You can Download KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current Questions and Answers Pdf, Notes help you to revise the complete syllabus.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
Chemical Effects of Electric Current Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
- Most liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of _______ and _______
- The passage of an electric current through a solution causes _______ effect.
- If you pass current through copper sulphate solution, copper gets deposited on the plate connected to the _______ terminal of the battery.
- The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another metallic object, by means of electricity, is called _______
Answer:
- Most liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of acids, bases, and salts.
- The passage of an electric current through a solution causes a Chemical effect.
- If you pass current through copper sulphate solution, copper gets deposited on the plate connected to the negative terminal of the battery.
- The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another material by means of electricity is called electroplating.
Question 2.
When the free ends of a tester are dipped into a solution, the magnetic needle shows deflection. Can you explain the reason?
Answer:
Yes, it is because the solution conducts electricity and the solution plays the role of a small cell.
Question 3.
Name three liquids, which when tested in the manner shown in Fig.14.9, may cause the magnetic needle to deflect.
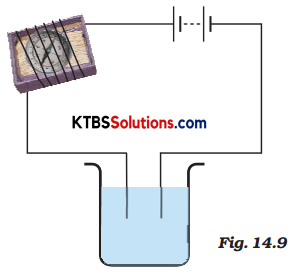
Answer:
Lemon water, vinegar, tap water.
Question 4.
The bulb does not glow in the setup shown in Fig. 14.10. List the possible reasons. Explain your answer.
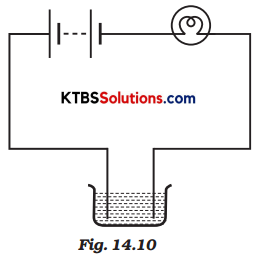
Answer:
The bulb does not glow because:
- The solution may not be a good conductor of electricity.
- The electricity in the circuit was very little.
- The bulb may be fused.
- The cells may be used up.
- The connections of wires may be loose.
Question 5.
A tester is used to check the conduction of electricity through two liquids labelled A and B. It is found that the bulb of the tester glows brightly for liquid A while it glows very dimly for liquid B. You would conclude that:
(i) Liquid A is a better conductor than liquid B.
(ii) Liquid B is a better conductor than liquid A.
(iii) Both liquids are equally conducting.
(iv) Conducting properties of liquid cannot be compared in this manner.
Answer:
(i) Liquid A is a better conductor than liquid B.
Question 6.
Does pure water conduct electricity? If not, what can we do to make it conducting?
Answer:
Pure water does not conduct electricity. It can be made conducting by adding acid, base or salt into it.
Question 7.
In case of fire, before the firemen use the water hoses, they shut off the main electrical supply of the area. Explain why they do this.
Answer:
Water is a good conductor of electric current. So, the firemen shut off the electric supply before spraying water to save themselves and other people from electrocution.
Question 8.
A child staying in the coastal region tests the drinking water and also the seawater with his tester. He finds that the compass needle deflects more in the case of seawater. Can you explain the reason?
Answer:
Drinking water has been processed and purified before supplying it to the houses. Many salts and minerals have been removed from it, so it has decreased its conductivity. On the other hand, seawater is rich in salts, and other acids, and basic substances, that is why it is a better conductor of electricity and deflects the needle more than the purified drinking water.
Question 9.
Is it safe for the electrician to carry out electrical repairs outdoors during heavy downpours? Explain.
Answer:
No, it is highly dangerous to carry on electric repairs in water, as water is a good conductor of electricity. It can cause electrocution.
Question 10.
Paheli had heard that rainwater is as good as distilled water. So she collected some rainwater in a clean glass tumbler and tested it using a tester. To her surprise, she found that the compass needle showed deflection. What could be the reasons?
Answer:
While it rains, the raindrops get mixed with the suspended particles of the air. So, they do not remain pure. It becomes a mixture of salts and other impurities thus shows the conduction of electricity.
Question 11.
Prepare a list of objects around you that are electroplated.
Answer:
The object that is electroplated are:
- Taps of water connection.
- Parts of the bicycle.
- Body (parts) of cars, motorcycle, and tractors
- The handle of the doors, etc
- Artificial jewellery
- Metallic almirahs.
- Buckles of clothes and belts, etc.
- Utensils
- Buckets.
Question 12.
