You can Download KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational Numbers InText Questions and Answers to help you to revise the complete syllabus.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational Numbers InText Questions
Try These (Page 6)
Question 1.
Complete the following table:
| Numbers | Commutative for | |||
| Addition | Subtraction | Multiplication | Division | |
| Rational Numbers | Yes | ______ | ______ | ______ |
| Integers | ______ | No | ______ | ______ |
| Whole Numbers | ______ | ______ | Yes | ______ |
| Natural Numbers | ______ | ______ | ______ | No |
Solution:
| Numbers | Commutative for | |||
| Addition | Subtraction | Multiplication | Division | |
| Rational Numbers | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Integers | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Whole Numbers | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Natural Numbers | Yes | No | Yes | No |
Try These (Page 7)
(i) Whole Numbers
Question 1.
Recall the associativity of the four operations for whole numbers through this table:
| Operation | Numbers | Remarks |
| Addition | _________ | Addition is associative |
| Subtraction | _________ | Subtraction is not associative |
| Multiplication | Is 7 × (2 × 5) = (7 × 2) × 5? Is 4 × (6 × 0) = (4 × 6) × 0? For any three whole numbers a, b and c, a × (b × c) = (a × b) × c | Multiplication is associative |
| Division | _________ | The division is not associative |
Fill in this table and verify the remarks given in the last column.
Check for yourself the associativity of different operations for natural numbers.
Solution:
| Operation | Numbers | Remarks |
| Addition | Let us take an example to show that addition is associative associative Is (7 + 2) + 6 = 7 + (2 + 6) 9 + 6 = 15 7 + (2 + 6) = 7 + 8 = 15 15 = 15, ∴ (7 + 2) + 6 = 7 + (2 + 6) Is (4 + 0) + 13 = 4 + (0 + 13) Let us take (4 + 0) + 13 = 4 + 13 = 17 4 + (0 + 13) = 4 + 13 = 17 ∴ (4 + 0) + 13 = 4 + (0 + 13) So, for any three whole numbers say a, b and c (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) | Addition is associative |
| Subtraction | Is 19 – (7 – 2) = (19 – 7) – 2 19 – (7 – 2) = 19 – 5 = 14 (19 – 7) – 2 = 12 – 2 = 10 14 ≠ 10 ∴ 19 – (7 – 2) = (19 – 7) – 2 Is 23 – (0 – 5) = (23 – 0) – 5 23 – (0 – 5) = 23 – (- 5) = 23 + 5 = 28 (23 – 0) – 5 = 23 – 5 = 18 28 ≠ 18 ∴ 23 – (0 – 5) ≠ (23 – 0) – 5 So, for any three whole numbers a, b and c a – (b – c) ≠ (a – b) – c | Subtraction is not associative |
| Multiplication | Is 7 × (2 × 5) = (7 × 2) × 5 7 × (2 × 5) = 7 × 10 = 70 (7 × 2) × 5 = 14 × 5 = 70 70 = 70 ∴ 7 × (2 × 5) = (7 × 2) × 5 Is 4 × (6 × 0) = (4 × 6) × 0 4 × (6 × 0) = 4 × 0 = 0 (4 × 6) × 0 = 24 × 0 = 0 0 = 0 ∴ 4 × (6 × 0) = (4 × 6) × 0 Hence, for any three whole numbers a, b and c a × (b × c) = (a × b) × c | Multiplication is associative |
| Division | Is 18 ÷ (6 ÷ 3) = 18 ÷ (6 ÷ 3) 18 ÷ (6 ÷ 3) = \(\left(\frac{18}{6}\right) \times \frac{1}{3}=1\) 18 ÷ (6 ÷ 3) = 18 ÷ \(\frac{6}{3}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\) = 3 × 3 = 9 = 3 × 3 = 9 1 ≠ 9 Hence, (18 ÷ 6) ÷ 3 ≠ 18 ÷ (6 ÷ 3) So, for any three whole numbers a, b and c (a ÷ b ) ÷ c ≠ a ÷ (b ÷ c) | Division is not associative |
(ii) Integers
Question 1.
