You can Download KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions and Identities InText Questions and Answers helps you to revise the complete syllabus.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions and Identities InText Questions
Try These (Page 138)
Question 1.
Give five examples of expressions containing one variable and five examples of expressions containing two variables.
(i) 3x
(ii) \(-\frac{5}{2} p\)
(iii) 3a + 5
(iv) 5 – x
(v) 2y – 7
Solution:
(i) 3x + y
(ii) -2a + 5y
(iii) 2pq – 3
(iv) \(-\frac{1}{5}\)ab + 7
(v) 2y – 7
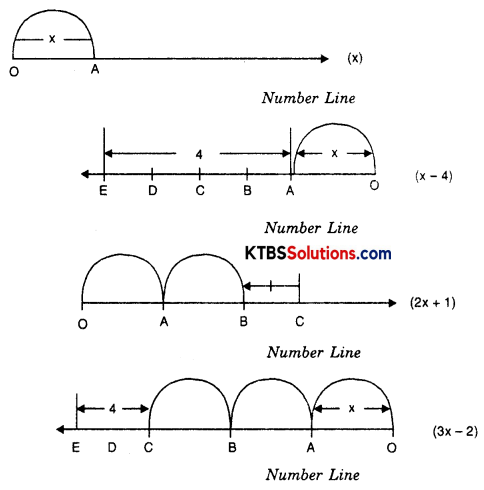
Question 2.
Show on the number line x, x – 4, 2x + 1, 3, -2.
Solution:
Try These (Page 138)
Question 1.
Classify the following polynomials as monomials, binomials, trinomials.
-x + 5, x + y + z, y + z + 100, ab – ac, 17
Solution:
-x + 5 → Binomial
x + y + z → Trinomial
y + z + 100 → Trinomial
ab – ac → Binomial
17 → Monomial
![]()
Question 2.
Construct.
(a) 3 binomials with the only x as a variable;
(b) 3 binomials with x and y as a variable;
(c) 3 monomials with x and y as variables;
(d) 2 polynomials with 4 or more terms.
Solution:
(a) Binomials with only x as a variable;
(i) x – 9
(ii) 3x – \(\frac{5}{2}\)
(iii) 2 – 7x
(b) Binomials with variable x and y
(i) 5x – 9y
(ii) \(\frac{2}{7}\)x + 5y
(iii) 3xy + 1
(c) Monomials with variables x and y
(i) 5x2y
(ii) axy
(iii) 4xy2
(d) (i) 3x – y + z – 2p
(ii) 5a – 2b + 8c + 7
Try These (Page 138)
Question 1.
Identify the coefficient of each term of expression
x2y2 – 10x2y + 5xy2 – 20
Solution:
Coefficient of each term 1, -10m, 5, -20
![]()
Try These (Page 138)
Question 1.
Write two terms which are like
(i) 7xy
(ii) 4mn2
(iii) 2l
Solution:
(i) 7xy, -5xy, \(-\frac{2}{3}\)xy are like terms
(ii) 4mn2, \(-\frac{1}{5}\) 4mn2, \(\frac{5}{9}\) 4mn2 are like terms
(iii) 2l, -5l, 6l, are like terms
Try These (Page 142)
Question 1.
Cara, you think of two more such situations, where we may need to multiply algebraic expressions?
[Hint: Think of speed and time;
Think of interest to be paid, the principal and the rate of simple interest; etc.]
Solution:
(i) Speed, Distance and time
Since Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { Time }}\)
Speed × Time = Distance
![]()
(ii) Principal, Time, Rate, Simple Interest
S.I. = \(\frac{P \times R \times T}{100}\)
Try These (Page 143)
Question 1.
Find 4x × 5y × 7z
First, find 4x × 5y and multiply it by 7z;
or first, find 5y × 7z and multiply it by 4x.
Is the result the same? What do you observe?
Does the order in which you carry out the multiplication matter?
Solution:
(i) 4x × 5y × 7z = 140xyz
(ii) 4x × 5y = 20xy
20xy × 7z = 140xyz
(iii) 5y × 7z = 35yz
35yz × 4y = 140yzx
Yes, the result is the same.
It is observed that when algebraic expressions are multiplied. The change in order does not affect the result.
Try These (Page 145)
Question 1.
Find the product:
(4p2 + sp + 7) × 3p
Solution:
3p(4p2 + sp + 7)
= (3p × 4p2) + (3p × 5p) + (3p × 7)
= 12p3 + 15p2 + 21p
Try These (Page 149)
Question 1.
Put -b in place of b in identity I. Do you get identity II.
Identities
I = (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
II = (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2
Solution:
If we put -b in place of b in identity I we get II identity
(a – b)2
= a2 + 2a(-b) + (b)2
= a2 – 2ab + b2
![]()
Try These (Page 149)
Question 1.
Verify Identity (IV), for a = 2, b = 3, x = 5.
Solution:
Identity (IV) = (x + a) + (x + b)
= x2 + (a + b)x + ab
If a = 2, b = 3, x = 5
(5 + 2) (5 + 3) = (5)2 + (2 + 3) × 5 + 2 × 3
(7) (8) = 25 + 5(5) + 6
56 = 25 + 25 + 6
56 = 56
Question 2.
Consider, the special case of Identity (IV) with a = b, what do you get? Is it related to Identity (I)?
Solution:
Identity (IV) = (x + a) + (x + b)
= x2 + (a + b) x + ab
If a = b
(x + b) (x + b)
= x2 + (b + b) x + b × b
= x2 + 2bx + b2
It is related to Identity I i.e.
(a + b)2 = (a + b)2 + 2ab + b2
![]()
Question 3.
Consider, the special case of Identity (IV) with a = c and b = -c. What do you get? Is it related to Identity (II)?
Solution:
Identity (IV) = (x + a) + (x + b)
= x2 + (a + b) x + ab
If a = -c and b = -c
(x – c) (x – c)
= x2 + (-c – c) x + (-c)(-c)
= x2 – 2cx + c2
It is related to Identity II i.e.
(a + b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2
Question 4.
Consider the special case of Identity (IV) with a = -c and b = -a. What do you get? Is it related to Identity (III)?
Solution:
Identity (IV) = (x + a) + (x + b)
= x2 + (a + b) x + ab
If b = -a then
(x + a) (x – a) = x2 + (a – a) x + a(-a)
= x2 – 0 + (-a2)
= x2 – a2
Yes, it is related to Identity III i.e.
(a + b) (a – b) = (a2 – b2)