Chapterwise 1st PUC Accountancy textbook solutions karnataka Board are given here in PDF format for understanding the concepts involved in the syllabus. If you are looking for Chapter-wise KSEEB Solutions for 1st PUC Accountancy Question Bank with Answers Solutions, Notes, Guide Pdf are given in Chapter wise format then this is the right page for you. Students are advised to download chapter wise 1st PUC Question Bank with Answers Karnataka solutions pdf to take their preparation to the next level. Go through this page and get all chapters pdf links of KSEEB solutions for 1st PUC Accountancy textbook solutions pdf & learn efficiently to score high marks.
Students can also read 1st PUC Accountancy Model Question Papers with Answers hope will definitely help for your board exams.

Karnataka 1st PUC Accountancy Question Bank with Answers
By taking the help of the best resources like Karnataka State Board Solutions for 1st PUC Accountancy Textbook Questions and Answers you all can easily understand the concepts involved in the latest KTBS Solutions are given in syllabus and gain more subject knowledge. Study 1st PUC Accountancy Question Bank with Answers Karnataka solutions on a daily basis and be confident to answer all the questions asked in the final exam. Chapter-wise KSEEB solutions for 1st PUC Accountancy PDF links are available below to download.
- Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting
- Chapter 2 Theory Base of Accounting
- Chapter 3 Recording of Transactions I
- Chapter 4 Recording of Transactions II
- Chapter 5 Bank Reconciliation Statement
- Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors
- Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
- Chapter 8 Bills of Exchange
- Chapter 9 Financial Statements
- Chapter 10 Financial Statements with Adjustments
- Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
- Chapter 12 Applications of computers in accounting
- Chapter 13 Computerised Accounting System
- Practical Oriented Questions
Karnataka 1st PUC Accountancy Blue Print of Model Question Paper
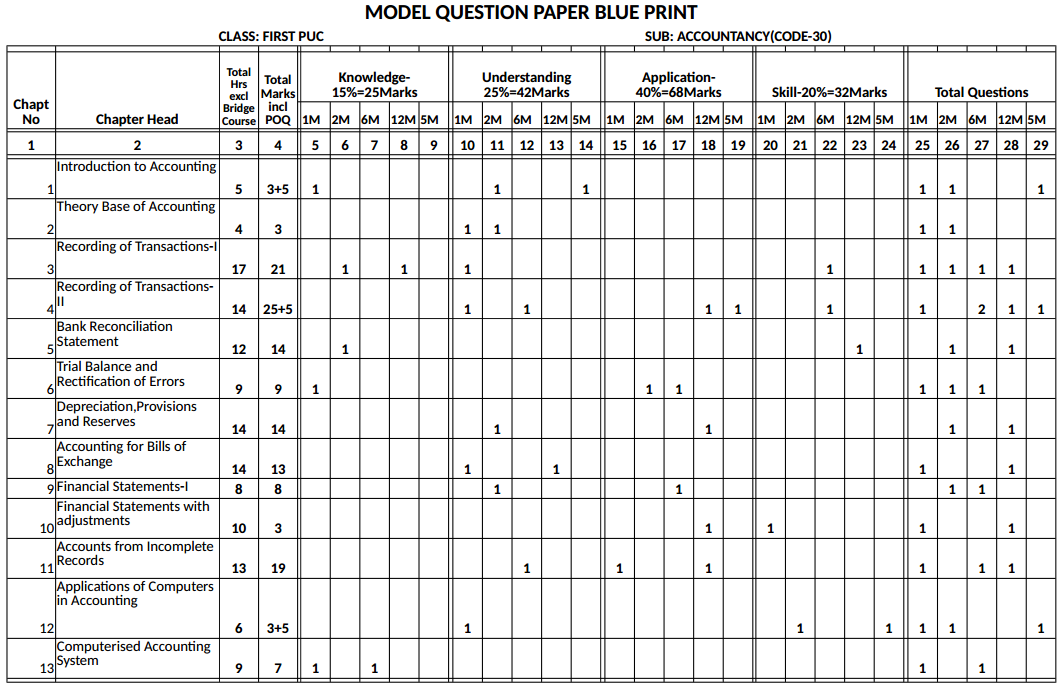
![]()
For the first time department of PU Education is releasing the Question Bank for 1 PUC Accountancy subject based on NCERT XI Standard Text Book. It has two volumes. I volume Financial Accounting Part-I consists of 8 chapters and II volume Financial Accounting Part-II consists of 7 chapters of which only 5 chapters are retained by department. All the chapters of first book and only 5 chapters in second book are retained. Chapter 14 and 15 of II volume are excluded.
