Students can Download 2nd PUC Basic Maths Previous Year Question Paper March 2017, Karnataka 2nd PUC Maths Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Basic Maths Previous Year Question Paper March 2017
Time: 3 Hours 15 Min.
Max.Marks: 100
Instructions:
- The question paper has 5 parts A, B, C, D and E. Answer all the pats.
- Part-A carries 10 marks\, Parts – B carries 20 marks, Part – C carries 3 marks, Part – D carries 30 marks and Pat- E carries 1 marks.
- Write the question number properly as indicated in the question paper.
Part – A
Answer All the ten questions: (10 × 1 = 10)
Question 1.
If \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & -3 & 5 \\ 6 & 2 & 4 \end{matrix} \right]\) find 5A’
Answer:
\(A’=\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 6 \\ -3 & 2 \\ 6 & 4 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} 5 & 30 \\ -15 & 10 \\ -25 & 20 \end{matrix} \right]\)
Question 2.
If nP4 = 360, find n.
Answer:
nP4 = n(n – 1)(n – 2)(n – 3) = 6.5.4.3 = 360
∴ n = 6
Question 3.
Symbolize the propositions “3x = 9 and x < 7″.
Answer:
P ∧ Q
![]()
Question 4.
If 5 : 20 = 3 : x, find the value of x.
Answer:
5x = 60 ⇒ x = 12
Question 5.
What rate of Interest is obtained by investing in 9% stock at 180?
Answer:
For face value 100 – income 9
![]()
Question 6.
If sin A = 3, find sin 3A.
Answer:
sin3A = 3sin A – 4 sin3A = \(3 \cdot \frac{3}{5}-4 \cdot\left(\frac{3}{5}\right)^{3}=\frac{9}{5}-\frac{108}{125}=\frac{175-108}{125}=\frac{67}{125}\)
Question 7.
Find the length of Latus Rectum of the parabola 3x2 + 8y = 0.
Answer:
3x2 = -8y ⇒ x2 = \(\frac{8}{3}\)y Length of L.R = 4a = \(\frac{8}{3}\)
Question 8.
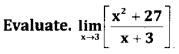
Answer:
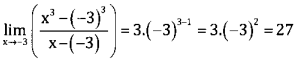
Question 9.
If y = elogcotx find \(\frac{d y}{d x}\)
Answer:
y = elogcotx
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = -cosec2x
Question 10.
Evaluate ∫Sec x (sec x. tan x)dx.
Answer:
∫(sec2 x-secx. tanx ) dx = tan x – sec x + c
Part – B
Answer any ten questions; (10 × 2 = 20)
Question 11.
If A = \(\left[ \begin{matrix} -4 & -3 \\ -2 & -1 \end{matrix} \right]\) , find A-1
Answer:
|A| = 4- 6 = -2 ≠ 0 ∴ A-1 Exists
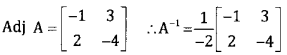
Question 2.
In how many ways can 6 people be selected out of 12 people so that
i. Two particular members must be included.
ii. Two particular members must be excluded.
Answer:
i. The number of selections one 10C4 way.
ii. The number of selections are 10C4 way.
![]()
Question 13.
If P(A) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) , P(B) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) ,P(A ∪ B) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 12 }\) . Find P(B/A)
Answer:
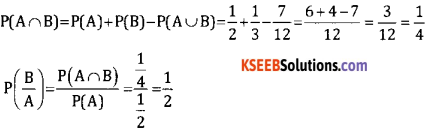
Question 14.
Write the converse and the contra positive of “IF x < 1 then it is a prime number”.
Answer:
Converse = if it is a prime number then x < 1
![]()
Question 15.
Two number are in the ratio 3 : 5 is added to each of them. The new ratio will be 2 : 3 find the numbers.
Answer:
The numbers are in the ratio 3 : 5
Let the common ratio be x.
Therefore the numbers are 3x and 5x.
If 5 is added to both the numbers the ratio become 2:3.
