You can Download Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Questions and Answers, 2nd PUC Biology Question Bank with Answers, Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Question Bank Chapter 3 Human Reproduction
2nd PUC Biology Human Reproduction NCERT Text Book Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Humans reproduce ………
Answer:
sexually
(b) Humans are ……………..
Answer:
viviparous
(c) Fertilization is …………….. in humans.
Answer:
internal
(d) Male and female gametes are ……….
Answer:
haploid
(e) Zygote is ………..
Answer:
diploid
(f) The process of release of ovum from a mature follicle is called ………
Answer:
ovulation.
(g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called ………
Answer:
Luteinizing hormone
(h) The fusion of male and female gamete is called ……….
Answer:
fertilization
![]()
(i) Fertilization takes place in …………
Answer:
ampullary isthmus in fallopian tube.
(j) Zygote divides to form which is implanted in uterus.
Answer:
Blastocyst
(k) The structure which provides vascular connection between foetus and uterus is
Answer:
umbilical cord.
Question 2.
Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
Answer:
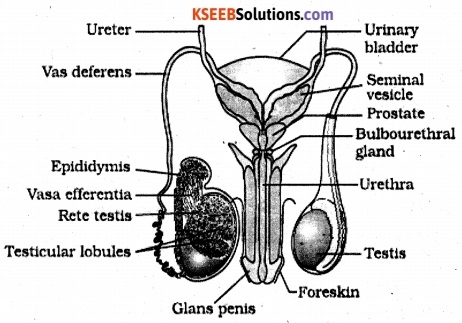
Question 3.
Draw a labelled diagram of female reproductive system.
Answer:
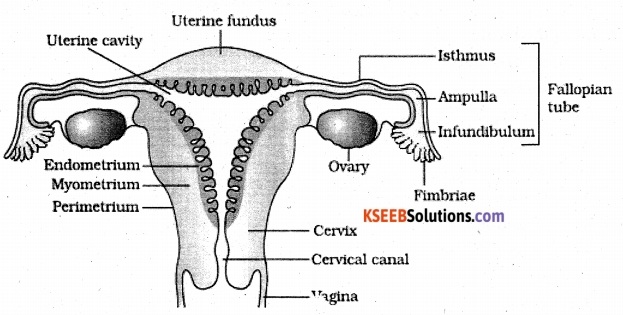
Question 4.
Write two major functions each of testis and ovary.
Answer:
Testis :
- Formation of sperms
- Secretion of hormone testosterone.
Ovary :
- Formation of ova
- Secretion of hormone oestrogen and progesterone.
![]()
Question 5.
Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubule.
Answer:
Testis has about 250 compartments (Testicular lobules) which contains 1-3 highly coiled seminiferous tubules. Each tubule is lined by 2 types of cells. Male germ cells (immature) (spermatogonic) and Sertoli cells.
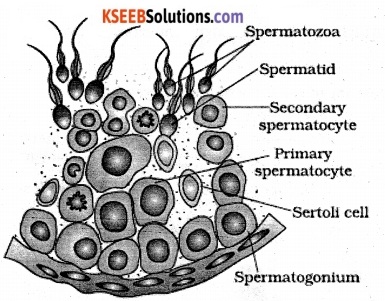
Male germ cells form sperms by meiosis and Sertoli cells provide nutrition to these germ cells. Male germ cells and Sertoli cells together form germinal epithelium. Seminiferous tubule is covered outside by basement membrane.
Question 6.
What is spermatogenesis ? Describe the process of spermatogenesis.
Answer:
Spermatogenesis is the production of sperms (n) by immature male germ cells (2n) at puberty inside the testis.
Hormonal role in spermatogenesis:
Spermatogenesis starts due to increase in secretion of GnRH (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone) by hypothalamus. GnRH acts on Anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of 2 gonadotropins – LH (Luteinizing Hormone) or ICSH (Interstitial Cell Stimulating Hormone) and FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone).
LH acts on Leydig cells for secreting testosterone and other androgens inturn stimulates process of spermatogenesis. FSH acts on sertoli cells which secretes some factors useful in spermiogenesis. Sertoli cells secrete inhebin that suppresses FSH synthesis.
