You can Download Chapter 9 Financial Statement Questions and Answers, Notes, 1st PUC Accountancy Question Bank with Answers Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Accountancy Question Bank Chapter 9 Financial Statement
1st PUC Financial Statement Two Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What do you mean by financial statements?
Answer:
The statements which explains the financial position of the concern for a particular period. Called financial statements.
Question 2.
Why do you prepare final accounts?
Answer:
For knowing exact financial position and financial result of the concern, final accounts to be prepared.
Question 3.
What is trading account?
Answer:
Trading a/c is a financial statement prepared for the purpose of finding out trading result or a gross profit or loss of a business concern for a particular period.
Question 4.
What is profit and loss a/c?
Answer:
It is a financial statement prepared at the period end for knowing business result, i.e., profit or loss. It is a nominal a/c contain all indirect expenses loss and indirect income and profit.
![]()
Question 5.
What is balance sheet?
Answer:
Balance sheet is prepared for the purpose of knowing financial position of a business in a given period. It contains assets and liabilities of a business.
Question 6.
Mention the statements prepared under final accounts.
Answer:
The Financial statements prepared under final accounts are :
- Trading account
- Profit and Loss a/c
- Profit and loss appropriation a/c
- Balance sheet
Question 7.
Arrange the following assets in the balance sheet of a sole trading concern in the order of permanence.
- Cash
- Building
- Closing stock
- Machinery
Answer:
- Cash
- Stock
- Machinery
- Building.
Question 8.
Where do you show the following in the balance sheet of a sole trading concern.
Answer:
(a) Bills payable
(b) Plant and machinery
(a) Bills payable = Balance sheet liability side
(b) Plant and machinery = Balance sheet assets side.
Question 9.
Name any four current assets.
Answer:
- Cash
- Bank
- Stock
- Debtors
Question 10.
Name any four fixed assets.
Answer:
- Machinery
- Goodwill
- Building
- Furniture
Question 11.
Mention any four items appeared in trading account debit side.
Answer:
The items appeared in trading a/c debit side are :
- Purchases
- Wages
- Freight charges
- Factory expenses
Question 12.
What is Net profit?
Answer:
Net profit is the surplus remaining after meeting all indirect expenses out of gross profit.
Question 13.
Differentiate profit and loss a/c and balance sheet.
Answer:
| Trial balance | Balance sheet |
| 1. It is a summary of ledger balance | 1. It is a summary of assets and liabilities |
| 2. It contain all balance | 2. It contain only real and personal a/c |
Question 14.
What is profit and loss appropriation a/c?
Answer:
The financial statement prepared at the period and to show now the profit of a company appropriat or the internal profit of the company allocation called ‘profit and loss appropriation’ account.
Question 15.
Write the object of balance sheet preparation.
Answer:
Balance sheet is prepared for the purpose of knowing financial position of a business concern.
![]()
Question 16.
Who is debtor?
Answer:
The person who purchase goods from business on credit it called debtor.
Question 17.
Mention four types of assets.
Answer:
- Tangible assets
- Intangible assets
- Fixed assets
- Current assets
Question 18.
What is bad debts?
Answer:
If the debtors not able or agree to pay their debts that protion treated as bad debts.
Question 19.
Write the meaning of gross profit.
Answer:
It is a positive trading result. The excess of sales and closing stock over purchases, direct expenses and opening stock called gross profit.
Question 20.
What is direct expenses?
Answer:
The expenses which directly involved in production called direct expenses. All direct expensses are recorded in trading a/c debit side.
Question 21.
What is Indirect expenses?
Answer:
The expenses which is not directly involved in production but relating to the business called indirect expenses. There expenses are recorded in profit and loss a/c debit side.
Question 22.
What is Final Accounts?
Answer:
Final accounts is the process of preparation of finanicial statements at the end of the year.
Question 23.
Differentiate trial balance and balance sheet.
Answer:
| Profit and loss a/c | Balance sheet |
| 1. It is a nominal a/c | 1. It is a real and personal a/c |
| 2. It is prepared to know the business result (profit / loss) | 2. It is prepared to know the financial position. |
| 3. It contains all expenses and income | 3. It contains assets and liabilities. |
1st PUC Financial Statement Six Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the objectives of preparing financial statements?
Answer:
The following are the objectives of preparing financial statements:
1. To ascertain profit earned or loss incurred by a business during an accounting period.
This is estimated by preparing Trading and Profit and Loss Account.
2. To ascertain the true financial position of a business. This is reflected by the Balance sheet.
3. To enable comparison of current year’s performance with that of the previous year’s, i. e., intra-firm comparisons. Also, to compare own performance with that of the other firms in the same industry, i.e., inter-firm comparisons.
4. To assess the solvency and credit worthiness of the business
5. To provide various provisions and reserves to meet unforeseen future conditions and to toughen the financial position of the business
6. To provide vital information to facilitate various users of accounting information in decision making process. [Any two]
Question 2.
What is the purpose of preparing trading and profit and loss account?
Answer:
The purposes of preparing Trading Account are:
a. To calculate gross profit earned or gross loss incurred during an accounting period
b. To estimate the cost of goods sold
c. To record direct expenses (i.e., expenses incurred on the purchases and manufacturing of goods)
d. To measure the adequacy and reasonability of direct expenses incurred by comparing purchases with direct expenses incurred
e. To compare the realized efficiency and performance with the desired or proposed targets
f. To calculate net profit or net loss
g. To ascertain net profit ratio and to compare this year’s net profit ratio with that of the desired and proposed target in order to assess the efficiency and effectiveness
h. To measure the adequacy and reasonability of indirect expenses incurred by ascertaining ratio between indirect expenses and net profit
i. To compare current year’s actual performance with desired and planned performance
j. To provide various provisions and reserves to meet unforeseen future conditions and to toughen the financial position of the business. [Any two]
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the concept of cost of goods sold.
Answer:
Cost of goods sold (COGS) is the cost of merchandise that is sold to the customers. It includes cost of raw materials purchased, direct expenses incurred, value of opening stock, i.e., the value of the last years unsold stock and excludes closing stock if any, i.e., the value of current year’s unsold stock or stock in need.
The formula to calculate COGS is:
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
Question 4.
What is a balance sheet? What are its characteristics?