∴ (3x + 5):(5x + 5)= 2 : 3
∴ 6x + 15 = 10x + 5
∴ x = 1
Thus, the numbers are 3x = 3 × 1 = 3 and 5x = 5 × 1 = 50.
Question 16.
Banker’s discount and banker’s gain on a certain bill due after sometime are 1250 and 50 respectively. Find the face value of the bill.
Answer:
BD = Ftr
Question 17.
Prove that sin 2A = \(\frac{2 \tan A}{1+\tan ^{2} A}\)
1+tan? A
Answer:
LHS = \(\frac{2 \sin A \cos A}{1}=\frac{2 \sin A \cos A}{\cos ^{2} A+\sin ^{2} A}\)
Divide both numerator and denominator by cos2 A we get
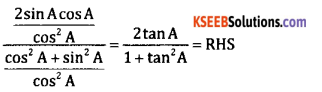
Question 18.
Show that cos \(\left(\frac{x}{4}-a\right)\) -cos\(\left(\frac{x}{4}+a\right)\) = \(\sqrt{2}\)sin a.
Answer:
Using transformation formula
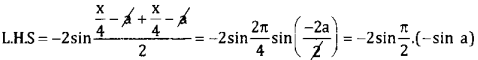
= 2.1sin a = 2sin a = RHS
Question 19.
Find the equation of the circle whose end points of a diameter are (3,4)and (2,-5).
Answer:
The equation of the circle is
(x – x1)(x – x2) + (y – y1)(y – y2)=0
(x – 3)(x – 2) + (y – 4)(y + 5)=0
x2 – 5x + 6 + y2 + y – 20= 0
x2 + y2 – 5x – y -14 = 0
Question 20.
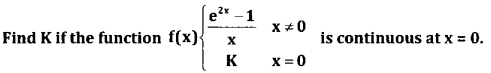
Answer:
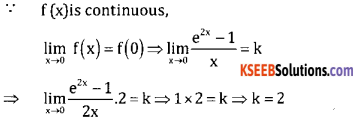
![]()
Question 21.
If y = xsinx, find \(\frac{d y}{d x}\)
Answer:
Given y = x sinx
Taking logm both sides
Log y = log xsinx
Log y = sinx. Logx
Differentiate w.rt
\(\frac{1}{y} \cdot \frac{d y}{d x}=\sin x \frac{1}{x}+\log x \cdot \cos x\)
\(\frac{d y}{d x}=y\left(\frac{\sin x}{x}+\log x \cdot \cos x\right) \text { where } y=x^{\sin x}\)
Question 22.
If the total cost of production is given by C = 5x2 + 2x + 3. Find average cost and marginal cost for an output of 10 units.
Answer:
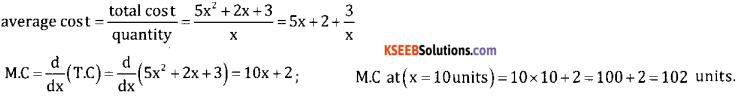
Question 23.
Evaluate: \(\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{x}+x} d x\)
Answer:
\(\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{x}+x} d x=\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{x}(1+\sqrt{x})} d x\)
\(=\int \frac{2 d t}{t}=2 \cdot \int \frac{1}{t} d t=2 \log t+c\)
= 2 log(1 + \(\sqrt{x}\)) + c
put 1 + \(\sqrt{x}\) =1
\(\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{x}}\) = dx = dt
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\) dx = dt
Question 24.
Evaluate: \(\int_{1}^{2}\left(x^{3}+e^{x}\right) d x\)
Answer:
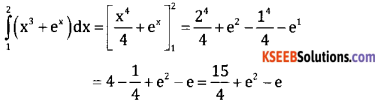
Part – C
Answer any ten question: (10 × 3 = 30)
Question 25.
