Students can Download Maths Chapter 12 Linear Programming Ex 12.1 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, 2nd PUC Maths Question Bank with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Maths Question Bank Chapter 12 Linear Programming Ex 12.1
2nd PUC Maths Linear Programming NCERT Text Book Questions and Answers Ex 12.1
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Question 1.
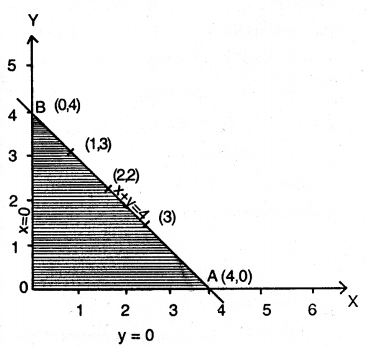
Maximize Z = 3x + 4y subject to the constraints : x + y ≤ 4, x ≥ 0, y ≥0.
Answer:
x + y = 4
| X | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| y | 2 | 1 | 3 |
put x = 0 y = 0
since 0 + 0 ≤ 0, equation is true.
∴ This will be shaded towards 0.
At A (4,0), Z = 3 x 4 = 12
At B (0,4), Z = 4 x 4= 16
∴ Z is maximised at B (0,4) = 16
![]()
Question 2.
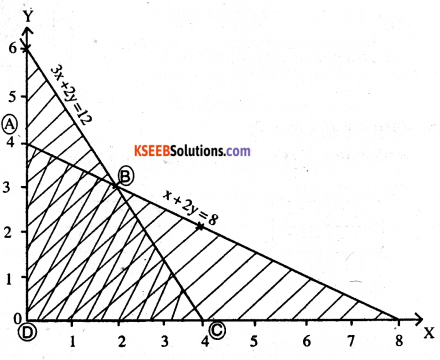
Minimize Z = -3x + 4y
subject to x + 2y ≤ 8; 3x + 2y ≤ 12; x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Answer:
x + 2y = 8
| X | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| Y | 3 | 2 | 4 |
0 + 0 < 8
true towards 0
3x + 2y = 12
| X | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| y | 9 | 0 | 6 |
0 + 0 <12
true shaded towards 0
ABCD is the solution region
x + 2y = 8
Put x = 0 ⇒ A(-0,4)
Put y = 0 ⇒ B(8,0)
At A (0,4) ⇒ Z= 16
At B (2, 3) ⇒ Z =-3 x 2+ 4 x 3 = 6
At C (4, 0) ⇒ Z = -12
At D (0,0) ⇒ z = 0
Hence Z is minimum at C (4, 0) = -12
![]()
Question 3.
Maximise Z = 5x + 3y
subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 15,5x +2y ≤ 10, x ≥ 0,y ≥ 0
Answer:
3x + 5y ≤ 15
| X | 0 | 5 |
| y | 3 | 0 |
0 + 0 <15
true, toward 0
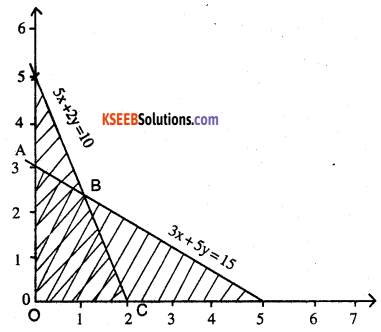
5x +2y = 10
| X | 2 | 0 |
| y | 0 | 5 |
ABCD is the solution region
At A(0,3) ,Z = 3 x 3 = 9
Question 4.
Minimum Z = 3x + 5y
such that x +3y ≤ 3, x+y ≥ 2, x, y ≥0.
