Karnataka State Board Solutions for 2nd PUC Economics Question Banks with Answers, Solutions, Notes, Guide Pdf are prevailing here in direct pdf links for effective exam preparation. Students who are studying for 2nd PUC Economics textbook solutions can refer to this page for grabbing KSEEB 2nd PUC Economics Solutions pdf chapter wise for free. By reading the textbook solutions. You Can Download 2nd PUC Question Bank with Answers from Karnataka State Board solutions, you will be able to understand all the exercises and score good marks.
Also, there are so many advantages that you can avail from the Karnataka State Board Solutions for 2nd PUC Economics Question Bank with Answers, Solutions pdf. So download 2nd PUC Economics Notes from KTBS Solutions Pdf via quick links & access them easily while preparation. Students can also read 2nd PUC Economics Model Question Papers with Answers hope will definitely help for your board exams.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Economics Question Bank with Answers
Provided Karnataka State Board solutions for 2nd PUC Economics textbook solutions are prepared by subject experts after ample research. So students are suggested to download the 2nd PUC Economics Question Bank with Answers and Textbook Solutions from the available PDF links and kickstart your preparations for final exams. You can download them freely & practice regularly to score high marks in the examinations. Access the below Chapter-wise links and learn complete by using 2nd PUC Economics Question Bank with Answers from Karnataka State Board solutions pdf.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Economics Question Bank with Answers in English
2nd PUC Economics Question Bank Part A – Micro Economics
- Chapter 1 Introduction to Micro Economics
- Chapter 2 Theory of Consumer Behaviour
- Chapter 3 Demand Analysis
- Chapter 4 Production and Cost
- Chapter 5 The Theory of the Firm and Perfect Competition
- Chapter 6 Imperfect Competitive Markets (Non-Competitive Markets)
2nd PUC Economics Question Bank Part B – Macro Economics
- Chapter 7 Introduction to Macro Economics
- Chapter 8 National Income Accounting
- Chapter 9 Money and Banking
- Chapter 10 Consumption and Investment Function
- Chapter 11 Government Budget and the Economy
- Chapter 12 Open Economy Macroeconomics
Karnataka 2nd PUC Economics Question Bank with Answers in Kannada
2nd PUC Economics Question Bank Part A – Micro Economics
- Chapter 1 Introduction to Micro Economics
- Chapter 2 Theory of Consumer Behaviour
- Chapter 3 Demand Analysis