If A = \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 & -1 \\ 1 & 4 \end{matrix} \right]\) and B = \(\left[ \begin{matrix} -3 & 2 \\ -1 & 4 \end{matrix} \right]\) show that (AB)’ = B’ A’
Answer:
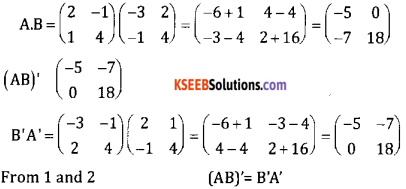
![]()
Question 26.
Prove that “if each element of any row (or column) of a determinant is the sum of two terms. Then the determinant can be expressed as the sum of sum of two determinants.”
Answer:
Let A = \(\left( \begin{matrix} a+\alpha & b+\beta \\ c & d \end{matrix} \right) \) = ad + αd -bc – cβ = ad – bc + αd – cβ
\(\Delta =\left( \begin{matrix} a+\alpha & b+\beta \\ c & d \end{matrix} \right)\)
\(=\left( \begin{matrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{matrix} \right) +\left( \begin{matrix} \alpha & \beta \\ c & d \end{matrix} \right) =\Delta ‘\)
∴ Δ = Δ’. Hence the property is proved.
Question 27.
Find the number of permutations of the letters of the word ‘UNIQUE’.
(i) How many of them end with ‘QUE?
(ii) How many of begin with ‘U’ and end with ‘E’?
(iii) How many of them begin with a consonant?
Answer:
“UNIQUE” has6 letter; U = 2 times
∴ Total words = \(\frac{6 !}{2 !}\) ways
(i) The words end with “QUE”=3!
(ii) The work begin with V and end with E = 4!
(iii) The words begin with a consonant (2 consonants are there N and Q) = \(\frac{4 !}{2 !}\)
Question 28.
Two card are drawn from a pack of playing cards, one after the other, find the probability of getting a queen in first and second draw .If the cards are drawn.
(i) With replacement
(ii) Without replacement
Answer:
(i) with replace: there are 52 cards out of which 4 are queens
∴ Probability of getting a queen = \(\frac{4}{52}\)
The card is replaced before the second draw. Again a card is drawn, getting a queen in the second draw = \(\frac{4}{52}\)
∴ Probability of getting two queens = \(\frac{4}{52} \times \frac{4}{52}=\frac{1}{169}\)
(ii) without replacement: when one card is not replaced there are 51 cards for the second draw with 3 queens.
∴ Probability of getting queen in second draw = \(\frac{3}{51}\)
∴ P(both queens) = Queen in Ist draw x queen in second draw = \(\frac{4}{52} \times \frac{3}{51}=\frac{12}{2625}\)
Question 29.
3 carpenters can earn 360 in 6 days working 9 hours a day. How much will 8 carpenters earn in 12 days working 6 hours a day?
Answer:
It is a direct proportion
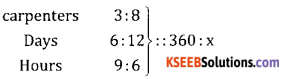
⇒ 3 × 6 × 9 × x = 8 × 12 × 6 × 360
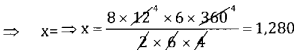
∴ 8 carpenters earn 1,280 in 12 days working 6 hrs day.
Question 30.
Banker’s gain on a bill due 6 months at 4%p.a is 20. Find the true discount. Banker’s discount and bill amount.
Answer:
Given
BG = ₹ 20, r = 4% = 0.04, t = 6 Months = \(\frac{6}{12}=\frac{1}{2}\)
TD = ?, BD = ?, F = ?
W.K.T. = BG = TD. tr
20 = TD \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 0.04
40 = 0.04 TD ⇒ TD = \(\frac{40}{0.04}\) = ₹ 1000
BD = BG + TD; = 20 + 1000 = 1020
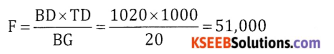
![]()
Question 31.
A man invests equal sums of money in 4%, 5% and 6% stock, each stock being at par. If the total income of the man is 3,600, find his total investment.
