Karnataka State Board Solutions for 2nd PUC Sociology Question Banks with Answers, Solutions, Notes, Guide Pdf are prevailing here in direct pdf links for effective exam preparation. Students who are studying for 2nd PUC Sociology textbook solutions can refer to this page for grabbing KSEEB 2nd PUC Sociology Solutions pdf chapter wise for free. By reading the textbook solutions. You Can Download 2nd PUC Question Bank with Answers from Karnataka State Board solutions, you will be able to understand all the exercises and score good marks.
Also, there are so many advantages that you can avail from the Karnataka State Board Solutions for 2nd PUC Sociology Question Bank with Answers, Solutions pdf. So download 2nd PUC Sociology Notes from KTBS Solutions Pdf via quick links & access them easily while preparation. Students can also read 2nd PUC Sociology Model Question Papers with Answers hope will definitely help for your board exams.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Sociology Question Bank with Answers
Provided Karnataka State Board solutions for 2nd PUC Sociology textbook solutions are prepared by subject experts after ample research. So students are suggested to download the 2nd PUC Sociology Question Bank with Answers and Textbook Solutions from the available PDF links and kickstart your preparations for final exams. You can download them freely & practice regularly to score high marks in the examinations. Access the below Chapter-wise links and learn complete by using 2nd PUC Sociology Question Bank with Answers from Karnataka State Board solutions pdf.

Karnataka 2nd PUC Sociology Question Bank with Answers in English
- Chapter 1 Making of Indian Society and Demography
- Chapter 2 Social Inequality, Exclusion and Inclusion
- Chapter 3 Inclusive Strategies
- Chapter 4 Family in India
- Chapter 5 Change and Development of Villages and Urbanisation in India
- Chapter 6 Market and Communication Systems
- Chapter 7 Social Movements
- Chapter 8 Social Change in India
Karnataka 2nd PUC Sociology Question Bank with Answers in Kannada
- Chapter 1 Making of Indian Society and Demography
- Chapter 2 Social Inequality, Exclusion and Inclusion
- Chapter 3 Inclusive Strategies
- Chapter 4 Family in India
- Chapter 5 Change and Development of Villages and Urbanisation in India
- Chapter 6 Economic, Political and Communication Systems
- Chapter 7 Social Movements
- Chapter 8 Social Change in India
Karnataka 2nd PUC Sociology Syllabus and Marking Scheme
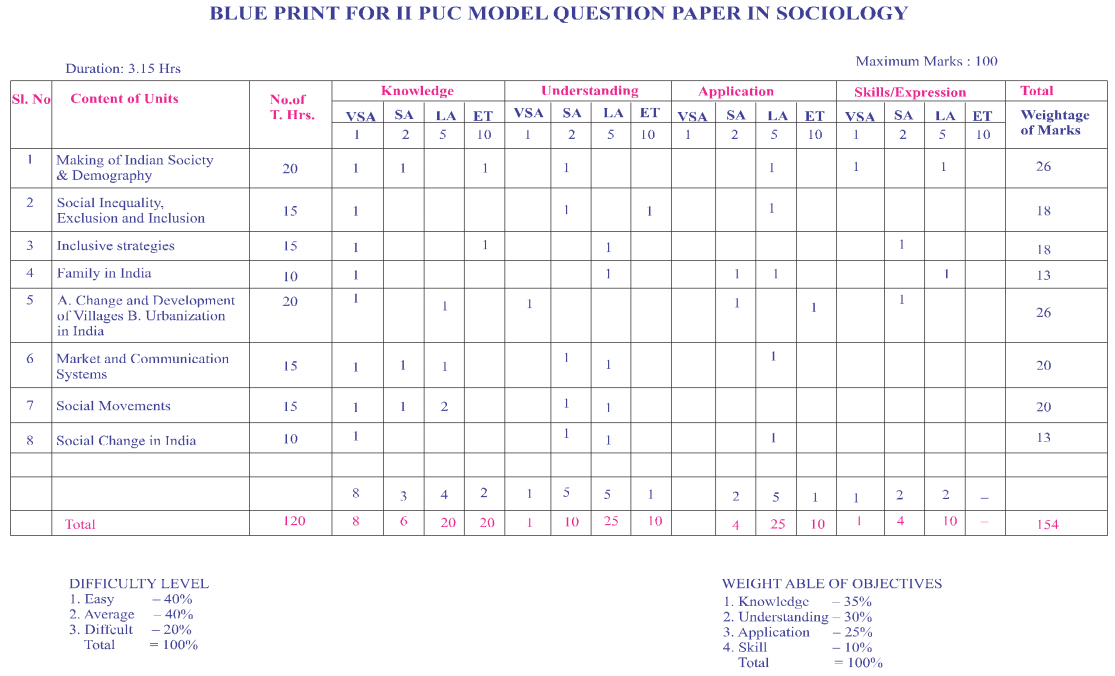
2nd PUC Sociology Blue Print of Model Question Paper
CHAPTER 1 MAKING OF INDIAN SOCIETY AND DEMOGRAPHY (10/20 Hours, 13/26 Marks)
1.1 Emergence of Pluralistic Society; Racial Groups in India, Origin of Indian Civilization, The Process of Aryanization, Development of Religio-Philosophical Literature, Christianity and Islam in India, Arrival of the Europeans
1.2 Unity in Diversity; Nature of Diversity; Regional, Linguistic, Religious, Cultural and Ethnic : The Nature of Unity in India; Regional Unity, Linguistic Unity, Religious Unity and Cultural Unity.