- Chapter 4 Production and Cost
- Chapter 5 The Theory of the Firm and Perfect Competition
- Chapter 6 Imperfect Competitive Markets (Non-Competitive Markets)
2nd PUC Economics Question Bank Part B – Macro Economics
- Chapter 7 Introduction to Macro Economics
- Chapter 8 National Income Accounting
- Chapter 9 Money and Banking
- Chapter 10 Consumption and Investment Function
- Chapter 11 Government Budget and the Economy
- Chapter 12 Open Economy Macroeconomics
Karnataka 2nd PUC Economics Syllabus and Marking Scheme
Karnataka 2nd PUC Economics Blue Print of Model Question Paper
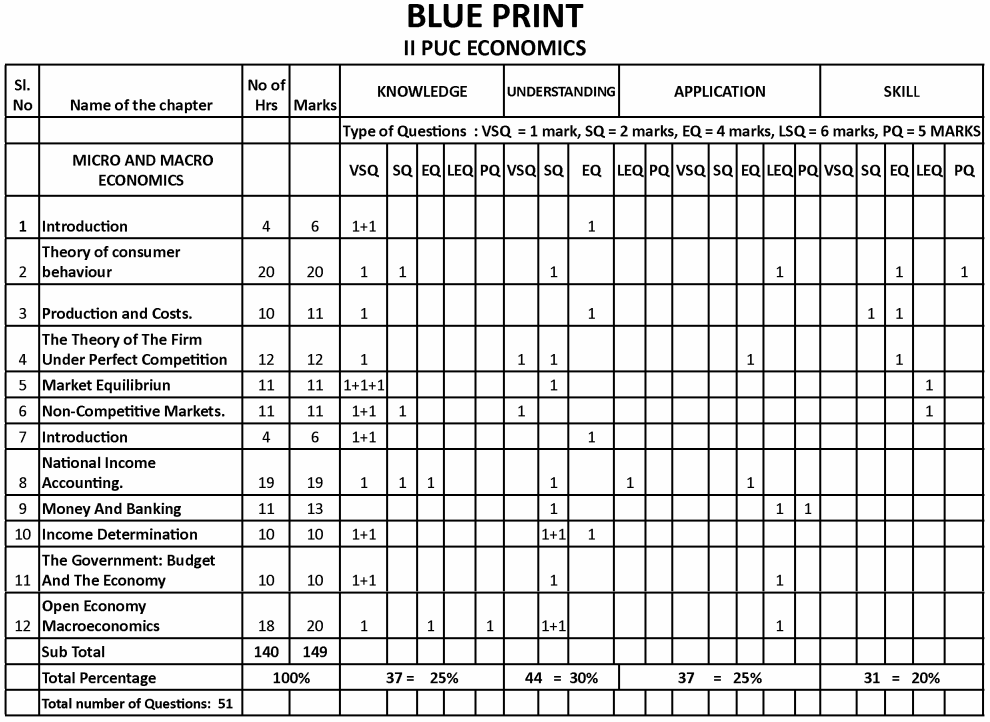
Features of Karnataka 2nd PUC Economics Question Bank with Answers
For the first time Pre-University Department has released the Question Bank for Second Year PUC Economics for both Commerce and Arts stream.
Second PUC Economics Text Book consists of two books.
- Introductory Micro Economics – contains 6 chapters
- Introductory Macro Economics – contains 6 chapters
First, Introductory Micro Economics should be taught and then Introductory Macro Economics. Information or concepts given in boxes are also to be taught.
The questions in the Question Bank are framed for all the chapters on the basis of these two books.
Following are the features of the 2nd PUC Economics Question Bank with Answers.
- Multiple Choice Questions – each question carries one mark.
- Fill in the blanks – each question carries one mark.
- Match the following – five marks
- Questions which are to be answered in a sentence/word – each question carries one mark.
- Questions which are to be answered in four sentences – each question carries two marks.
- Questions which are to be answered in about twelve sentences – each question carries four marks.
- Questions which are to be answered in about twenty sentences – each question carries six marks.
- Assignment and Project-oriented questions – each question carries five marks.
- Test, Mid-term and Annual Examination Question Papers should be based on this Question Bank.
- Programme of Work, a Model Question Paper with Blue-print are given in the end of the Question Bank.
PART-A MICRO-ECONOMICS
1. CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS (10 Hours)
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 The Concept of an Economy
- 1.3 Basic Problems of an Economy
- 1.4 Organisation of Economic Activities 1 Centrally Planned Economy – Market Economy – Mixed Economy.
- 1.5 Positive and Normative Economics
- 1.6 Deductive and Inductive Methods of Economics
- 1.7 Concepts of Micro and Macro-economics.