Answer:
Income from 1 st stock is \(\frac{4 x}{100} 2^{n d} \text { is } \frac{5 x}{100} 3^{n d} \text { is } \frac{6 x}{100}\)
Given total income = 3,600
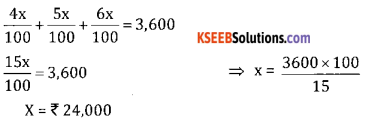
Hence his total investment = 3x = 3(24,000) = ₹72,000
Question 32.
A shopkeeper announces a discount of 10% on a washing machine set. The marked price of washing machine is 12000.how much will a customer have to pay for buying the washing machine set if the rate of sales tax is 8%?
(i) The VAT paid by the shopkeeper
(ii) Total amount that the consumer pays for the washing machine.
Answer:
Given Discount = 10%, m. p = ₹ 12,000, S.T = 8%
Amount paid = S.P =?
Discount of 10% on mp = 10% of ₹12,000
\(=\frac{10}{100} \times 12,000=71,200\)
New m.p=12,000 – 1,200 = ₹10,800
∴ Total amount to be paid = 10,800+8% of 10,800
\(=10,800+\frac{8}{100} \times 10,800\) = 10,800 + 864 = ₹11,664
Question 33.
Find Equation of the parabola whose vertex is at (0,0),axis is y axis and passes Through \(\left(\frac{1}{2}, 2\right)\) also find equation of directrix.
Answer:
It is given that vertex of the parabola V(0,0)and symmetric about y – axis so its equation is x2 = 4ay or x2 = – 4ay,
since the parabola passess through the point \(p\left(\frac{1}{2}, 2\right)\) so it lies in the 1st quadrant.
∴ It is an upward parabola x2 = 4ay
∴ It passess though the point p\(\left(\frac{1}{2}, 2\right)\) we have
\(\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}=4 \times a \times 2 \Rightarrow a=\frac{1}{32}\)
∴ Required parabola is x2 = 4 ⇒ x2 = \(\frac{1}{8} y\)
Question 34.
If x = a(θ – sin θ), y = a(1 – cos θ) then prove that dy = cot \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\cot \frac{\theta}{2}\)
Answer:
Given x = a (θ – sin θ),y = a (1 – cos θ)
Differentiate both w.r.t we get
\(\frac{d x}{d \theta}\) = a(1-cose) \(\frac{d y}{d \theta}\) = a(-(sinθ)) – asinθ
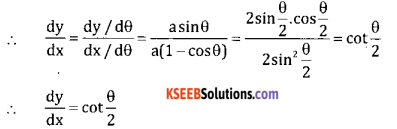
Question 35.
The surface aera of a spherical soap bubble increasing at the rate of 0.6 cm2/sec. find the rate at which its volume is increasing when its radius is 3 cm.
Answer:
\(\frac{d A}{d t}=0.6 \mathrm{cm}^{2} / \mathrm{sec}, \frac{d V}{d t}=? r=3 \mathrm{cm}\)
Surface Area = 4πr
\(\frac{d A}{d t}=4 \pi \cdot 2 r \frac{d r}{d t}=8 \pi r \frac{d r}{d t}\)
0.6 = 8 × π × 3 × \(\frac{d r}{d t}\)
\(\therefore \quad \frac{d r}{d t}=\frac{0.6}{24 \pi} \mathrm{cm} / \mathrm{sec}\)
\(\therefore \quad v=\frac{4}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
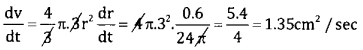
![]()
Question 36.
Find the maximum or minimum value of the function f(x)= 9x2 + 12x + 2.
Answer:
Given f(x) = 9x2 + 12x + 2 i
∴ f'(x) = 18x + 12
f”'(x) = 19
For a function to be maximum or minimum f'(x) = 0
∴ 18x + 12 = 0 ⇒ x = \(\frac{-12}{18}=\frac{-2}{3}\)
Put x = \(\frac{-2}{3}\) in equation (3) f'(x) = 18 > 0
∴ f(x) is minimum at x = \(\frac{-2}{3}\) and minimum value is f \(\left(\frac{-2}{3}\right)\)
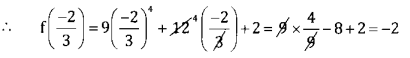
∴ Minimum value = -2.