Answer:
Balance sheet is a statement prepared to ascertain values of assets and liabilities of a business on a particular date. It is called Balance sheet as it contains balances of real and personal accounts, which are not closed on a particular date.
Characteristics of Balance Sheet
It is a statement of assets and liabilities.
The total of Assets side must be equal to Liabilities sides.
It is prepared at a particular date.
It helps in ascertaining the financial position of the business.
Question 5.
State whether the following statements are items of capital or revenue expenditure:
a. Expenditure incurred on repairs and w hite washing at the time of purchase of an old building in order to make it usable.
b. Expenditure incurred to provide one more exit in cinema hall is compliance with a government order.
c. Registration fees paid at the time of purchase of a building
d. Expenditure incurred in the maintenance of a tea garden which will produce tea after four years.
e. Depreciation charged on a plant.
f. The expenditure incurred in erecting a platform on which a machine will be fixed.
g. Advertising expenditure, the benefits of which will last for four years.
Answer:
a. Capital expenditure
b. Revenue expenditure
c. Capital expenditure
d. Capital expenditure
e. Revenue expenditure
f. Capital expenditure
g. Deferred Revenue expenditure
Question 6.
Distinguish between capital and revenue expenditure
Answer:
Following points of distinction between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure are worth noting:
a. Capital expenditure increases earning capacity of business where as revenue expenditure is incurred to maintain the earning capacity.
b. Capital expenditure is incurred to acquire fixed assets for operation of business where as revenue expenditure is incurred on day-to-day conduct of business.
c. Revenue expenditure is generally recurring expenditure and capital expenditure is nonrecurring by nature.
d. Capital expenditure benefits more than one accounting year where as revenue expenditure normally benefits one accounting year.
e. Capital expenditure (subject to depreciation) is recorded in balance sheet whereas revenue expenditure (subject to adjustment for outstanding and prepaid amount) is transferred to trading and profit and loss account.
Question 7.
What is an operating profit?
Answer:
Operating profit is a profit earned through normal activities of a business. It is the excess of gross profit over operating expenses. In other words, it is the excess of operating revenue over operating cost. It is also termed as earnings before interest and tax (EBTI).
It does not include incomes and expenses that are not related to main course of the business. It is calculated by following formulae:
Operating Profit = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
or
Operating Profit = Sales – Operating cost
Operating Profit = Sales – COGS – Operating Expenses
Operating expenses include office and administrative expenses, selling and distribution
Expenses, discount, bad debts, etc.
![]()
1st PUC Financial Statement Long Answers
Question 1.
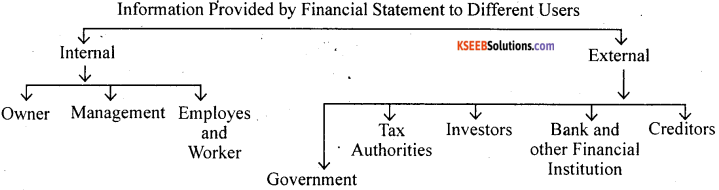
What are financial statements? What information do they provide?
Answer:
Every business firm wants to know its financial position at the end of an accounting period. In order to assess its financial position, profit earned or loss incurred during an accounting period, the book value of its assets and liabilities is to be ascertained. In order to serve this purpose, financial statements are prepared. Financial statements are the statements showing profitability and financial position of a business at the end of the year. It includes:
Income statements: Trading and profit and loss account, which represents direct and indirect expenses, incurred to generate revenues. On one hand, trading account discloses either gross profit or gross loss; on the other hand, profit and loss account discloses either net profit or net loss.
Statement of financial position: Balance Sheet, which enlists the book value of all the assets and liabilities of the firm. Balance sheet discloses the true financial position, solvency and credit worthiness of the business.
Question 2.
What are closing entries? Give four examples of closing entries.
Answer:
The balances of all nominal accounts are transferred to the Trading and Profit and Loss Account. The entries required for such transfers are termed as closing entries. The examples of closing entries are given below.
Closing entries to transfer the following items to the debit side of trading account form Trail Balance:

Closing entries to transfer the following items to the credit side of trading account from Trial Balance:

Closing entries to transfer the following items to the debit side of Profit and Loss Account from Trial Balance:

Closing entries to transfer the following items to the credit side of Profit and Loss Account from Trial Balance:

Question 3.
Discuss the need of preparing a balance sheet.
Answer:
The need to prepare a Balance Sheet are given below.
a. It helps in determining the nature and book value of various assets, such as fixed assets, investments, current assets, etc. at the end of an accounting period.
b. It helps in ascertaining the nature and amount of various liabilities like long term liabilities, current liabilities, provisions, etc., which a business owes.
c. It discloses important information about capital invested in a business. The additional capital invested during the accounting period, drawings of the owners and profit (or loss) added to (or deducted from) the capital of the business.
d. It helps I assessing the solvency of a business.
e. It discloses the true financial position of a business at a particular point of time.
f. It lays down the basis for maintaining new books for next accounting period.
![]()
Question 4.
What is meant by Grouping and Marshalling of assets and liabilities? Explain the ways in which a balance sheet may be marshalled.
Answer:
The rationale behind preparing financial statements is to present a summarized version of all financial activities in such a manner that all users can interpret and understand the information easily, appropriately and also take decisions accordingly
Grouping of assets and liabilities: Grouping means showing similar assets and liabilities under a single head. For example, all assets that can be used for more than a year are clubbed together under the heading ‘fixed assets’, to example, building, furniture, machinery, etc.
Marshalling of asset and liabilities: When assets and liabilities are shown in a particular order of liquidity or permanence, they are said to be marshalled.
In order to liquidity: Liquidity means convertibility into cash. Assets that can be converted into cash in least possible time, i.e., more liquid assets are recorded first, followed by the lesser liquid assets. In a balance sheet, cash in hand is recorded at first and goodwill at last. In the same way, liabilities that are to be paid first, i.e., high priority liabilities are recorded first, followed by the lower priority ones. In a balance sheet, current liabilities are recorded first and then the li9ng term liabilities and capital at the last.
Balance Sheet of ……………………….. as on ……………………..