The associativity of the four operations for integers can be seen from this table:
| Operation | Numbers | Remarks |
| Addition | Is (-2) + [3 + (-4)] = [(-2) + 3] + (-4)? Is (-6) + [(-4) + (-5)] = [(-6) + (-4)] + (-5)? For any three integers a, b and c, a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c | Addition is associative |
| Subtraction | Is 5 – (7 – 3) = (5 – 7) – 3? | Subtraction is not associative |
| Multiplication | Is 9 × [(-5) × (-3)] = [9 × (-5)] × (-3)? Is (-13) × [(-17) × (-5)] = [(-13) × (-17)] × (-5)? For any three integers a, b and c, a × (b × c) = (a × b) × c | Multiplication is associative |
| Division | Is [(-15) ÷ 5] ÷ (-3) = (-15) ÷ [5 ÷ (-3)]? | Division is not associative |
Solution:
| Operation | Numbers | Remarks |
| Addition | Is (-2) + [3 + (-4)] = [(-2) + 3] + (-4) (-2) + [3 + (-4)] = (-2) + [3 – 4] = -2 + (-1) = -2 – 1 = -3 [(-2) + 3] + (-4) = [-2 + 3] + (-4) = (1) + (-4) = 1 – 4 = -3 Is (-6) + [(-4) + (-5)] = [(-6) + (-4)] + (-5) (-6) + [(-4) + (-5)] = (-6) + [-4 – 5] = -6 + (-9) = -6 – 9 = -15 [(-6) + (-4)] + (-5) = [-6 – 4] + (-5) = [-10] + (-5) = -10 – 5 = -15 -15 = -15 ∴ (-6) + [(-4) + (-5)] = [(-6) + (-4)] + (-5) So, for any three integers a, b and c, a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c | Addition is associative |
| Subtraction | Is 5 – (7 – 3) = (5 – 7) – 3 5 – (7 – 3) = 5 – 4 = 1 (5 – 7) – 3 = – 2 – 3 = -5 1 ≠ -5 5 – (7 – 3) ≠ (5 – 7) – 3 So, for any three integers a, b and c, a – (b – c) ≠ (a – b) – c | Subtraction is not associative |
| Multiplication | Is 9 × [(-5) × (-3)] = [9 × (-5)] × (-3) 9 × [(-5) × (-3)] = 9 × [15] = 135 [9 × (-5)] × (-3) = -45 × -3 = 135 135 = 135 9 × [(-5) × (-3)] = [(9) × (-5)] × (-3) Is (-13) × [(17) × (-5)] = [(-13) × 17] × (-5) (-13) × [(17) × (-5)] = (-13) × (-85) = 1105 [(-13) × 17] × (-5) = [-221] × (-5) = -221 × -5 = 1105 1105 = 1105 ∴ (-13) × [17 × (-5)] = [(-13) × 17] × (-5) So, for any three integers a, b and c, a × (b × c) = (a × b) × c | Multiplication is associative |
| Division | Is [(-15) ÷ 5] ÷ (-3) = (-15) ÷ [5 ÷ (-3)] [(-15) ÷ 5] ÷ (-3) = \(\left[\frac{-15}{5}\right]\) ÷ (-3) = -3 ÷ (-3) = 1 [(-15) ÷ 5] ÷ (-3) = (-15) ÷ \(\left[\frac{5}{-3}\right]\) = -15 × \(\frac{-3}{5}\) = 9 \(\frac{5}{3}\) ≠ 9 [(-15) ÷ 5] ÷ (-3) ≠ (-15) ÷ [5 ÷ (-3)] So, for any three integers a, b and c, (a ÷ b) ÷ c ≠ a ÷ (b ÷ c) | Division is not associative |
Try These (Page 10)
Question 1.
| Numbers | Associative for | |||
| Addition | Subtraction | Multiplication | Division | |
| Rational numbers | ______ | ______ | ______ | No |
| Integers | ______ | ______ | Yes | ______ |
| Whole numbers | Yes | ______ | ______ | ______ |
| Natural numbers | ______ | No | ______ | ______ |
Solution:
| Numbers | Associative for | |||
| Addition | Subtraction | Multiplication | Division | |
| Rational numbers | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Integers | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Whole numbers | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Natural numbers | Yes | No | Yes | No |
Try These (Page 13)
Question 1.
Find using distributivity.
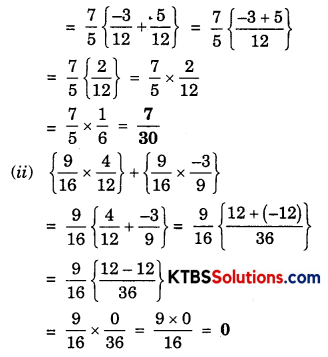
(i) \(\left\{\frac{7}{5} \times\left(\frac{-3}{12}\right)\right\}+\left\{\frac{7}{5} \times \frac{5}{12}\right\}\)
(ii) \(\left\{\frac{9}{16} \times \frac{4}{12}\right\}+\left\{\frac{9}{16} \times \frac{-3}{9}\right\}\)
Solution:
(i) \(\left\{\frac{7}{5} \times\left(\frac{-3}{12}\right)\right\}+\left\{\frac{7}{5} \times \frac{5}{12}\right\}\)
Try These (Page 17)
Question 1.
Write the rational number for each point labeled with a letter.
Solution:
(i) A = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
B = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
C = \(\frac{5}{5}\)
D = \(\frac{8}{5}\)
E = \(\frac{9}{5}\)
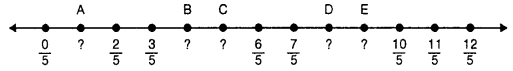
(ii) -J = \(\frac{-11}{6}\)
I = \(\frac{-8}{6}\)
H = \(\frac{-7}{6}\)
G = \(\frac{-5}{6}\)
F = \(\frac{-2}{5}\)