Question 37.
Evaluate ∫ x log x dx.
Answer:
Integrating by part we get
![]()
Question 38.
Evaluate \(=\int_{0}^{1} \frac{2 x+5}{x^{2}+5 x+3} d x\)
Answer:
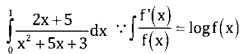
[log (x2 + 5x +3)],
log (1 +5 + 3) – log (0 + 0 + 3)
log 9 – log 3 = log \(\frac { 9 }{ 3 }\) = log 3
Part – D
Answer any six question (6 × 5 = 30)
Question 39.
Find the middle terms in the expansion of \(\left(3 x-\frac{2}{x^{2}}\right)^{15}\)
Answer:
Find the middle term in the expansion of
\(\left(3 x-\frac{2}{x^{2}}\right)^{15}\)
Answer:
Here n = 15 and odd, so we have two middle terms i.e, \(\frac{n+1}{2}=\frac{15+1}{2}=8^{t h}\) and 8 + 1 = 9th terms to find 8 thterm to find 8 th term pur r = 7

Question 40.
Resolve into partial fractions \(\frac{3 x+2}{(x+3)^{2}(x-2)}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{3 x+2}{(x-2)(x+3)^{2}}=\frac{A}{x-2}+\frac{B}{x+3}+\frac{C}{(x+3)^{2}}\)
(3x + 2) = A(x + 3)2 + B(x – 2) (x + 3) + C(x – 2)
Put x = 2, 6 + 2 = A(2 + 3)2 + B(0)+C (0)
8 = 25A ⇒ A = \(\frac{8}{25}\)
Put X=-3, -9 + 2 = A(0) + B(0) +C(-5)
-7 = -5C ⇒ C = \(\frac{7}{5}\)
Comparing the co-efficients of x2 on both sides
0 = A + B ⇒ B = -A = \(\frac{8}{25}\)
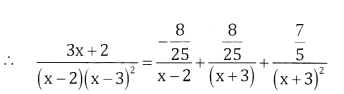
![]()
Question 41.
Verify if the proposition [~p ∧ (p∨q)] → q is a tautology, contradiction or neither.
Answer:
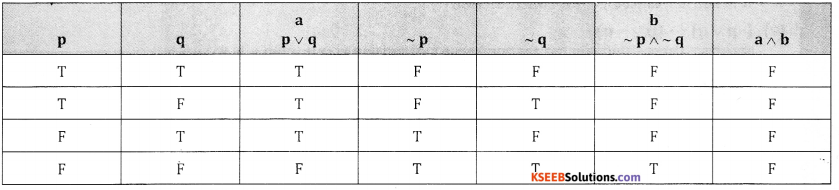
last column we conculde that it is a contradiction
Question 42.
₹ 5,625 is dividend among A,B and C so that A receives one half as much as B and C together receive and B receives one fourth of what A and C together receive. Find the share of A,b and c.
Answer:
Given A + B + C = 5625 … (1)
And A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (B + C) ⇒ 2A = B + C … (2)
Also B = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)(A + C) ⇒ 4B = A+C … (3)
From 1 and 2 we have
A + B + C = 5625 ⇒ A + 2A = 5625
⇒ 3A = 5625
⇒ A = ₹1875
Again from 1 and 3 we get B+ 4B = 5625
⇒ 5B = 5625
⇒ B = ₹1125
∴ from eqn (1) c = 5625 – A – B = 5625 – 1875.1125 = 2625 ₹
∴ A’s share is 1875 B’s share is 1125, c’s share 2625
Question 43.