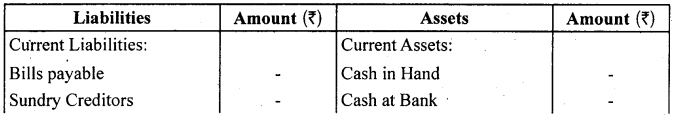
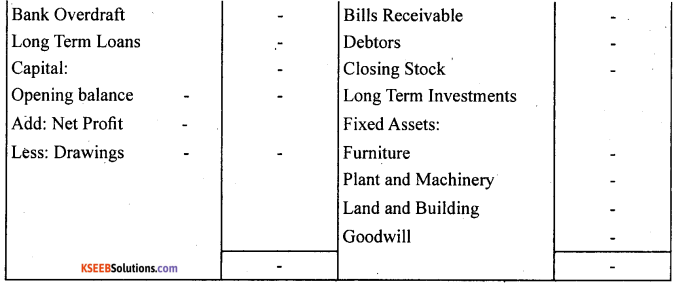
In order of permanence: It is just reverse of the above method. In this assets and liabilities are arranged in their reducing level of permanence. The assets with higher degree of permanence are recorded first, followed by the assets with lower degree of permanence. For example: goodwill, land and building have the highest degree of permanence and hence are recorded at the top, whereas, cash at bank and cash in hand are recorded at the bottom. In the same way, liabilities are shown according to their life in the business. Liabilities with higher level of permanence like, capital is recorded at the top and other liabilities with lower permanence are recorded at the bottom.
Balance sheet of ………………………….. as on ……………………………
Following is the proforma of a balance sheet in the order of permanence :
Balance sheet as on or as at …………………….
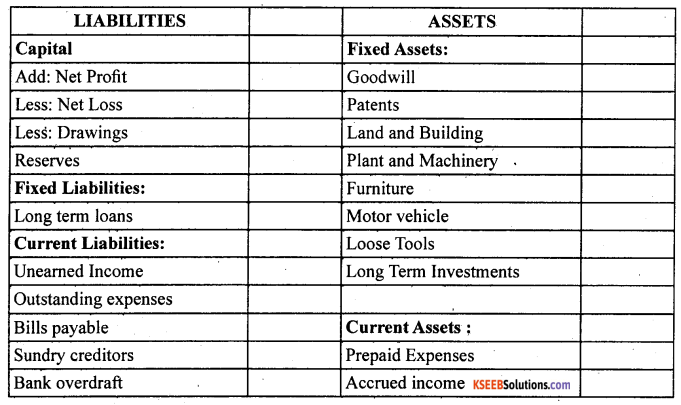
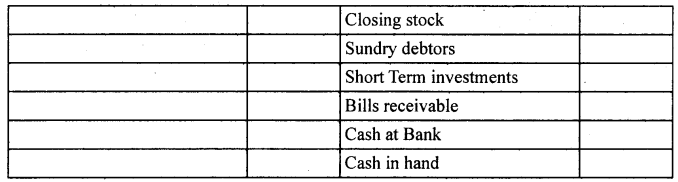
Meaning, characteristic, need and structure of the balance sheet: The balance sheet is a statement of assets and liabilities of a business enterprise and shows the financial position at a given date informations contained in a balance sheet is true only on that date. The balance sheet is a part of the final account. But it is not an account, it is only a statement. In a balance sheet the totals of assets and liabilities are always equal. It portrays the accounting equation.
A balance sheet has to be prepared to know the financial position of the business, and the nature and values of its assets and liabilities. All the accounts which have not been closed till the preparation of the profit and loss account are shown in the balance sheet. Assets and liabilities shown in the balance sheet are marshalled in order of liquidity or in order of permanence.
![]()
1st PUC Financial Statement Numerical Questions
Question 1.
From the following balances taken from the books of Simmi and Vimmi Ltd. For the year ending March 31,2003, calculate the gross profit.

Answer:
Financial statement-I
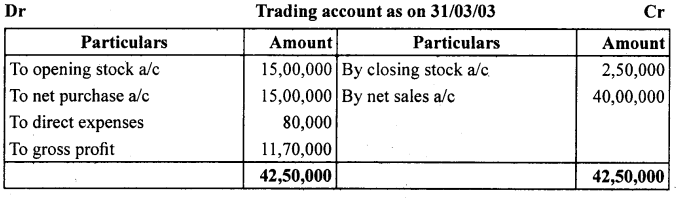
Question 2.
From the following balance extracted from the books ofM/s Ahuja and Nanda. Calculate the amount of:
(a) Cost of goods available for sale
(b) Cost of goods sold during the year
(c) Gross Profit

Answer:
(a) Cost of goods available for sale
= Opening stock + Net purchases + Wages
Net Purchases = Credit purchase + cash purchase – purchase return
Net purchase = 7,50,000 + 3,00,000 – 10,000
= 10,40,000
Cost of goods available for sale = 25,000 + 10,40,000 + 1,00,000
= 11,65,000
(b) Cost of goods sold during year = Net sales – Gross profit
or
= Opening stock + Net purchase + D.E – Closing stock.
= 25,000 + 10,40,000 + 1,00,000 – 30,000
= 11,35,000
(c)
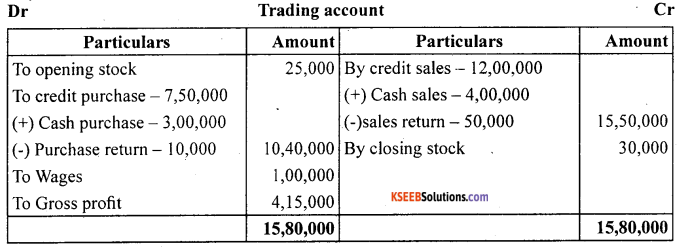
Question 3.
Calculate the amount of gross profit and operating profit on the basis of the following balances extracted from the books of M/s Rajiv & Sons for the year ended March 31, 2005.
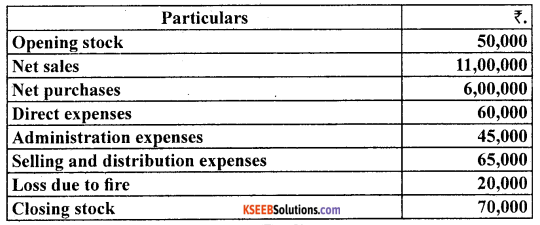
Answer:
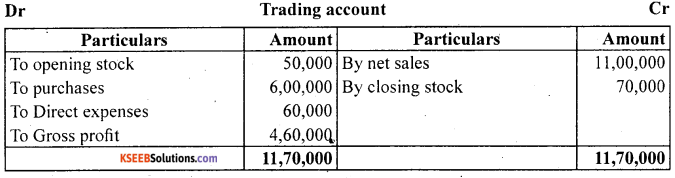
Operating Profit = Net profit + Non operating expenses – Non operating incomes.
