You can Download KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 6 Square and Square Roots Ex 6.4 Questions and Answers to help you to revise the complete syllabus.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 6 Square and Square Roots Ex 6.4
Question 1.
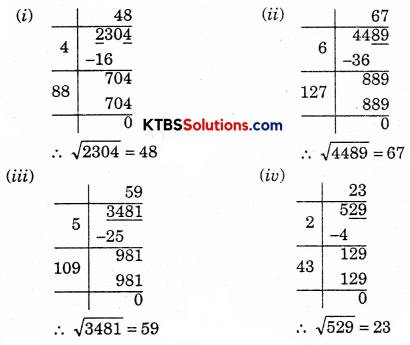
Find the squarer root of each of the following numbers by the Division method.
(i) 2304
(ii) 4489
(iii) 3481
(iv) 529
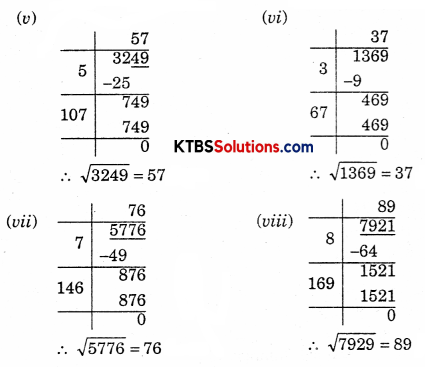
(v) 3249
(vi) 1369
(vii) 5776
(viii) 7921
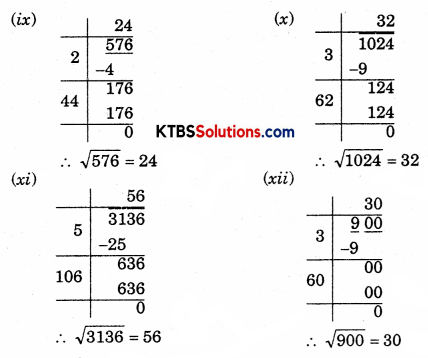
(ix) 576
(x) 1024
(xi) 3136
(xii) 900
Solution:
Question 2.
Find the number of digits in the square root of each of the following numbers (without any calculation).
(i) 64
(ii) 144
(iii) 4489
(iv) 27225
(v) 390625
Solution:
(i) 64
The total digit in the given number is 2, which is even.
Hence the number of digits in the square root of 64 is
\(\frac{n}{2}=\frac{2}{2}=1\)
(ii) 144
The number of digits is 3, which is odd.
Hence, the number of digits in the square root of 144 is
\(\frac{n+1}{2}=\frac{3+1}{2}=2\)
(iii) 4489
The number of digits is 4, which is even.
Hence, the number of digits in the square root of 4489 is
\(\frac{n}{2}=\frac{4}{2}=2\)
![]()
(iv) 27225
The number of digits is 5, which is odd.
Hence, the number of digits in the square root of 27225 is
\(\frac{n+1}{2}=\frac{5+1}{2}=3\)
(v) 390625
The number of digits is 6, which is even.
Hence, the number of digits in the square root of 390625 is
\(\frac{n}{2}=\frac{6}{2}=3\)
Question 3.
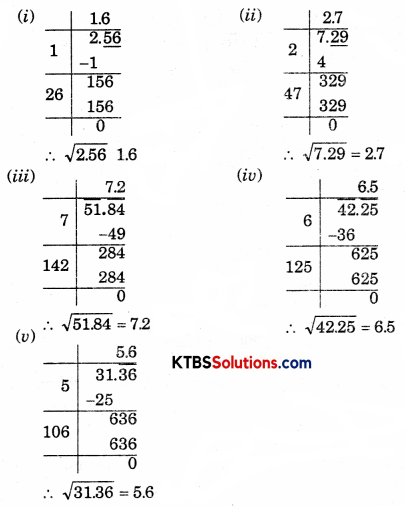
Find the square root of the following decimal numbers.
(i) 2.56
(ii) 7.29
(iii) 51.84
(iv) 42.25
(v) 31.36
Solution:
Question 4.
Find the least number which must be subtracted from each of the following numbers, so as to get a perfect square. Also, find the square root of the perfect square so obtained.
(i) 402
(ii) 1989
(iii) 3250
(iv) 825
(v) 4000
Solution:
(i) 402