A company has 80% learning effect and spends 500 hours for the prototype. Estimate the labour cost of producing 7 engines of new order if the labour cost is 40 per hour.
Answer:
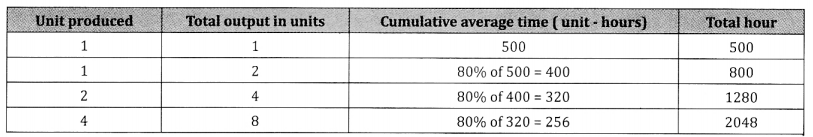
Total hours of 8 engines = 2,048
Total hours of 1 engine = 500
∴ Total hours for 7 engines = 1,548 hrs
If the labour cost is ₹ 40 per hour.
Total Labour cost of producing 7 engines = 1,548 × 40 = ₹61,920
Question 44.
Solve the L.P.P. graphically
Maximize Z = 5x +3y
Subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 15, 5x + 2y ≤ 10, x ≤ 0,y ≤ 0.
Answer:
Consider 3x + 5y =15 5x + 2y = 10
Put x = 0, y = 3(0,3) put x = 0, y = 5, (0,5)
Put 0, x = 5, (5,0) put y = 0, x= 2,(2,0)
Plot the above lines in the graph sheet and shade OABC is the solution region
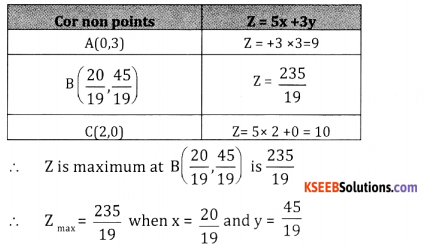
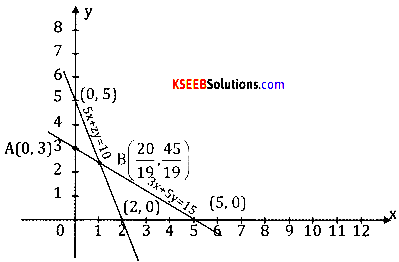
![]()
Question 45.
In any AABC, prove that sin 2A + sin 2B – sin 2C = 4 Cos A Cos B sin C
Answer:
LHS = sin2A + sin 2B -sin 20
= 2sin (A+ B). Cos (A – B) – 2 sin C Cos C[ using transformation formula]
= 2sin C. Cos (A – B) – 2sin C. Cos C
= 2sin C[Cos (A – B) – Cos C]
= 2 sin C [Cos (A – B)+ Cos (A + B)] ∵ Cos (A + B) = – Cos C
= 2 sin C. 2.cos A. Cos B
= 4 Cos A. sin C. Cos B [∵ CosC + CosD = 2cos \(\frac{C+D}{2} \cos \frac{C-D}{2}\)]
= 4 cos A. Cos B. sin C
= RHS
∴ sin 2A + sin 2 B sin 2 C = 4 Cos A. Cos B. sin C.
Question 46.
Find the equation of the circle passing through the point (1, 4)and (5,2) and has its centre on the line x – 2y + 9 =0.
Answer:
Let equation of the required circle is
x2 + y2 > + 2gy + 2fy + c = 0<br ?–> Given this equation passes through the points (1,-4) and (5,2)
(1,4) (1)2 + (-4)2 2g(1) + 2f(-4) + c = 0
2g – 8f + C +17 = 0 … (1)
(5,2) 52 +22 + 2g (5) 2f(2) + c= 0
10g + 4f + C + 29 = 0 …. (2)
Also center (-g,-f) lies on the line x – 2 y + 9 = 0
-g -2(-f) + c = 0
-g + 2f + c = 0 … (3)
Solving equations 1,2 and 3 we get
G = -3 f = 3,c = -47
G = 1 f = 2, c = 4
The required equation are
x2 + y2 + 6x – y – 47 = 0
x2 + y2 – 2x – 4y + 4 = 0
Question 47.