Operating profit = Sales – (opening stock + Net purchases + D.E + Indirect expenses) + closing stock.
= 11,00,000 – (50,000+6,00,000+60,000+45,000+65,000)4-70,000
= 11,00,000-8,20,000+70,000 =3,50,000
![]()
Question 4.
Operating profit earned by M/s Arora & Sachdeva in 2005-06 was ₹ 17,00,000. Its . non-operating incomes were ₹ 1,50,000 and non-operating expenses were ₹ 3,75,000.
Calculate amount of net profit earned by the firm.
Answer:
Operating profit = 17,00,000
Non-operating incomes = 1,50,000
Non-operating expenses = 3,75,000
Net profit = ?
Net profit = operating profit + Non-operating incomes – Non-operating expenses
= 17,00,000+1,50,000-3,75,000
Net profit = 14,75,000
Question 5.
The following are the extracts from the trial balance of M/s Bhola and Sons as on March 31,2005.
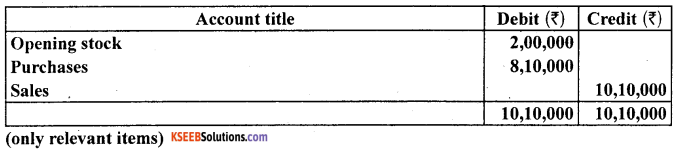
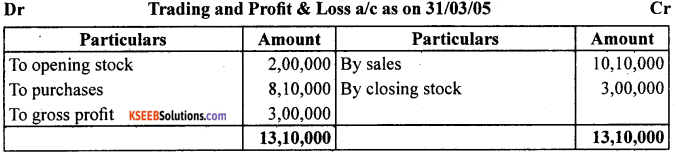
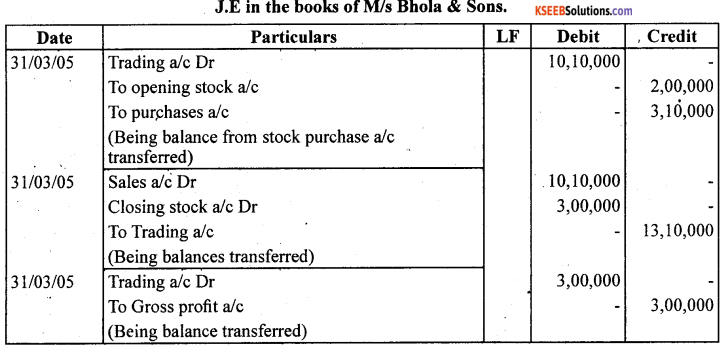
Closing stock as on date was valued at ₹ 3,00,000.
You are required to record the necessary journal entries and show how the above items will appear in the trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet of M/s Bhola & Sons.
Answer:
Question 6.
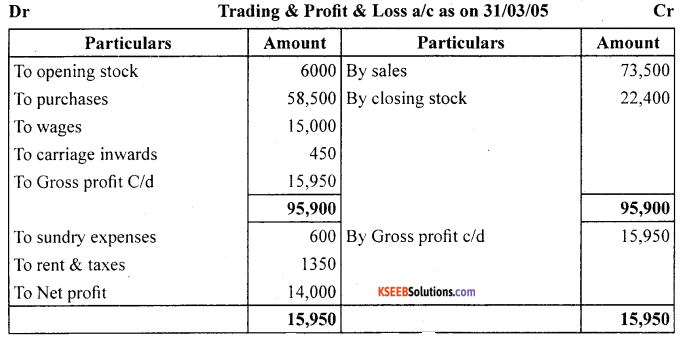
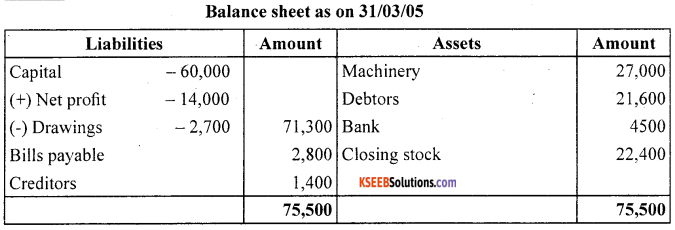
Prepare Trading and Profit and Loss account and Balance sheet as on March 31,2005:
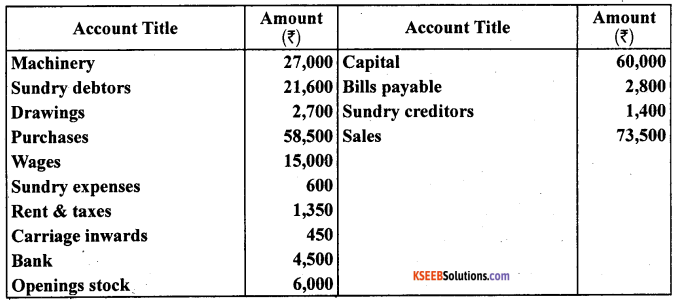
Closing stock as on March 31, 2005 ₹ 22,400
Answer:
![]()
Question 7.