The process that you saw in Activity 14.7 is used for the purification of copper. A thin plate of pure copper and a thick rod of impure copper are used as electrodes, Copper from the impure rod is sought to be transferred to the thin copper plate. Which electrode should be attached to the positive terminal of the battery and why?
Answer:
The impure copper rod should be attached to the positive terminal because the free copper will get drawn towards the negative terminal to be get deposited, so the copper from the impure rod will get collected in the pure copper plate.
Chemical Effects of Electric Current Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why it is very dangerous to operate an electrical appliance with wet hands?
Answer:
If someone operates electrical appliances with wet hands, there is a chance of getting electrocuted.
Question 2.
Define conductors.
Answer:
Materials which allow an electric current to pass through them are called conductors, e.g., aluminium copper, etc.
Question 3.
Do liquids also conduct electricity?
Answer:
Yes, tap water, lemon juice, and acids are some of the liquids which conduct electricity.
Question 4.
When is the circuit of the tester complete and when is it not complete?
Answer:
When the liquid between the two ends of the tester allows the electric current to pass, the circuit of the tester becomes complete. The current flow in the circuit and the bulb glows. When the liquid does not allow the electric current to pass, the circuit of the tester is not complete and the bulb does not glow.
Question 5.
What effect does the current product when it flows through the conducting solution?
Answer:
The passage of an electric current through a conducting solution causes chemical reactions. As a result, bubbles of gas may be formed on the electrodes. Deposits of metal may be seen on electrodes. Changes in colour of solutions may occur. The reaction would depend on what solution and electrodes are used. These are some of the chemical effects of the electric current.
Question 6.
What is electroplating?
Answer:
The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another material by means of electricity is called electroplating.
Activities
Activity 1.
Join the free ends of the tester together for a moment. This completes the circuit of the tester and the bulb should glow. However, if the bulb does not glow, it means that the tester is not working.
Question (i).
Can you think of the possible reasons? Is it possible that the connections are loose? Or, the bulb is fused? Or, your cells are used up?
Answer:
Yes, it is possible that the connections are loose, or the bulb is fused, or our cells are used up.
Activity 2.
Collect a few small plastics or rubber caps of discarded bottles and clean them. Pour one teaspoon of lemon juice or vinegar in one cap. Bring your tester over this cap and let the ends of the tester dip into lemon juice or vinegar as shown in Fig. 14.2 Take care that the ends are not more than 1 cm apart but at the same time do not touch each other.
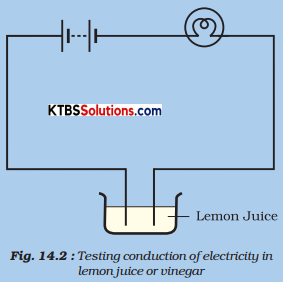
Fig. Testing conduction of electricity in lemon juice or vinegar
Question (i).
Does the bulb of the tester glow?
Answer:
Yes, the bulb glows.
Question (ii).
Does lemon juice or vinegar conductor electricity?
Answer:
Yes, lemon juice or vinegar conductor electricity.
Question (iii).
How would you classify lemon juice or vinegar-a good conductor or a poor conductor?
Answer:
As a good conductor.
Activity 3.
Take the tray from inside a discarded matchbox. Wrap an electric wire a few times around the tray. Place a small compass needle inside it. Now connect one free end of the wire to the terminal of a battery. Leave the other end free. Take another piece of wire and connect it to the other terminal of the battery. (Fig.).
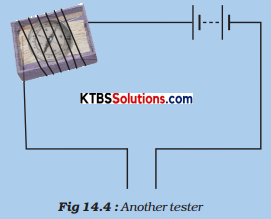
Join the free ends of two wires momentarily. The compass needle should show deflection. Your tester with two free ends of the wire is ready. Now repeat Activity using this tester.
Question (i).
Do you find a deflection in the compass needle the moment you dip the free ends of the tester in lemon juice?
Answer:
Yes, we see a deflection in the compass needle.