- 1.8 Uses of Microeconomics
- 1.9 Limitations of Micro-economics
CHAPTER 2 THEORY OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR (12 Hours)
- 2.1 Introduction
- 2.2 Utility Analysis
- 2.3 Cardinal and Ordinal Approach
- 2.4 Concepts of Utility
- 2 .5 Concept of Consumer Behaviour Budget Line and Budget Set
- 2.6 Indifference Curve Analysis – Meaning of Indifference Curve – Map and Properties :
- 2.7 Optimal Choice of the Consumer
CHAPTER-3 DEMAND ANALYSIS (10 Hours)
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.2 Demand – Meaning and its determinants
- 3.3 Demand Function
- 3.4 Law of Demand – Normal and Inferior goods, Substitutes and Complementaries – Shifts in Demand curve
- 3.5 Elasticity of Demand – Concepts of Elasticity – Price Elasticity, Income Elasticity, Cross Elasticity
CHAPTER 4 PRODUCTION AND COST (12 Hours)
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Concept of production function – Isoquants, Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution – Concept of Total Product, Average Product and Marginal Product – Short Run and Long Run analysis of production – The Law of Variable proportion – Returns to scale
- 4.3 Production Cost – Concept of Cost – Classification of Short run cost – Long run cost – Other types of costs
CHAPTER 5 THE THEORY OF THE FIRM AND PERFECT COMPETITION (12 Hours)
- 5.1 Introduction
- 5.2 Meaning of Market, Firm and Industry
- 5.3 Market Structure – Meaning and Features of Perfect Competitive Market
- 5.4 Revenue – Total Revenue, Average Revenue, Marginal Revenue
- 5.5 The Relationship between Total Revenue, Average Revenue snd Marginal Revenue under Perfect Competition
- 5.6 Supply – Short run and Long run supply curve of a firm – Determinants of supply – Law of Supply
- 5.7 Price Elasticity of Supply
- 5.8 Equilibrium under Perfect Competition
CHAPTER 6 IMPERFECT COMPETITIVE MARKETS (NON-COMPETITIVE MARKETS) (13 Hours)
- 6.1 Introduction
- 6.2 Monopoly – Features, Total Revenue (TR), Average Revenue (AR) and Marginal Revenue (MR) – Short-run and Long-run Equilibrium
- 6.3 Monopolistic Competition – Meaning, Features, Short-run equilibrium
- 6.4 Oligopoly – Characteristics
- 6.5 Duopoly – Meaning
PART-B MACRO ECONOMICS
CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION (7 Hours)
- 7.1 The Concept of Macroeconomics
- 7.2 Emergence of Macroeconomics
- 7.3 Nature and Scope of Macro-economics
- 7.4 Limitations of Macro-economics
- 7.5 Differences between Micro and Macro-economics
CHAPTER 8 NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING (9 Hours)
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2 Basic Concepts of National Income
- 8.3 Circular flow of Income
- 8.4 Some Macro-economic Identities Gross
- 8.5 Measurement of National Income Income
- method, Expenditure method and Product or Value Added method
- 8.6 Difficulties in Measuring National Income
- 8.7 National Income and Welfare
CHAPTER 9 MONEY AND BANKING (12 Hours)
- 9.1 Introduction
- 9.2 Definition and Functions of Money
- 9.3 Demand for Money – Transactionary motive, Precautionary motive and Speculative motive
- 9.4 Supply of Money – Measures of Money supply
- 9.5 Commercial Banks – Meaning and function s of Commercial Banks Credit creation by Commercial Banks
- 9.6 Central Bank – Meaning and Functions of RBI – Monetary Policy of RBI – Objectives and Instruments
CHAPTER 10 CONSUMPTION AND INVESTMENT FUNCTION (8 Hours)
- 10.1 Introduction
- 10.2 Concepts of Consumption, Income, Savings and Investment
- 10.3 Keynes Consumption Function, Average Propensity to Consume (APC), Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC), Importance and determinants of Consumption function, IDA Investment Function, Meaning, types and determinants of Investments
- 10.4 Investment Function, Meaning, types and determinants of Investments
- 10.5 Multiplier
CHAPTER 11 GOVERNMENT BUDGET AND THE ECONOMY (8 Hours)
- 11.1 Introduction
- 11.2 Budget – Meaning, types and components
- 11.3 Fiscal Policy – Meaning, Objectivities
- 11.4 Instruments of Fiscal Policy – Public Expenditure – Public Revenue – Public Debt – Deficit Financing
- 11.5 Budget Deficits – Meaning and types
CHAPTER 12 OPEN ECONOMY (7 Hours)
- 12.1 Introduction
- 12.2 Meaning of Closed and Open Economies
- 12.3 Basic Concepts of Trade – Unilateral, Bi-Lateral and Multilateral Trade
- 12.4 Balance of Trade (BOT) and Balance of Payments (BOP)
- 12.5 Foreign Exchange Market – Meaning, Determination of exchange rate, Exchange rate systems
We wish the data shed above will benefit you at the time of your preparation & gain good scores. So, download Karnataka State Board 2nd PUC Economics Question Bank with Answers from here and become a topper in the final examinations. Moreover, keep in touch with our site & get all updated chapter wise KSEEB State Board Solutions for all subjects.