If y = log \((x-\sqrt{x^{2}+1})\) show that (x2 + 1) y2 + xy, =0.
Answer:
If y = log \((x-\sqrt{x^{2}+1})\)
Differentiate w.r.t x
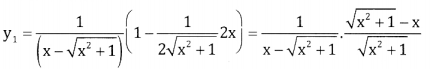
\(=\frac{-1}{\sqrt{x^{2}+1}}\)
\(\sqrt{x^{2}+1}\) .Y1 = -1 S.B.S we get
(x2 + 1) y = (-1)2 = 1
Again differentiate w.r.tx
(x2 + 1) 2y1 y2 + y21(2x) = 0
Divide by 2 y1
(x2 + 1)y2 + xy1 = 0
Question 48.
Find the area enclosed between the parabola 4y = 3x2 and the line 3x – 2y + 12 =0.
Answer:
The given curve is 4y = 3x2
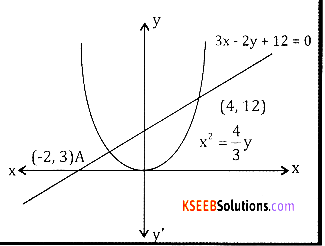
y = \(\frac{3}{4} x^{2}\) … (1)
The given line is 3x – 2y + 12 = 0
⇒ \(y=\frac{3 x+12}{2}\) … (2)
Solving (1) and (2) we get
\(\frac{3 x+12}{2}=\frac{3}{4} x^{2}\)
6x2 – 12x – 48 = 0
⇒ x2 – 2x – 8= 0 ⇒ (x + 2)(x – 4) = 0 ⇒ x= -2, x = 4
∴ The point of intersection are A(-2,3)and B (4,12)
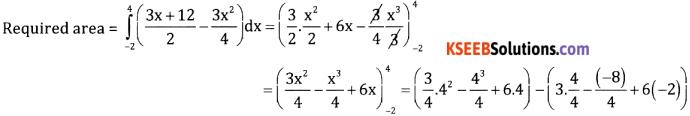
= (12 – 16 + 24) – (3 + 2 – 12)
A = 20 + 7 = 27 sq. units
![]()
Part – E
Answer any one question: (1 × 10 = 10)
Question 49.
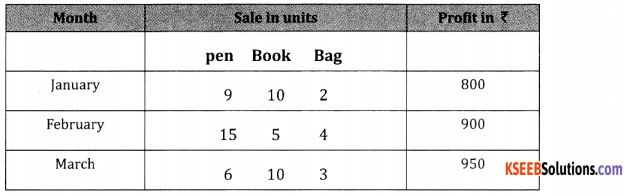
(a) A sales person’s sales details are given below.
Answer:
(b) Find profit for each pen, book and bag using matrix method.
Answer:
Assume the rate of commission for product A = x’
Assume the rate commission for product B = y’
Assume he rate of commission for product C = z’
Total Commission in Jan ⇒ 9x + 12y + 2z = 800
Total Commission in Feb ⇒ 15x + 5y + 4z = 900
Total Commission in Mar ⇒ 6x + 10y + 3z = 950
In matrix form, A = \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 9 & 12 & 2 \\ 15 & 5 & 4 \\ 6 & 10 & 3 \end{matrix} \right]\) B = \(\left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{matrix} \right]\) C = \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 800 \\ 900 \\ 950 \end{matrix} \right]\)
Formula : Ax = B
⇒ x = A-1B
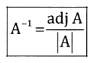
| A |= 9[(15 – 40)] -12 [(45 – 241)] +2 [(150 – 30)]
= 9[-25] -12 (21) + 2 (120)
= -225 – 252 +240 = -237 ≠ 0
∴ A-1 exists
(b) Find the value of (1.01)5 using Binomial theorem, upto 4 decimal places.