Answer:
x + 3y = 3
| X | 3 | 0 |
| y | 0 | 1 |
0 + 0,3 false
∴ shading away from 0
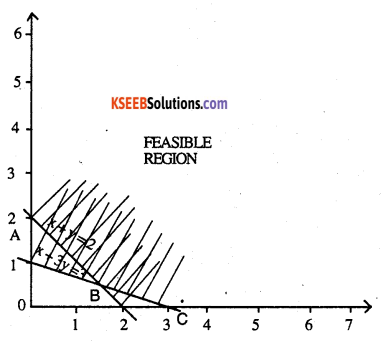
x + y = 2
| X | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| y | 2 | 0 | 1 |
0 + 0 ,2 false
shading away from 0
Away from 0
corner points of feasible region are
A (0,2); Z = 5 x 2 = 10
B (1.5, 0.5); Z = 7
C (3,0); Z = 3 x 3 = 9
∴ Z is minimum at B (1.5,0.5) = 7.
![]()
Question 5.
Maximise Z = 3x +2y
subject to x + 2y ≤ 10, 3x + y ≤ 15, x, y ≥ 0.
Answer:
x + 2y = 10
| X | 0 | 6 | 4 |
| y | 5 | 4 | 3 |
0 + 0 < 10
True
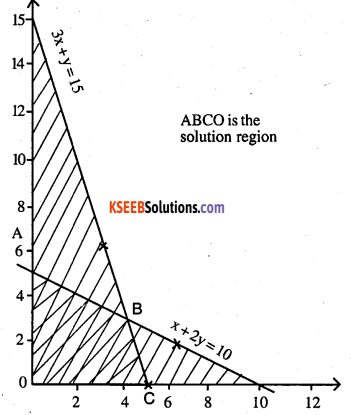
3y + y = 15
| X | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| y | 0 | 3 | 6 |
0 + 0 < 15
True
ABCO is the solution region
At A (0,5) Z = 2 x 5 = 10
At B (4, 3) Z = 3 x 4+ 2 x 3 = 18
At C (5,0) Z = 3 x 5 = 15
∴ Z is maximized at B (4, 3) = 18.
Question 6.
Minimise Z = x + 2y
subject to 2x + y ≥ 3, x + 2y ≥ 6, x, y ≥ 0
Answer:
2x + y = 3
| X | 1 | 0 |
| y | 1 | 3 |
0 + 0, 0 false
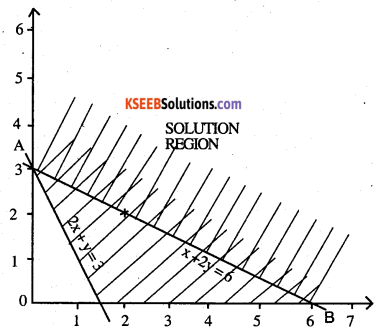
x + 2y = 6
| X | 6 | 0 | 2 |
| y | 0 | 3 | 2 |
0 + 0 ,6 false
An and above O is the solution region
At A(0,3) Z = 2 x 3 = 6
At B(6,0) Z = 6
Z is maximum at all points on line AB = 6
Here minimum of Z occurs at 2 points A & B.
![]()
Show that the minimum of Z occurs at more than two points.
Question 7.
Minimise and Maximise Z = 5x + 10 y
subject to x + 2y ≤ 120, x + y ≥ 60, x – 2y ≥ 0,x,y ≥ 0.
Answer:
x + 2y = 120
| X | 60 | 0 | 20 |
| Y | 30 | 60 | 50 |
0 + 0 ,120
True
x + y = 60
| X | 30 | 20 | 40 |
| Y | 30 | 40 | 20 |
0 + 0 >0
false
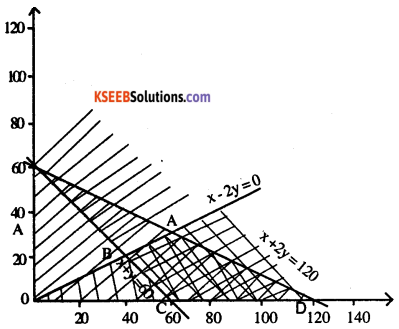
x – 2y =0
| x | 20 | 0 | 40 |
| y | 10 | 0 | 20 |
40 – 20 > 0
ABCD is the solution region
At A (60, 30) Z = 5 x 60 + 10 x 30 = 600
At B (40, 20) Z = 5 x 40+10 x 20 = 400
At C (60,0) Z = 5 x 60 = 300
At D (120,0) Z = 5 x 120 = 600
Z is minimized at C (60,0) = 300
Z is maximized at 2 points A (60,30), D (120,0)
∴ maximum value is 600 at all
points on the line joining A (60,30) and D (120,0)
![]()
Question 8.