1.3 National Integration – Meaning and Definitions Challenges to National Integration – Regionalism, Communalism, Linguism, Extremism and Terrorism. Measures to Strengthen National Integration Demographic Profile of India; Major Characteristics of
1.4 Demographic Profile of India; Demographic profile of Karnataka. Population Policy of India.
CHAPTER 2 SOCIAL INEQUALITY; EXCLUSION AND INCLUSION (15 Hours, 18 Marks)
2.1 Social Inequality and Exclusion – Meaning and Definition of Social Inequality, Exclusion and Inclusion.
2.2 Exclusion based on Caste: Meaning and Definition of Caste. Changes in Caste System – Caste in Pre-Independence Period, Caste in Post Independence India: Functional changes in the Caste System, The changes in the Role of Caste System
2.3 Concept of Dominant Caste (M. N. Srinivas).
2.4 The Backward Classes in India; Meaning of Scheduled Castes, Problems or Disabilities of Scheduled Castes – Economic, Social and Religious
2.5 Tribes – Changing Concept of Tribe, Demographic Aspects, Geographical Distribution of Indian Tribes – Scheduled Tribes – Problems of Indian Tribes – Three views on Tribal Welfare- Tribal Panchasheela.
2.6 Other Backward Classes (OBCs) – Problems of other Backward Classes (OBCs), Criteria of Backwardness; Kalelkar and Mandal Commissions; Karnataka State Backward Class Commissions – An Overview
CHAPTER 3 INCLUSIVE STRATEGIES (15 Hours, 18 Marks)
3.1 Affirmative Action related to SCs, STs and Women: Meaning of Affirmative Action and Protective Discrimination;
Constitutional Safeguards for the Upliftment of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, Legislative Measures for the Upliftment of Scheduled Castes, Developmental Measures for the Upliftment of Scheduled Castes, The Role of Gandhi and B. R. Ambedkar, The Role of Non-Governmental Organizations in the Upliftment of SCs and STs, Sulabh Shouchalaya
3.2 Tribal Welfare Programmes; Economic Programmes, Educational Programmes, Research Programmes, Health, Housing and other Schemes.
3.3 Gender inequality; Concept of Sex and Gender, Gender discrimination, Towards Equality Report 1974. Women Empowerment; Meaning and Definition of Women’s Empowerment, Strategies for Empowerment of Women, The National Commission for Women, Self-Help Groups (SHG), Structure of the Self-Help Group, Micro Finance; Meaning, Features Types, Principles; Streeshakti, Shri Kshethra Dharmasthala Rural Development Project, Lijjat Papad and SEWA.