Remainder 2.
So, 2 is subtracted
= 402 – 2
= 400 is a perfect square.
= √400
= 20
![]()
(ii) 1989

Remainder 53.
So, 53 should be subtracted from 1989 to make it a perfect square
1989 – 53 = 1936
= √1936
= 44
(iii) 3250

Remainder = 1.
So, 1 should be subtracted from 3250 to make it a perfect square
∴ 3250 – 1 = 3249
= √3249
= 57
(iv) 825
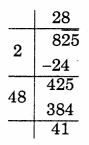
Remainder = 41
So, 41 should be subtracted from 825 to make it a perfect square
∴ 825 – 41 = 784
= √784
= 28
(v) 4000

Remainder = 31
So, 31 should be subtracted from 4000 to make it a perfect square.
∴ 4000 – 31 = 3969
= √3969
= 63
![]()
Question 5.
Find the least number which must be added to each of the following numbers, so as to get a perfect square. Also, find the square root of the perfect square so obtained.
(i) 525
(ii) 1750
(iii) 252
(iv) 1825
(v) 6412
Solution:
(i) 525
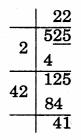
Remainder = 41
∴ 222 < 525
Take next number, 232 < 525
= 529 – 525
= 4
So, 4 should be added to 525 to make it a perfect square
√529 = 23
(ii) 1750
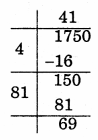
Remainder = 69
∴ 412 < 1750
Take next number 422
= 1764 – 1750
= 14
So, add 14 to 1750 to make it a perfect square
√1764 = 42
(iii) 252
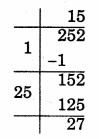
Remainder = 27
∴ 152 < 252
Take next number 162
= 256 – 252
= 4
So, 4 should be added to 252 to make it a perfect square
√256 = 16
(iv) 1825
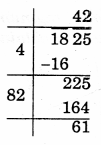
Remainder = 61
∴ 422 < 1825
Take next number 432
= 1849 – 1825
= 24
So, 24 should be added to 1825 to make it a perfect square
1825 + 24 = 1849
√1849 = 43
(v) 6412
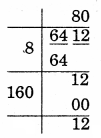
Remainder = 12
∴ 802 < 6412
Take next number 812
= 6561 – 6412
= 149
So, 149 should be added to 6412 to make it a perfect square
6412 + 149 = 6561
√6561 = 81
![]()
Question 6.
Find the length of the side of a square whose area is 441 m2.
Solution:
Let the side of square = x m
Area of square = (side)2
⇒ x2 = 441
⇒ x = √441
⇒ x = 21 m
The side of the square is 21 m
Question 7.
In a right triangle ABC, ∠B = 90°.
(a) If AB = 6 cm, BC = 8 cm, find AC
(b) If AC = 13 cm, BC = 5 cm, find AB
Solution:
(a) Since, ABC is a right-angled triangle B = 90°
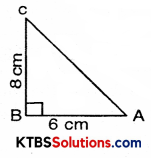
∴ AC2 = BC2 + AB2
= 82 + 62
= 64 + 36
= 100
AC = √100 = 10 cm
(b) AC2 = AB2 + BC2
⇒ (13)2 = AB2 + 52
⇒ 169 = AB2 + 25
⇒ 169 – 25 = AB2
⇒ 144 = AB2
⇒ √144 = AB
⇒ 12 = AB
⇒ AB = 12 cm
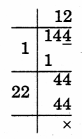
Question 8.
A gardener has 1000 plants. He wants to plant these in such a way that the number of rows and the number of columns remain the same. Find the minimum number of plants he needs more for this.
Solution:

312 < 1000
Take next number 322
322 – 1000
1024 – 1000 = 24
So, 24 should be added to 1000 to make it a perfect square.
Hence, 24 plants are needed.
![]()
Question 9.
There are 500 children in a school. For a P.T. drill, they have to stand in such a manner that the number of rows is equal to the number of columns. How many children would be left out in this arrangement?
Solution:
Let the number of rows = x
Number of columns = x
Total student = x2
∴ x2 = 500
x = √500 (But it should be perfect square)
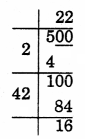
Remainder = 16
So, 16 students would be left in this arrangement.