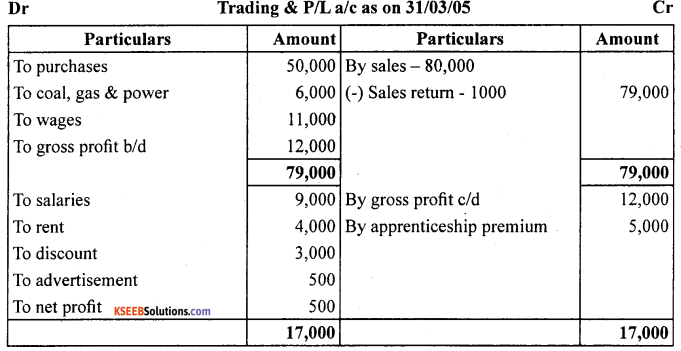
The following trial balance is extracted from the books of M/s Ram on March 31,2005. You are required to prepare trading and profit and loss account and the balance sheet as on date:
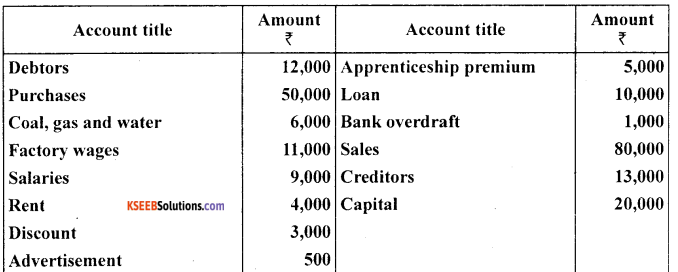

Answer:
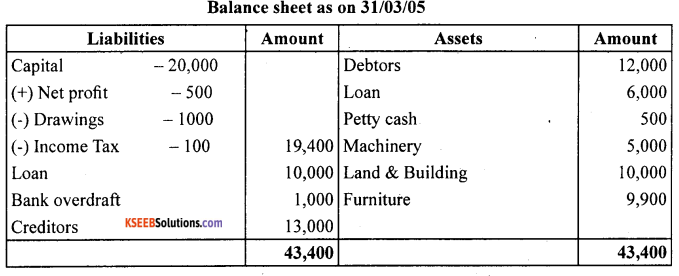
Question 8.
The following is the trial balance of Manju Chawla on March 31,2006. You are required to prepare trading and profit and loss account and a balance sheet as on date:
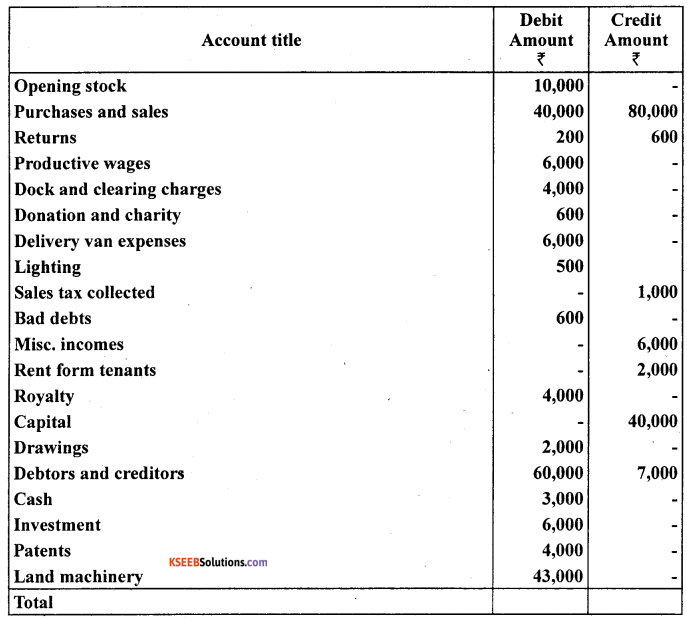
Closing Stock ₹ 2,000
Answer:
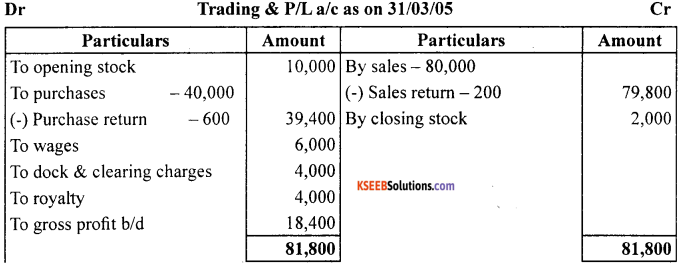
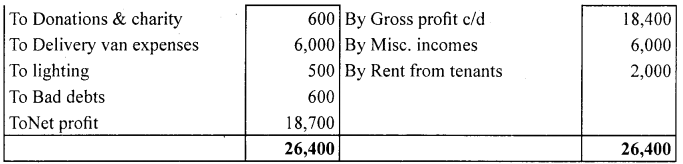
![]()
Question 9.
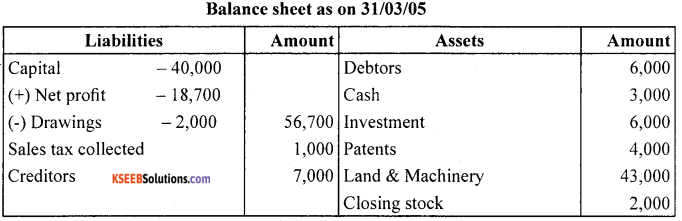
The following is the trial balance of Mr. Deepak as on March 31,2005. You are required to prepare trading account. Profit and loss account and a balance sheet as on date :
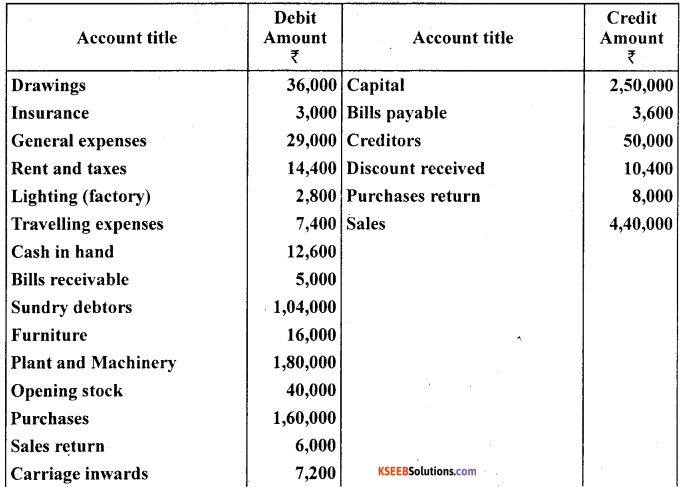
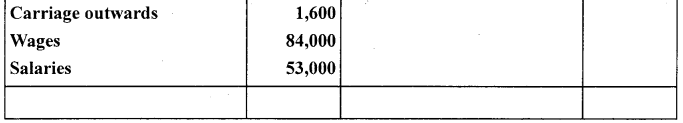
Closing Stock ₹35,000
Answer:
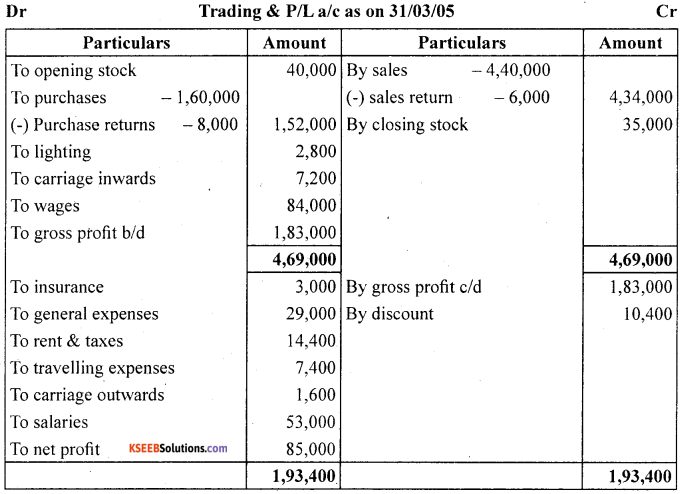
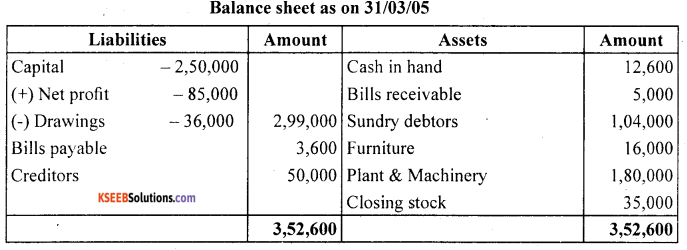
Question 10.
Prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet from the following particulars as on March 31,2005.
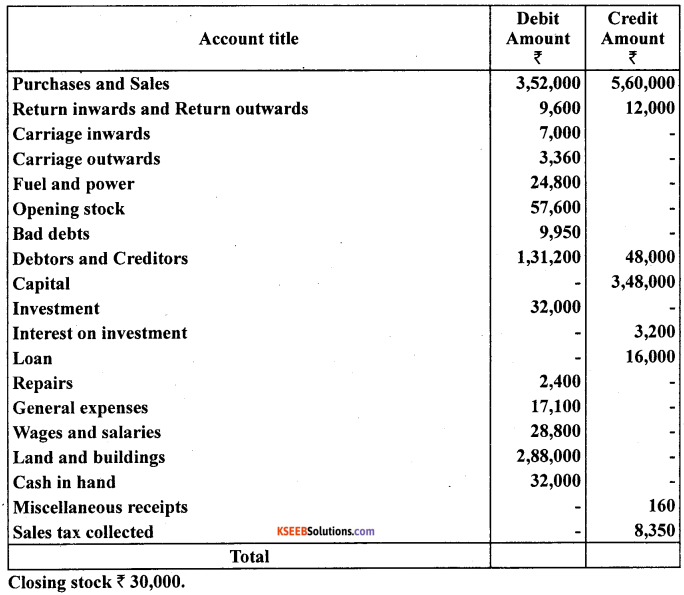
Answer:
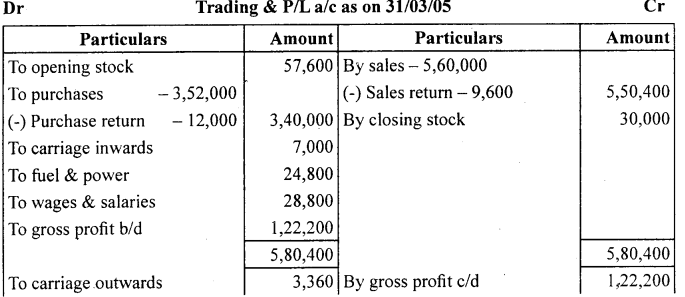
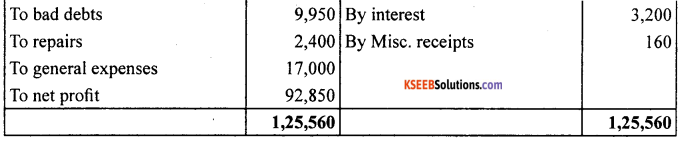
![]()
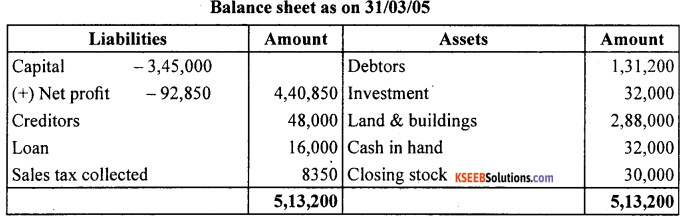
Question 11.
From the following trial balance of Mr. A. Lai, prepare trading, profit and loss account and balance as on March 31,2005
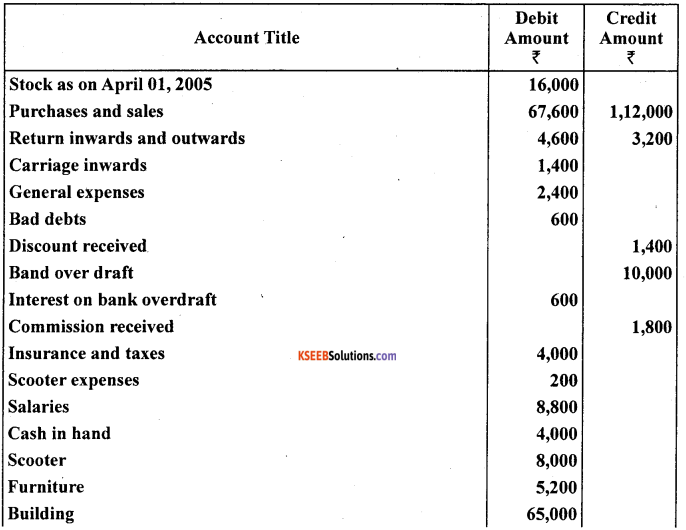

Answer:
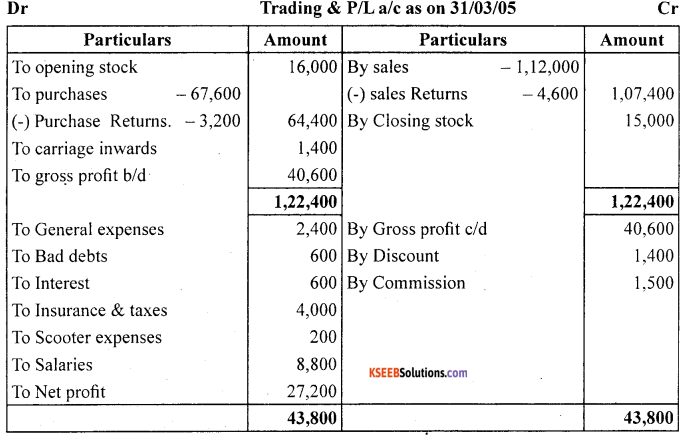
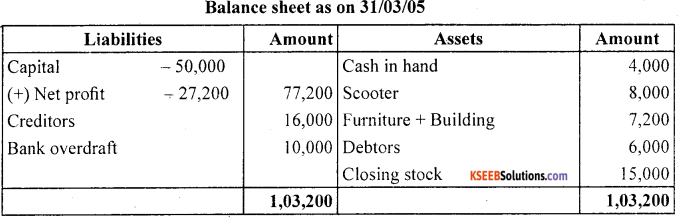
Question 12.
prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet of M/s Royal Traders from the following balances branches as on March 31,2005
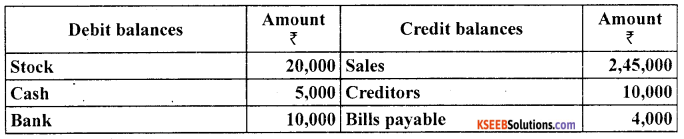
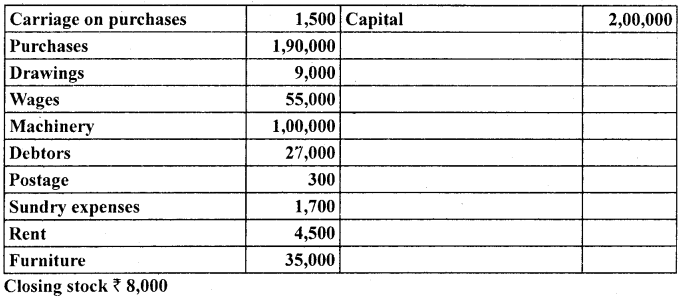
Answer:
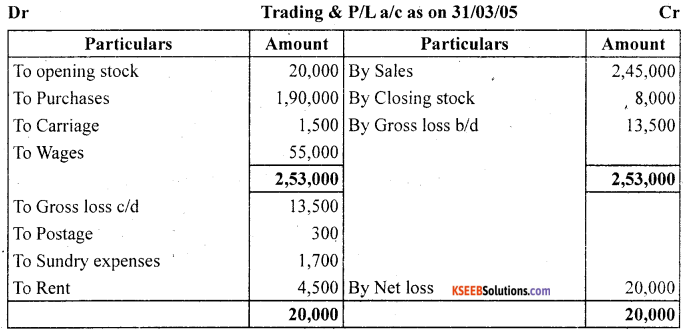
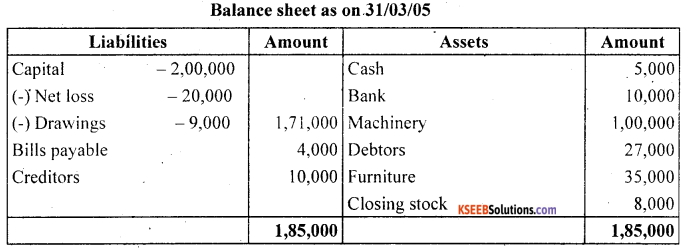
![]()
Question 13.
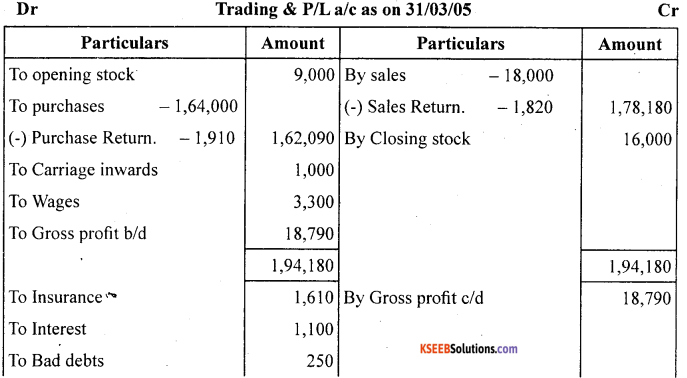
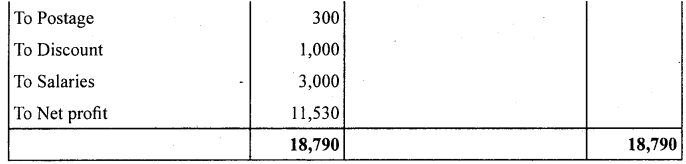
Prepare trading and profit and loss account from the following particulars of M/s Neema Traders as on March Traders as on March 31,2005.
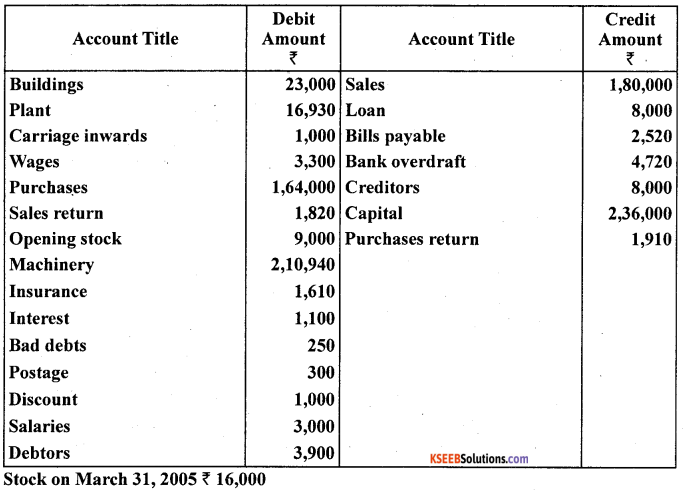
Answer:
Question 14.
