You can Download KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System Questions and Answers Pdf, Notes help you to revise the complete syllabus.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
Stars and the Solar System Textbook Questions and Answers
Choose the correct answer in Questions 1 – 3.
Question 1.
Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
(a) An asteroid
(b) A satellite
(c) A constellation
(d) A comet
Answer:
(c) A constellation
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following is NOT a planet of the sun?
(a) Sirius
(b) Mercury
(c) Saturn
(d) Earth
Answer:
(a) Sirius
Question 3.
Phases of the moon occur because:
(а) We can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
(b) Our distance from the moon keeps changing.
(c) The shadow of the Earth covers only a part of the moon’s surface.
(d) The thickness of the moon’s atmosphere is not constant.
Answer:
(a) We can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks:
- The planet which is farthest from the sun is _________
- The planet which appears reddish in colour is _________
- A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a _________
- A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as _________
- Shooting stars are actually not _________
- Asteroids are found between the orbits of _________ and _________
Answer:
- The planet which is farthest from the Sun is Neptune.
- The planet which appears reddish in colour is Mars.
- A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a constellation.
- A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as a satellite.
- Shooting stars are actually not stars.
- Asteroids are found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
![]()
Question 5.
Mark the following statements is true (T) or false (F):
- Pole star is a member of the solar system. ( )
- Mercury is the smallest planet in the solar system. ( )
- Uranus is the farthest planet in our solar system. ( )
- INSAT is an artificial satellite. ( )
- There are nine planets in our solar system. ( )
- Constellation Orion can be seen only with the telescope. ( )
Answer:
- Pole star is a member of the solar system. (F)
- Mercury is the smallest planet in the solar system. (T)
- Uranus is the farthest planet in our solar system. (F)
- INSAT is an artificial satellite. (T)
- There are nine planets in our solar system. (F)
- Constellation Orion can be seen only with the telescope. (F)
Question 6.
Match items in Column A with one or more items of Column B:
| A | B |
| (i) Inner planets | (a) Saturn |
| (ii) Outer planets | (b) Pole star |
| (iii) Constellation | (c) Great Bear |
| (iv) Satellite of the Earth | (d) Moon |
| (e) Earth | |
| (f) Orion | |
| (g) Mars |
Answer:
| A | B |
| (i) Inner planets | (g) Mars, (e) Earth |
| (ii) Outer planets | (a) Saturn |
| (iii) Constellation | (c) Great Bear, (f) Orion |
| (iv) Satellite of the Earth | (d) Moon |
Question 7.
In which part of the sky can you find Venus if it is visible as an evening star?
Answer:
In the western sky.
Question 8.
Name the largest planet of the solar system.
Answer:
Jupiter.
Question 9.
What is a constellation? Name any two constellations.
Answer:
The stars forming a group that has a recognizable shape is called a constellation.
- Ursa major
- Orion
![]()
Question 10.
Draw sketches to show the relative positions of prominent stars in:
(a) Ursa major and
(b) Orion
Answer:
(a) Ursa major and
(b) Orion
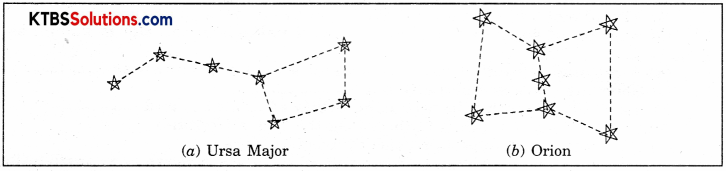
Question 11.
Name two objects other than planets which are members of the solar system.
Answer:
Meteors and Asteroids.
Question 12.
Explain how you can locate the pole star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answer:
To locate the pole star we should look towards the northern part of the sky and identify Ursa Major. We may look at the two stars at the end of Ursa Major. A straight line passing through these stars is imagined and is extended towards the north direction. This line will lead to a star which is not too bright. This is the Pole star.
Question 13.
Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain.
Answer:
No, no star moves in the sky. They appear to move from east to west because the Earth rotates from west to east about its axis.
![]()
Question 14.
Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you understand by the statement that a star is eight light-years away from the Earth?
Answer:
The distance of stars is so large that it cannot be expressed in terms of kilometers. That is why very large distances are expressed in another unit known as light year. One light-year is the distance traveled by light in one year. If the distance of a star is eight light-years, it means that this distance is the distance travelled by light in eight years.
Question 15.
The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the Earth. Calculate the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the Earth. How many Earths can Jupiter accommodate?
Answer:
If the radius of the Earth is r.
Then, the radius of Jupiter is 11r.
So, ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the Earth is = \(\frac{\frac{4}{3} \pi(11 r)^{3}}{\frac{4}{3} \pi r^{3}}\) = 1331 : 1
So, 1331 Earth can accommodate Jupiter.
Question 16.
Boojho made the following sketch (Fig.) of the solar system. Is the sketch correct? If not, correct it.
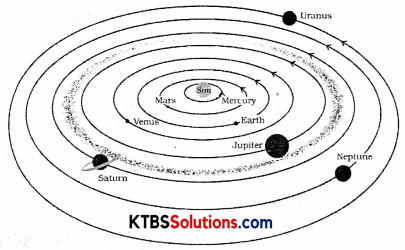
Answer:
No, the sketch is not correct. The correct sketch is
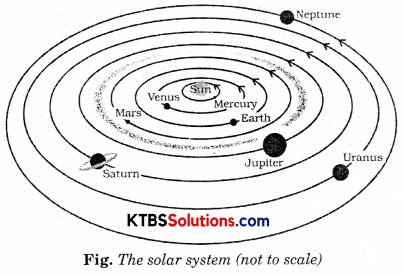
Stars and the Solar System Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why the village sky was so different from the night sky in big cities?