CHAPTER 4 FAMILY IN INDIA (10 Hours, 13 Marks)
4.1 Meaning, Definitions and Characteristics of Joint Family
4.2 Types of Joint Family: Patriarchal: Illom, Matriarchal: Taravad-Narasinganavar family – An example of patriarchal joint family
4.3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Joint Family Structural and Functional changes – Causes for changes
CHAPTER 5 CHANGES AND DEVELOPMENT OF VILLAGES AND URBANIZATION IN INDIA (20 Hours, 26 Marks)
5.1 Meaning and Characteristics of Village Community, Characteristics of Village Community, Villages Studies and its importance
5.2 Problems of Indian Villages – Social, Economic and Agricultural Problems – Farmer Suicides in Karnataka, Causes of Agrarian Crisis, Understanding Farmer Suicides, The Committees to study the Agrarian Issues in Karnataka, Recent Policy initiatives
5.3 Rural Developmental Programmes; Meaning of Rural Development, Land Reforms, The Green Revolution, Panchayath Raj, Community Development Programme (CDP), Integrated Rural Development Programme (IRDP) and MGNAREGA.
5.4 Changes in Indian Villages: Continuous Migration of People towards the Cities, Farm to Non-farm and Special Economic Zone (SEZ).
5.5 Meaning and Definitions of Cities and Urbanization, Historical Background of Urbanization in India.
5.6 Problems of Indian Cities- Urban poverty, Slums, etc., Solutions to Urban Problems.
CHAPTER 6 MARKET AND COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (15 Hours, 20 Marks)
6.1 The Market as a Social Institution: Meaning of Market and features of Market, Sociological Perspectives on Market and the Economy. Weekly Market as a Social Institution and Bastar Tribal Market – Chhattisgarh,
6.2 Traditional Business Communities – Caste Based Trade among theNakarattars of Tamil Nadu, Social Organisation of Markets – Pushkar Annual Fair.
6.3 Virtual Markets Emergence of Virtual Markets and online Shopping Sites in India.
6.4 Interlinking of Markets and Mcdonaldization.
6.5 Mass Media:
6.5.1 Meaning of Mass Media and Functions of Mass Media.
6.5.2 Types of Mass Media; Print Media and Electronic Media.
6.5.3 Recent Trends in Mass Media.
6.5.4 Role of Media in the Contemporary World.
CHAPTER 7 SOCIAL MOVEMENTS (15 Hours, 18 Marks)
7.1 Social Movements in India; Meaning, Definitions of Social Movement, Major Components of Social Movements, New Components of Social Movements, Types of Social Movements
7.2 Farmers’ Movement; Meaning and Types of Farmers’ Movement, Kathleen Gough, Factors facilitating Peasant Movement in India, Farmers’ Movements in Karnataka, Kagodu Movement/Kagodu Satyagraha, The Malaprabha Agitation, Navalgunda and Nargunda incidents, Anti-Price Rise Agitation, The Rise of Rudrappa’s Raitha Sangha, Entry of Prof. M. D. Nanjudaswamy, Major issues of KRRS Movement, Neera Movement, Post-1980 Issues and Developments and PDF and KPRS.
7.3 Backward Class and Dalit Movement; The Course of the Movement, Sri Sahu Maharaj and Satya Shodak Samaj, Justice Party and Non-Brahmin Movement in Madras, The Self¬Respect Movement or the Dravidian Phase, Non=Brahmin Movement in Karnataka, Non-Brahmin Movement in Kerala, SriNarayana Guru Dharma ParipalanaYogam (SNDP), Dalit Movement in the Post-Independence Period
7.4 Women’s Movement in India; Pre – Independence Phase, Post-Independence Phase, Changing context and Widening concerns
CHAPTER 8 SOCIAL CHANGES IN INDIA (10 Hours, 13 Marks)
8.1 Social changes in India; Introduction to Social Changes in India
8.2 Sanskritization; Meaning and Definition of Sanskritization, Major Factors of Sanskritization, Criticisms of Sanskritization,
8.3 Westernisation; Meaning and Definition of Westernization, The Impact of Westernization, Criticisms of Westernization
8.4 Modernisation; Meaning and Definition of Modernization; Causes for Modernization, Process of Modernization in India
8.5 Globalization; Meaning and Definition of Globalization; Factors Contributing to Globalization; Two Major Dimensions of Global Outlook; Homogenization and Hybridization of culture; Barbie Doll – Truly a Global Citizen.
We wish the data shed above will benefit you at the time of your preparation & gain good scores. So, download Karnataka State Board 2nd PUC Sociology Question Bank with Answers from here and become a topper in the final examinations. Moreover, keep in touch with our site & get all updated chapter wise KSEEB State Board Solutions for all subjects.