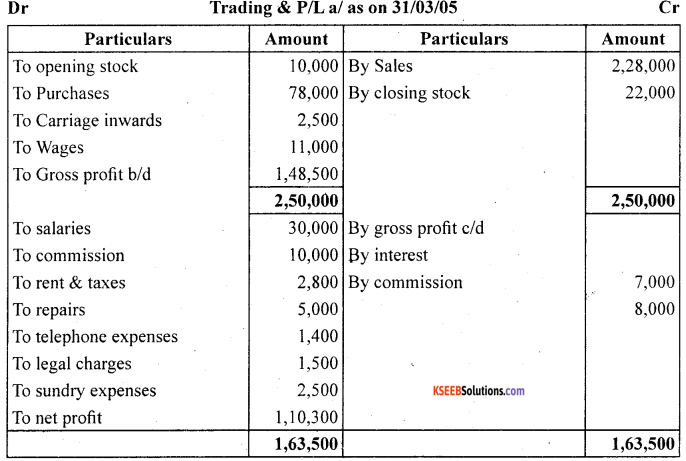
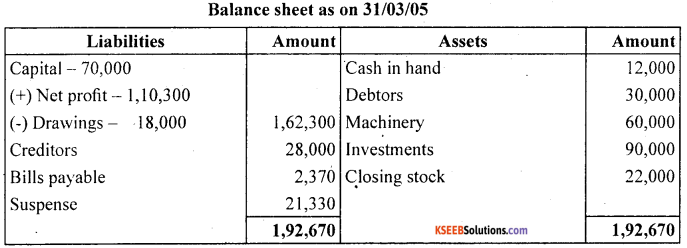
From the following balances of M/s Nilu Sarees as on March 31,2005. Prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet as on date.
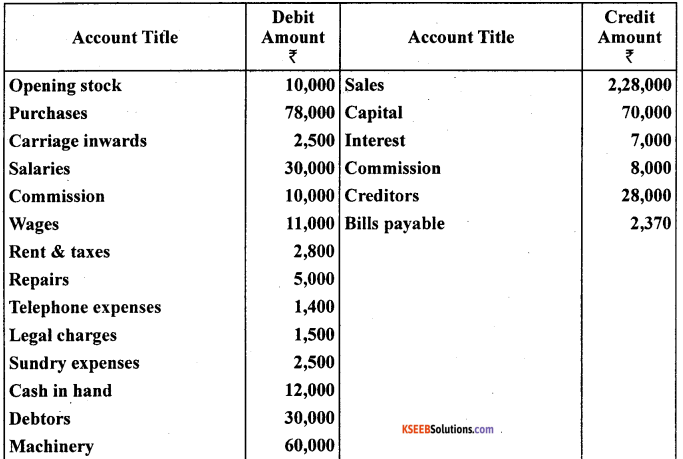
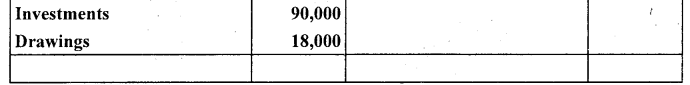
Closing stock on March 31,2005 ₹ 22,000
Answer:
![]()
Question 15.
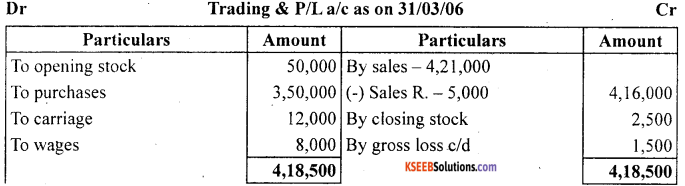
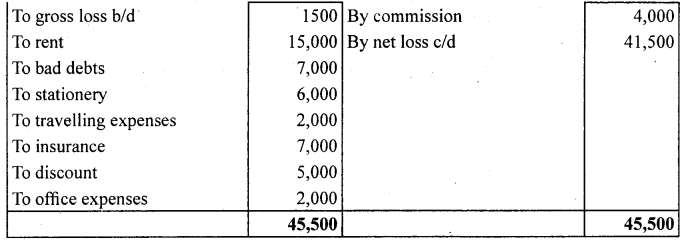
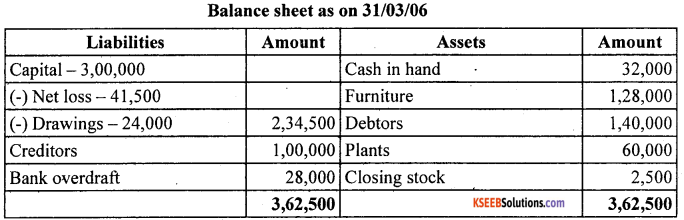
Prepare trading and profit and loss account of M/s Sports Equipments for the year ended March 31,2006 and balance sheet as on that date:
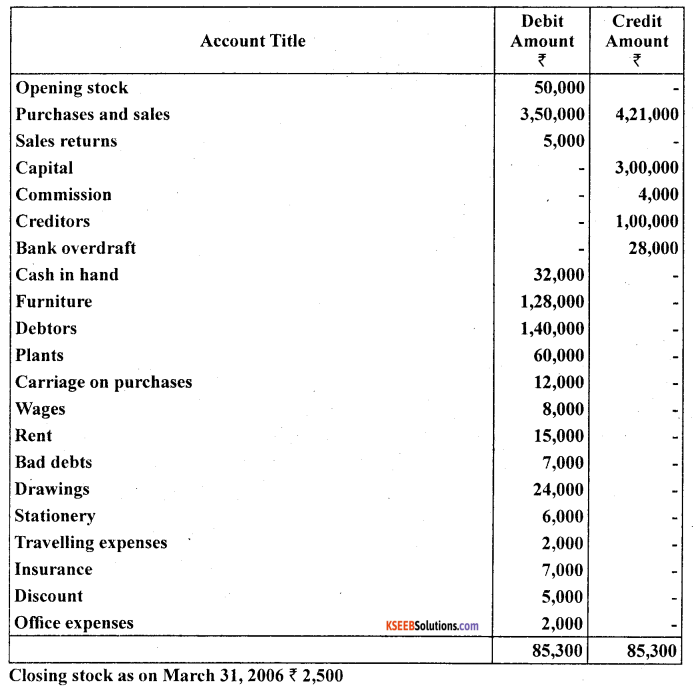
Answer: