increases output voltage VO this indicates that the +ve half cycle of input ac signal voltage is amplified through -ve half cycle.
During the -ve half cycle of ac input signal, the forward bias of emitter-base junction decreases. Due to this base current IB decreases & hence collector current IC decreases. As a result of this ICRC decreases the. output voltage V0 is +ve. This indicates that the -ve half cycle of input ac signal voltage is amplified through +ve half cycle.
Thus, the weak input signal is amplified & output signal is out of phase with the input signal by 180°
VI. Answer any three of the following questions ( 3 × 5 = 15 )
Question 33.
Charges 2 µ C, 4 µ C and 6 µ C are placed at the three corners A, B and C respectively of a square ABCD of side x metre. Find, what charge must be placed at the fourth corner so that the total potential at the center of the square is 0
Answer:
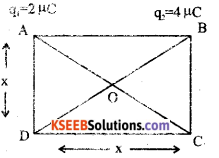
In the Δle ABC
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
AC2 = x2 + x2
AC2 = 2x2
∴ AC = √2 x,.m
![]()

Question 34.
A wire having length 2.0m, diameter 1.0 mm and resistivity 1.963 × 10-8 Ω m is connected in series with a battery of emf 3 V and internal resistance 1 Calculate the resistance of the wire and current in the circuit.
Answer:
Given,
length (l) = 2m
Diameter (D) = 1mm = 1 × 10-3 m
∴ radius (r) = \(\frac{\mathrm{D}}{2}\) = 0.5 × 10-3 m
resistivity (f) = 1.963 × 10-8Ωm
E = 3V Internal senstarce (r) = 1 Ω
R=? I = ?
We have,

![]()
Question 35.
An inductor and a bulb are connected in series to an AC source of 220 V, 50 Hz. A current of 11A flows in the circuit and phase angle between voltage and current is \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) radians. Calculate the impedance and inductance of the circuit.
Answer:
Given,
Vrms = 220v, f = 50 Hz
Irms = 11A
Φ = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) radian, Z=?, L =?

Question 36.
In Young’s double slit experiment while using a source of light of wavelength
4500 Å, the fringe width is 5mm. 1f the distance between the screen and the plane of the slits ¡s reduced to half, what should be the wavelength of light to get fringe 4 mm?
Answer:
Given,
wavelength (λ) 45OOA°= 45OO × 10-10 m
fringe width (w) = 5mm = 5 × 10-3 m
D = \(\frac { D }{ 2 }\)
wavelength (λ1) = ?
fringe width (w1) = 4mm = 4 × 10-3 m
we have, fringe width (w) = \(\frac{\lambda \mathrm{D}}{\mathrm{d}}\)
5 × 10-3 =4500 × 1010 × \(\frac { D }{ d }\)
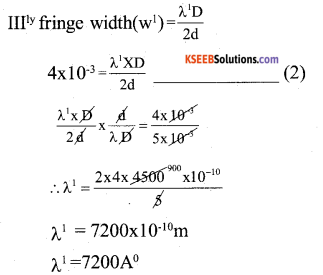
![]()
Question 37.
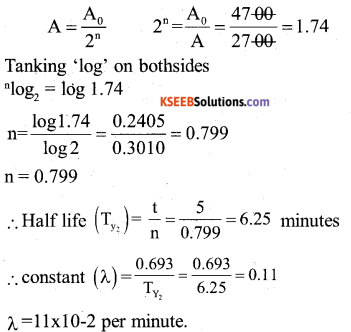
The activity of a radioactive substance is 4700 per minute. Five minutes later the activity is 2700 per minute. Find
a) decay constant and
b) half – life of the radioactive substance.
Answer:
Given A0=4700 per minute
A = 2700 per minute
t = 5 minute λ = ? Ty2 = ?
we have,