Minimise and Maximise Z = x + 2y
subject to x + 2y ≥ 100, 2x – y ≤ 0, 2x + y ≤ 200; x, y ≥ 0.
Answer:
x + 2y = 100
| x | 100 | 50 | 20 |
| y | 0 | 20 | 40 |
0 + 0>100
0 – 0 < 0 False
2x – y = 0
| x | 100 | 20 | 10 |
| y | 200 | 40 | 20 |
0 – 0 < 0
False
2x +y = 200
| x | 100 | 50 | 60 |
| y | 0 | 100 | 80 |
0 + 0 <200
True
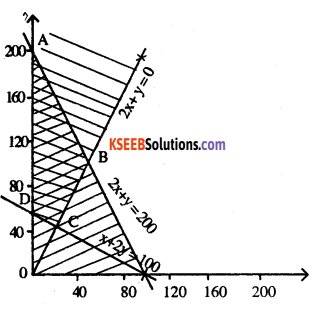
ABCD is the solution .
At A (0,200), Z = 2 x 200 = 400
At B (50,100), Z = 50 + 2 x 100 = 250
At C (20,40), Z = 20 + 2x 40= 100
At D (0,50), Z = 2 x 50 =100
Z is maximised at A (0,200) = 400
Z is minimised at 2 points C (20,40) & D (0, 50) = 100
![]()
Question 9.
Maximise Z = -x + 2y, subject to the constraints:
x ≥ 3, x + y ≥ 5 , x + 2y ≥ 6, y ≥ 0
Answer:
x + y = 5
| x | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| y | 4 | 2 | 3 |
0 + 0, 5
False
0,3
False
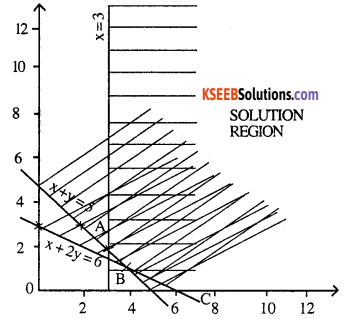
x + 2y = 6
| x | 0 | 4 | 2 |
| y | 3 | 1 | 2 |
0 + 0
False
ABC is the solution region
At A (3,2) Z =-3+2 x 2=1
At B (4,1) Z = -4 + 2 x 1 = -2
At C (6, 0) Z = -6 = -6
Z is maximised at A (3,2) = 1 and
minimised at C (6,0) = -6
![]()
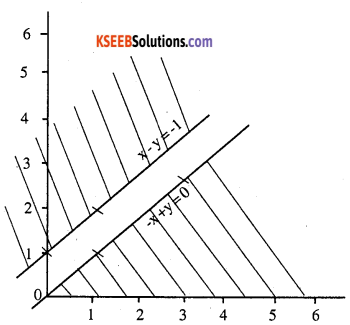
Question 10.
Maximise Z = x + y,
subject to x – y ≤ -1, -x +y ≤ 0, x, y ≥ 0.
Answer:
x – y = -1
| x | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| y | 2 | 1 | 3 |
0 – 0 ,-1
False
x + 2y = 6
| x | 0 | 4 | 2 |
| y | 3 | 1 | 2 |
0 + 0 , 0 False,
Since there is no common shaded region, there is no feasible solution region. Hence maximum of Z does not exist.