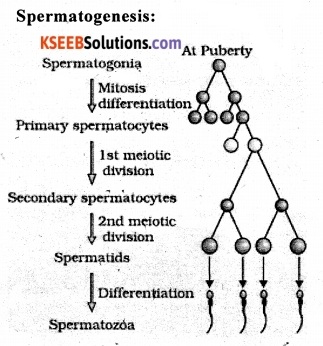
It is production of haploid spermatozoa from diploid spermatogonia inside testis at puberty. At puberty, Spermatogonium undergoes mitosis forms 2 spermatogonia A and B. Both A and B are diploid with 46 chromosomes each.
A: Function as mother spermatogonia.
B : Grow in size to function as primary spermatocytes.
They then undergo meiosis to form 2 haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes (23 chromosomes). They then undergo 2nd meiotic division forming 4 haploid spermatids. These spermatids are transferred into spermatozoa (sperms) by spermiogenesis. After spermiogeneses, sperm heads become embedded into Sertoli cells and are released from seminiferous tubules by process called spermiation.
Question 7.
Name hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Answer:
[Explained in Answer to Question Number 67-Hormones are: GnRH, FSH, LH / ICSH, testosterone, Inhibin
Question 8.
Define spermiogenesis and spermiation.
Answer:
- Spermiogenesis: Development and differentiation of a spermatozoa (n) from a spermatid (n).
- Spermiation: The detachment of fully mature spermatozoa from Sertoli cells is called spermiation.
![]()
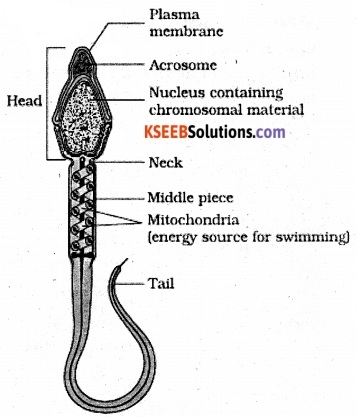
Question 9.
Draw a labelled diagram of sperm.
Answer:
Question 10.
What are the major components of seminal plasma?
Answer:
Fructose, fibrinogen, profibrinolysin, Calcium bicarbonate, prostaglandins, mucus, (seminal plasma + sperms = semen)
Question 11.
What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
Answer:
Male accessory ducts :
(i) Intra testicular Genital Duct system (till vasa efferentia) – Cilia lining them fails in passage of sperms.
(ii) Extra testicular / Excretory Genital Duct system:
- Epididymis – Store sperms, ejects sperms during ejaculation, destroys older sperms.
- Vasa deferentia – conduction of sperms
- Ejaculatory ducts – conduct sperms and secretion of seminal vesicles are also conducted
- Urinogenital duct – conduct sperms.
Male accessory glands:
- Seminal resides – produce seminal plasma (60 – 70 %)
- Prostate Gland – seminal plasma (20 – 30%)
- Bulbourethral gland – 5% seminal plasma
Question 12.
What is oogenesis ? Give a brief action of oogenesis.
Answer:
Process of formation, development and maturation of haploid ovum or female gamete from diploid germinal cell of the ovary.
Cells of the germinal epithelium of ovary undergoes repeated mitotic divisions to form diploid Oogonia or gamete mother cells. They are formed in the fetal ovary in large number by mitotic division form primary oocyte.
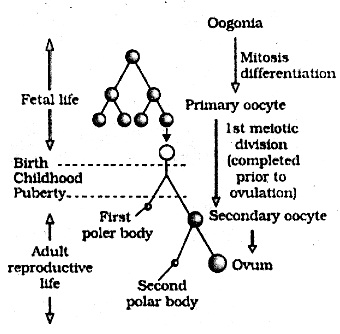
The primary oocyte enlarges and matures by taking food from the surrounding follicle cells. The mature primary oocyte undergoes its first meiotic division. It is an unequal division resulting in the formation of a large haploid secondary oocyte and a tiny first polar body or polocyte. The secondary oocyte remains bulk of the nutrient ride cytoplasm of the primary oocyte. The secondary oocyte undergoes second meiotic division which doesn’t proceed beyond metaphase until a sperm enters it. Ovulation occurs at this stage and the secondary oocyte is transferred to the fallopian tube.