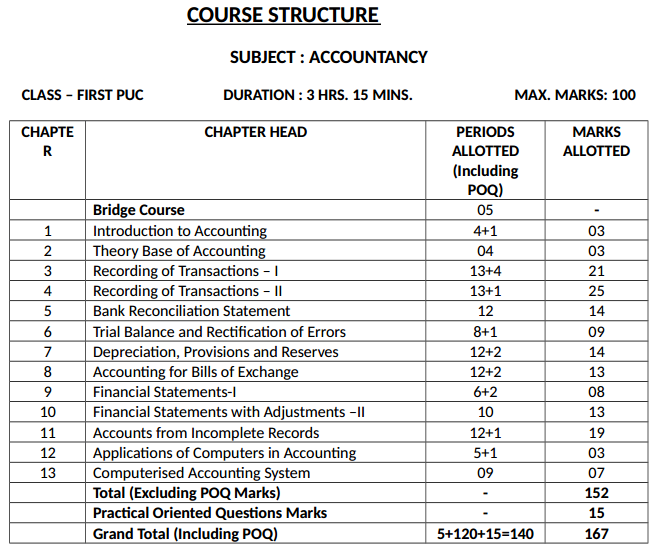
1st PUC Accountancy Course Structure
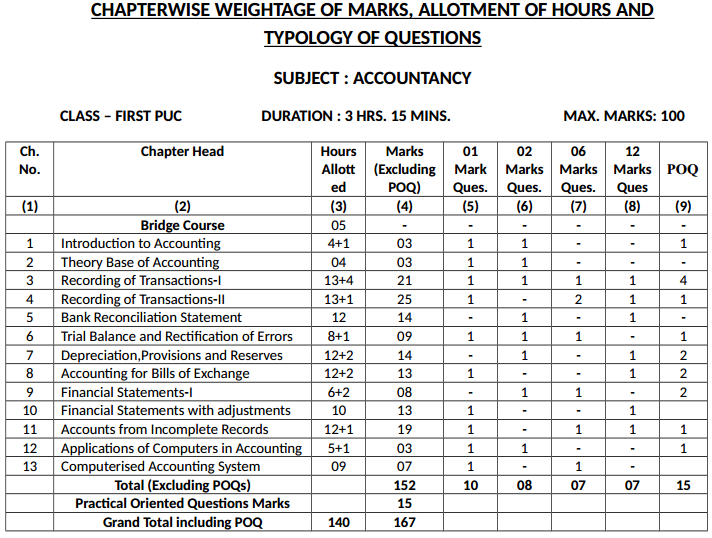
1st PUC Accountancy Chapterwise Weightage of Marks, Allotment of Hours and Typology of Questions
1st PUC Accountancy General Guidelines/Instructions:
- Availability of teaching hours in a year will be 140 only.
- Split-up of available teaching hours:
05 Hours – For bridge course
120 Hours – For completion of course content (excluding POQ)
15 Hours – For the completion of 15 POQs - Duration of Annual Examination will be 3 Hours and 15 Minutes only.
- Maximum marks of a question paper will be 167.
- While framing the questions, weightage should be given to instructional objectives as follows:

- While preparing the question paper due weightage should be given to the difficulty level as follows:
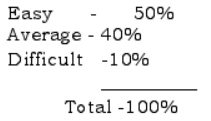
- Detailed Course structure, Question Paper Design, Blue Print, Program of work and Chapter-wise Questions are given for the use of lecturers and students.
- Tests, Mid-term and Annual Examination question paper should be strictly as per the stipulated Question Paper Pattern only.
- Coverage of syllabus should be as per the given Program of work only.
- Rules of Debit and Credit should be taught by using Accounting Equation Method only (Assets, Liabilities, Capital, Incomes and Expenses Accounts).
Special Note: For the purpose of knowledge and understanding, more number of items/transactions are given in the problems. However, Question Paper setter should adhere strictly to the specific instructions given pertaining to each topic. Q.P.setter has a freedom to select appropriate items/transactions or modify the questions, if necessary, to suit the scheme of evaluation.
1st PUC Accountancy Specific Instructions (Section-wise):
Section-A: One Mark Questions:
- No question should be based on a trivial information or contents.
- Note that, before selecting a very short answer type questions, think of the intended answer first to which that answer is the only appropriate response.