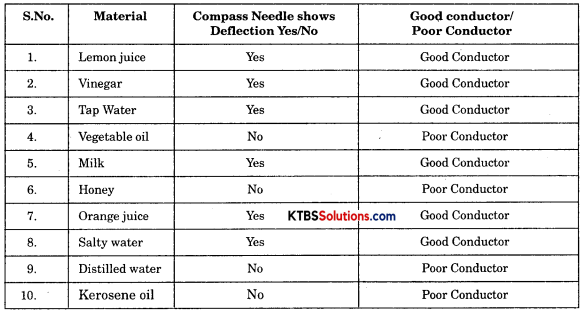
Take out the ends of the tester from the lemon juice, dip them in water and then wipe them dry. Repeat the activity with other liquids such as tap water, vegetable oil, milk, honey. (Remember to wash and wipe dry the ends of the tester after testing each liquid). In each case observe whether the magnetic needle shows deflection or not. Record your observations in Table 14.1.
Question (ii).
Table 14.1.: Good/Poor Conducting Liquids
Answer:
Table 14.1: Good/Poor Conducting Liquids
Activity 4.
Take about two teaspoonfuls of distilled water in a clean and dry plastic or rubber cap of a bottle. (You may obtain distilled water from your school science lab. You may also get distilled water from a medical store or a doctor or a nurse). Use the tester to test whether distilled water conducts electricity or not.
Question (i).
What do you find?
Answer:
We find that bulb does not glow.
Question (ii).
Does distilled water conduct electricity?
Answer:
No.
Question (iii).
Now dissolve a pinch of common salt in distilled water. Again test What do you conclude this time?
Answer:
The bulb of the tester glows. This shows that when a pinch of salt is dissolved in distilled water, it conducts electricity.
Activity 5.
Take three clean plastic or rubber caps of bottles. Pour about two teaspoonfuls of distilled water into each of them. Add a few drops of lemon juice or dilute hydrochloric acid to distilled water in one cap. Now in the second cap containing distilled water, add a few drops of a base such as caustic soda or potassium iodide. Add a little sugar to the distilled water in the third cap and dissolve it.
Question (i).
Test which solutions conduct electricity and which do not. What results do you obtain?
Answer:
We find that all three solutions conduct electricity. It means acids, bases, and salts, when mixed in the distilled water, conduct electricity.
Activity 6.
Take out carbon rods carefully from two discarded cells. Clean their metal caps with sandpaper. Wrap copper wires around the metal caps of the carbon rods and join them to a battery (Fig.). We call these two-rod electrodes.
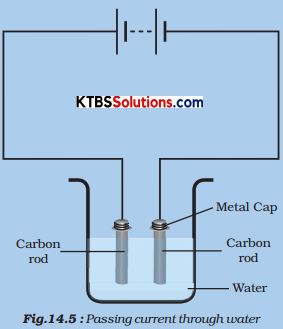
(Instead of carbon rods, you may take two iron nails about 6 cm long.) Pour a cupful of water into a glass/plastic bowl. Add a teaspoonful of salt or a few drops of lemon juice to the water to make it more conducive. Now immerse the electrodes in this solution. Make sure that the metal caps of the carbon rods are outside the water. Wait for 3-4 minutes. Observe the electrodes carefully.
Question (i).
Do you notice any gas bubbles near the electrodes?
Answer:
Oxygen and hydrogen gas bubbles are formed near the electrodes.
Question (ii).
Can we call the change taking place in the solution a chemical change?
Answer:
Yes, it is a chemical change.
Activity 7.
We will need copper sulphate and two copper plates of size around 10 cm x 4 cm. Take 250 ml of distilled water in a clean and dry beaker. Dissolve two teaspoonfuls of copper sulphate in it. Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to copper sulphate solution to make it more conducting. Clean copper plates with sandpaper. Now rinse them with water and dry them. Connect the copper plates to the terminals of a battery and immerse them in copper sulphate solution (Fig.).
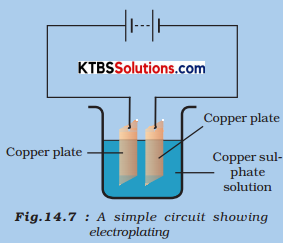
Allow the current to pass for about 15 minutes. Now remove the electrodes from the solution and look at them carefully.
Question (i).
Do you find any difference in any one of them?
Answer:
Yes, there is a deposition of copper on one of the electrodes.
Question (ii).
Do you find a coating over it?
Answer:
Yes, I can find a coating over the electrode.
Question (iii).
What colour is the coating?
Answer:
It is of green-blue colour.
Question (iv).
Note down the terminal of the battery with which this electrode is connected.
Answer:
The electrode is connected with the negative terminal of the battery.