![]()
Question 13.
Draw a labelled diagram of section through ovary
Answer:
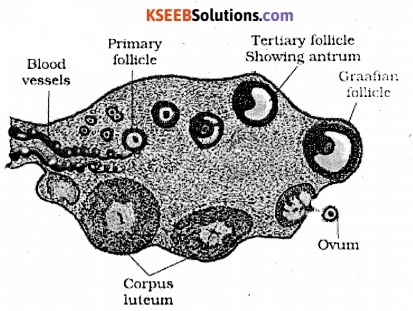
Question 14.
Draw a labelled diagram of Graafian follicle.
Answer:
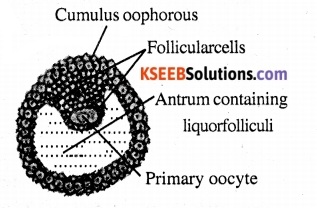
Question 15.
Draw diagramatic representation of various events during menstrual cycle.
Answer:
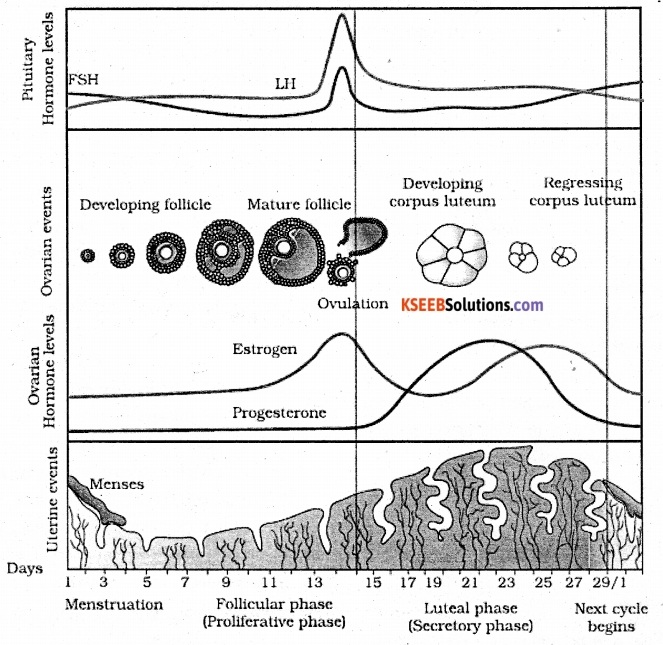
Question 16.
Name the functions of the following.
(a) Corpus luteum
(b) Endometrium
(c) Acrosome
(d) Sperm tail
(e) Fimbriae
Answer:
(a) Corpus luteum : Secretion of mainly progesterone and small quantity of estrogen. Some androgens are also formed by theca cells.
(b) Endometrium : Nourishment and implantation of blastoeyst and later foetus if fertilization has occurred. Otherwise cyclic changes of growth and degeneration.
(c) Acrosome : Contains sperm lysin for separating cells of corona radiata and piercing through zona pellucida.
(d) Sperm Tail: Vibratile part that helps in swimming of sperm in the genital tract of female for reaching the ovum.
(e) Fimbriae : The finger like projection occurs at the edges of infundibulum which helps in the collection of ovum after ovulation.
![]()
Question 17.
Identify True / False statements. Correct each false statement to make it true,
(a) Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells.
(b) Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells.
(c) Leydig cells are found in ovary
(d) Leydig cells synthesize androgens
(e) Oogenesis occurs in corpus luteum.
(f) Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy.
(g) Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience.
Answer:
(a) False: Spermatogenesis substances androgen binding protein and intubin are produced by Sertoli cells.