- Question should be frame in a clear, precise and unambiguous language, well within the comprehension of the students.
- Question should be straight, simple, understandable, free from grammatical and spelling errors.
- Questions should be selected from stipulated chapters only(see chapter-wise distribution of marks)
- Generally, questions of knowledge and understanding are best suited to this section.
- Each and every question should test a definite objective
- Typology of questions are as follows:
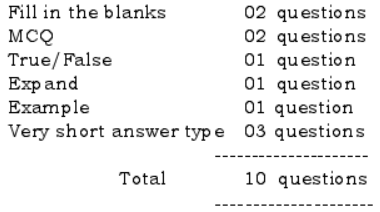
- Questions under different types which generate the same answers which are based on the same concepts or contents are not to be asked.
- Very small application/skill based questions may also be selected under this section.
- Answer to all the questions of section-A should be placed continuously at one place only.
Section-B: Two Marks Questions:
- Questions should be selected from the stipulated chapters only (See chapter-wise distribution of Marks)
- Questions should be selected to suit the scheme.
- Questions under this section may be in a question form/statement form/small calculations, etc. (for theory question only)
- Questions under this section may be as follows:-
Definitions, meanings, features, merits, demerits, types, examples, steps, differences, methods, small calculations, journal entry, etc.
Section-C: Six Marks Questions:
- Questions/ problems should be selected from the stipulated chapters only. (See chapter-wise distribution of marks)
- Items, transactions, entries, etc. should suit to the scheme of evaluation.
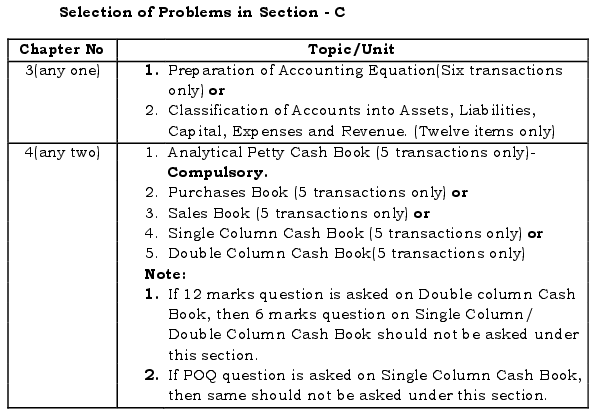
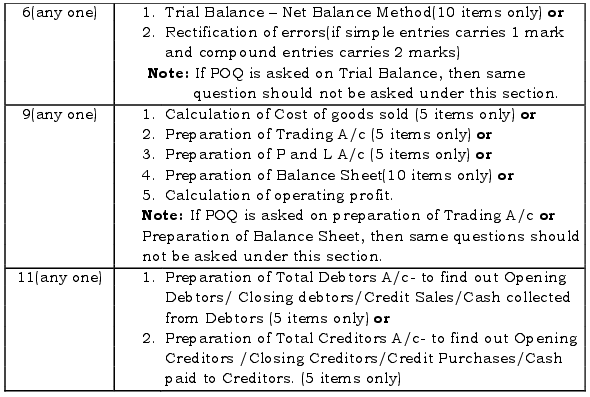
- Out of seven questions, 1 theory based question should be taken from chapter No. 13 (Computerised Accounting System) only.
- Selection of the remaining questions (problems)
Section-D: Twelve Marks Questions:
- Problems should be selected from the stipulated chapters only. (See chapter-wise distribution of marks)
- Items, transactions, entries, etc., should suit to the scheme of evaluation.