Answer:
(1.01)5 = (1 + 0.1)5
= 15 + 5C1 (0.01) + 5C2 (0.01)2 + 5C3 (0.01)3 + 5C4 (0.01)4 + 5C5 (0.01)5
= 1 + 5(0.01) + 10(0.001) + 10(0.000001)+ neglect the next terms
= 1 + 0.05 + 0.001 + 0.00001
= 1.0510 correct up to 4 decimals
Question 50.
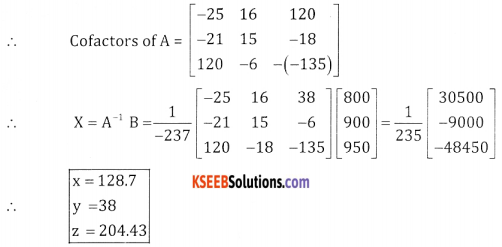
(a) If is measured in radians, then prove that \(\lim _{\theta \rightarrow 0} \frac{\sin \theta}{\theta}=1\)
Answer:
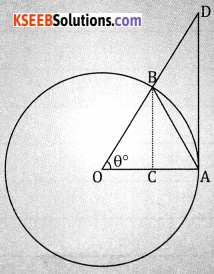
Let ‘0’ the centre of unit circle, assume that θ is measured in positive radians
![]()
Fromn the figure, we have area of ∆AOB = area of sector AOB = area of ∆AOD
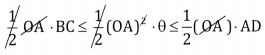
∴ Area of sector = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (radius)2 × angle in radians
From the triangle DOA, tan θ = \(\frac{\mathrm{DA}}{\mathrm{OA}}\) ∴DA = rtan θ
From the triangle BOC, sin θ = \(\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{OB}}\) ∴ BC = rsin θ
(1) becomes
⇒ BC ≤ θ ≤ DA
⇒ sin θ ≤ θ ≤ tan θ
Dividing by sin θ
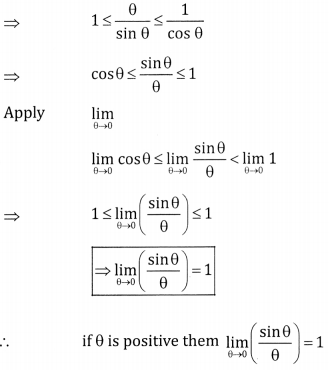
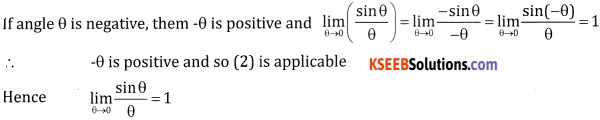
![]()
(b) The angles of elevation of the summit of a hill from the top and bottom of a building are 30° and 60° respectively. If the height of the building is ‘H’m, show that the height of the hill is \(\frac{3 h}{2}\)
Answer:
Let AB represents the height of the hill
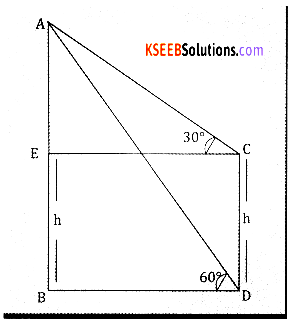
And CD represents the height of the tower
By the given data (AOB = 60°,|ACE = 30°
![]()
DC = h
From the rt angled ∆ABD we have
Tan 60° = \(\frac{A B}{B D} \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\frac{A B}{B D} \Rightarrow B D=\frac{A B}{\sqrt{3}}\) … (1)
Again from the rt angled ∆AEC
Tan 30 = \(\frac{A F}{E C}=\frac{A E}{B D}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{A B-B E}{B D}=\frac{A B-h}{B D}\)
BD = √3(AB – h) … (2)
From 1 and 2 we have
\(\frac{A B}{\sqrt{3}}\) = √3(AB – h)
AB = 3(AB – h); AB = 3AB – 3h; 3h = 3AB – AB
⇒ AB = \(\frac{3 h}{2}\)
∴ The height of the hill = \(\frac{3 h}{2}\)