(b) False: Spermatozoa differentiate from spermatids with the help of spermatogenic factors produced by Sertoli cells.
(c) False: Leydig cells are found in testis.
(d) True.
(e) False: Oogenesis occurs inside the ovary.
(f) True.
(g) True.
Question 18.
What is menstrual cycle? Which hormone regulates menstrual cycle?
Answer:
A series of cyclic changes found in the reproductive tract of human female during her reproductive life that recur at intervals of about 28 days and is characterised by menstruation in the first 3-4 days.
Hormone :
- GnRH (Gonado tropin Releasing Hormone)
- FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
- LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
Question 19.
What is parturition ? Which hormones are involved in the induction of parturition ?
Answer:
- The process of delivering of full developed foetus or baby at the end of pregnancy period through vigorous contraction of uterus is called parturition.
- Estrogen (amount of estrogen is more than progesterone) and oxytocin are the hormones involved in the induction of parturition.
Question 20.
In our society women are blame for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct ?
Answer:
Sex chromosome pattern in female is xx, i.e., both the gametes are with ‘X’ chromosome. In males, sex chromosome is X Y i.e., one gamete with ‘X’ chromosome and other gamete with ‘Y’. So 50% sperms carry ‘X’ and 50% carry ‘Y’. Female child is produce when the sperm with ‘X’ chromosome fertilizes egg with ‘X’ chromosome. A male child is produce when sperm with ‘Y’ chromosome fertilizes egg with ‘X’ chromosome. Therefore sex of a baby depends on father not on mother.
Question 21.
(a) How many egg are released by a human ovary in a month ?
(b) How many eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to identical twins ?
(c) Would your answer change if the twins born were fraternal ?
Answer:
(a) One
(b) One
(c) Yes, fraternal twins are born due to the fertilization of 2 or more eggs.
Question 22.
How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog, which gave birth to 6 puppies?
Answer:
Six eggs were released by the ovary of a female dog.
2nd PUC Biology Human Reproduction Additional Questions and Answers
2nd PUC Biology Human Reproduction One Mark Questions
Question 1.
Where are sperm produced in the testis?
Answer:
In the seminiferous tubules of testis.
Question 2.
What is the role of placenta?
Answer:
Provide nutrition to the developing embryo.
Question 3.
What is the function of amniotic fluid?
Answer:
Protects foetus from shock.
Question 4.
Name the germ layer from which gonad develops.
Answer:
Mesoderm
Question 5.
Name the sperm lysin ? Which organelle secretes it ?
Answer:
Hyaluronidase; Acrosome.
Question 6.
Define gametogenesis.
Answer:
The process of formation of male and female gamete in the gonads is called gametogenesis.
![]()
Question 7.
The spermatogonia of an animal contains 32 chromosomes. What will be the number of chromosomes in its
(a) secondary spermatocyte
(b) spermatids respectively
Answer:
(a) Secondary spermatocyte – 16 chromosome
(b) spermatids -16 chromosome
Question 8.
Name the structure formed from Graafian follicle after ovule?
Answer:
Corpus luteum
Question 9.
Name the hormone secreted by corpusluteum.
Answer:
Progesterone.
Question 10.
Define spermiogenesis ? Where does it occur ?
Answer:
The process of the transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa is called spermiogenesis. It occurs in the seminiferous tubules of testis.
Question 11.
Why middle piece of the sperm called power house of the sperm ?
Answer:
Middle piece contains numerous mitochondria which produce energy for sperm movement.
Question 12.
Define Oogenesis.
Answer:
The process of formation of mature female gametes.
Question 13.
Name the fluid filled space in the tertiary follicle.
Answer:
Antrum
Question 14.
What is the significance of secondary oocyte retaining the bulk of nutrient rich cytoplasm of the primary oocyte ?
Answer:
These reserve food materials nourish the embryo till implantation.
Question 15.
When do the levels of FSH and LH reach the maximum in the menstrual cycle ?
Answer:
The peak level of FSH and LH is reached in the middle of (14th day) menstrual cycle.
Question 16.
Define implantation?
Answer:
Implantation is the process in which the mammalian embryo (blastocyst) becomes attached to the endometriosis of the uterus.
Question 17.
What are the stem cells in human embryo?
Answer:
Stem cells are those cells in the inner mass of the blastocyst, which have the potency to give rise to all tissues and organs.
Question 18.
What is colostrum ? How does it provide initial protection against diseases to new born infants. Give reason.
Answer:
The milk produced during initial few days of lactation is called colostrum. It consists of several antibodies like IgA etc. which are essential for the development of resistance in new born babies.
2nd PUC Biology Human Reproduction Two Marks Questions
Question 1.
Name 2 types of cells present in the inner lining of seminiferous tubules. What are their functions?
Answer:
Two types of cells in the inner lining of seminiferous tubule are
- Spermatogonia : Spermatogonia produces male gamete called spermatozoa.
- Sertoli cells : Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the developing spermatozoans.
Question 2.
Where are Leydig cells present? What is their role in reproduction?
Answer:
- Ley dig cells are located in the interstitial space (space between the seminiferous tubule) in the testis.
- They secrete testicular hormones called androgens, mainly testosterone, this hormone regulates spermatogenesis.
Question 3.
Differentiate between vasa efferentia and vas deferens.
Answer:
- Vasa efferentia are the ducts that leave the testis to open into epididymis. These are located inside the testis and are extra abdominal and do not receive the ducts of any glands.
- Vas deferens is the duct continues from epididymis. This ascends into the abdominal cavity. It receives the ducts of seminal vesicle.
![]()
Question 4.
Where are fimbriae present in a human female reproductive system ? Give their function.
Answer:
Fimbriae are present in the free edges of the infundibulum of the fallopian tube. Then help in the easy capture of ova during ovulation.
Question 5.
Differentiate between endometrium and myometrium.
Answer:
- Endometrium is the innermost glandular layer that lines the uterine cavity. It undergoes cylindrical changes during menstrual cycle. Implantation occurs in this layer.
- Myometrium is the middle thick layer of smooth muscles of the uterine wall. It doesn’t undergo any changes during menstrual cycle. It is responsible for the uterine movement.
Question 6.
Give the differences between spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis.
Answer:
Spermatogenesis:
It is the process of the formation of mature spermatozoa in the testis. It involves meiotic and mitotic division. It is controlled by hormones like leutenising hormone (LH) and androgen (testesterone).
Spermiogenesis:
It is the process of the transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa. It doesn’t involve any cell division. It is controlled by LH which stimulates the Sertoli cells to secrete the factors needed for spermiogenesis.
Question 7.
Mention the sites of action of the hormones – GnRH and FSH, during spermatogenesis in human males. Give one function of each of the hormones.
Answer:
GnRH acts on anterior pituitary and FSH acts on Sertoli cells of seminiferous tubules.
GnRH stimulates the release of two gonadotropin – Follicle stimulating hormone and leutenising hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. FSH stimulates the Sertoli cells to secrete some factors necessary for spermiogenesis.
Question 8.
Why does the coitus not leads to pregnancy all the time?
Answer:
Pregnancy occurs when the sperm and ovum reaches the ampullary isthmus junction of the fallopian tube at the same time. During every coitus both are not reaching at this position together.
Question 9.
Given below is the diagram of the sectional view of human ovum just after ovulation.
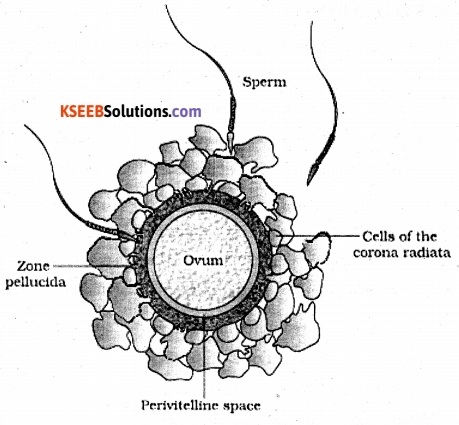
Mention the site of fertilization in the fallopian tube of human female where the ovum and sperm meet.