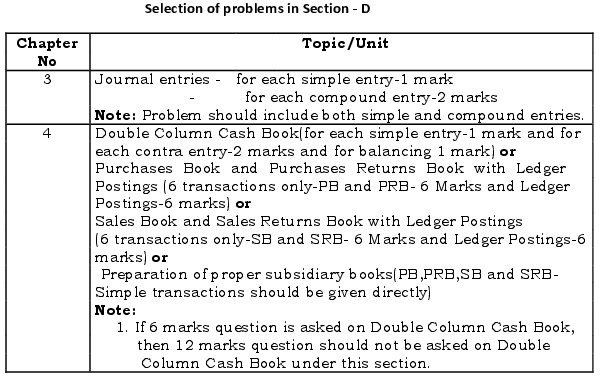
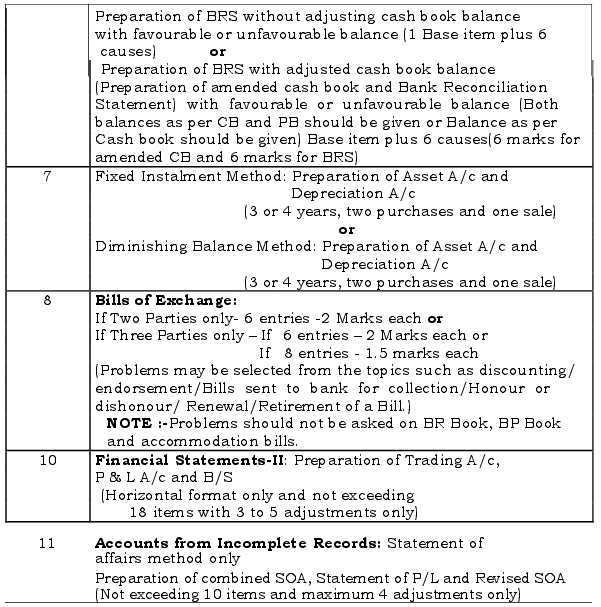
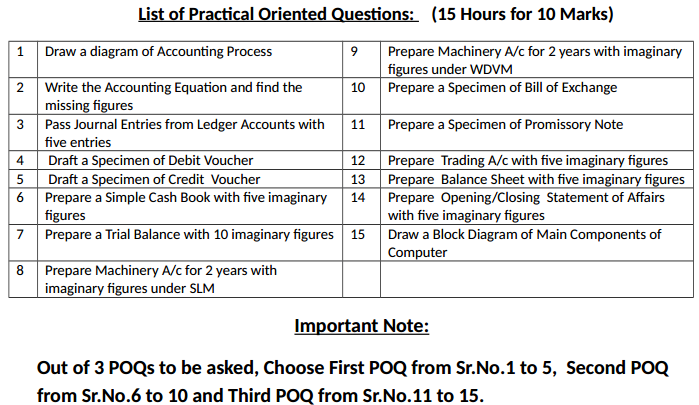
Section-E: Practical Oriented Questions for 5 Marks:
1. Three questions are to be selected from the given list only. (See the blue print)
2. Selection of 3 questions:-
First question: from Sr.No.l to 5 in the list of POQs.
Second question: from Sr. No. 6 to 10 in the list of POQs.
Third question: from Sr. No. 11 to 15 in the list of POQs.
This should be strictly followed while setting the question paper.
Important Note:- Care should be taken to avoid duplication of questions in the different sections of the question paper.
1st PUC Accountancy Suggested Question Paper Design
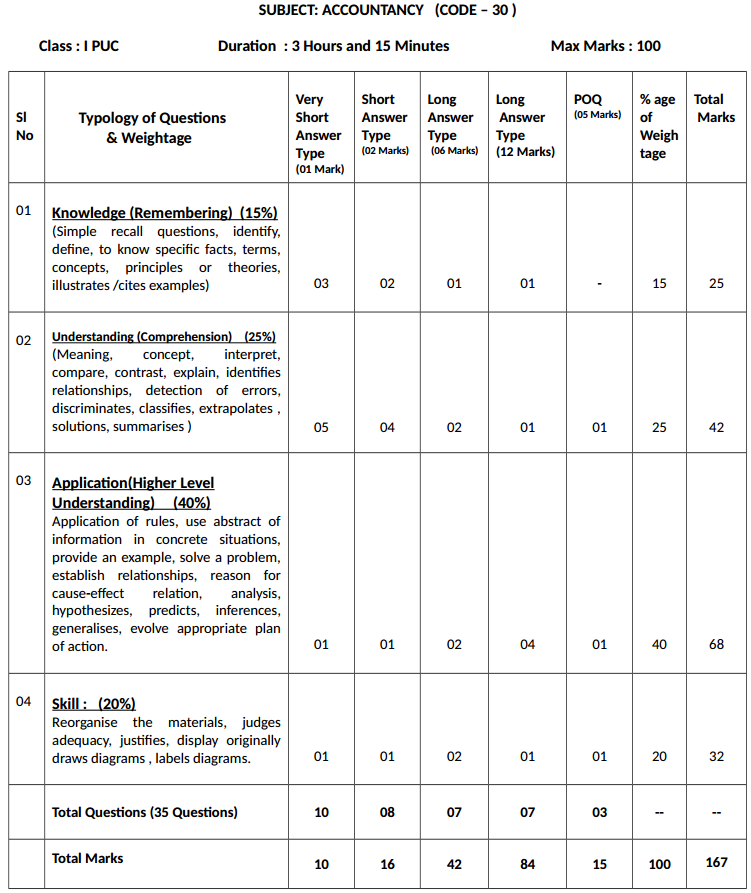
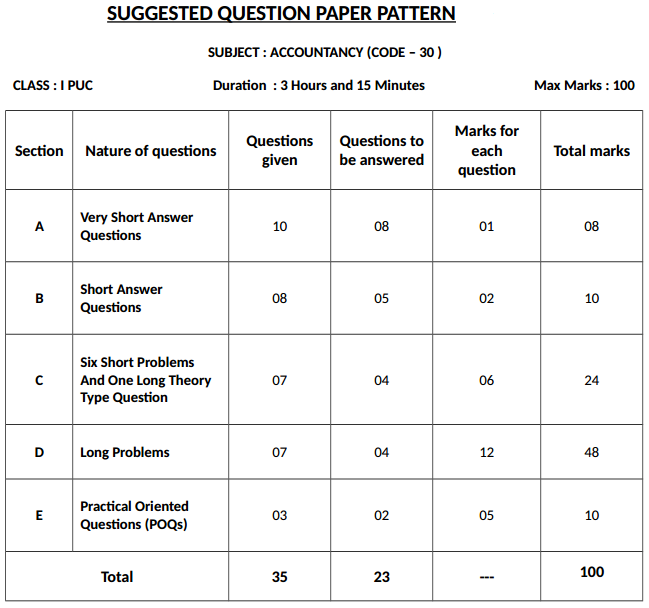
Karnataka 1st PUC Accountancy Syllabus
1. Introduction to Accounting
1.1 Meaning of Accounting
1.2 Accounting as source of information
1.3 Objectives of Accounting
1.4 Role of Accounting
1.5 Basic Terms in Accounting: Entity, Transaction, Assets, Liabilities, Capital, Sales, Revenues, Expenses, Expenditure, Profit, Gain, Loss, Discount, voucher, Goods, Drawings, Purchases, Stock, Debtors, Creditors.
2. Theory Base of Accounting
2.1 Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
2.2 Basic accounting concepts:
Business Entity, Money Measurement, Going concern, Accounting Period, Cost, Dual, Aspect, Revenue Recognition, Matching Full Disclosure Consistency, Conservatism (Prudence) Materiality, Objectivity.
2.3 Systems of Accounting
2.4 Basic of Accounting
2.5 Accounting Standards
2.6 International Financial Reportirig Standards
3. Recording of Transactions – I
3.1 Business Transactions and Source Document
3.1.1 Preparation of Accounting Vouchers
3.2 Accounting Equation:
3.3 Using Debit and Credit
3.4 Books of Original Entry
3.4.1 Journal
3.5 Ledger
3.5.1 Classification of Ledger Accounts
3.6 Posting from Journal
4. Recording of Transactions – II
4.1 Cash Books
4.1.1 Single Column Cash Book
4.1.2 Double Column Cash Book
4.1.3 Petty Cash Book
4.1.4 Balancing of Cash Book
4.2 Purchases Book
4.3 Purchases Returns Book
4.4 Sales Book
4.5 Sales Returns Book
4.6 Journal Proper
4.7 Balancing the Accounts
5. Bank Reconciliation Statement
5.1 Need for reconciliation
5.1.1 Timing differences
5.1.2 Differences caused by errors
5.2 Preparation of BRS
5.3 Preparation of BRS – without adjusting Cash Book Balance
6. Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors
6.1 Meaning of Trial Balance
6.2 Objectives of preparing Trial Balance
6.2.1 To ascertain the arithmetical accuracy of ledger accounts
6.2.2 To help in locating errors
6.2.3 To help in the preparation of the financial statements
6.3 Preparation of Trial Balance
6.3.1 Total Method
6.3.2 Balance Method
6.3.3 Totals-Cum-Balance Method
6.4 Significance of Agreement of Trial Balance
6.4.1 Classification of Errors
6.4.2 Errors of Commission
6.4.3 Errors of Omission
6.4.4 Errors of Principle
6.4.5 Compensating Errors
6.5 Searching of Errors
6.6 Rectification of Errors
6.6.1 Rectification of errors which do not afffect the trial balance
6.6.2 Rectification of errors affecting Trial Balance
6.6.3 Rectification of errors in the next accounting year
7. Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
7.1 Depreciation
7.1.1 Meaning of Depreciation
7.1.2 Features of Depreciation
7.2 Depreciation and other similar terms
7.2.1 Depletion
7.2.2 Amortisation
7.3 Causes of Depreciation (7.3.1 to 7.3.4)
7.4 Need for Depreciation (7.4.1 to 7.4.4)
7.5 Factors affecting the amount of Depreciation (7.5.1 to 7.5.4)
7.6 Methods of Calculating Depreciation Amount
7.6.1 Straight Line Method
7.6.1.1 Advantages of Straight Line Method
7.6.1.2 Limitations of SLM
7.6.2 Written down value method
7.6.2.1 Advantages of WDVM
7.6.2.2 Limitations of WDVM
7.7 SLM and WDVM : A Comparative Analysis
7.7.1 Basic of charging Depreciation
7.7.2 Annual Charge of Depreciation
7.7.3 Total charge against P and L A/c (Depreciation + Repair charges)
7.7.4 Recognition by Income Tax Law
7.7.5 Suitability
7.8 Methods of recording depreciation
7.8.1 Charging depreciation to Asset A/c
7.8.2 Creating Provision for Depreciation A/c / Accumulated Depreciation A/c
7.9 Disposal of Asset
7.9.1 Use of Asset Disposal A/c
7.10 Effect of any addition or extension to the existing asset
7.11 Provisions
7.11.1 Accounting treatment for Provisions
7.12 Reserves
7.12.1 Difference between Reserve and Provision
7.12.2 Types of Reserves
7.12.3 Difference between Revenue Reserve and Capital Reserve
7.12.4 Importance of Reserves
7.13 Secret Reserve
8. Bills of Exchange
8.1 Meaning of Bills of Exchange
8.1.1 Parties to Bills of Exchange
8.2 Promissory Note
8.2.1 Parties to Promissory Note
8.3 Advantages of Bills of Exchange
8.4 Maturity of Bill
8.5 Discounting of Bill
8.6 Endorsement of Bill