Answer:
The village sky is fascinating because there is no bright light and the atmosphere is clear.
Question 2.
Do you find any star-like object which dies not twinkle?
Answer:
Yes, this object is a planet.
![]()
Question 3.
What are new moon day and full moon day?
Answer:
New moon day is the day when the moon is not visible to us. Full moon day is the day when the moon appears as a full circle.
Question 4.
What is the crescent moon?
Answer:
The next day after the new moon day, only a small part of the moon appears in the sky, which is called the crescent moon.
Question 5.
Why does Sun which is also a star appear so large compared to the other stars?
Answer:
The stars are million times farther away than the Sun. This means that Sun is nearest to the Earth. That is why the Sun appears so bright.
Question 6.
What is a light-year?
Answer:
Large distances expressed are expressed in a unit called year. It is the distance travelled by light in one year. The speed of light is about 300,000 km per second.
Question 7.
What is the Solar system?
Answer:
The Sun and the celestial bodies which revolve around it form the solar system.
![]()
Question 8.
What keeps objects revolving around Sun?
Answer:
The gravitational attraction between the Sun and objects keeps them revolving around it.
Question 9.
Name the star which is nearest to earth.
Answer:
Sun.
Question 10.
Draw the diagram of the solar system.
Answer:
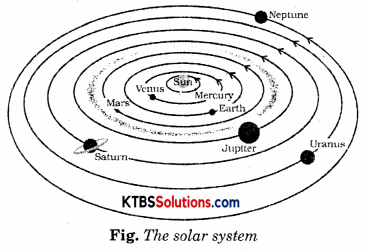
Question 11.
Name the planet nearest to Sun.
Answer:
Mercury (Budh).
Question 12.
Why is it very difficult to observe it?
Answer:
It is very difficult to observe it because it is very close to the sun. Most of the time it is hidden in the glare of the sun.
![]()
Question 13.
Name the planet which shows phases like the moon?
Answer:
Venus.
Question 14.
Name the planet which is the second planet in terms of its distance from the sun?
Answer:
Venus.
Question 15.
Name the plant in the solar system on which life is known to exist.
Answer:
Earth.
Question 16.
Why does life exist on earth?
Answer:
Some special environmental conditions are responsible for the existence and continuation of life on the Earth. These include just the right distance from the Sun so that it has the right temperature range, the presence of water and a suitable atmosphere, and a blanket of ozone.
Question 17.
Name the star which has a slightly reddish appearance.
Answer:
Mars.
Question 18.
What is the other name of Mars?
Answer:
Red Planet.
![]()
Question 19.
Name the largest planet.
Answer:
Jupiter.
Question 20.
Name the planet which has a maximum number of moons and how many moons it has?
Answer:
Saturn has a maximum number of moons. It has 30 moons.
Question 21.
Name the outermost planets of the solar system.
Answer:
Uranus and Neptune.
Question 22.
What are asteroids?
Answer:
There is a large gap in between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter (Fig.). This gap is occupied by a large number of small objects that revolve around the Sun. These are called asteroids.
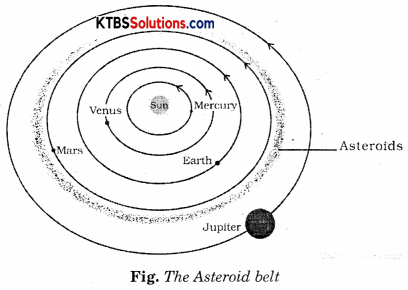
Question 23.
What are meteors?
Answer:
Meteors are very small stone-like objects revolving around the sun. They are seen as a bright streak of light that flashes for a moment across the sky.
Question 24.
What is the other name of meteors?
Answer:
Another name of meteors is Shooting Stars.
![]()
Question 25.
What are artificial satellites?
Answer:
Artificial satellites are man-made satellites revolving around the earth.
Question 26.
Mention the names of few artificial satellites.
Answer:
INSAT-3E, Kalpana Chawla-I, Sputnik-I, Aryabhatta, IRS, etc.
Activities
Activity 1.
Draw a circle of about 1 m diameter on the ground. Ask one of your friends to stand at the center of this circle. You revolve around your friend in such a manner that your face always remains towards him.
Question (i).
Can your friend see your back?
Answer:
No, my friend cannot see my back.
Question (ii).
How many rotations did you complete in one revolution?
Answer:
I completed only one rotation in one revolution.
Activity 2.
Stand in the centre of a big room and start rotating.
![]()
Question (i).
In which direction will the objects in the room appear to move?
Answer:
The objects appear to move in the opposite direction.
Question (ii).
Do you see them moving in the direction opposite to your motion?
Answer:
Yes.
Activity 3.
Take an umbrella and open it. Make about 10-15 stars out of white paper. Paste one star at the position of the central rod of the umbrella and others at different places on the cloth near the end of each spoke (Fig.). Now rotate the umbrella by holding its central rod in your hand. Observe the stars on the umbrella.
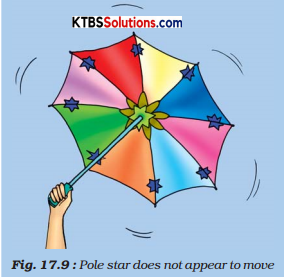
Question (i).
Is there any star which does not appear to move? where is this star located?
Answer:
Yes, the star situated at the central rod of the umbrella does not appear to move.
Question (ii).
If there were a star located where the axis of rotation of the Earth meets the sky, could this star also be stationary?
Answer:
Yes.
![]()
Activity 4.
Observe some constellation for a few hours. Do you find any change in its shape? Do you find any change in its position?
Answer:
We observe that the shape of the constellation remains the same. The constellation appears to move in the sky from east to west.