Answer:
Ampullary – Isthmus Junction.
Question 10.
How it blastula / blastocyte differ from Morula ?
| Blastocyte | Morula |
| (a) It is a hollow sphere of 32 or more cells formed by the rearrangement of blastomeres. (b) Zona pellucida disintegrates with the enlargement of blastocoel |
(a) It is a solid sphere of 8-16 cells blastomeres by cleavage of zygote. (b) Zona pellucida is intact. |
Question 11.
What are chroionic villi ? What is their fate?
Answer:
The finger like projections of the trophoblast produced after implantation are called chronic villi. Chroionic villi and uterine tissue become interdigitated with each other and jointly form the placenta.
Question 12.
Name the hormones secreted by human placenta.
Answer:
The hormones secreted by human placenta are;
- Human chorionic gonadotropin
- Progesterone
- Human placental lactogen
- Estrogen
Question 13.
Write the functions of placenta in humans.
Answer:
(a) It helps to supply oxygen and nutrients to the foetus.
(b) It helps in the removal of CO2 and other waste product formed by the foetus.
(c) Acts as endocrine gland by secreting hormone like human placental lactogen, human chorionic gonadotropin, estrogen and progesteron which are necessary to maintain pregnancy.
2nd PUC Biology Human Reproduction Three/Five Marks Questions
Question 1.
Describe the accessary ducts of human male reproductive system.
Answer:
The accessory ducts include rete testis, vasaefferentia, epididymis and vas deferens.
The seminiferous tubules end as short, straight tubules into rete testis. From the rete testis, 10-20 fine tubules called vasa efferentia leave the testis and open into epididymis. Epididymis is a single convoluted tubule that is located along the posterior surface of the testis.
The epididymis leads into vas deferens that ascends into the abdomen and loops over the urinary bladder. It receives the ducts of seminal vesicle to form ejaculatory duct, that runs through the prostrate and opens into the urethra, just after its origin from the urinary bladder. The urethra receives the ducts of prostrate and bulbo urethral glands and runs through the penis to its external opening called urethral meatus.
Question 2.
Name the cells found
(a) inside the seminiferous tubules
(b) outside the seminiferous tubules in a human testis. Mention the function of each of them.
Answer:
(a) Inside the seminiferous tubules are
- Spermatogonial cells
- Sertoli cells
(b) Outside the seminiferous tubules are Ley dig cells.
Functions:
- Spermatogonial cells form spermatozoa.
- Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the germ cells and help in spermiogenesis.
- Ley dig, cells secrete the male sex hormone, testesterone.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the accessory glands of human male reproductive system and mention their functions.
Answer:
The male accessory glands include
- a pair of seminal vesicle
- a prostrate gland
- a pair of bulbo urethral gland.
(1) a pair of seminal vesicle:
The secretion from these glands constitute the seminal plasma, which is rich in calcium fructose and certain enzymes.
(2) a prostrate gland:
Seminal plasma provides the fluid medium for the-sperm to swim in the female reproduction tract, towards the ovum.
(3) a pair of bulbo urethral gland:
It provides nourishment to the sperm. The secretions from bulbourethral glands help in the lubrication of the penis.
Question 4.
Describe the structure of mammary glands of a human female with labelled diagram.
Answer:
A mammary gland consists of glandular tissue and variable quantity of fat. The glandular tissue is divided into 15 – 20 mammary lobes and each lobe contains clusters of cells called alveoli, which opens into mammary tubules. The mammary tubules of each be join to form a mammary duct. Several mammary ducts join to form a wider mammary ampulla, which is connected to lactiferous duct through which milk comes out.
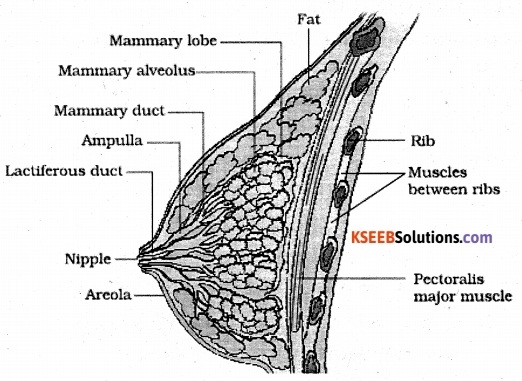
Question 5.