8.7 Accounting Treatment
8.7.1 In the books of Drawer / Promissor
8.7.2 In the books of Acceptor / Promissory
8.8 Dishonour of Bill
8.8.1 Noting Charges
8.9 Renewal of the Bill
8.10 Retiring of the Bill
8.11 Bills Receivable and Bills Payable Books:
8.11.1 Bills Receivable Book
8.11.2 Bills Payable Book
8.12 Accommodation Bills
9. Financial Statements – 1
9.1 Stakeholders and their Information Requirements
9.2 Distinction between Capital and Revenue
9.3 Financial Statements
9.4 Trading and Profit and Loss Account
9.5 Operating Profit (EBIT)
9.6 Balance Sheet
9.7 Opening Entry
10. Financial Statements
10.1 Need for Adjustments
10.2 Closing Stock
10.3 Outstanding Expenses
10.4 Prepaid Expenses
10.5 Accrued Income
10.6 Income Received in Advance
10.7 Depreciation
10.8 Bad Debts
10.9 Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts
10.10 Provision for Discount on Debtors
10.11 Manager’s Commission
10.12 Interest on Capital
11. Financial Statements
11.1 Meaning of Incomplete Records
11.2 Reasons for Incompleteness and its Limitations
11.3 Ascertainment of Profit and Loss
11.4 Preparing Trading and Profit and Loss Account and the Balance Sheet
11.4.1 Ascertainment of Credit Purchases
11.4.2 Ascertainment of Credit Sales
11.4.3 Ascertainment of B/R and B/P
11.4.4 Ascertainment of missing information through summary of cash
12. Applications of Computers in Accounting
12.1 Meaning and Elements of Computer system
12.2 Capabilities of Computer System
12.3 Limitations of a Computer
12.4 Components of Computer
12.5 Evolution of Computerised Accounting
12.6 Features of Computerised Accounting System
12.7 Management Information System and Accounting Information System
12.7.1 Designing of Accounting Reports
12.7.2 Data Interface between the Information System
13. Computerised Accounting System
13.1 Concept of computerised Accounting System
13.2 Comparison between Manual and Computerised Accounting
13.3 Advantages of Computerised Accounting System
13.4 Limitations of Computerised Accounting System
13.5 Sourcing of Accounting Software
13.6 Generic Considerations before Sourcing an Accounting Software
We believe that the shared knowledge about Karnataka State Board solutions for 1st PUC Accountancy Question Bank with Answers benefits you a lot in your exam preparation. If you need more information on the same then stay connected with our site & get updated details on KTBS Solutions PDF for all Subjects.