(a) Explain the role of ovarian hormones in inducing changes in the uterus during menstrual cycle.
(b) What triggers release of oxytocin at the time of parturition ?
Answer:
(a) Estrogen influences the uterus in the follicular phase. The endometrin is regenerated through protection. Progesterone influences the uterus in the luteal phase, the endometrin becomes further thickened and vascular for implantation
(b) Foetal ejection triggers the release of oxytocin.
Question 6.
Describe the events that take place during in fertilization in human being.
Answer:
Fertilization refers to the fusion of a sperm and ovum in humans occurs in the ampullary isthmic junction of the fallopian tube.When a sperm comes in contact with the zona pellucida of the ovum, it induces changes in the membrane that. blocks the entry of other sperms. The secretions of acrosome help the sperm to digest the zona pellucida and plasma membrane of the ovum and enter into its cytoplasm.
The entry of sperm induces the completion of secondary meiotic division of the secondary oocyte resulting in the formation of a second polar body and a large ootid. The haploid nucleus of the ootid and that of the sperm fuse to form a diploid zygote.
![]()
Question 7.
Describe the major steps in the development of a fertilized egg upto complete differentiation into blastocyst ready for implantation.
Answer:
- The mitotic division called cleavage divisions start in the zygote as it moves through the isthmus of fallopian tube towards the uterus.
- The divisions result is 2,4,8,16 daughter cells, called blastomeres; the embryo with 8-16 blastomeres is a solid spherical structure and is called as morula.
- The morula continues to divide and the blastomeres rearrange themselves as it moves further into the uterus.
- As a result a hollow spherical structure, called blatocyst is formed.
- The blastocyst has an outer layer of cells, called trophoblast and an inner group of cells, called inner cell mass attached at one end of the trophoblast.
- The trophoblast layer becomes attached to the endometrium and the inner cell mass gets ready to form the embryo proper.
Question 8.
Draw a labelled diagram showing a human foetus developing within the uterus.
Answer:
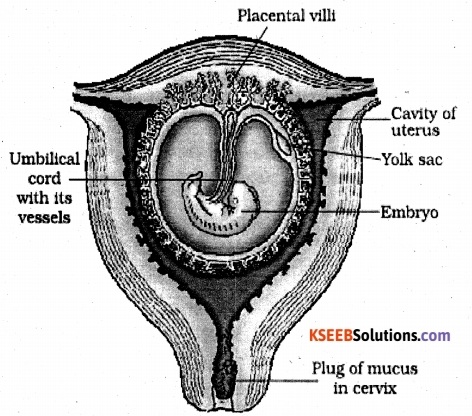
Question 9.
What is Oogenesis ? Give a brief account of Oogenesis.
Answer:
Oogenesis is the process of formation of mature female gametes or ova. These cells start division and enter prophase I of meiosis and remain suspended at that stage; these are called primary oocyte.
Each primary oocyte is surrounded by a layer of granulosa cells and become the primary follicle. When the primary follicle becomes surrounded by more layers of granulosa cells, it is called secondary follicle.
The secondary follicle transforms into tertiary follicle. With the development of a fluid filled cavity (antrum) around the primary oocyte.
The granulosa cell become organised into an outer layer, called theca external and an internal interna. At this stage, the primary oocyte completes meiosis I and form a larger haploid secondary oocyte and a tiny polar body.
A tertiary follicle grow further and changes into mature follicle or agrarian follicle. The secondary oocyte secretes a new membrane called zona pellucida around it. At this stage the follicle ruptures to release the secondary oocyte, which moves into the fallopian tube. The secondary oocyte completes meiosis II only when a sperm enters its cytoplasm, it form a larger cell and Ootid and a smaller cell, the second polar body.